GIS test 2, Intro to remote sensing
Define remote sensing
Getting info on emitted or reflected light energy from a considerable distance away- typically with tools such as satellites, aircraft or drones
When using technology for remote sensing, what is being sensed/what are we looking for?
Reflected or emitted electromagnetic energy
What are the seven steps of the remote sensing data cycle?
Energy Source, Atmospheric Interaction, Interaction with Target, Recording Information, processing, analysis, application
What is the difference between passive and active remote sensing?
Passive: captures reflected or emitted energy
Active: Emits energy towards a target and measures the return value
Which type of remote sensing is often cheaper and simpler?
Passive remote sensing
What is the source of the energy that passive remote sensing picks up on? What does this mean for the timing of when we use passive remote sensing?
The sun, we can't use it at night
What are the two types of active remote sensing?
LiDAR and Radar
Define electromagnetic energy
The flow of energy at the speed of light
through free space
Define wavelength. What units is it normally measured in?
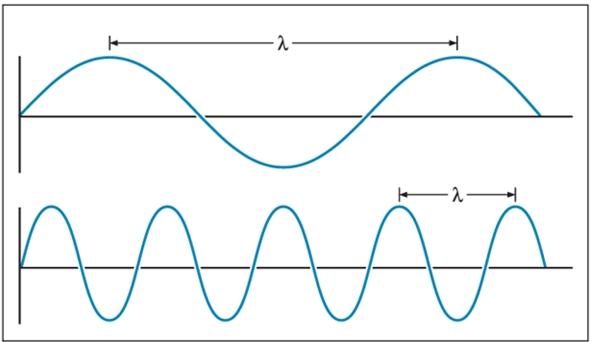
Distance between the crests of two waves. Typically measured in micrometers (μm) or nanometers (nm)
Define frequency. What unit is it normally described with?
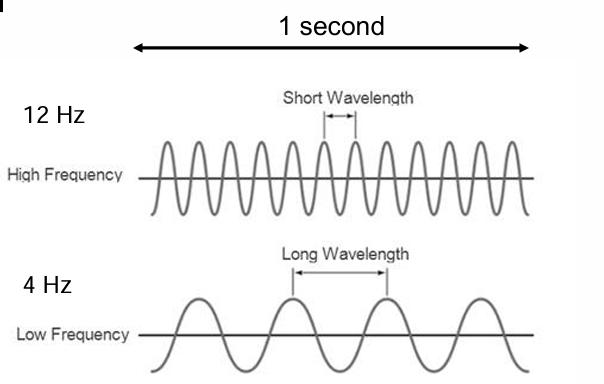
Number of cycles of a wave past a fixed point in a second. Unit is hertz (Hz)
If seven wave cycles pass a fixed point in a second what is the frequency?
7 Hz
Frequency has an _____________ relationship with wavelength. This means that a ________ wavelength will have a _______ frequency and vise versa.
Inverse, short, high
Define amplitude. What does this look like on a graph?
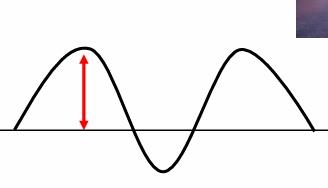
The maximum strength of the electric and magnetic fields. The distance from the peak of a crest the midline of the graph.
Energy travels at a constant. What is the constant?
The speed of light (299,792,458 m/s)
From shortest to longest what are the seven radiation types on the electromagnetic spectrum?
Gamma rays, X-rays, Ultraviolet, Visible light, Infrared, Microwaves and Radio waves
A _______ _______ absorbs all incoming energy which raises its temperature. As it heats up, it emits ________ wavelengths.
black body, shorter
White bodies perfectly reflect all energy _________ in all ______________.
equally, directions
What is Wein's Law?
The peak wavelength of radiation emission is inversely related to the temperature of the emitting body.
AKA
A hotter object emits shorter wavelengths and vise versa
What is the Stefan–Boltzmann Constant?
In a black body the total intensity radiated over all wavelengths increases with temperature.
AKA
Any energy a black body absorbs will increase its temperature
A black body re-emits energy as quickly as it absorbs it when? What law is this?
When it reaches an equilibrium temperature, Planck's Law
The spectrum of radiation emitted by an object is dependant on ____________ alone. Not shape or composition.
temperature
The sun emits __________________ radiation while the Earth emits ________________ radiation.
shortwave, longwave
What portion of the electromagnetic spectrum does visible light cover?
0.34 micrometers (400 nm) to 0.7 micrometers (700nm)
What element is most plentiful in our atmosphere? What percentage of our atmosphere is it?
Nitrogen gas (N2), 78%
When Energy passes through space and interacts with the atmosphere what are the three possible outcomes of the interaction?
absorption, scattering or transmission (re-emission)
How many times does energy pass through the atmosphere before it is picked up by satellites?
twice (once incoming from the sun, another after being reflected by the earth)
Describe atmospheric scattering.
Redirection of electromagnetic energy when
it hits particle or
gas molecules
Because our atmosphere causes scattering, what is it called?
A scattering medium
What are the three factors that scattering depends on?
1. The size of the wavelength in relation to the scattering
particle
2. The distance travelled through the scattering
medium
3. The Density of the scattering medium
Scattering of light by particles smaller than the
wavelength
being scattered (ex. fine dust, N2, O2) is called what? Where does
this occur and what effect does it have?
Rayleigh Scattering, upper atmosphere, blue sky because it impacts shorter wavelengths (like red) the most
Scattering of light caused by atmospheric particles
about the
same size as the scattered wavelength (ex. Dust, pollen, smoke) is
called what? Where does this occur and what does it affect most?
Mie Scattering, lower atmosphere, longer wavelengths
Scattering of light caused by a particle
larger than the
wavelength being scattered (ex. Large dust particles and water
droplets) is called what? What effect does it have?
Nonselective Scattering, causes clouds and fog to appear white
What are the three important components/elements of the atmosphere in relation to energy absorption?
Ozone, carbon dioxide, and water vapor
What electromagnetic energy does Ozone absorb?
Ultraviolet energy
What are Atmospheric Windows?
Wavelengths where most of the energy
passes through the
atmosphere/Areas of the electromagnetic spectrum that are not severely
influenced by atmospheric absorption
What electromagnetic energy does Carbon Dioxide (CO2) absorb?
Infrared radiation
Does water vapour absorb longwave or shortwave radiation?
both
Nitrous Oxide (NO) and methane combined absorb how many small portions of the electromagnetic spectrum?
2
What is transmission (in a remote sensing context)?
when energy passes through a target (think light through a dense tree canopy)
What is absorption? How is this used in plants?
when energy is trapped and held by a surface, In plants, absorbed energy is used for photosynthesis
What is reflection? What are the two classifications of reflection?
when energy "bounces" off the target and is
redirected, Specular and diffuse
Describe specular and diffuse reflection.
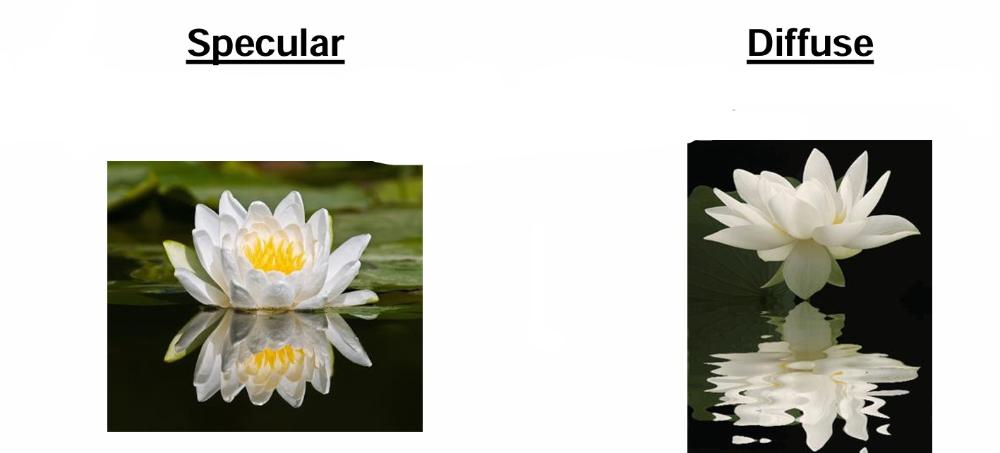

Specular: Reflection from smooth surfaces that
produce a
single, clear reflection
Diffuse: Rough surfaces that reflect light in
multiple directions
In a perfect scenario the angle of ____________ is always equal to the angle of ____________.
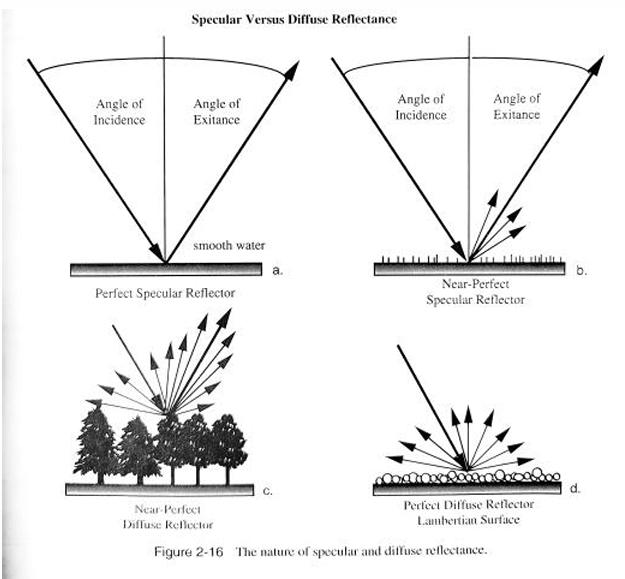
incident, reflection
What is incident energy? What is the equation for it?
The total amount of energy per wavelength that
interacts with
an object
I=R+A+T
What is Spectral reflectance? What is the equation for it?
The percentage of total energy per wavelength
reflected from
the surface
p = (R/I) * 100
Healthy vegetation will absorb _________ and _______ wavelengths, reflect ________, and strongly reflect ____________.
red and blue, green, near-infrared (NIR)
With the loss of chlorophyll in autumn what wavelengths are being reflected less? What is the visual result of this?
green and NIR, yellow/reddish appearance
What is a spectral signature?
A unique identifier for a particular item generated
by charting
the reflected energy per wavelength
Because of spectral signatures, in theory plants can be identified based on their spectral signatures. Why is this difficult to do in practice?
Vegetation often exists in a heterogeneous environment and A single pixel (of a raster) may contain many different plant species
When can we practically use remote sensing to identify different types of vegetation?
Homogenous vegetation, such as crops or for different types of land cover
What is the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
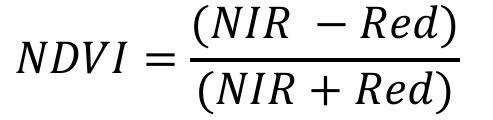
A method of measuring vegetation using NIR and red energy
What is the range of values NDVI can be? What NDVI number do you want for healthy vegetation?
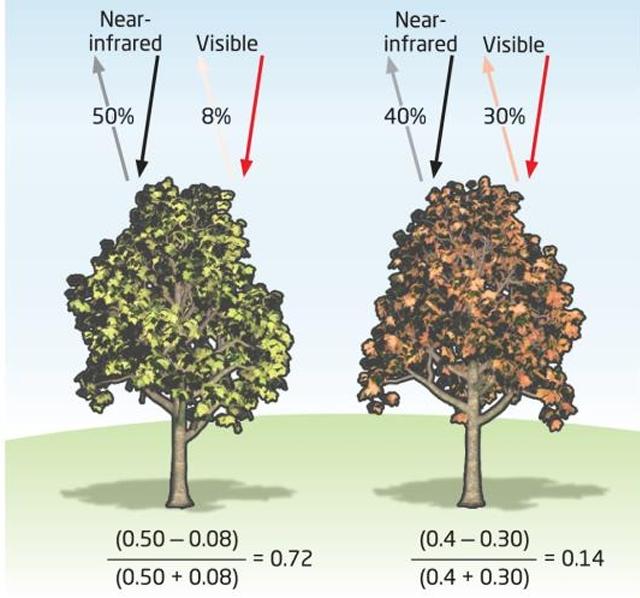
-1 to +1, Higher positive values
What are the three example uses of NDVI the lecture notes list?
Estimate primary productivity over varying biomes, Identify eco-regions, Assess the length of the growing season
What is the Leaf Area Index (LAI)?
Ratio of total one-sided green leaf area per unit of
ground area
AKA
Measure of leaf material relative to the ground below
What is the value range for LAI and what are its potential uses listed in the lecture slides?
0-10, assess ecosystem health, understand evapotranspiration, and monitor crops
What is the Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FPAR)?
The fraction of incoming solar radiation that is absorbed for photosynthesis
What is the Normalized Burn Ratio (NBR) used for? What are its value ranges?
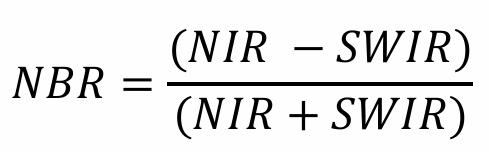
Used to identify burned areas and
provide a measure of burn
severity, -1 to +1
Water absorbs which longer wavelengths the most?
NIR and visible
Rank these urban materials from least to most reflective:
- Red bricks
- Asphalt
- Concrete
Asphalt, Red bricks, concrete