GIS test two, digital image processing and analysis
Remotely sensed images by themselves are not valuable. They need to be _________________.
Analyzed
Preprocessing involves raw _____________ images with no _________________.
satellite, corrections
What are Radiometric corrections?
Correcting for sensor irregularities,
unwanted sensor noise, or
atmospheric noise
What are the two types of radiometric corrections?
Sensor irregularities and atmospheric irregularities
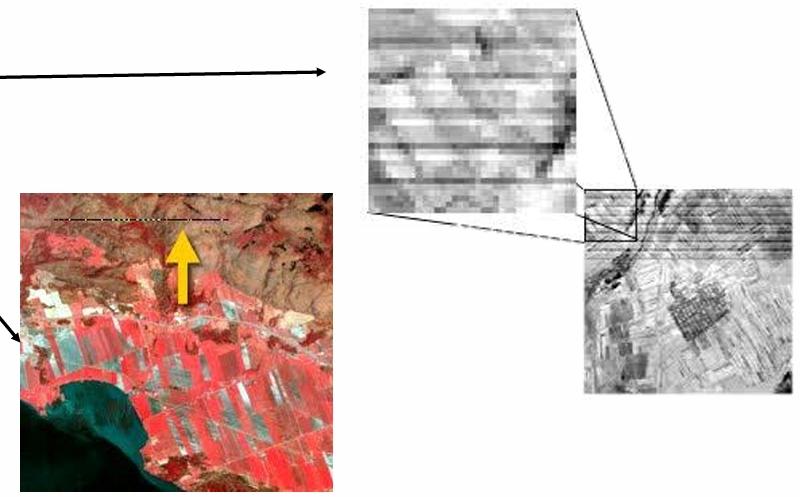
What are the two types of sensor irregularities shown here?
Stripping and dropped lines
What are Pseudo invariant calibration sites (PICS) used for?
Calibrating sensors or accounting for variation within sensors
For corrections to smaller images (like one taken by a drone) what manual method can be done to correct portions of the image?
Ground target collection
What is geometric correction?
The identification of image coordinates (rows, columns) at several known points using ground control points (GCPs)
AKA= telling an image where it is in the real world using reference points
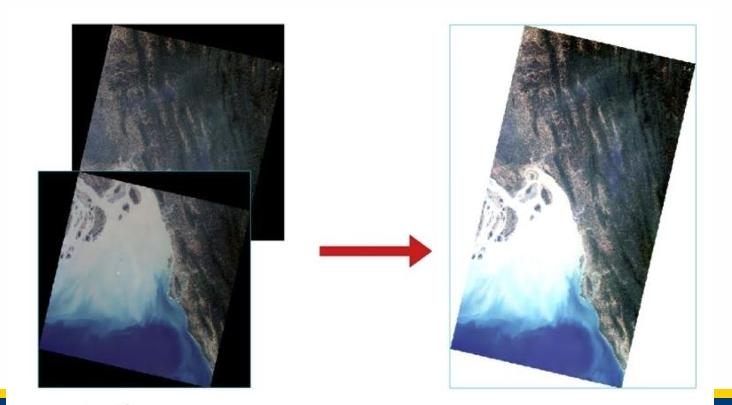
Composite images consist of at least _____ images. They ___________ the area covered, can remove_________, and reduce ____-_________ angles
2, increase, clouds, off-nadir
__________ ________________ is used to improve the appearance of
imagery to assist with _________
interpretation without changing
the data.
Image Enhancement, visual
What does contrast refer to?
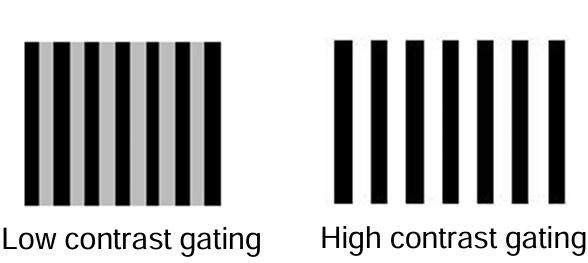
the difference in luminance or colour that makes
object details distinguishable
Contrast enhancement does what?

Changes the original values in the image to be displayed using the full range of available values
What is an Image histogram?
A graphical representation of the brightness values
that
comprise an image
What is a Linear Contrast Stretch?
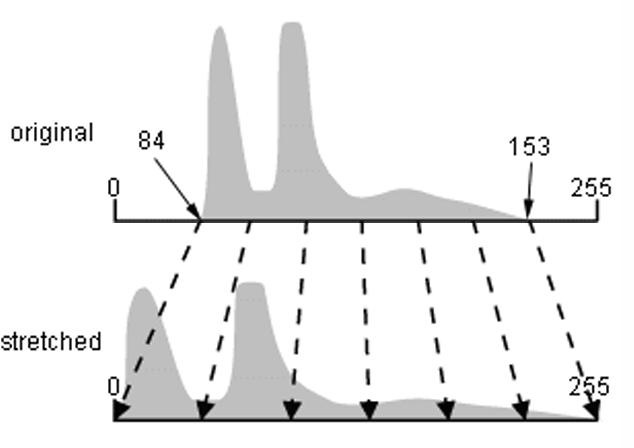
When the minimum and maximum values
of a histogram are
stretched so the data fills the whole 0-255 range.
How does a percent clip work? What does it increase?
A chosen percentage of the highest an lowest values of an image are "clipped" from the histogram and everything that remains is stretched fill the gaps. Contrast is increased.
A _____________ ______________ stretch Assigns more display values (range) to frequently occurring portions of the histogram. What data is this method the better approach for?
Histogram equalization, Better approach for data that is not normally distributed
What is spatial frequency? What texture will areas with high spatial frequency have? Low spatial frequency?
Variation in tone that appears in an image, rough areas where changes in tone are abrupt, smooth areas with little variation in tone
What does spatial filtering do?
Highlights or suppresses specific features in an image based on spatial frequency

Which image has high spatial frequency? Which has low spatial frequency?
Top=high, bottom=low
Low pass, high pass, edge detection, and directional are all types of what?
Spatial Filtering
What is moved over pixels in an image to create a new value for the central pixel in spatial filtering?
a "window"
Which type of spatial filtering smooths data by reducing local variation and removing noise, typically using the mean or median values of the window? What is it removing?
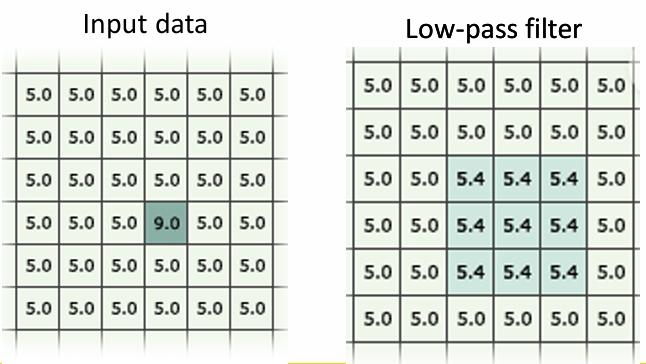
Low Pass Filtering, Removes extreme values in the data
Which type of spatial filtering sharpens the appearance of fine detail in an image like boundaries between features? What are cells being weighted to remove?

High Pass Filtering, Cells are weighted to remove low frequency variations
What do edge detection filters highlight (give an ex)? What is this type of filter identifying?
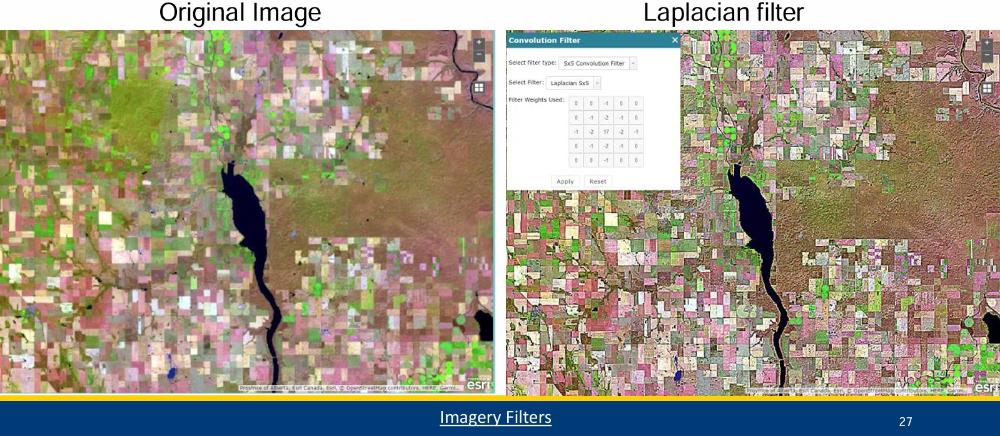
linear features such as roads or field
boundaries, Identifies
points in an image where brightness values change sharply
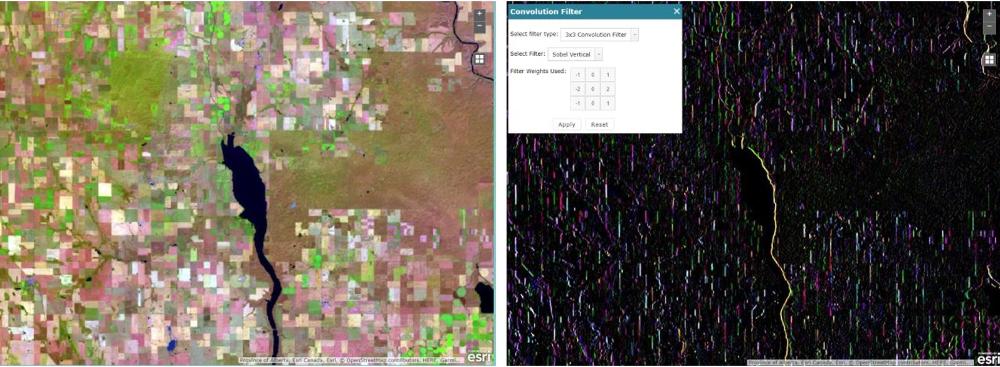
What type of spatial filter is Used to highlight features in a specific direction?
Directional filter
What is Image Transformation?
The Generation of a new image from two or more sources which highlight a feature of interest
Image transformation involves the combined processing of multiple ____________ _________ and applies simple ____________ operations.
spectral bands, arithmetic

What type of image transformation is being preformed here?
Hint: It's used to identify changes that occurred in the time between two images
Image subtraction
What does spectral ratioing do? What one of the two examples given in lecture?
It enhances the variation between spectral bands. Normalized burn ratio (NBR) or Normalized vegetation index (NDVI)
What does PCA stand for, what does it do and why?
Principal component analysis, reduces redundancy between multispectral bands via compressing them together as they are often highly correlated and contain similar information
______________ are the new bands that result from
statistical
procedures in Principal component analysis (PCA)
Components
Name two potential types of features that could be in Foundation mapping
- Land use and land cover (forest, grass, urban cover)
- Cartographic features (roads, building footprints, natural features)
- Terrain and elevation
- Hydrographic flow (watersheds, rivers, floodplain maps)
What type of map does foundational mapping create?
A thematic map
What does a thematic map map?
the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area
Describe how you would design a remote sensing plan from start to finish.
QA=quality assurance
QC=quality control
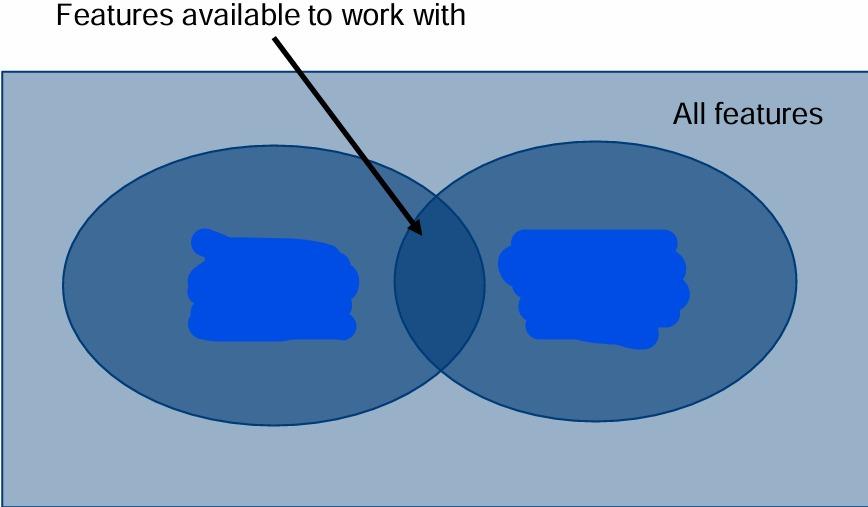
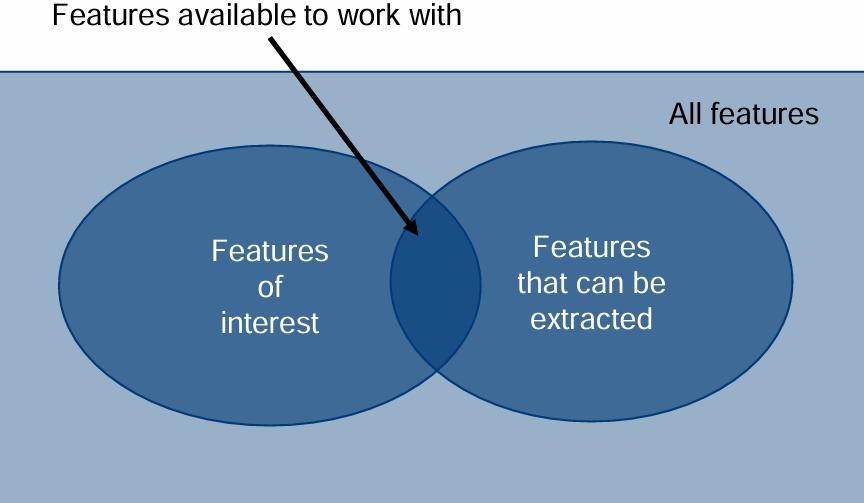
What are the labels in the Venn diagram?
Why does pixel based classification work? Is it preferred to use reflectance or DN values for this technique? What type of map does this create?
Because different features have different spectral signatures and can be differentiated by those features, reflectance, a thematic map
What are spectral classes?
Groups of pixels that have similar brightness values within their spectral channels
What are information classes?
Categories of interest that analysts are trying to identify in the imagery (e.g., crop type, forest types, rock type…)
What is Unsupervised Pixel-Based Classification? What are its main pros and cons?
When an algorithm sorts information into classes and labels them numerically.
Pros=computer can pick up on information humans would probably miss
Cons=Human needs to interpolate unlabelled classes, risk of over or under classification
What is Supervised Pixel-Based Classification? What are its main pros and cons?
When an analyst manually creates training samples of different features to tell the computer which values mean what. The algorithm then gives back named classes in a thematic raster.
Pros=There is significant control over the logic of the classification,
Cons=The thematic raster may be noisy at the pixel level, accuracy dependant on training data, human bias, training data formation is time consuming
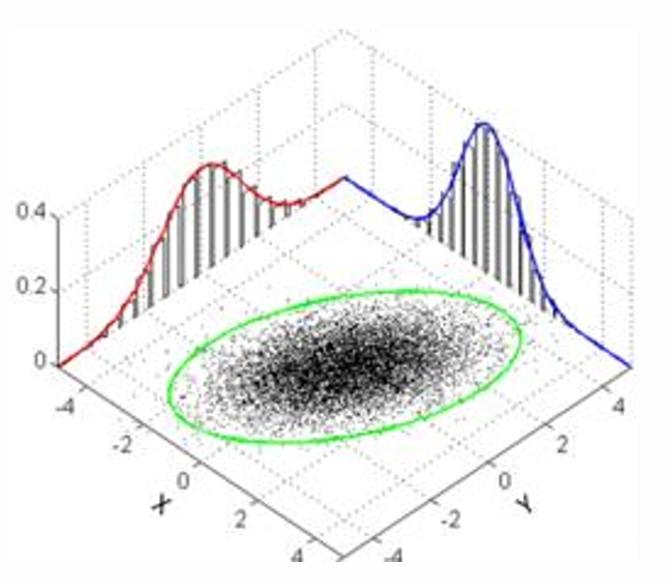
What is this?
Multivariate Distribution
What do Object-Oriented Approaches to classification and extraction do?
Group pixels into representative polygons
What does image segmentation do?

Groups pixels with similar characteristics into larger
objects
so The image is divided into homogenous regions
In Image segmentation are classes assigned to individual pixels or entire objects?
Entire objects
What are the pros and cons of Image Object-Oriented Approaches to classification and extraction?
Pros= contextual information, reduces pixel noise
cons=computationally intensive, not effective for coarse resolution, requires a model
What is deep learning based on? What research does it originate from?
Neural networks, artificial intelligence
What is a primary technique for applying deep learning to imagery?
convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
What does object identification with deep learning output?

a feature layer of polygons, showing where the objects are located.
What does pixel classification with deep learning output?
a raster with a class for each pixel
What are some pros and cons to using deep learning?
Pros=incorporates spatial and spectral clues, can classify based on objects or pixels
Cons=Needs many samples, requires an expert to teach (parameters, evaluation when teaching), over and under classification
What is the term for The combining or merging of data from multiple sources to extract better/more information.
Data integration
What are examples of data integration?
Radar, LiDAR