Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
GIS test 2, Intro to remote sensing
front 1 Define remote sensing | back 1 Getting info on emitted or reflected light energy from a considerable distance away- typically with tools such as satellites, aircraft or drones |
front 2 When using technology for remote sensing, what is being sensed/what are we looking for? | back 2 Reflected or emitted electromagnetic energy |
front 3 What are the seven steps of the remote sensing data cycle? | back 3 Energy Source, Atmospheric Interaction, Interaction with Target, Recording Information, processing, analysis, application |
front 4 What is the difference between passive and active remote sensing? | back 4 Passive: captures reflected or emitted energy Active: Emits energy towards a target and measures the return value |
front 5 Which type of remote sensing is often cheaper and simpler? | back 5 Passive remote sensing |
front 6 What is the source of the energy that passive remote sensing picks up on? What does this mean for the timing of when we use passive remote sensing? | back 6 The sun, we can't use it at night |
front 7 What are the two types of active remote sensing? | back 7 LiDAR and Radar |
front 8 Define electromagnetic energy | back 8 The flow of energy at the speed of light |
front 9 Define wavelength. What units is it normally measured in? | back 9 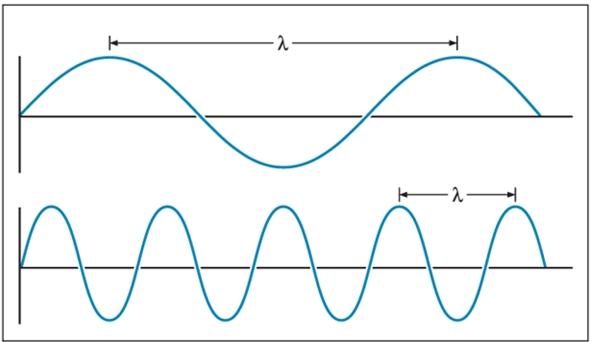 Distance between the crests of two waves. Typically measured in micrometers (μm) or nanometers (nm) |
front 10 Define frequency. What unit is it normally described with? | back 10 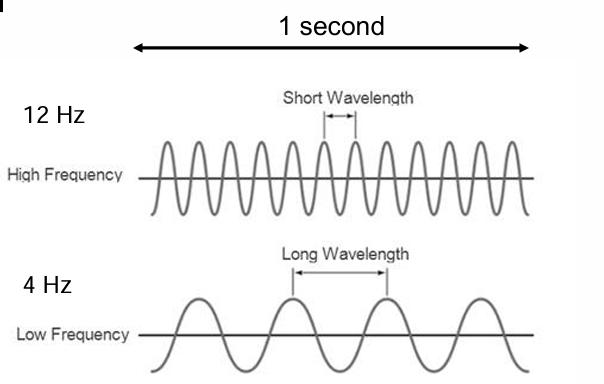 Number of cycles of a wave past a fixed point in a second. Unit is hertz (Hz) |
front 11 If seven wave cycles pass a fixed point in a second what is the frequency? | back 11 7 Hz |
front 12 Frequency has an _____________ relationship with wavelength. This means that a ________ wavelength will have a _______ frequency and vise versa. | back 12 Inverse, short, high |
front 13 Define amplitude. What does this look like on a graph? | back 13 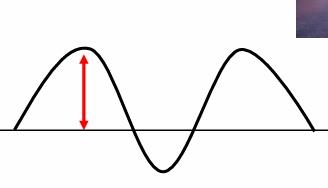 The maximum strength of the electric and magnetic fields. The distance from the peak of a crest the midline of the graph. |
front 14 Energy travels at a constant. What is the constant? | back 14 The speed of light (299,792,458 m/s) |
front 15 From shortest to longest what are the seven radiation types on the electromagnetic spectrum? | back 15 Gamma rays, X-rays, Ultraviolet, Visible light, Infrared, Microwaves and Radio waves |
front 16 A _______ _______ absorbs all incoming energy which raises its temperature. As it heats up, it emits ________ wavelengths. | back 16 black body, shorter |
front 17 White bodies perfectly reflect all energy _________ in all ______________. | back 17 equally, directions |
front 18 What is Wein's Law? | back 18 The peak wavelength of radiation emission is inversely related to the temperature of the emitting body. AKA A hotter object emits shorter wavelengths and vise versa |
front 19 What is the Stefan–Boltzmann Constant? | back 19 In a black body the total intensity radiated over all wavelengths increases with temperature. AKA Any energy a black body absorbs will increase its temperature |
front 20 A black body re-emits energy as quickly as it absorbs it when? What law is this? | back 20 When it reaches an equilibrium temperature, Planck's Law |
front 21 The spectrum of radiation emitted by an object is dependant on ____________ alone. Not shape or composition. | back 21 temperature |
front 22 The sun emits __________________ radiation while the Earth emits ________________ radiation. | back 22 shortwave, longwave |
front 23 What portion of the electromagnetic spectrum does visible light cover? | back 23 0.34 micrometers (400 nm) to 0.7 micrometers (700nm) |
front 24 What element is most plentiful in our atmosphere? What percentage of our atmosphere is it? | back 24 Nitrogen gas (N2), 78% |
front 25 When Energy passes through space and interacts with the atmosphere what are the three possible outcomes of the interaction? | back 25 absorption, scattering or transmission (re-emission) |
front 26 How many times does energy pass through the atmosphere before it is picked up by satellites? | back 26 twice (once incoming from the sun, another after being reflected by the earth) |
front 27 Describe atmospheric scattering. | back 27 Redirection of electromagnetic energy when |
front 28 Because our atmosphere causes scattering, what is it called? | back 28 A scattering medium |
front 29 What are the three factors that scattering depends on? | back 29 1. The size of the wavelength in relation to the scattering
particle |
front 30 Scattering of light by particles smaller than the | back 30 Rayleigh Scattering, upper atmosphere, blue sky because it impacts shorter wavelengths (like red) the most |
front 31 Scattering of light caused by atmospheric particles | back 31 Mie Scattering, lower atmosphere, longer wavelengths |
front 32 Scattering of light caused by a particle | back 32 Nonselective Scattering, causes clouds and fog to appear white |
front 33 What are the three important components/elements of the atmosphere in relation to energy absorption? | back 33 Ozone, carbon dioxide, and water vapor |
front 34 What electromagnetic energy does Ozone absorb? | back 34 Ultraviolet energy |
front 35 What are Atmospheric Windows? | back 35 Wavelengths where most of the energy |
front 36 What electromagnetic energy does Carbon Dioxide (CO2) absorb? | back 36 Infrared radiation |
front 37 Does water vapour absorb longwave or shortwave radiation? | back 37 both |
front 38 Nitrous Oxide (NO) and methane combined absorb how many small portions of the electromagnetic spectrum? | back 38 2 |
front 39 What is transmission (in a remote sensing context)? | back 39 when energy passes through a target (think light through a dense tree canopy) |
front 40 What is absorption? How is this used in plants? | back 40 when energy is trapped and held by a surface, In plants, absorbed energy is used for photosynthesis |
front 41 What is reflection? What are the two classifications of reflection? | back 41 when energy "bounces" off the target and is
|
front 42 Describe specular and diffuse reflection. | back 42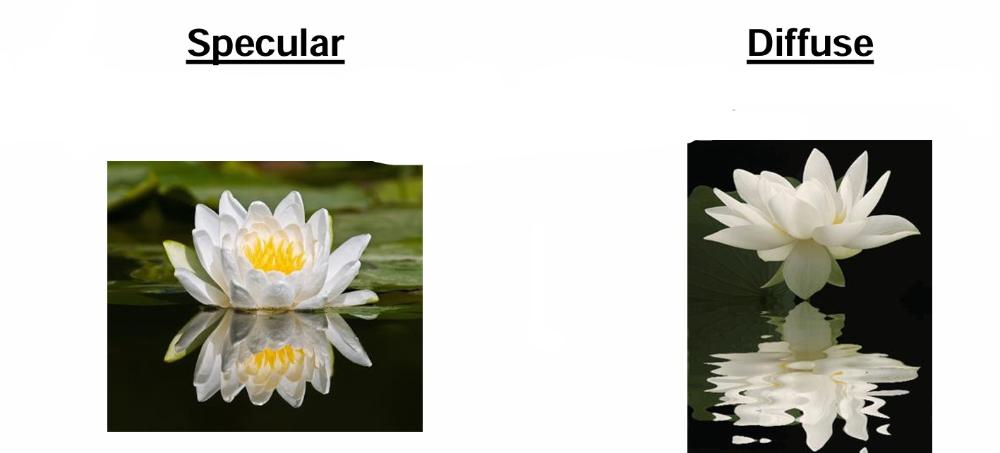  Specular: Reflection from smooth surfaces that Diffuse: Rough surfaces that reflect light in |
front 43 In a perfect scenario the angle of ____________ is always equal to the angle of ____________. | back 43 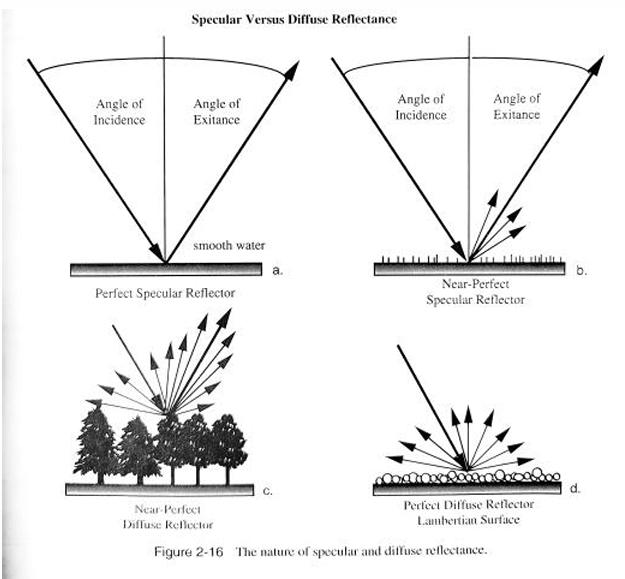 incident, reflection |
front 44 What is incident energy? What is the equation for it? | back 44 The total amount of energy per wavelength that I=R+A+T |
front 45 What is Spectral reflectance? What is the equation for it? | back 45 The percentage of total energy per wavelength p = (R/I) * 100 |
front 46 Healthy vegetation will absorb _________ and _______ wavelengths, reflect ________, and strongly reflect ____________. | back 46 red and blue, green, near-infrared (NIR) |
front 47 With the loss of chlorophyll in autumn what wavelengths are being reflected less? What is the visual result of this? | back 47 green and NIR, yellow/reddish appearance |
front 48 What is a spectral signature? | back 48 A unique identifier for a particular item generated |
front 49 Because of spectral signatures, in theory plants can be identified based on their spectral signatures. Why is this difficult to do in practice? | back 49 Vegetation often exists in a heterogeneous environment and A single pixel (of a raster) may contain many different plant species |
front 50 When can we practically use remote sensing to identify different types of vegetation? | back 50 Homogenous vegetation, such as crops or for different types of land cover |
front 51 What is the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | back 51 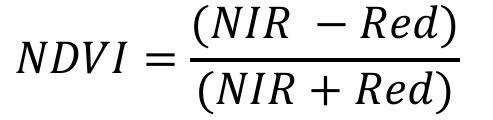 A method of measuring vegetation using NIR and red energy |
front 52 What is the range of values NDVI can be? What NDVI number do you want for healthy vegetation? | back 52 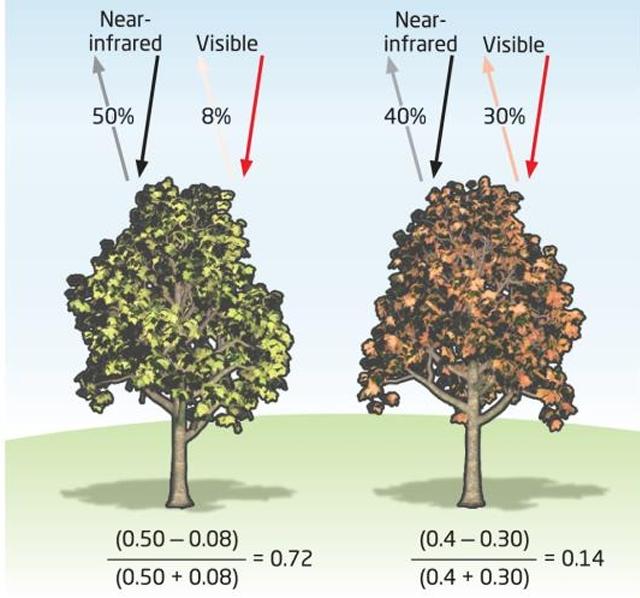 -1 to +1, Higher positive values |
front 53 What are the three example uses of NDVI the lecture notes list? | back 53 Estimate primary productivity over varying biomes, Identify eco-regions, Assess the length of the growing season |
front 54 What is the Leaf Area Index (LAI)? | back 54 Ratio of total one-sided green leaf area per unit of AKA Measure of leaf material relative to the ground below |
front 55 What is the value range for LAI and what are its potential uses listed in the lecture slides? | back 55 0-10, assess ecosystem health, understand evapotranspiration, and monitor crops |
front 56 What is the Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FPAR)? | back 56 The fraction of incoming solar radiation that is absorbed for photosynthesis |
front 57 What is the Normalized Burn Ratio (NBR) used for? What are its value ranges? | back 57 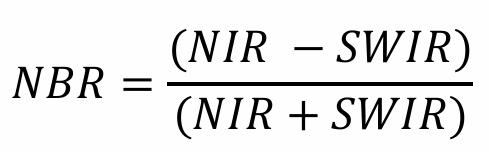 Used to identify burned areas and |
front 58 Water absorbs which longer wavelengths the most? | back 58 NIR and visible |
front 59 Rank these urban materials from least to most reflective:
| back 59 Asphalt, Red bricks, concrete |