Chapters 19-20 Organic Chemistry II
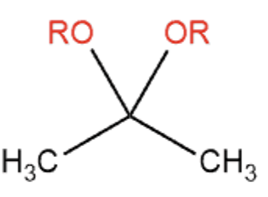
Name That Functional Group!
Acetal
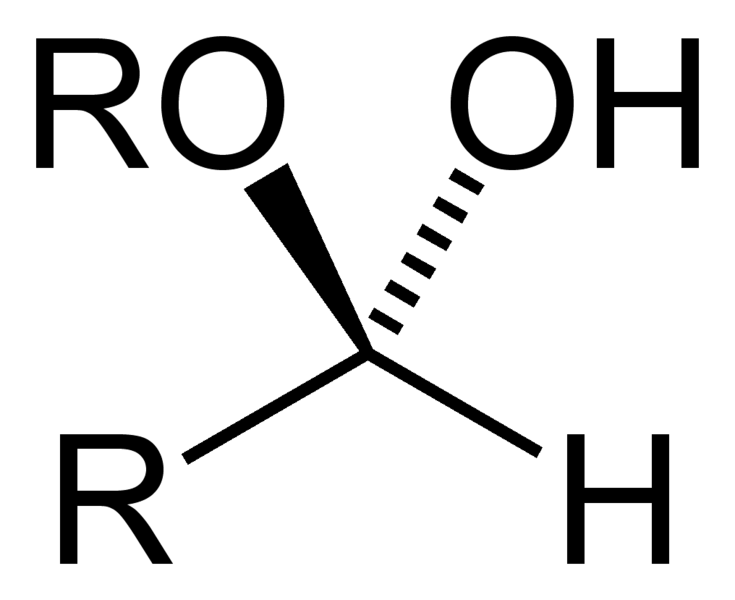
Name That Functional Group!
Hemiacetal
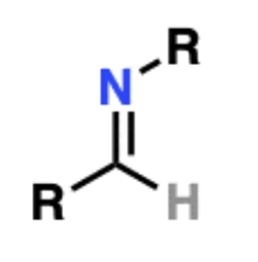
Name That Functional Group!
Imine
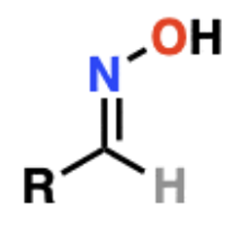
Name That Functional Group!
Oxime
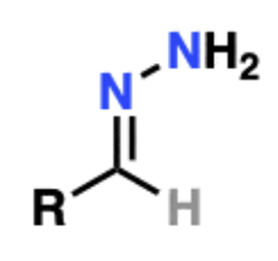
Name That Functional Group!
Hydrazone
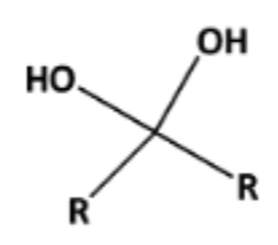
Name That Functional Group!
Gem-diol (hydroxyl groups are on the same carbon)
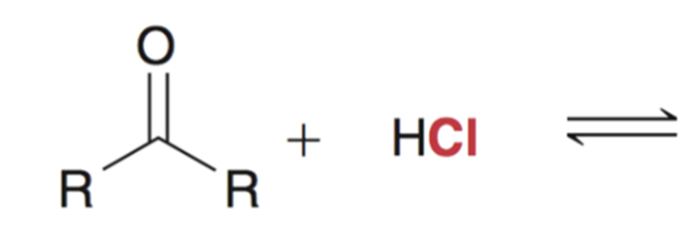
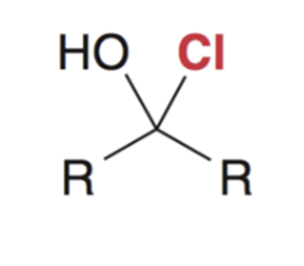
Reaction favors starting materials if nucleophile is a weak base (aka a good leaving group)

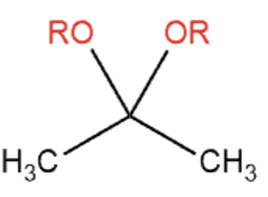
Alcohols attack carbonyl groups to form acetals. Common catalysts are TsOH and sulfuric acid

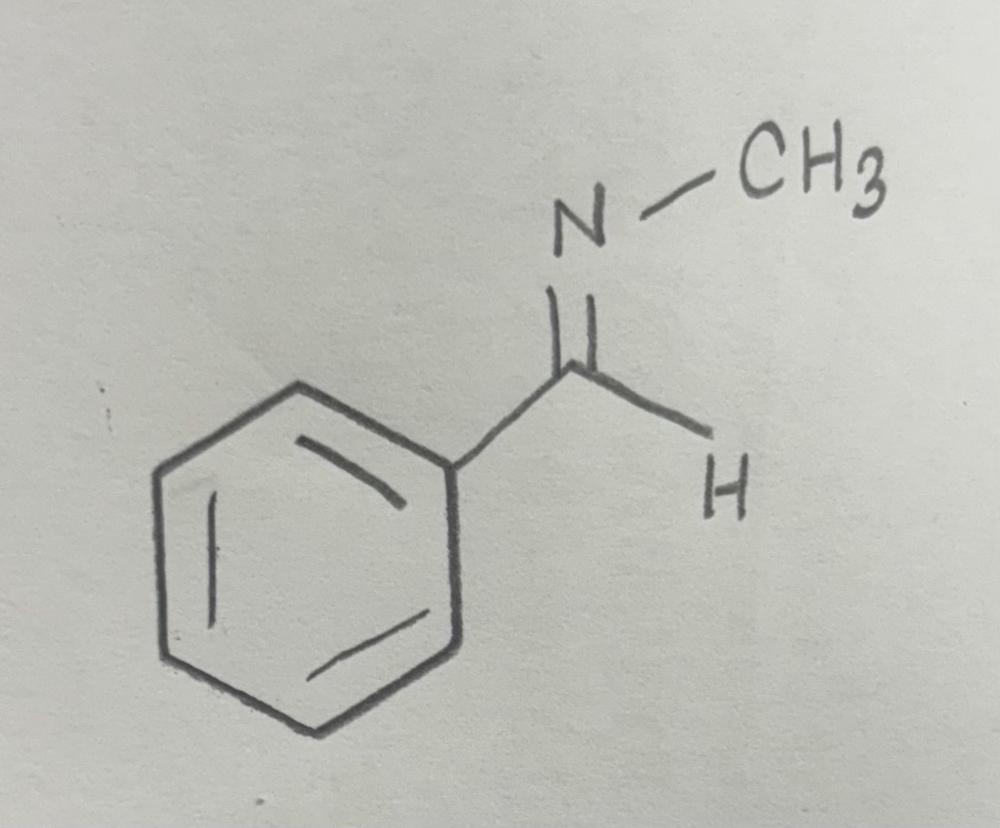
Imine formation using primary amine

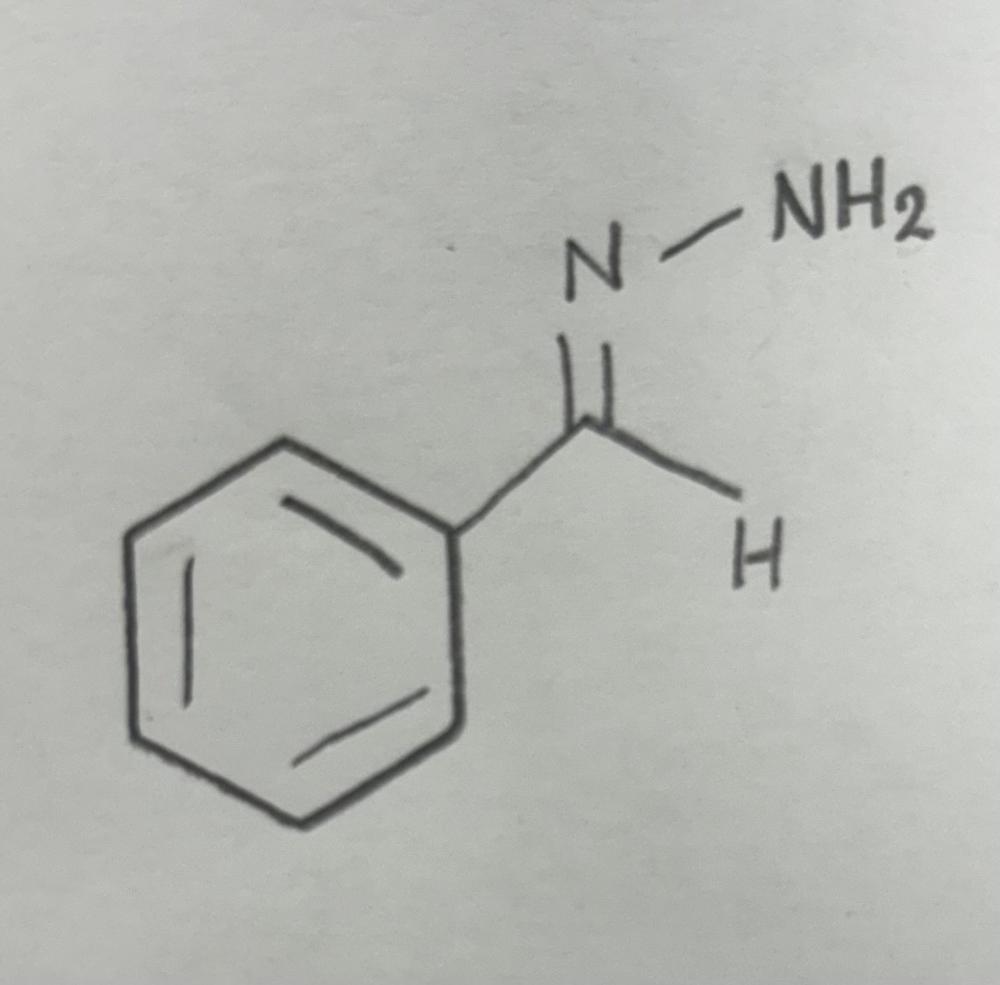
Hydrazone formation using primary amine
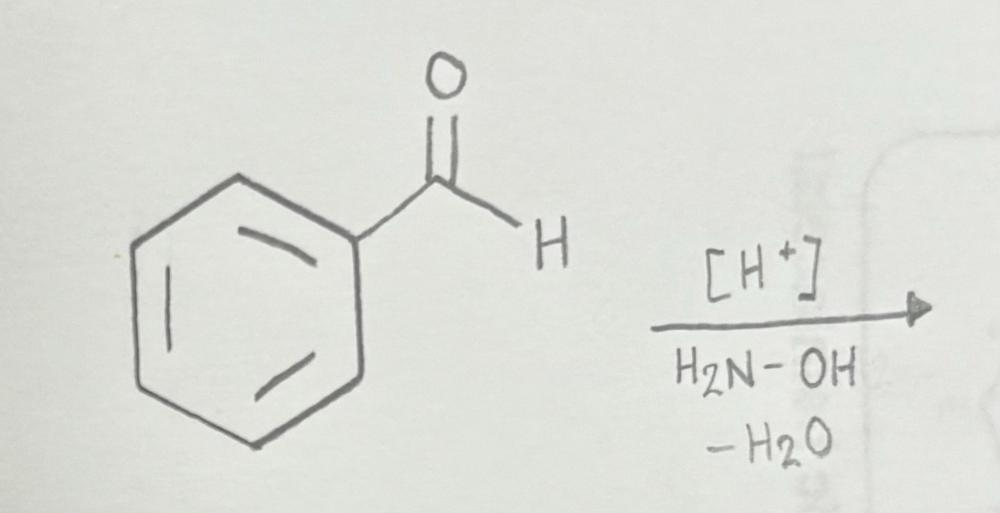
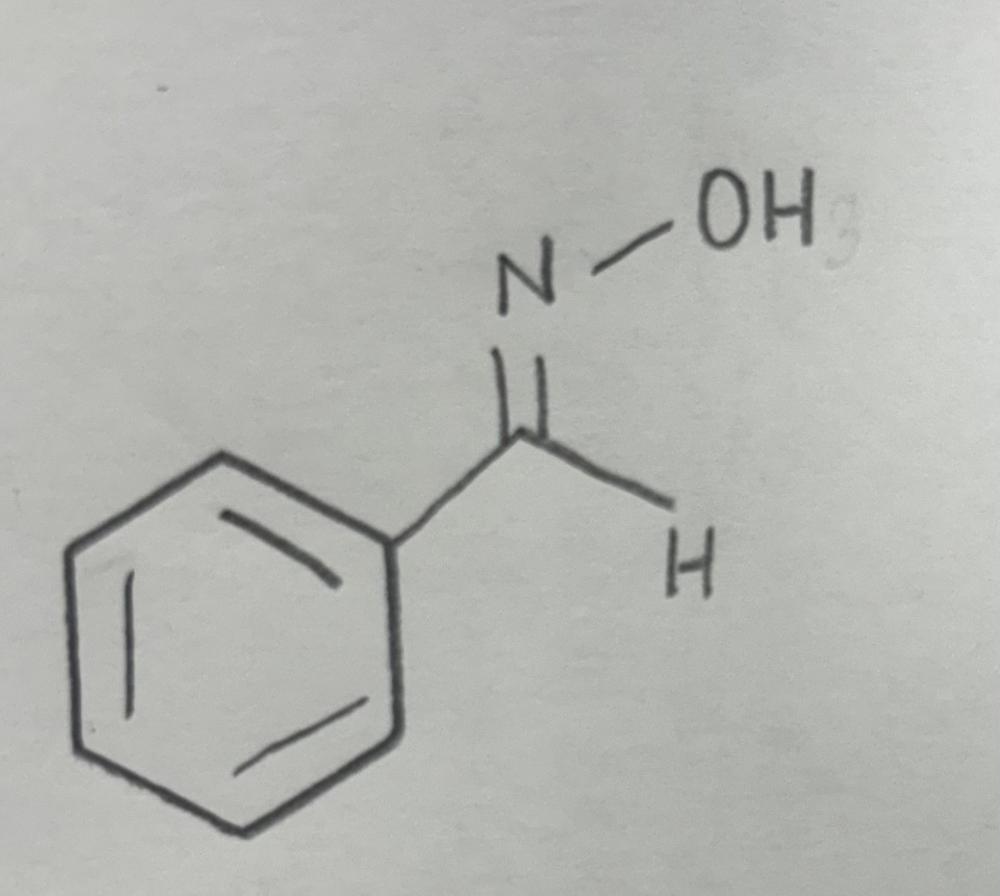
Oxime formation using primary amine

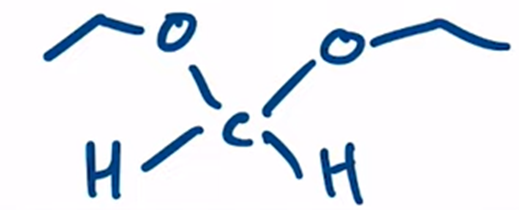
Acetal formation from formaldehyde products are favored with aldehydes
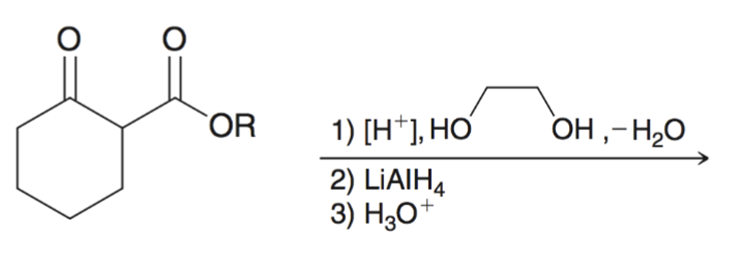
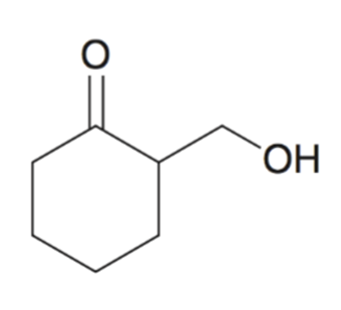
Using cyclic acetal as a protecting group
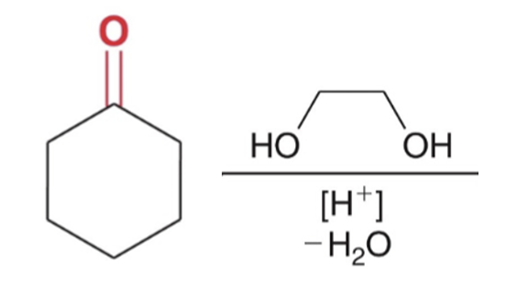
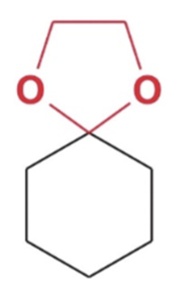
Cyclic acetal formation, Minus water favor products

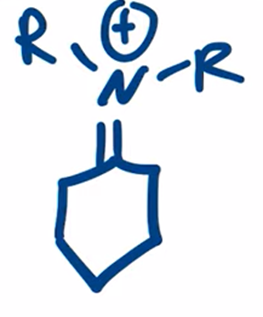
Secondary amine forms enamine

Name That Functional Group!
Enamine
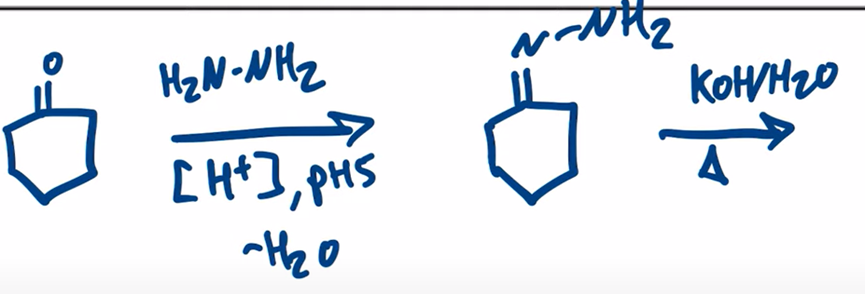
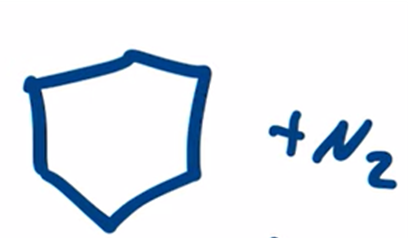
Wolff-Kishner Reduction obtain alkane from aldehyde or ketone by forming a hydrazone
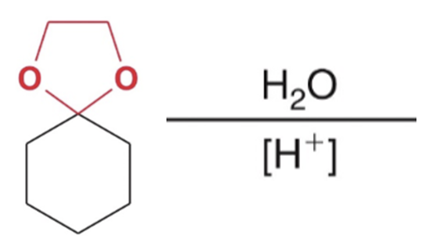
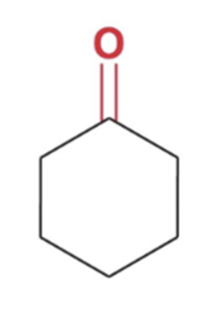
Reverse cyclic acetal formation, adding water favor reactants
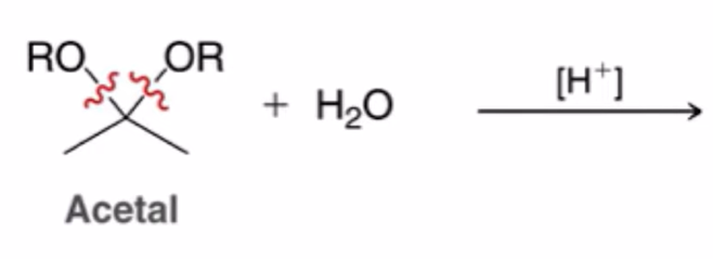
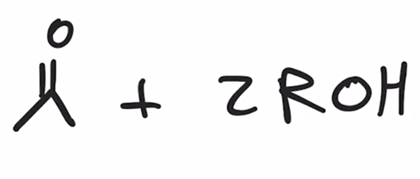
hydrolysis of acetals to yield ketone or aldehyde
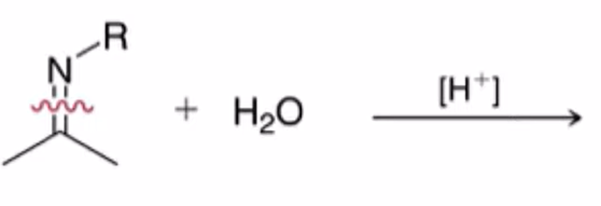
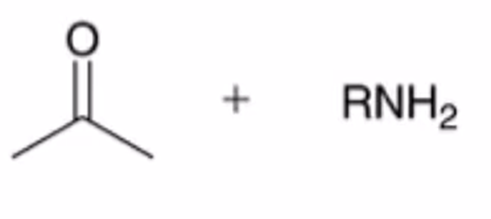
hydrolysis of imine to yield ketone or aldehyde
ALSO WORKS WITH HYDRAZONES AND OXIMES
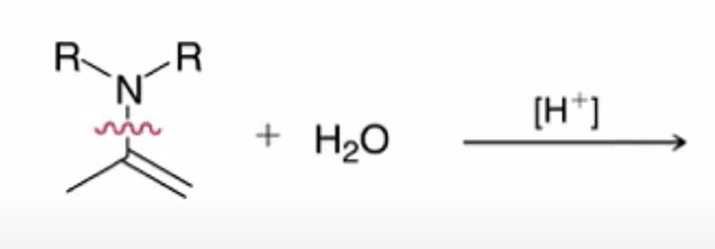
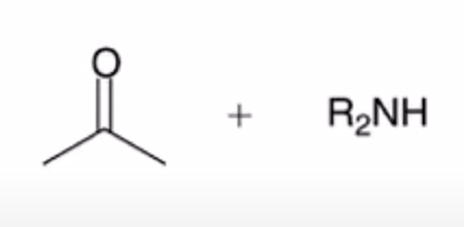
hydrolysis of enamine to yield ketone or aldehyde


under acidic conditions, an aldehyde or ketone will react with 2 equivalents of thiol to produce a thioacetal

Name That Functional Group!
Thioacetal
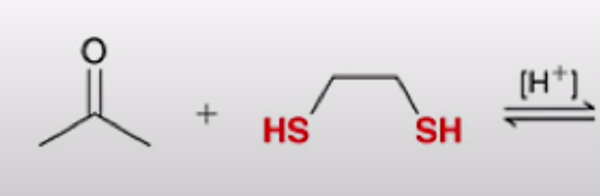
Formation of a cyclic thioacetal
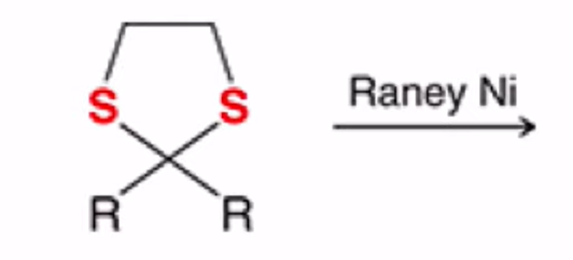
Cyclic thioacetal can be desulfurized using Raney nickel, yielding the alkane
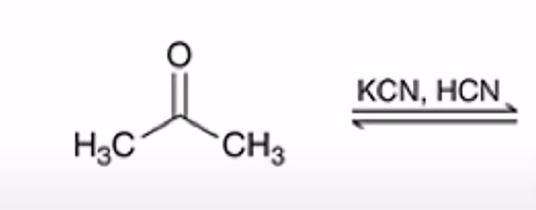

Formation of a cyanohydrin

Name That Functional Group!
Cyanohydrin
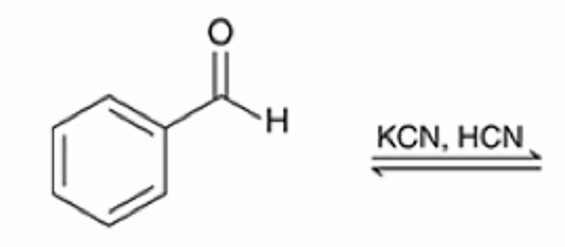
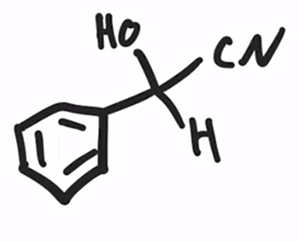
Formation of a cyanohydrin
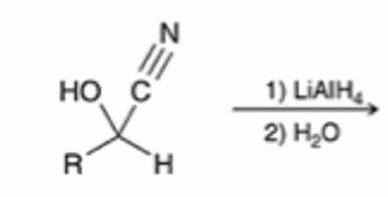
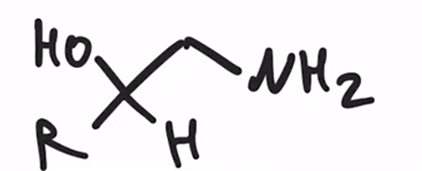
LAH REDUCTION: Cyanohydrin to primary amine
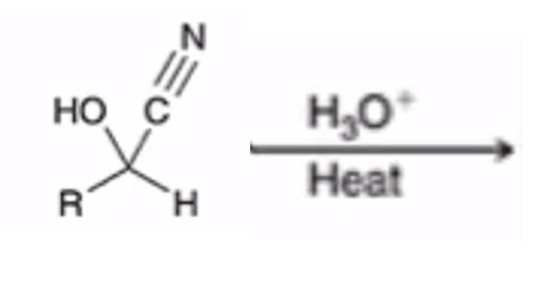
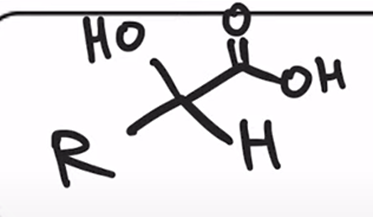
Acidification of cyanohydrin yields the carboxylic acid (oxidation)
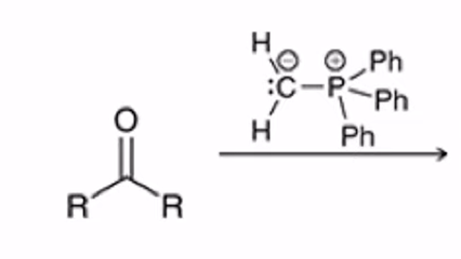
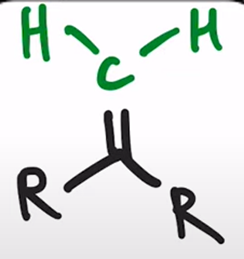
Wittig Reaction
Benzene ring or electron donating group makes (E)-alkene will be preferred
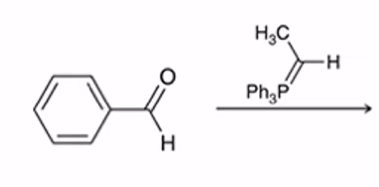
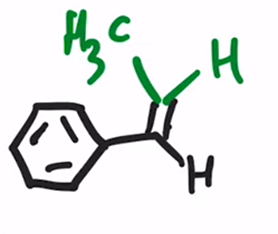
Wittig Reaction
Benzene ring or electron donating group makes (E)-alkene will be preferred
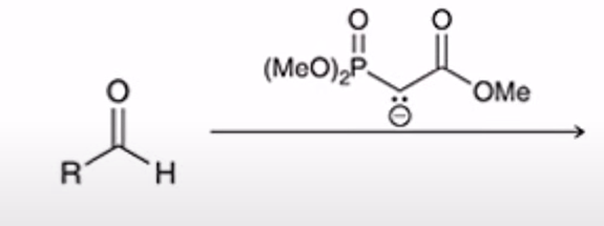
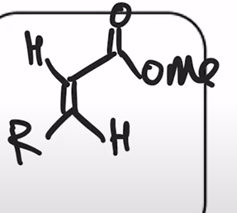
Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons Reaction (HWE reaction)
phosphonate easter carbanion reagent (HWE reagent) reacts with aldehyde or ketone to yield the (E)-alkene as the major product
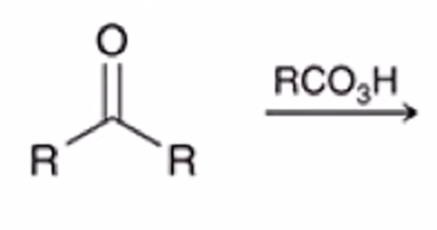
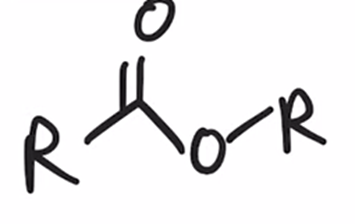
Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
Ketone converted to ester when treated with peroxy acid
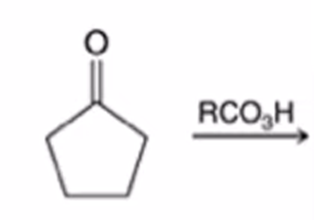
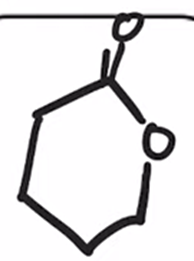
Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
Cyclic ketone to a lactone (cyclic ester)

Name That Functional Group!
Lactone (cyclic ester)

Name That Functional Group!
Acid Anhydride

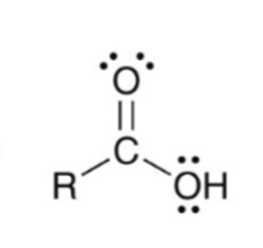
Forming a carboxylic acid via Grignard reagent and CO2

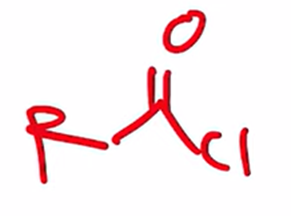
Preparation of acid chloride
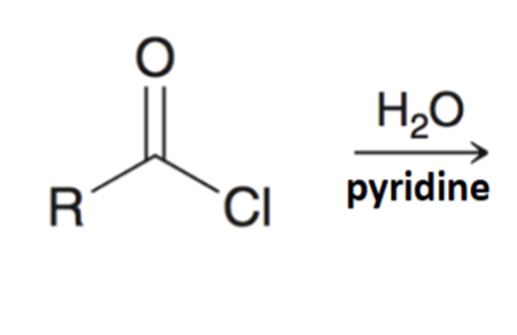
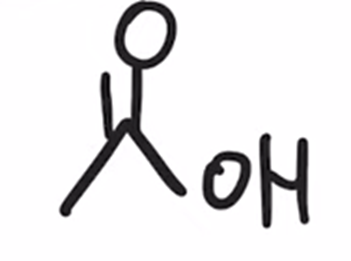
Reverse preparation of acid chloride via hydrolysis
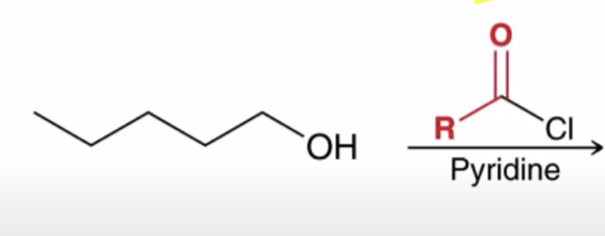
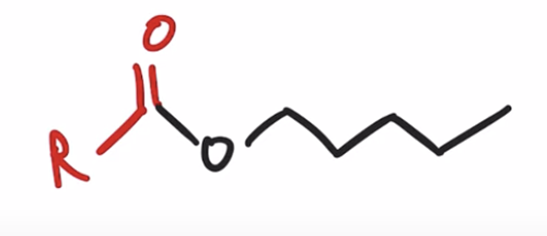
Acid chlorides react with an alcohol to make an ester
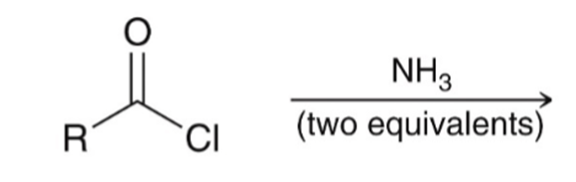
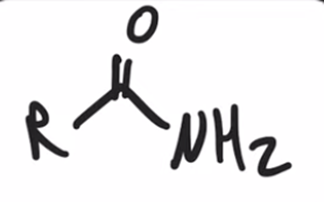
"Aminolysis" Acid chloride reacts with an amine to convert to an amide
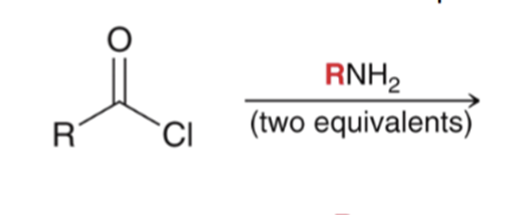
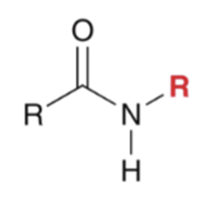
"Aminolysis" Acid chloride reacts with an amine to convert to an amide. Second equivalent of amine mops up HCl
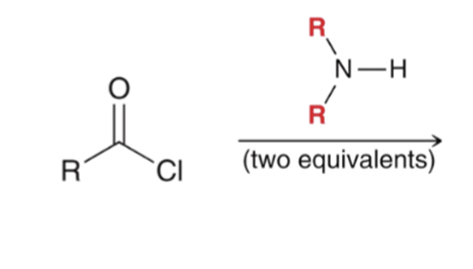
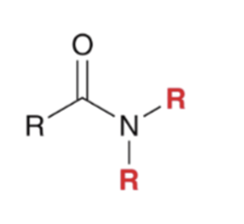
"Aminolysis" Acid chloride reacts with an amine to convert to an amide . Second equivalent of amine mops up HCl
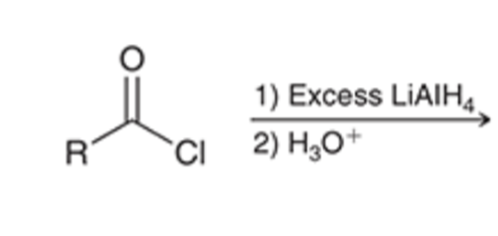
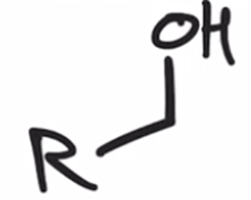
Acid chloride reduced to alcohol using LAH
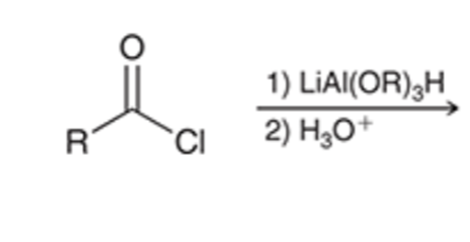
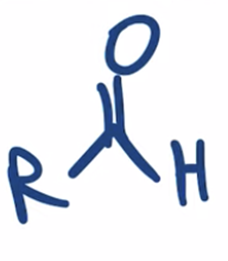
Stop the reduction of an acid chloride to an alcohol at the ALDEHYDE stage by using a bulkier hydride reagent
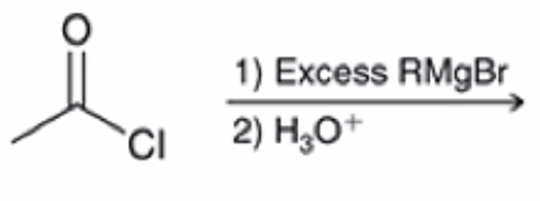
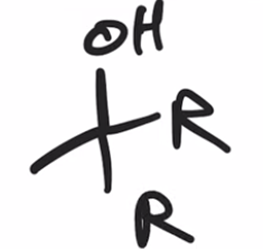
Acid chloride reacts with Grignard reagent and ADDS R GROUP TWICE IN PLACE OF Cl
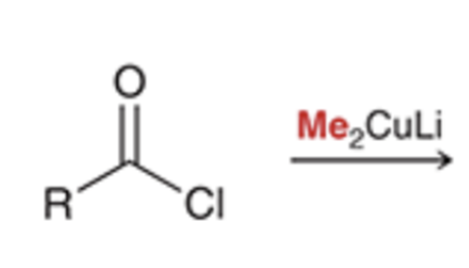
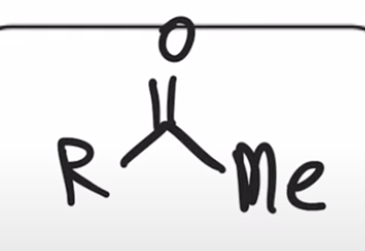
Gilman reagent replaces chloride with alkyl group
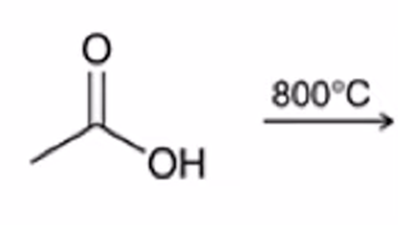
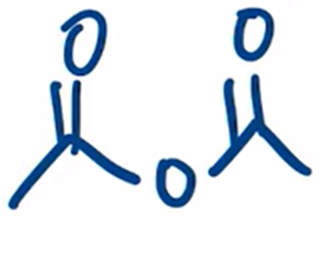
excess heating used to convert carboxylic acid to an anhydride
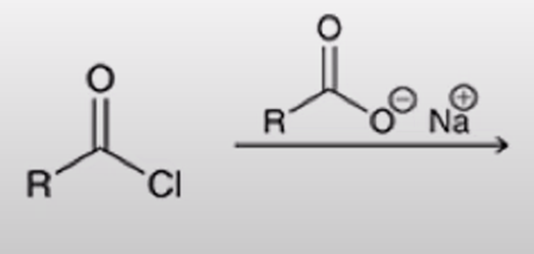
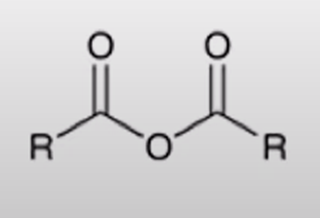
acid chloride + carboxylate salt turn into anhydride
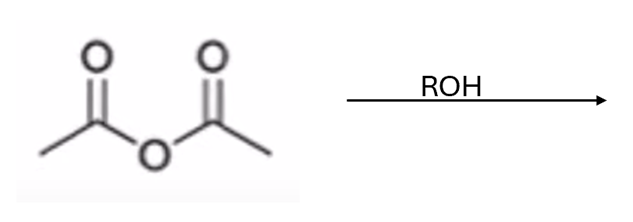
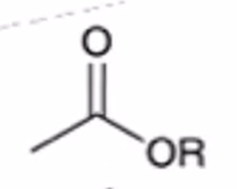
anhydride to ester
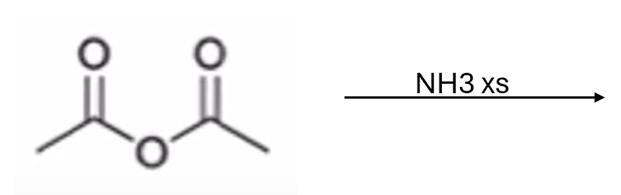
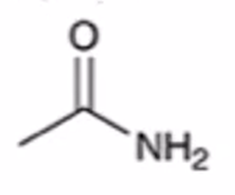
anhydride to amide
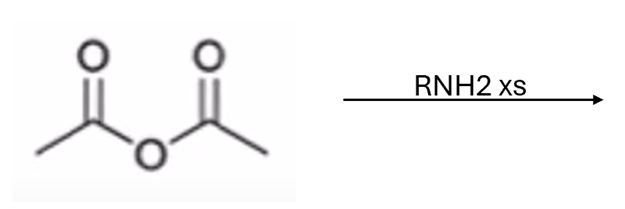
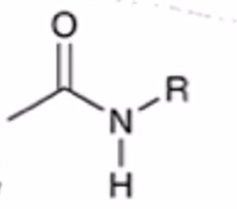
anhydride to amide
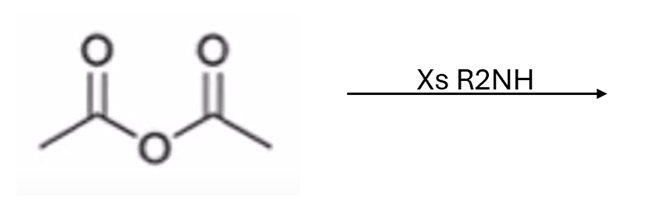
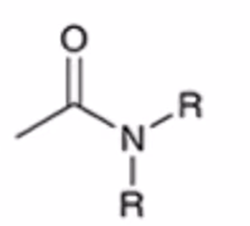
anhydride to amide
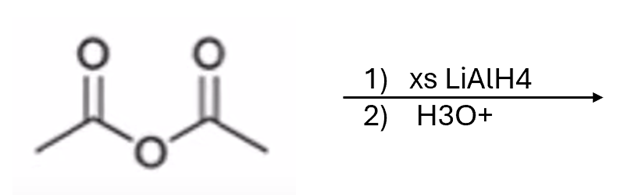
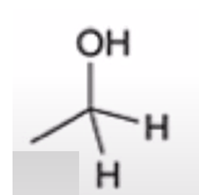
anhydride to alcohol
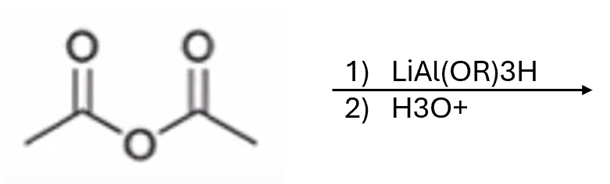
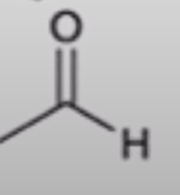
anhydride to aldehyde
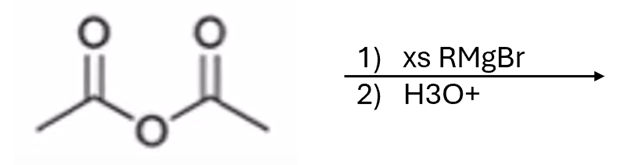
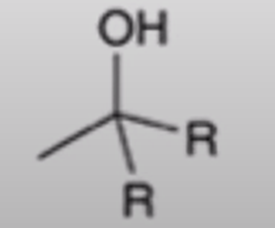
Grignard adds R group twice and creates an alcohol
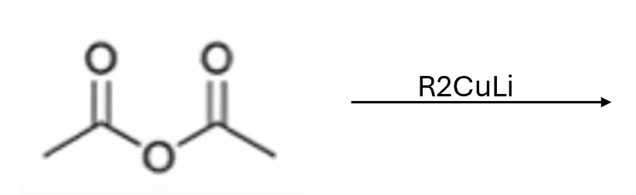
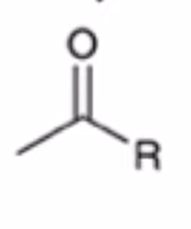
Gilmen reagent converts anhydride to ketone
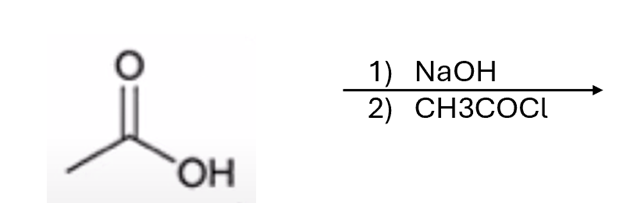
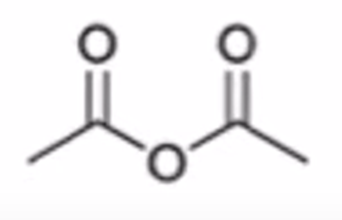
carboxylic acid to anhydride
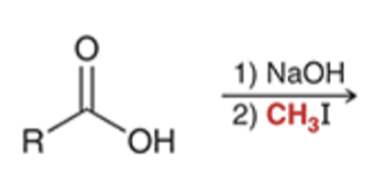
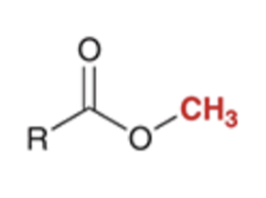
preparation of esters via SN2 reaction
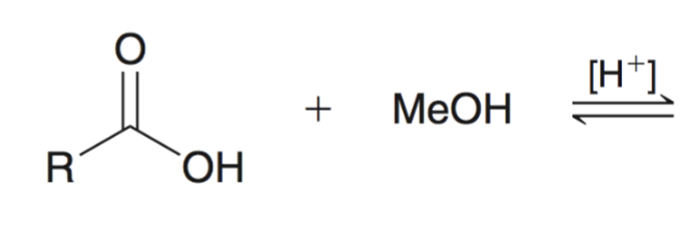

Fischer Esterification
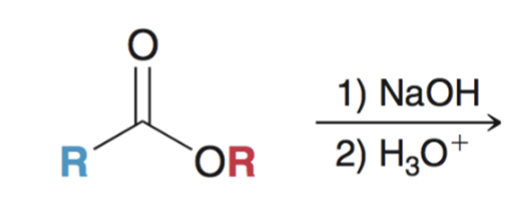
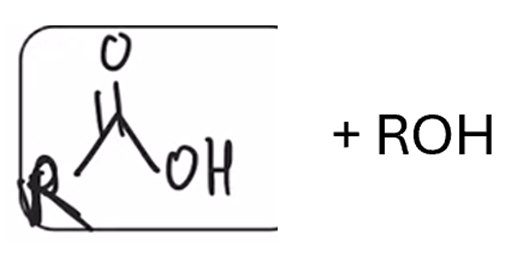
Saponification (hydrolysis using basic conditions) converts ester to carboxylic acid
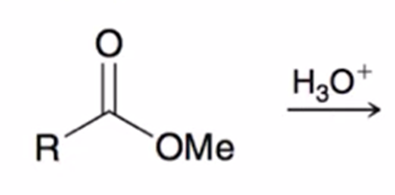
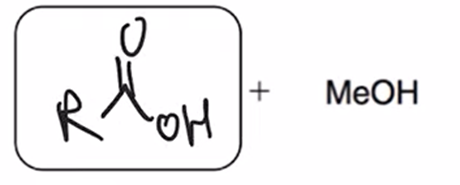
acid hydrolysis (reverse of Fischer esterification) coverts ester to carboxylic acid
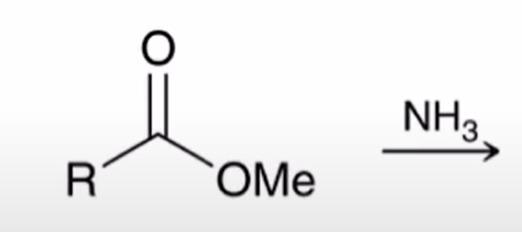

Aminolysis of esters converts ester to amine it is slow and has little synthetic utility
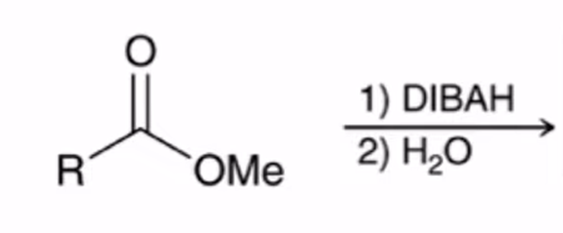
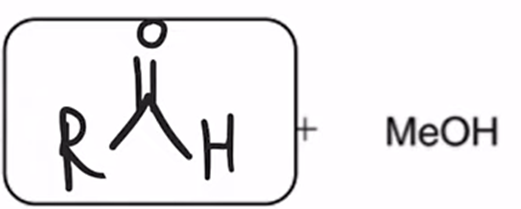
DIBAH Reduction of ester converts ester to aldehyde
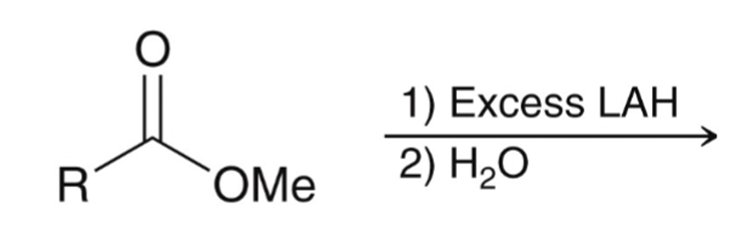
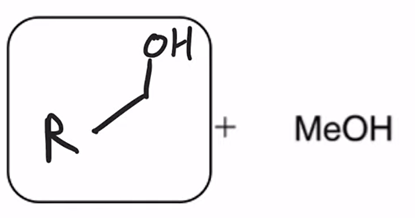
LAH reduction of ester converts ester to alcohol
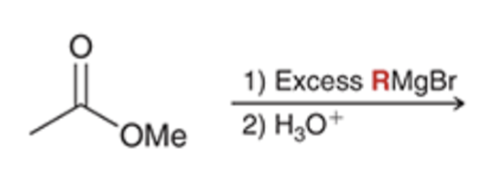
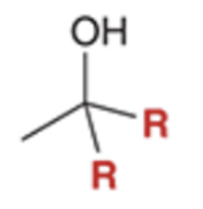
Grignard reacts and converts carbonyl to alcohol and adds R group twice
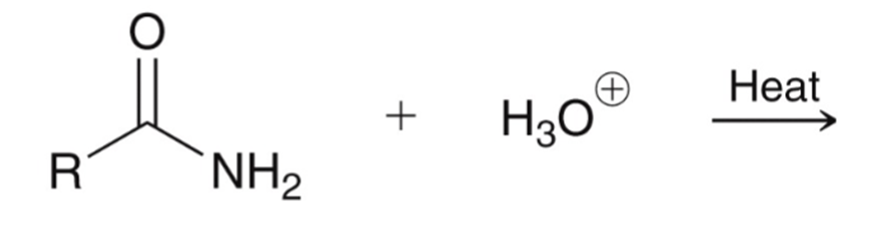
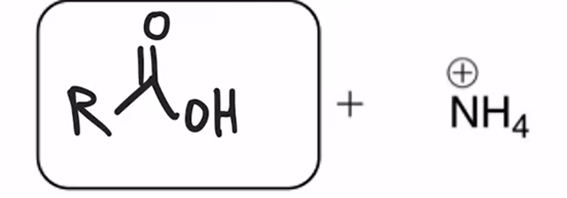
Amide hydrolyzed to a carboxylic acid
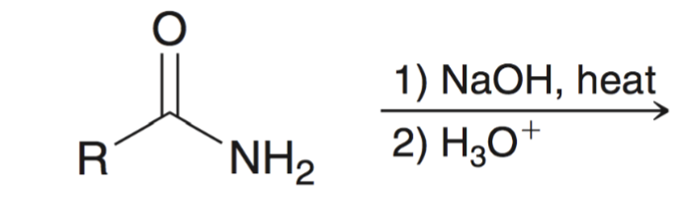
base hydrolysis of amides converts amide to carboxylic acid
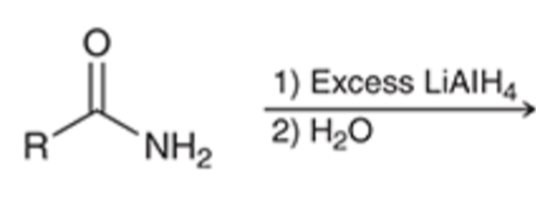

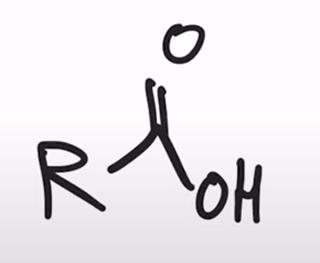
LAH reduction removes carbonyl group

Preparation of nitrile using SN2 (does not work with tertiary alkyl halides
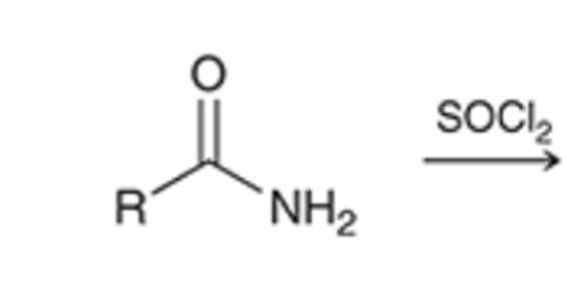
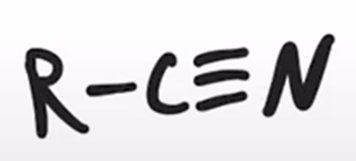
thionyl chloride converts amide to a nitrile
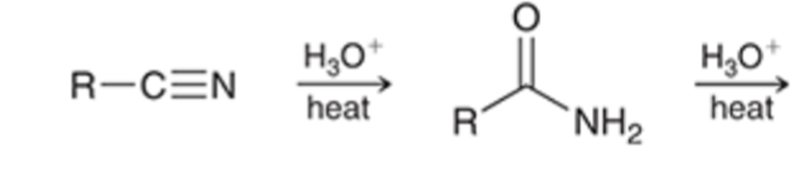
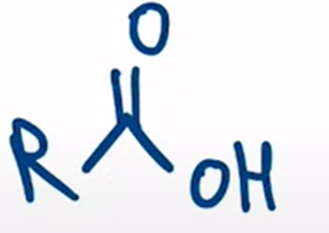
nitriles can be hydrolyzed to the carboxylic acid going through an amide intermediate
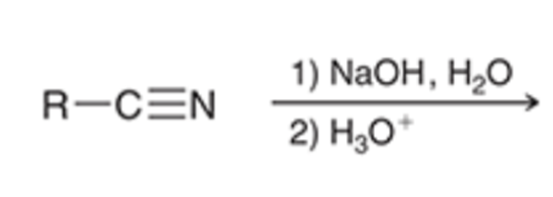

nitriles can be hydrolyzed to the carboxylic acid in basic conditions
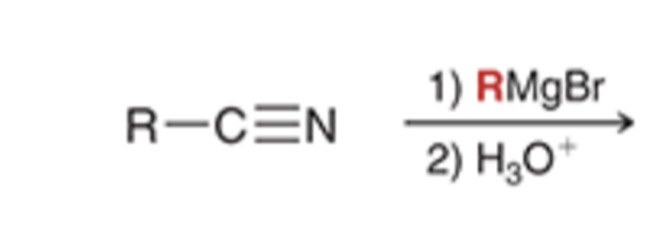
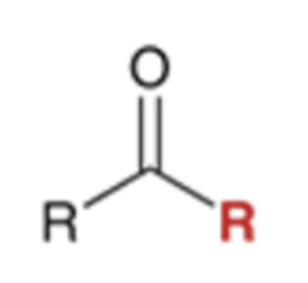
Grignard reagent converts nitriles to a ketone
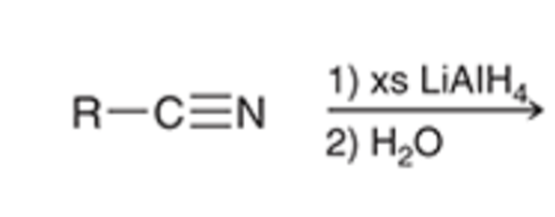

LAH reductions converts nitriles to a primary amine