GIS test 2, Aerial images
What is Remote Sensing?
Getting info on emitted or reflected light energy from a considerable distance away- typically with tools such as satellites, aircraft or drones
Who described observing a solar eclipse using a camera obscura in 1038?
*camera obscura=dark chambre in latin
Al Hazen
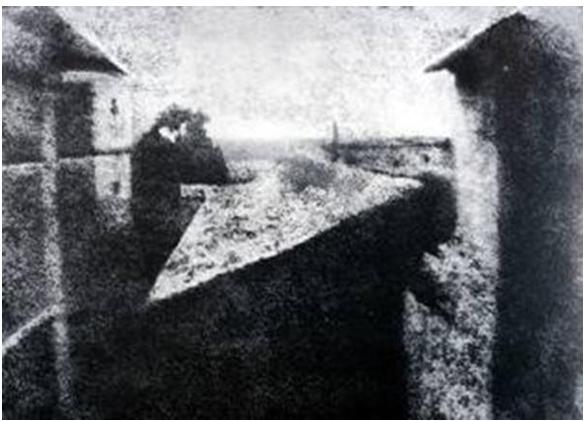

Who crated the first photograph in 1826?
Joseph Niépce
The device that uses two pictures of the same scene with a slight offset mounted side-by-side to give the impression of a 3D image is called what?
(Hint we used it in lab)
The Stereoscope
Which French man used a hot air balloon to take the first aerial photo of Paris (1858)?
Gasper Felix Tournachon, aka “Nadar"

Who is the Father of Kite Photography?
Arthur Batut

Which global events increased the interest in aerial reconnaissance leading to the use of pigeons to take covert aerial photos?
WW1 and WW2
In 1981 NASA acquired its first ER-2, and a second in 1989 (these are high altitude planes). What satellite components did they help develop?
Sensors
Rank these Canadian aerial photography instances from most to least recent.
- A) The Interdepartmental Committee on Air Surveys and National Air Photo Library are established
- B) Imperial Oil
scientists photograph a swampy
section of the Slave River - C) The Canadian Air Board makes recommendations for how aerial photographs could be used
B, C, A
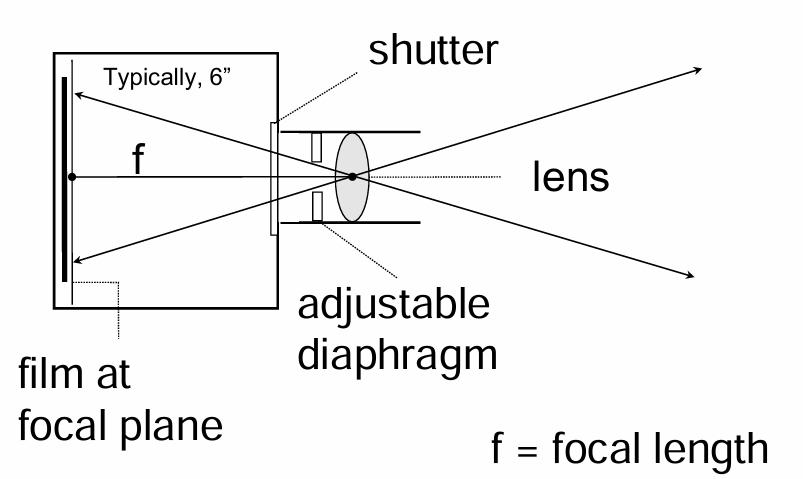
This tool is used to take aerial pictures from aircraft. What is it?
Single lens camera
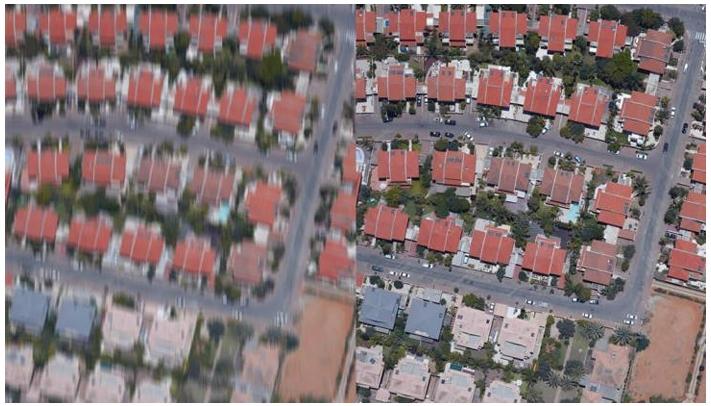

What technology (developed in 1987) takes an image from the left to the right?
Forward Motion Compensation (FMC)
_______-___________ mounts are used to correct for pitch and roll caused by turbulence
Gyro-stabilized
The ___________ _________ (center of the photo) has the least distortion
principal point

_______ ____________ causes tall objects to lean away from the principal point towards the edges of the photo
Relief displacement
_____________________ removes the effects of terrain and relief displacement to create _______________ with uniform scale
Orthorectification, orthophotos
True orthophotos provide the appearance of looking ____________ _________ on all objects
straight down

_______________ _________________ have a ____ or less tilt, Reduced image distortion, a Nearly constant _______, and are Mainly used for photogrammetry and image interpretation
Vertical Photographs, 3 %, scale
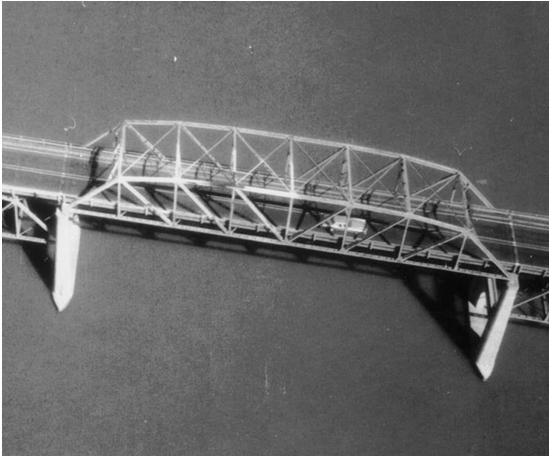
_______-______________ _________________ have a Greater than 3 % tilt without visible __________, Covers a large area, Creates a familiar perspective, but the _________ is distorted.
Low-Oblique Photographs, horizon, scale
High-Oblique Photograph example
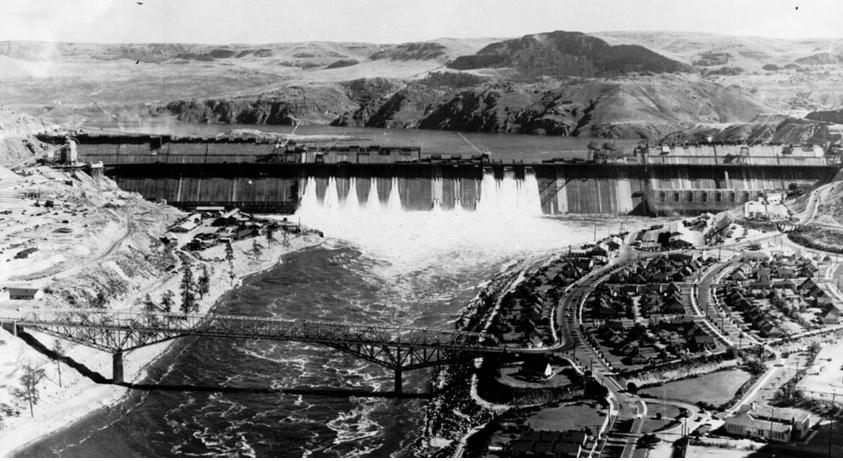

Grand Coulee Dam on the Columbia River, Washington State
Define Panchromatic

Only a portion of the visible
light spectrum, creates greyscale images
Define Colour imagery

Captures red, green, and blue light
to create true colour composites
Define Colour-infrared (CIR)

Images captured with film sensitive to infrared light (not visible to the naked eye)
Define Parallax
the difference in the apparent position of an object
viewed
from two different positions
(switch between closed eyes quickly to create effect)
What is NADIR?
the point or line directly below the image collection instrument, not always the principal point
On a National Topographic System (NTS) map which photos are plotted?
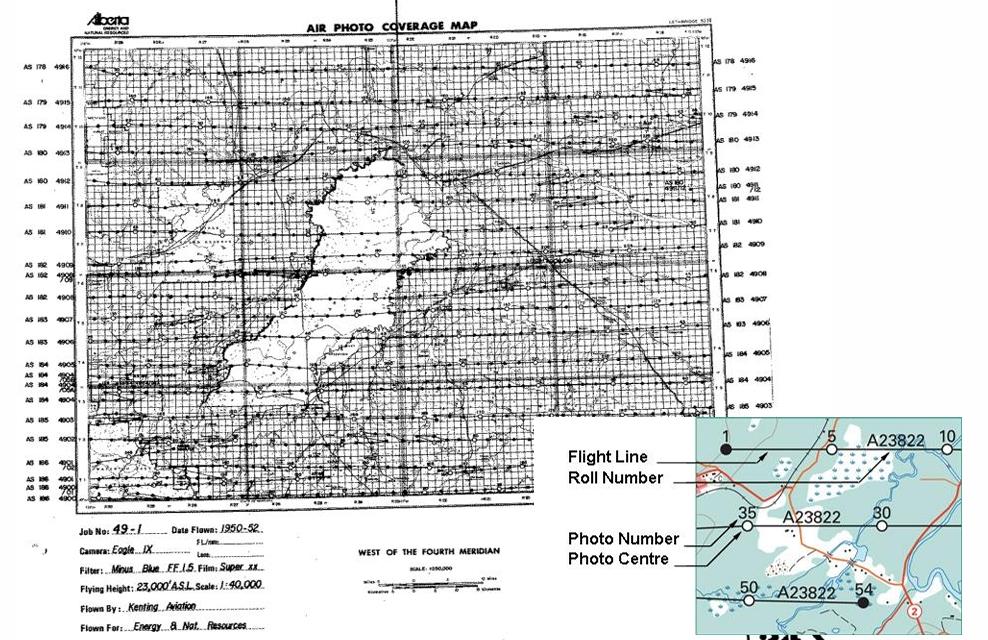
The first, last, and every 5th photo
What is a stereo pair?
2 overlapping aerial images with different viewpoints that can be viewed under a stereoscope to create image parallax
What are Fiducial Marks?
Built in markers that appear in the final stereopair images
In stereopair images where is the principal point in a geometric sense and in relation to the Fiducial Marks?
Geometric center of the photograph and The intersection of the fiducial marks on the image
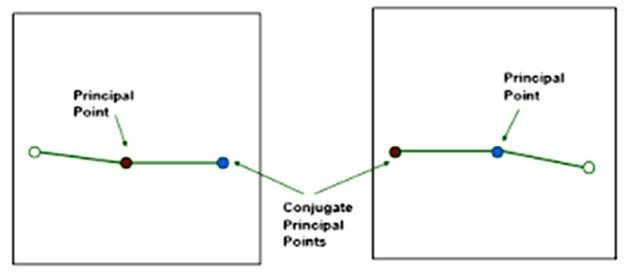
In stereopair images where is the Conjugate Principal Point
The location of the PP from one photo on
the adjacent photo in
the flight line
What do each of these variables represent?
RF = f/H
RF- Representative fraction
f- focal length
H- flying height above terrain
What is the common focal length?
152.598 mm OR 6”
What is the another way to calculate the representative fraction?

Variations of scale in aerial photography are a product of what? (2)
tilt and topography
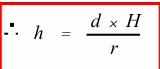
Height can be measured based on relief displacement. Describe the variables in this equation:
h = building height
• d = building height in an image
• H
= flying height above ground
• r = distance from the PP
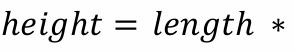
Buildings, where relief displacement
is not clear, may be
measured based
on shadow. What variable is missing from this equation?
tan a
When visually interpreting an image you need to consider Site and association. What does that mean?
Characteristics and relationships between
objects in the image,
what makes sense in the image context?
Name 5 aspects to Visual Image Interpretation (there are 8 in total)
1. Pattern
2. Site and association
3. Size
4.
Shadow
5. Shape
6. Texture
7. Tone
8. Time