Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
GIS test 2, Aerial images
front 1 What is Remote Sensing? | back 1 Getting info on emitted or reflected light energy from a considerable distance away- typically with tools such as satellites, aircraft or drones |
front 2 Who described observing a solar eclipse using a camera obscura in 1038? *camera obscura=dark chambre in latin | back 2 Al Hazen |
front 3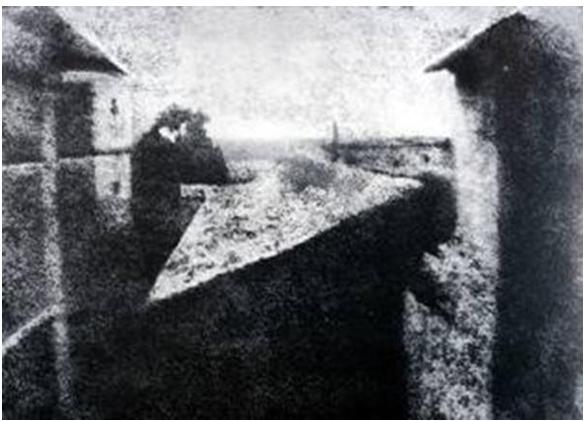  Who crated the first photograph in 1826? | back 3 Joseph Niépce |
front 4 The device that uses two pictures of the same scene with a slight offset mounted side-by-side to give the impression of a 3D image is called what? (Hint we used it in lab) | back 4 The Stereoscope |
front 5 Which French man used a hot air balloon to take the first aerial photo of Paris (1858)? | back 5 Gasper Felix Tournachon, aka “Nadar" |
front 6  Who is the Father of Kite Photography? | back 6 Arthur Batut |
front 7  Which global events increased the interest in aerial reconnaissance leading to the use of pigeons to take covert aerial photos? | back 7 WW1 and WW2 |
front 8 In 1981 NASA acquired its first ER-2, and a second in 1989 (these are high altitude planes). What satellite components did they help develop? | back 8 Sensors |
front 9 Rank these Canadian aerial photography instances from most to least recent.
| back 9 B, C, A |
front 10 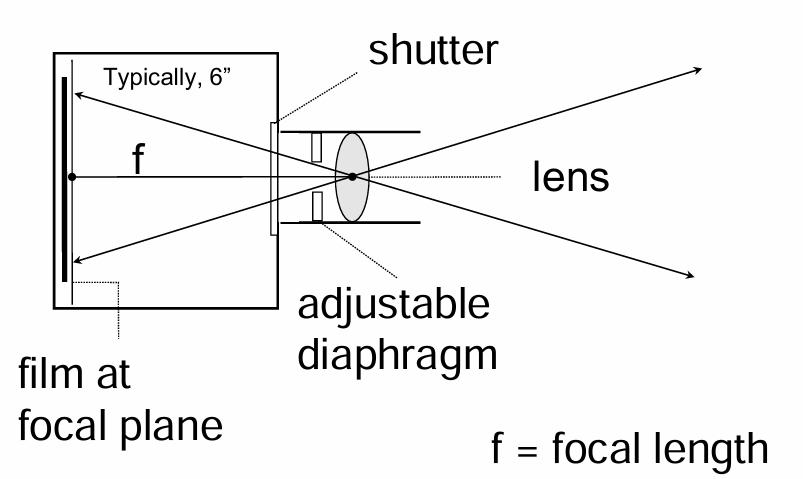 This tool is used to take aerial pictures from aircraft. What is it? | back 10 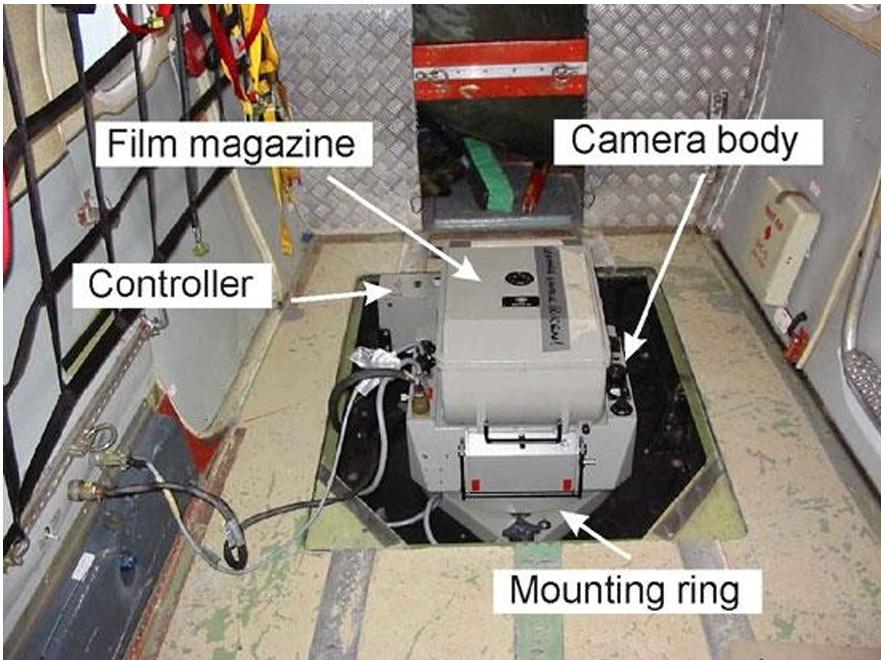 Single lens camera |
front 11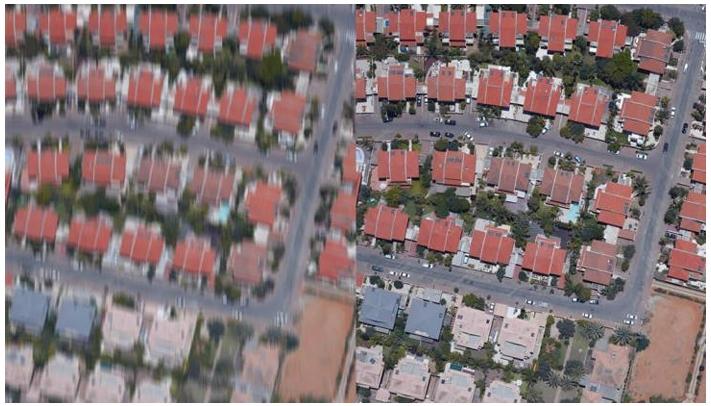  What technology (developed in 1987) takes an image from the left to the right? | back 11 Forward Motion Compensation (FMC) |
front 12 _______-___________ mounts are used to correct for pitch and roll caused by turbulence | back 12 Gyro-stabilized |
front 13 The ___________ _________ (center of the photo) has the least distortion | back 13 principal point |
front 14  _______ ____________ causes tall objects to lean away from the principal point towards the edges of the photo | back 14 Relief displacement |
front 15 _____________________ removes the effects of terrain and relief displacement to create _______________ with uniform scale | back 15 Orthorectification, orthophotos |
front 16 True orthophotos provide the appearance of looking ____________ _________ on all objects | back 16 straight down |
front 17  _______________ _________________ have a ____ or less tilt, Reduced image distortion, a Nearly constant _______, and are Mainly used for photogrammetry and image interpretation | back 17 Vertical Photographs, 3 %, scale |
front 18 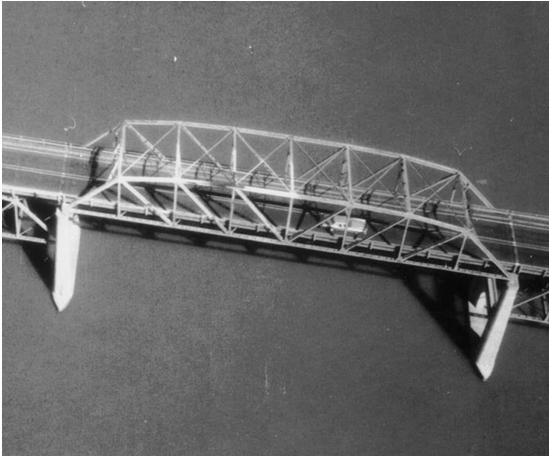 _______-______________ _________________ have a Greater than 3 % tilt without visible __________, Covers a large area, Creates a familiar perspective, but the _________ is distorted. | back 18 Low-Oblique Photographs, horizon, scale |
front 19 High-Oblique Photograph example | back 19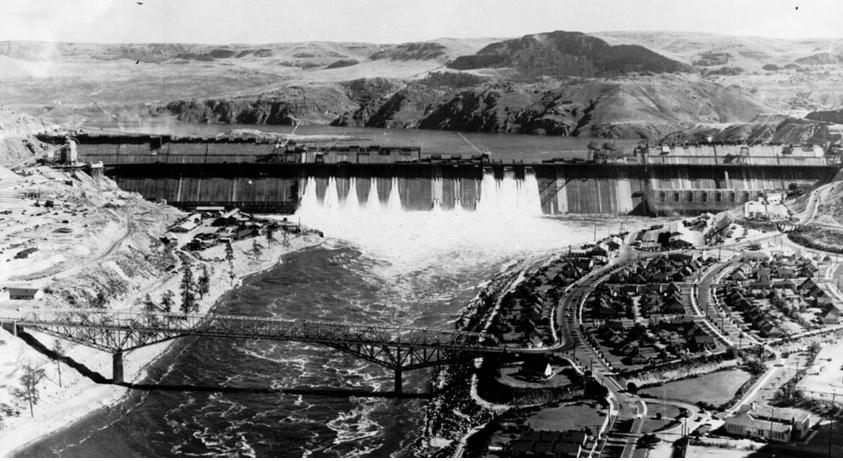  Grand Coulee Dam on the Columbia River, Washington State |
front 20 Define Panchromatic | back 20  Only a portion of the visible |
front 21 Define Colour imagery | back 21  Captures red, green, and blue light |
front 22 Define Colour-infrared (CIR) | back 22  Images captured with film sensitive to infrared light (not visible to the naked eye) |
front 23 Define Parallax | back 23 the difference in the apparent position of an object (switch between closed eyes quickly to create effect) |
front 24 What is NADIR? | back 24 the point or line directly below the image collection instrument, not always the principal point |
front 25 On a National Topographic System (NTS) map which photos are plotted? | back 25 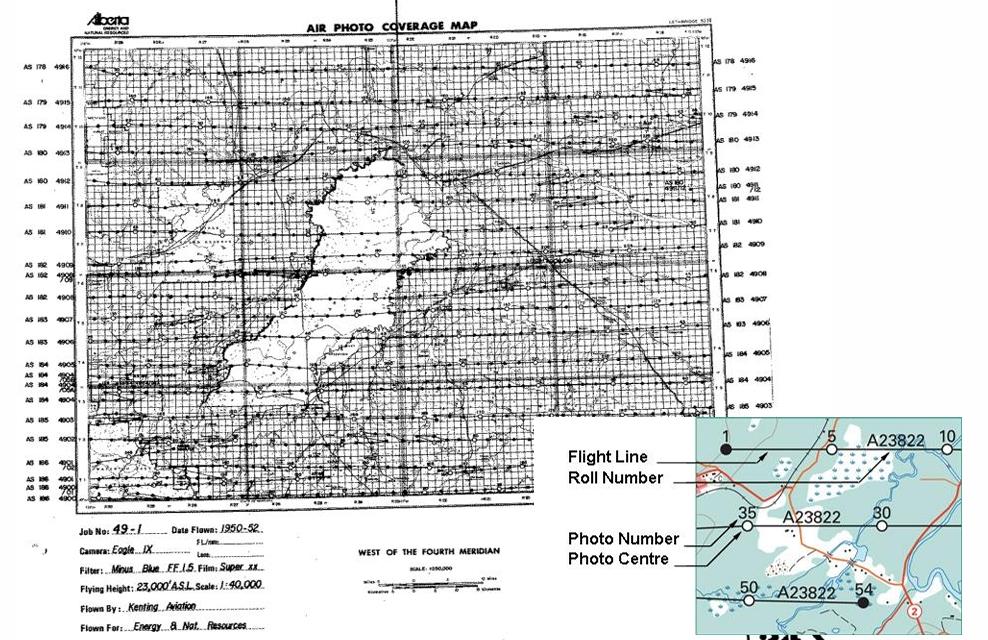 The first, last, and every 5th photo |
front 26 What is a stereo pair? | back 26 2 overlapping aerial images with different viewpoints that can be viewed under a stereoscope to create image parallax |
front 27 What are Fiducial Marks? | back 27 Built in markers that appear in the final stereopair images |
front 28 In stereopair images where is the principal point in a geometric sense and in relation to the Fiducial Marks? | back 28 Geometric center of the photograph and The intersection of the fiducial marks on the image |
front 29 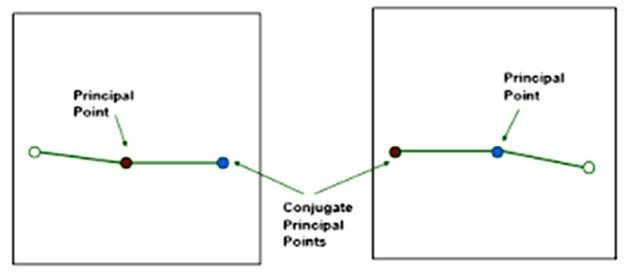 In stereopair images where is the Conjugate Principal Point | back 29 The location of the PP from one photo on |
front 30 What do each of these variables represent? RF = f/H | back 30 RF- Representative fraction f- focal length H- flying height above terrain |
front 31 What is the common focal length? | back 31 152.598 mm OR 6” |
front 32 What is the another way to calculate the representative fraction? | back 32  |
front 33 Variations of scale in aerial photography are a product of what? (2) | back 33 tilt and topography |
front 34 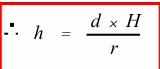 Height can be measured based on relief displacement. Describe the variables in this equation: | back 34 h = building height |
front 35 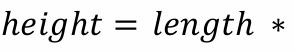 Buildings, where relief displacement | back 35 tan a |
front 36 When visually interpreting an image you need to consider Site and association. What does that mean? | back 36 Characteristics and relationships between |
front 37 Name 5 aspects to Visual Image Interpretation (there are 8 in total) | back 37 1. Pattern |