Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P II Lab Practical #4
front 1  A | back 1 adrenal gland |
front 2  B | back 2 renal artery |
front 3  C | back 3 renal vein |
front 4  D | back 4 kidney |
front 5  E | back 5 ureter |
front 6  F | back 6 uterus |
front 7  G | back 7 urinary bladder |
front 8  H | back 8 urethra |
front 9  A | back 9 renal pyramids |
front 10  B | back 10 renal cortex |
front 11  C | back 11 minor calyx |
front 12  D | back 12 ureter |
front 13  E | back 13 renal pelvis |
front 14  F | back 14 renal papilla |
front 15  G | back 15 minor calyx |
front 16  H | back 16 interlobar vessels |
front 17  I | back 17 arcuate vessels |
front 18  A | back 18 renal sinus |
front 19  B | back 19 renal pelvis |
front 20  C | back 20 hilum |
front 21  D | back 21 renal papilla |
front 22  E | back 22 ureter |
front 23  F | back 23 renal cortex |
front 24  G | back 24 renal medulla |
front 25  H | back 25 renal pyramid |
front 26  I | back 26 minor calyx |
front 27  J | back 27 major calyx |
front 28  K | back 28 kidney lobe |
front 29  L | back 29 renal columns |
front 30  M | back 30 fibrous capsule |
front 31  A | back 31 renal cortex |
front 32  B | back 32 renal medulla |
front 33  C | back 33 major calyx |
front 34  D | back 34 papilla of pyramid |
front 35  E | back 35 minor calyx |
front 36  F | back 36 renal pyramid in renal medulla |
front 37  G | back 37 renal column |
front 38  H | back 38 fibrous capsule |
front 39  I | back 39 cortical radiate vein |
front 40  J | back 40 cortical radiate artery |
front 41  K | back 41 arcuate vein |
front 42  L | back 42 arcuate artery |
front 43  M | back 43 interlobar vein |
front 44  N | back 44 interlobar artery |
front 45  O | back 45 segmental arteries |
front 46  P | back 46 renal vein |
front 47  Q | back 47 renal artery |
front 48  R | back 48 renal pelvis |
front 49  S | back 49 ureter |
front 50 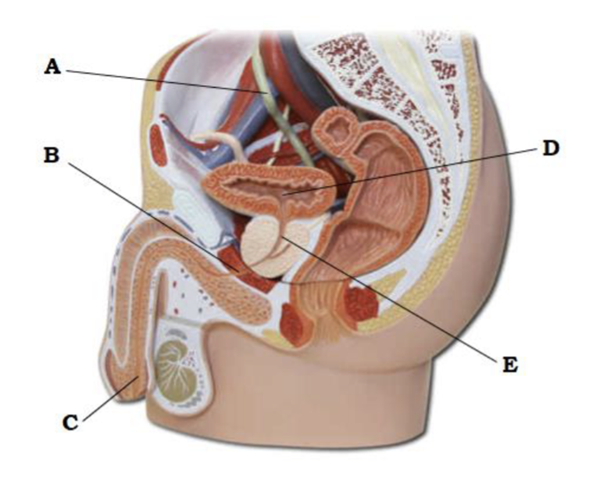 A | back 50 ureter |
front 51  B | back 51 membranous urethra |
front 52  C | back 52 spongy urethra |
front 53  D | back 53 urinary bladder |
front 54  E | back 54 prostatic urethra |
front 55 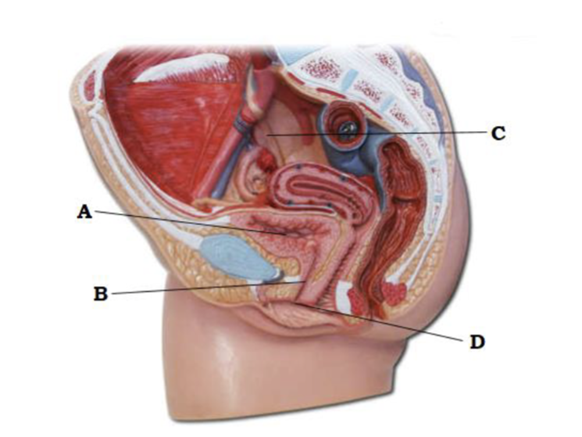 A | back 55 urinary bladder |
front 56  B | back 56 urethra |
front 57  C | back 57 ureter |
front 58  D | back 58 external urethral orifice |
front 59 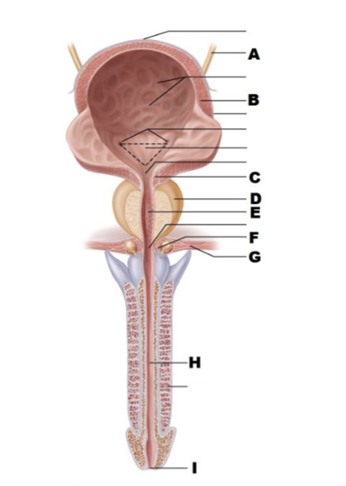 A | back 59 ureter |
front 60  B | back 60 detrusor |
front 61  C | back 61 internal urethral sphincter |
front 62  D | back 62 prostate |
front 63  E | back 63 prostatic urethra |
front 64  F | back 64 external urethral sphincter |
front 65  G | back 65 urogenital diaphragm |
front 66  H | back 66 spongy urethra |
front 67  I | back 67 external urethral orifice |
front 68 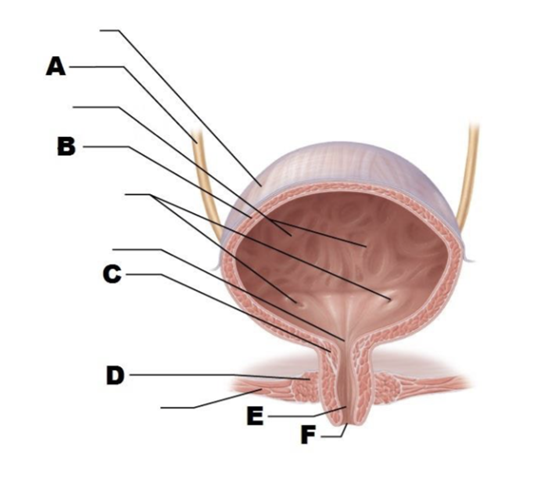 A | back 68 ureter |
front 69  B | back 69 detrusor |
front 70  C | back 70 internal urethral sphincter |
front 71  D | back 71 external urethral sphincter |
front 72  E | back 72 urethra |
front 73  F | back 73 external urethral orifice |
front 74 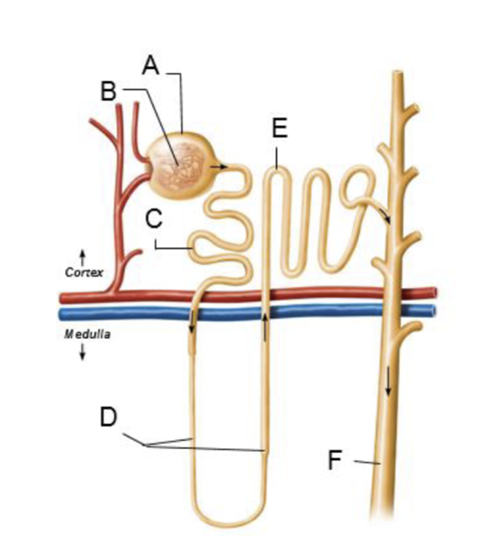 A | back 74 glomerular capsule |
front 75  B | back 75 glomerulus |
front 76  C | back 76 proximal convoluted tubule |
front 77  D | back 77 nephron loop |
front 78  E | back 78 distal convoluted tubule |
front 79  F | back 79 collecting duct |
front 80  A | back 80 cortical nephron |
front 81  B | back 81 juxtamedullary nephron |
front 82  C | back 82 glomerulus |
front 83  D | back 83 glomerular capsule |
front 84  E | back 84 proximal convoluted tubule |
front 85  F | back 85 peritubular capillaries |
front 86  G | back 86 ascending limb of nephron loop |
front 87  H | back 87 nephron loop |
front 88  I | back 88 descending limb of nephron loop |
front 89  J | back 89 collecting duct |
front 90  K | back 90 distal convoluted tubule |
front 91  L | back 91 vasa recta |
front 92  A | back 92 cortical radiate vessels |
front 93  B | back 93 arcuate vessels |
front 94  C | back 94 descending limb of loop of Henle |
front 95  D | back 95 interlobar vessels |
front 96  E | back 96 collecting duct |
front 97  F | back 97 ascending limb of loop of Henle |
front 98  G | back 98 distal convoluted tubule |
front 99  H | back 99 efferent arterioles |
front 100  I | back 100 proximal convoluted tubule |
front 101  J | back 101 afferent arterioles |
front 102  K | back 102 renal corpuscles |
front 103 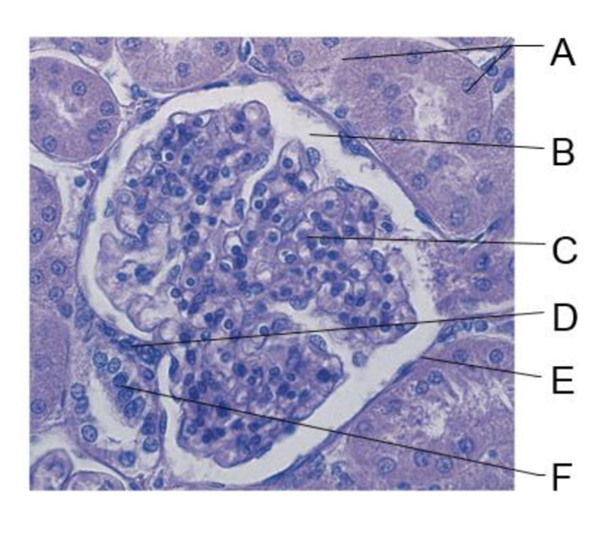 A | back 103 cuboidal epithelium of renal tubule |
front 104  B | back 104 glomerular capsular space |
front 105  C | back 105 glomerulus |
front 106  D | back 106 granular cells |
front 107  E | back 107 parietal layer of glomerular capsule |
front 108  F | back 108 macula densa |
front 109 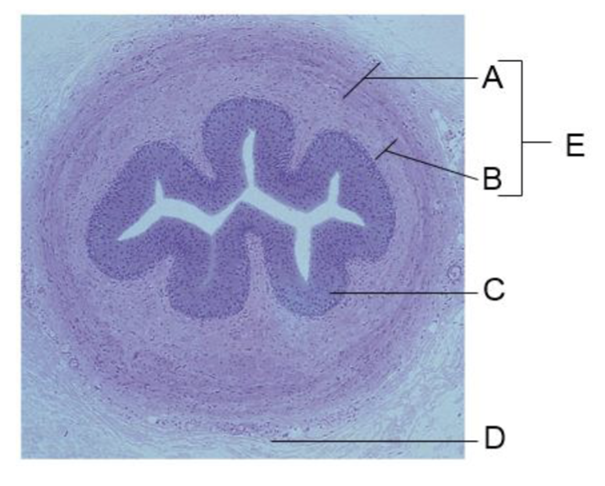 A | back 109 circular layer |
front 110  B | back 110 longitudinal layer |
front 111  C | back 111 transitional epithelium |
front 112  D | back 112 adventitia |
front 113  E | back 113 smooth muscle |
front 114 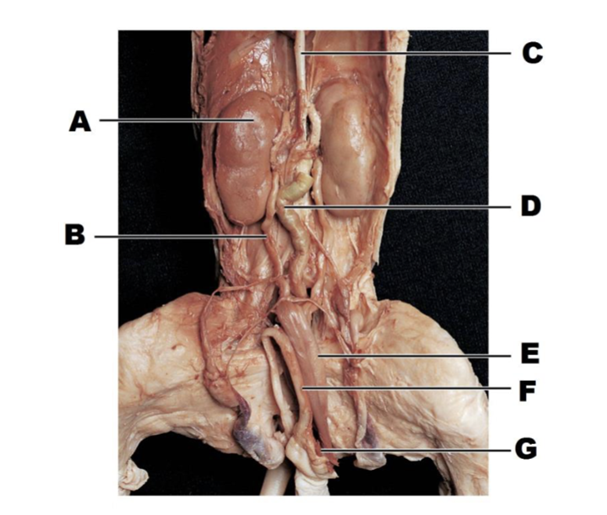 A | back 114 kidney |
front 115  B | back 115 ureter |
front 116  C | back 116 inferior vena cava |
front 117  D | back 117 descending portion of colon |
front 118  E | back 118 urinary bladder |
front 119  F | back 119 penis |
front 120  G | back 120 umbilical vein |
front 121  A | back 121 inferior vena cava |
front 122  B | back 122 ureter |
front 123  C | back 123 urinary bladder |
front 124  D | back 124 ureter (cut) |
front 125  E | back 125 urethra |
front 126  F | back 126 kidney |
front 127  G | back 127 descending portion of colon |
front 128  H | back 128 uterine horns |
front 129  I | back 129 uterus |
front 130  J | back 130 urogenital sinus |
front 131 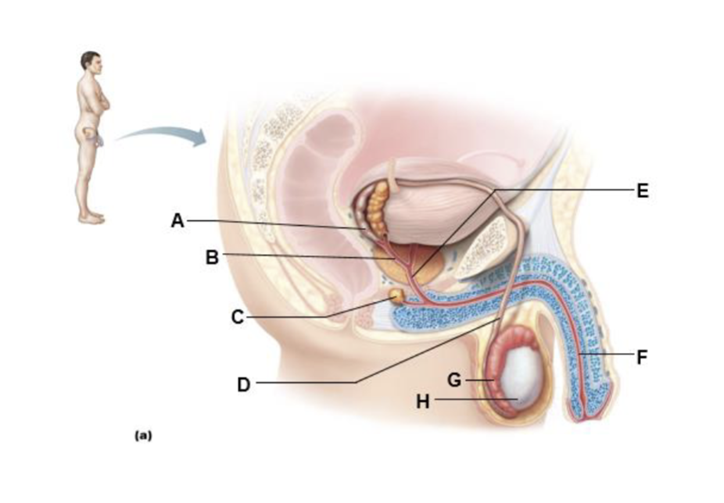 A | back 131 ampulla of ductus deferens |
front 132  B | back 132 ejaculatory duct |
front 133  C | back 133 bulbo-urethral gland |
front 134  D | back 134 ductus (vas) deferens |
front 135  E | back 135 prostatic urethra |
front 136  F | back 136 spongy urethra |
front 137  G | back 137 epididymis |
front 138  H | back 138 testis |
front 139  A | back 139 urinary bladder |
front 140  B | back 140 prostate |
front 141  C | back 141 prostatic urethra |
front 142  D | back 142 intermediate part of urethra |
front 143  E | back 143 root of penis |
front 144  F | back 144 body (shaft) of penis |
front 145  G | back 145 glans penis |
front 146  H | back 146 external urethral orifice |
front 147  I | back 147 prepuce (foreskin) |
front 148  J | back 148 spongy urethra |
front 149  K | back 149 testis |
front 150  L | back 150 corpus spongiosum |
front 151  M | back 151 epididymis |
front 152  N | back 152 corpora cavernosa |
front 153  O | back 153 ductus deferens |
front 154  P | back 154 crus of penis |
front 155  Q | back 155 bulb of penis |
front 156  R | back 156 urogenital diaphragm |
front 157  S | back 157 bulbo-urethral gland and duct |
front 158  T | back 158 ejaculatory gland |
front 159  U | back 159 seminal gland |
front 160  V | back 160 ampulla of ductus deferens |
front 161  W | back 161 ureter |
front 162 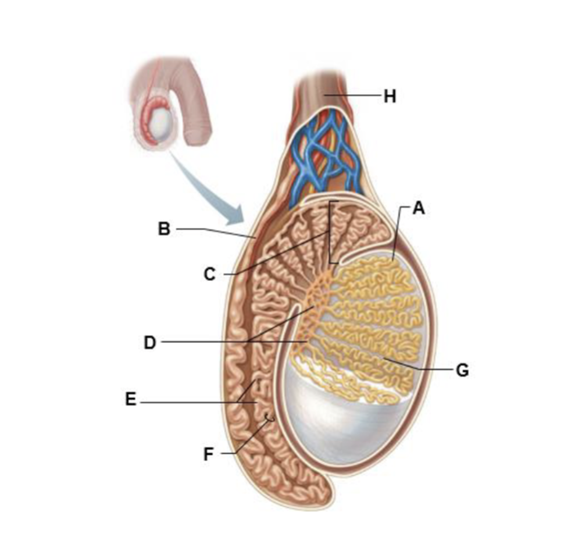 A | back 162 seminiferous tubule |
front 163  B | back 163 ductus (vas) deferens |
front 164  C | back 164 head of epididymis |
front 165  D | back 165 rete testis |
front 166  E | back 166 body of epididymis |
front 167  F | back 167 duct of epididymis |
front 168  G | back 168 septum |
front 169  H | back 169 spermatic cord |
front 170 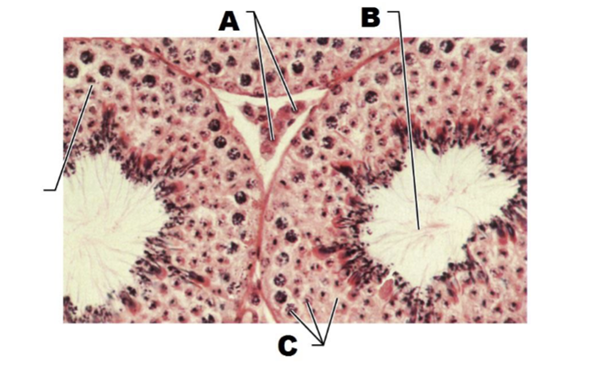 A | back 170 interstitial endocrine cells |
front 171  B | back 171 immature sperm |
front 172  C | back 172 spermatogenic cells |
front 173 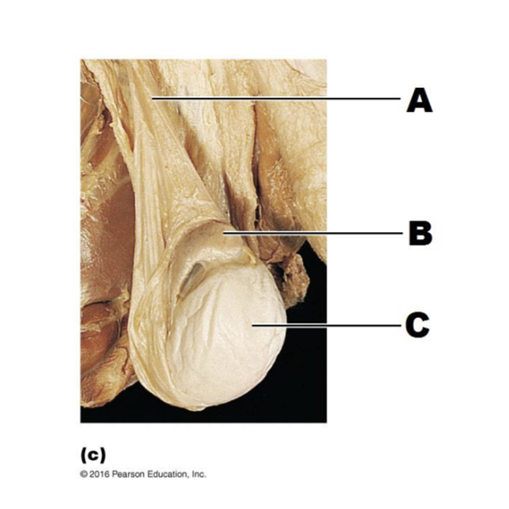 A | back 173 spermatic cord |
front 174  B | back 174 epididymis |
front 175  C | back 175 testis |
front 176 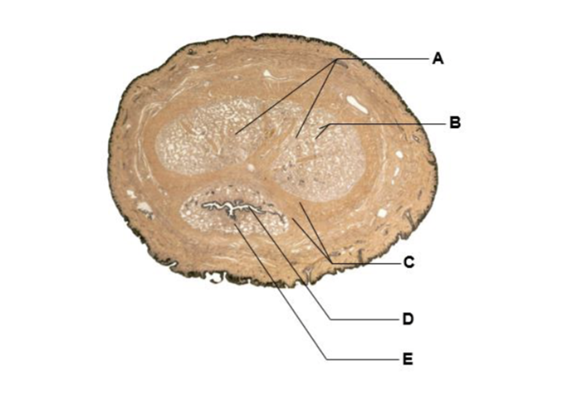 A | back 176 corpore cavernosa |
front 177  B | back 177 venous cavities |
front 178  C | back 178 tunic albuginea |
front 179  D | back 179 lumen of spongy urethra |
front 180  E | back 180 corpus spongiosum |
front 181 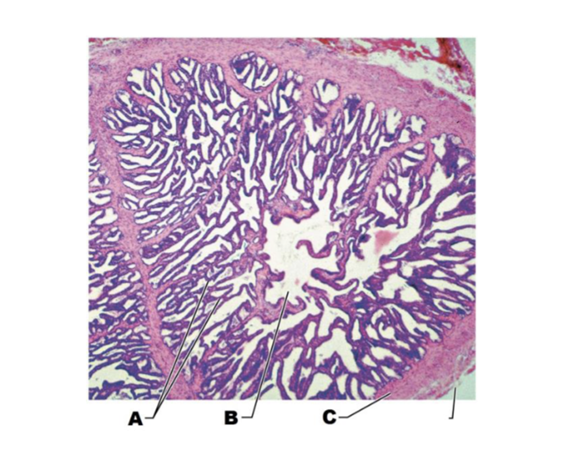 A | back 181 mucosal folds |
front 182  B | back 182 lumen of seminal tubule |
front 183  C | back 183 muscular wall |
front 184 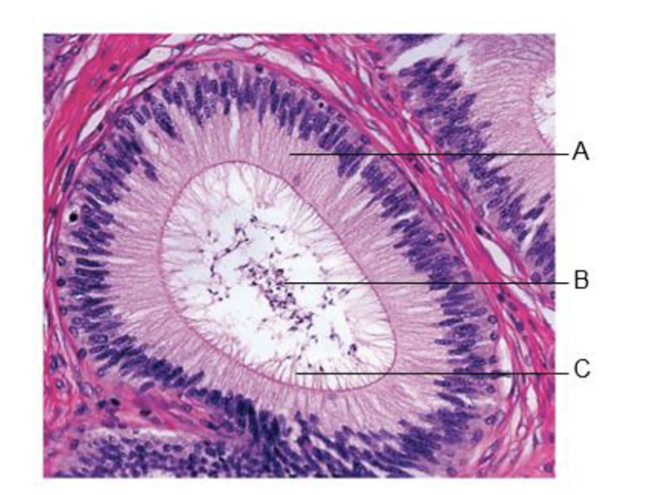 A | back 184 pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
front 185  B | back 185 sperm in lumen |
front 186  C | back 186 stereocilia |
front 187 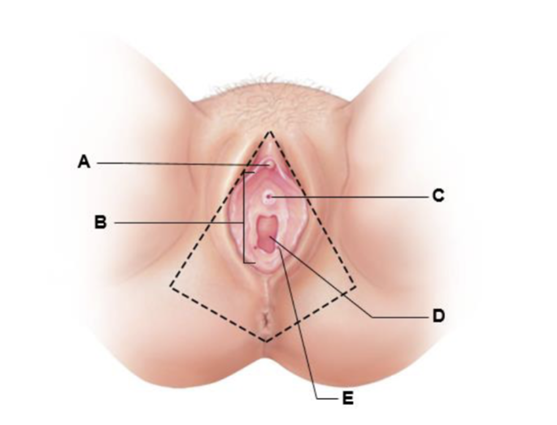 A | back 187 clitoris gland |
front 188  B | back 188 vestibule |
front 189  C | back 189 external urethral orifice |
front 190  D | back 190 vaginal orifice |
front 191  E | back 191 opening of the duct of the greater vestibular gland |
front 192 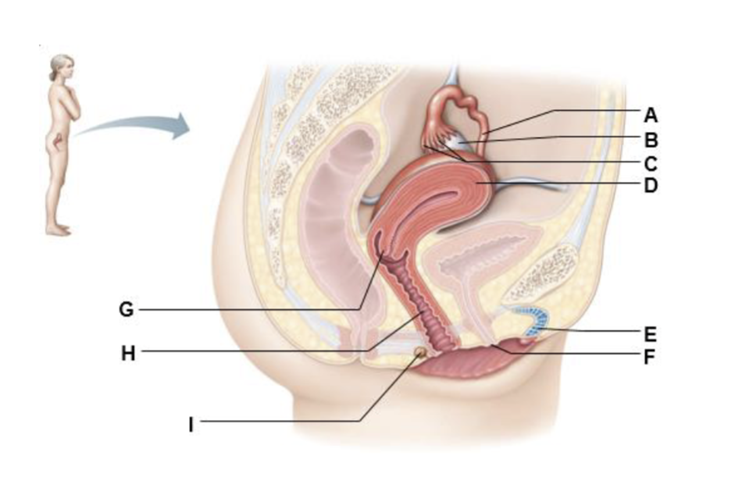 A | back 192 uterine tube |
front 193  B | back 193 ovary |
front 194  C | back 194 fimbrae |
front 195  D | back 195 uterus |
front 196  E | back 196 clitoris |
front 197  F | back 197 external urethral orifice |
front 198  G | back 198 cervix |
front 199  H | back 199 vagina |
front 200  I | back 200 greater vestibular gland |
front 201  A | back 201 broad ligament |
front 202  B | back 202 body of uterus |
front 203  C | back 203 cervix |
front 204  D | back 204 ovary |
front 205  E | back 205 uterine (fallopian tube) |
front 206  F | back 206 fimbriae |
front 207  G | back 207 infundibulum |
front 208  H | back 208 isthmus |
front 209  I | back 209 ampulla |
front 210  J | back 210 endometrium |
front 211  K | back 211 vagina |
front 212 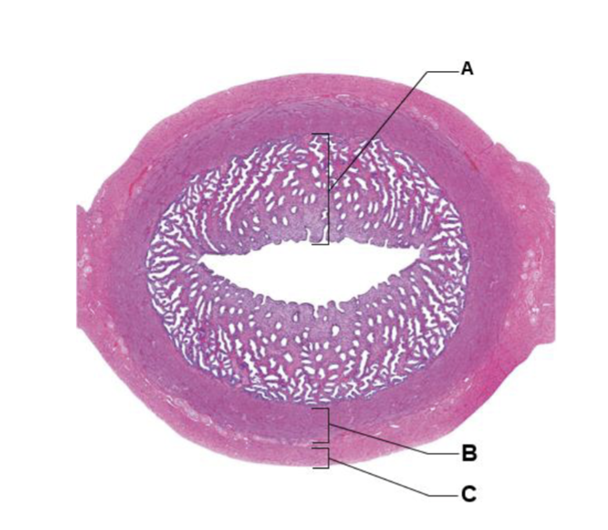 A | back 212 endometrium |
front 213  B | back 213 myometrium |
front 214  C | back 214 serosa |
front 215  A | back 215 serosa |
front 216  B | back 216 smooth muscle |
front 217  C | back 217 highly folded mucosa |
front 218  D | back 218 lumen |
front 219 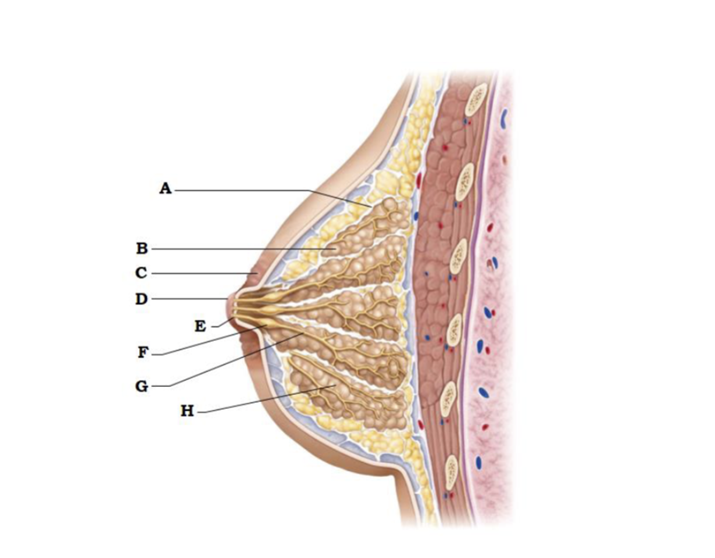 A | back 219 suspensory ligament |
front 220  B | back 220 lobe |
front 221  C | back 221 areola |
front 222  D | back 222 nipple |
front 223  E | back 223 opening of lactiferous duct |
front 224  F | back 224 lactiferous sinus |
front 225  G | back 225 lactiferous duct |
front 226  H | back 226 lobule containing alveoli |
front 227 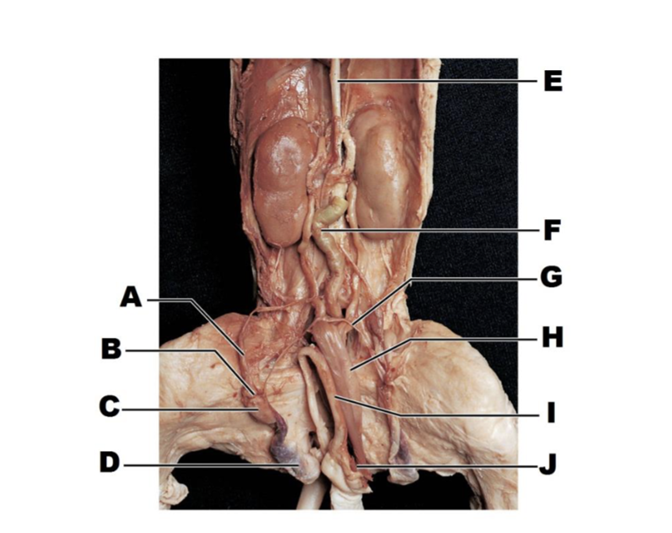 A | back 227 spermatic cord |
front 228  B | back 228 epididymis (head) |
front 229  C | back 229 testis |
front 230  D | back 230 scrotal sac |
front 231  E | back 231 inferior vena cava |
front 232  F | back 232 colo |
front 233  G | back 233 ductus deferens |
front 234  H | back 234 urinary bladder |
front 235  I | back 235 penis |
front 236  J | back 236 umbilical vein |
front 237 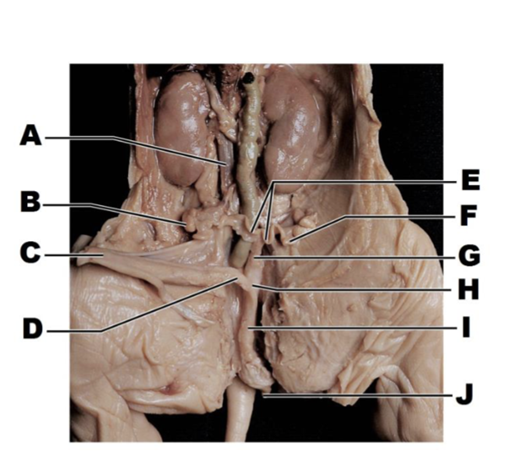 A | back 237 inferior vena cava |
front 238  B | back 238 ovary |
front 239  C | back 239 urinary bladder |
front 240  D | back 240 urethra |
front 241  E | back 241 uterine horns |
front 242  F | back 242 uterine tube |
front 243  G | back 243 body of uterus |
front 244  H | back 244 vagina |
front 245  I | back 245 urogenital sinus |
front 246  J | back 246 genital papilla |
front 247 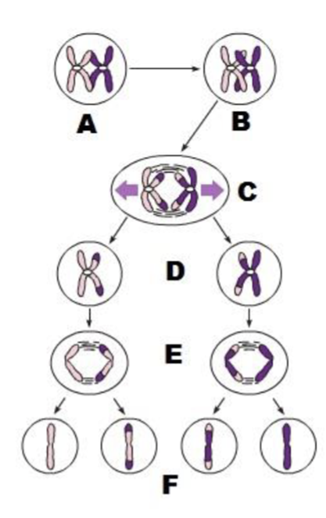 A | back 247 prophase I tetrads form by synapis of homologous |
front 248  B | back 248 crossover form |
front 249  C | back 249 anaphase I homologous separate |
front 250  D | back 250 daughter cells of Meiosis I |
front 251  E | back 251 anaphase II sister chromatids separate |
front 252  F | back 252 daughter cells of meosis II |
front 253 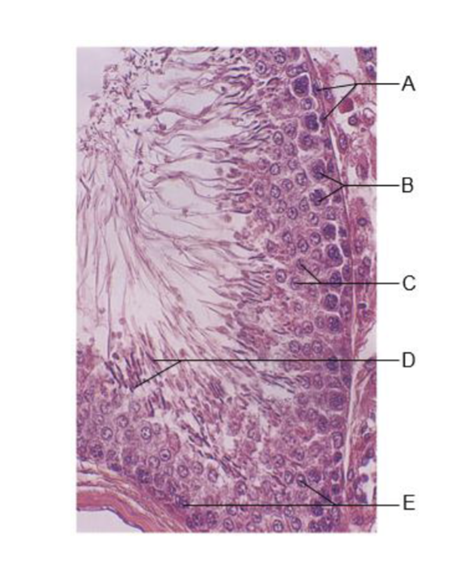 A | back 253 spermatogonia |
front 254  B | back 254 primary spermatocytes |
front 255  C | back 255 spermatids |
front 256  D | back 256 immature sperm in lumen |
front 257  E | back 257 sustentocytes (of testis) |
front 258 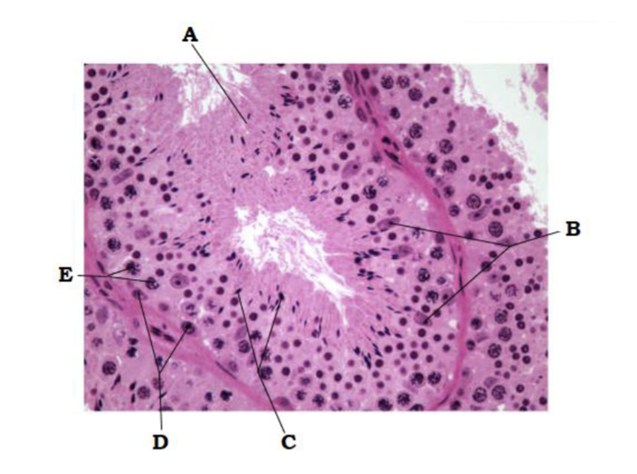 A | back 258 seminiferous tubule |
front 259  B | back 259 sustentacular cell nuclei |
front 260  C | back 260 spermatids |
front 261  D | back 261 spermatogonia |
front 262  E | back 262 primary spermatocytes |
front 263 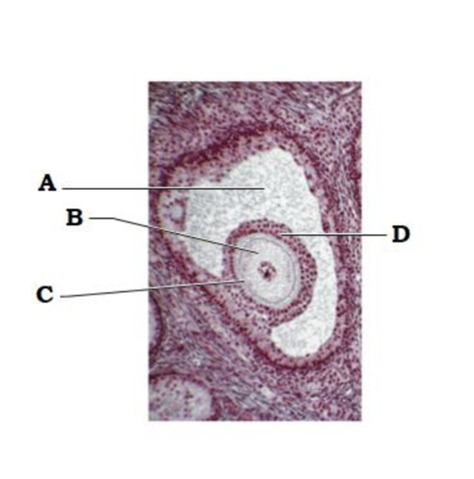 A | back 263 antrum |
front 264  B | back 264 secondary oocyte |
front 265  C | back 265 zona pellucida |
front 266  D | back 266 corona radiata |
front 267 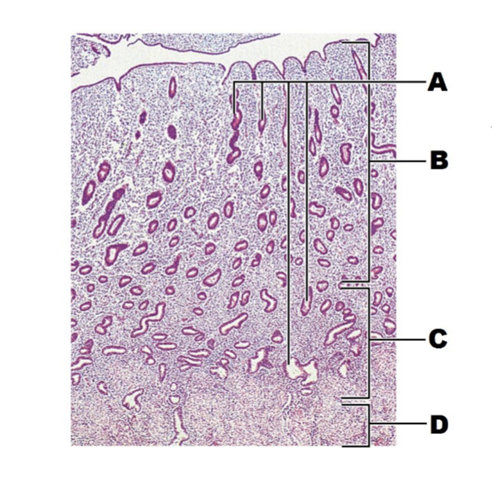 A | back 267 glands |
front 268  B | back 268 functional layer |
front 269  C | back 269 basal layer |
front 270  D | back 270 myometrium |
front 271  A | back 271 myometrium |
front 272  B | back 272 endometrium |
front 273  C | back 273 elaborated glands |
front 274  A | back 274 medulla |
front 275  B | back 275 corpus luteum |
front 276  C | back 276 developing corpus luteum |
front 277  D | back 277 corona radiata |
front 278  E | back 278 ovulated secondary oocyte |
front 279  F | back 279 zona pellucida |
front 280  G | back 280 secondary oocyte |
front 281  H | back 281 antrum |
front 282  I | back 282 vesicular (antral) follicle |
front 283  J | back 283 late secondary follicle |
front 284  K | back 284 granulosa cells |
front 285  L | back 285 secondary follicle |
front 286  M | back 286 cortex |
front 287  N | back 287 degenerating corpus luteum (corpus albicans) |
front 288  O | back 288 primary follicles |
front 289 describe the process of synapsis | back 289 the homologous chromosomes become closely aligned along their entire length |
front 290 how does crossover introduce variability in the daughter cells? | back 290 where crossover occur, chromosome breakage occurs, and parts are exchanged. This results in chromosomes with different parental contributions |
front 291 define homologous chromosome | back 291 chromosomes that carry genes for the same traits (one+ parental chromosome; the other = maternal chromosome |
front 292 What are the hormones produced by the corpus luteum | back 292 Progesterone and estrogen |
front 293 secondary spermatocyte | back 293 haploid, product of meiosis I |
front 294 spermatogonium | back 294 primitive stem cell |
front 295 sustentocyte | back 295 provides nutrients to developing sperm |
front 296 spermatid | back 296 haploid, product of meiosis II |
front 297 sperm | back 297 haploid, product of spermiogenesis |
front 298 What uterine tissue undergoes dramatic changes during the menstrual cycle? | back 298 endometrium |
front 299 primary oocyte | back 299 forming part of the primary follicle in the ovary |
front 300 secondary oocyte | back 300 in the uterine tube before fertilization in the vesicular follicle of the ovary |
front 301 ovum | back 301 in the uterine tube shortly after fertilization |
front 302 when during the female menstrual cycle would fertilization be unlikely? Explain why? | back 302 any time but the three-day interval (days 14-16) around ovulation (twenty-eight-day cycle is assumed) |
front 303 amount of LH in the blood during menstruation IS LESS THAN | back 303 amount of LH in the blood at ovulation |
front 304 amount of FSH in the blood on day 6 of the cycle GREATER THAN | back 304 amount of FSH in the blood on day 20 of the cycle |
front 305 amount of estrogen in the blood during menstruation LESS THAN | back 305 amount of estrogen in the blood at ovulation |
front 306 amount of progesterone in the blood on day 14 LESS THAN | back 306 amount of progesterone in the blood on day 23 |
front 307 amount of estrogen in the blood on day 10 GREATER THAN | back 307 amount of progesterone in the blood on dy 10 |
front 308 Menstruation | back 308 Days 1-5. Endometrium is sloughing off primary follicle begins to grow |
front 309 Proliferative | back 309 Days 6-14. Endometrium repaired, glands and blood vessels proliferate. Endometrium thickens Follicular growth continues and vesicular follicle(s) produced. Estrogen secreted and peaks at day 14. Ovulation occurs on the 14th day. |
front 310 Secretory | back 310 Days 15-28. Vascular supply increases and glands begin secretory activity. Ruptured follicle is converted to a corpus luteum, which begins to produce progesterone (and some estrogen). Peaks at day 23 and then begins to decline. |