Lab Exam 2
Which part of the neuron sends electrical impulses to the next neuron?
Axon
T/F: Binding of O2 to hemoglobin is irreversible.
False
What type of cellular junction is found in the lining of the intestinal wall and blocks transport through the intercellular space?
tight junction
Which leukocyte fights parasitic worm infections?
Eosinophil
Which leukocyte is the "memory bank" of the immune system?
Lymphocyte
Which leukocyte transforms into wandering macrophages?
Monocyte
Which leukocyte is responsible for allergic reactions by releasing histamine?
Basophil
What is the function of osteoblasts in bone tissue?
generate or build up bone tissue
What is the cell shape of skeletal muscle?
Cylindrical
What type of control is true of skeletal muscle>
Voluntary
Name one function of adipose connective tissue.
Insulation
What type of gland secretes products directly into the bloodstream?
endocrine
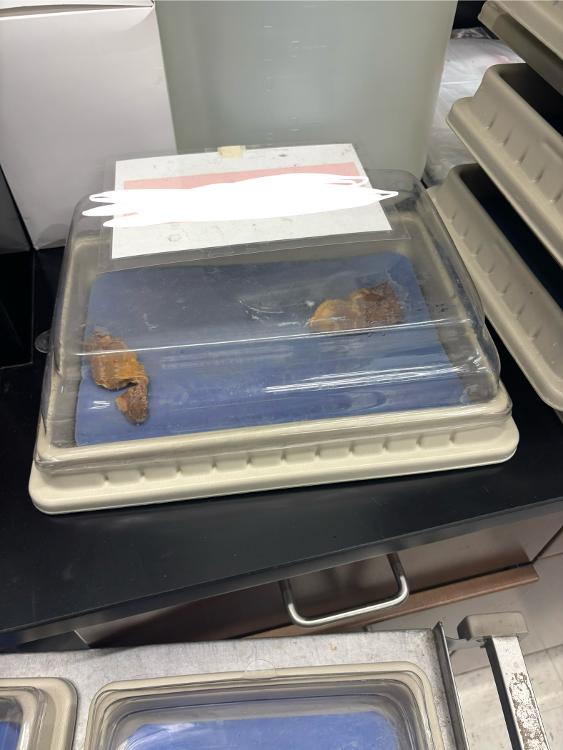

What is this organ?
pancreas
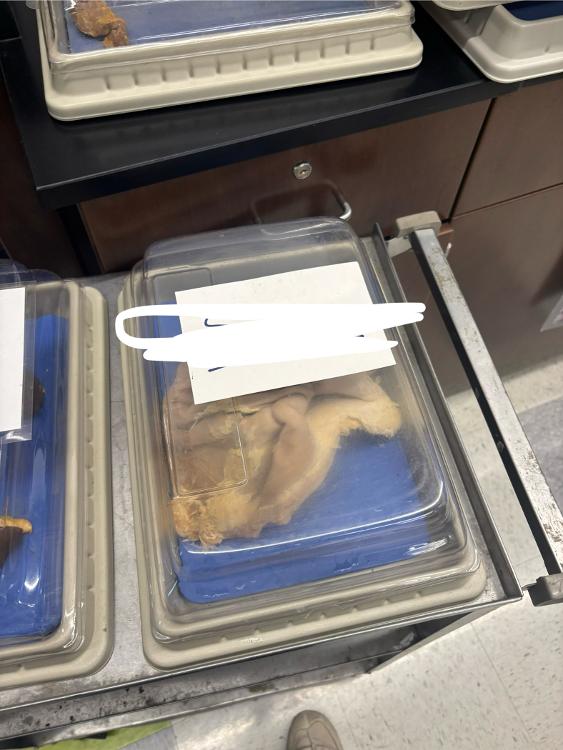

What is this organ?
Stomach
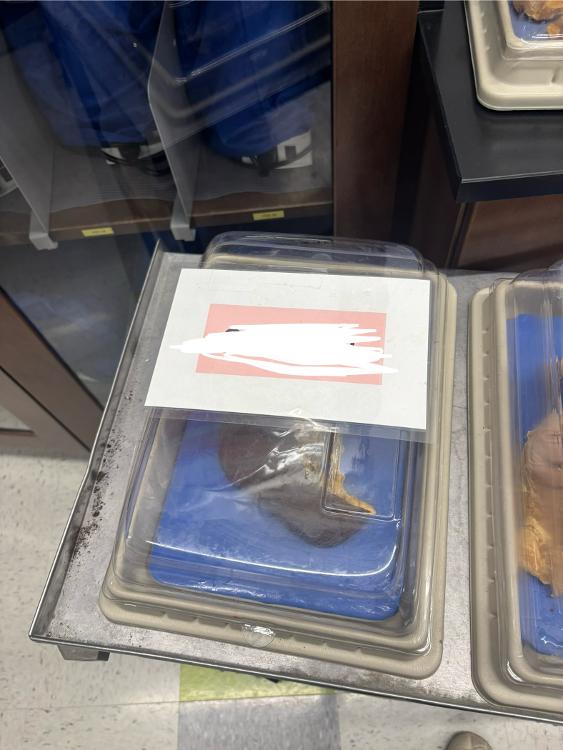

What is this organ?
Spleen
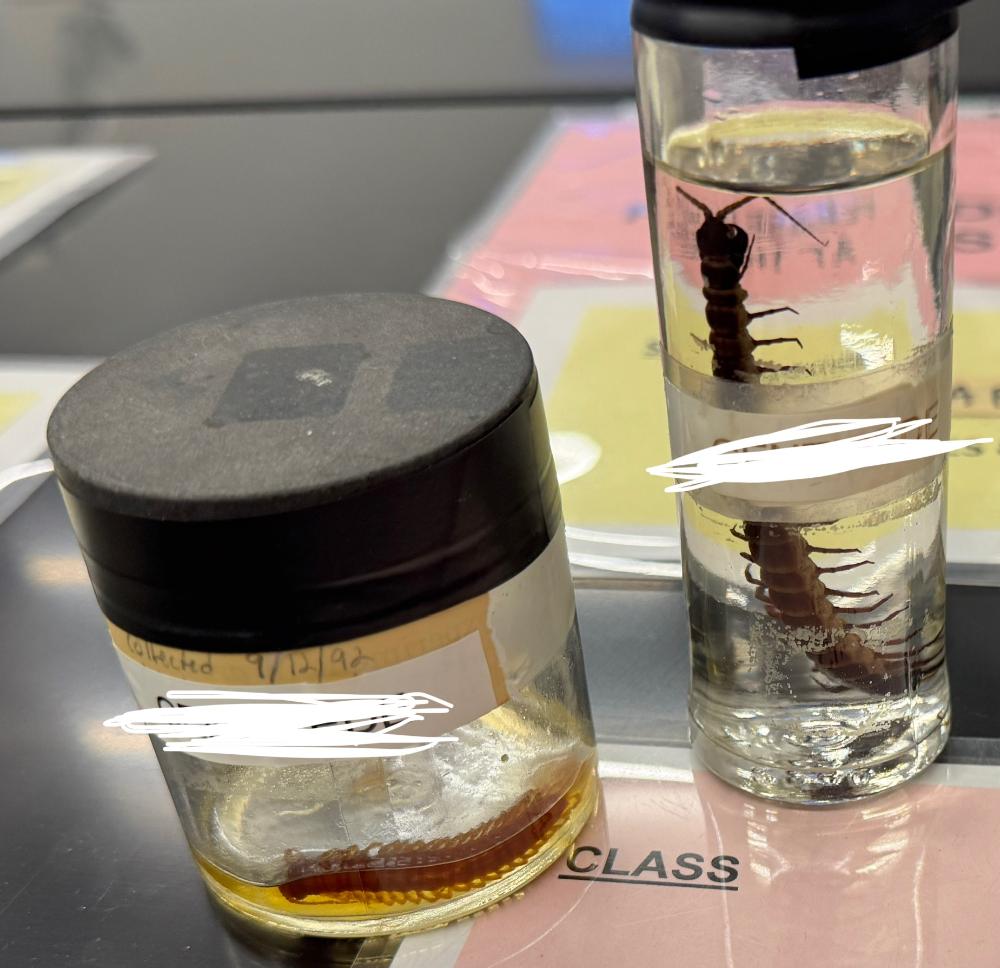

What class is this organism from?
Chilopoda (centipedes)
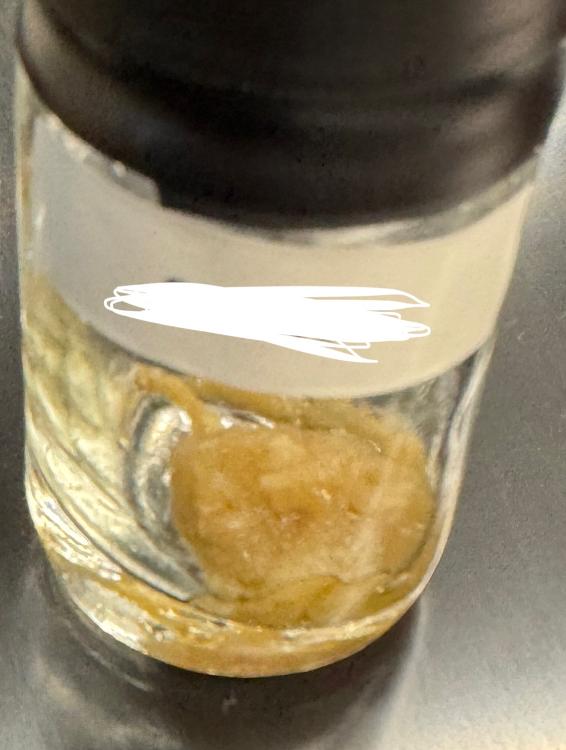

What is this organism?
Sponge
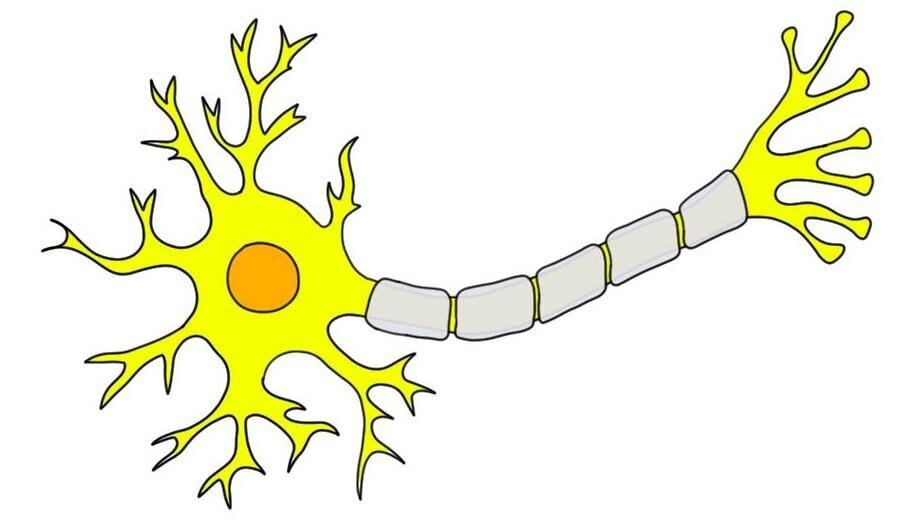
Identify the three components of a neuron.
Axon, dendrite, soma
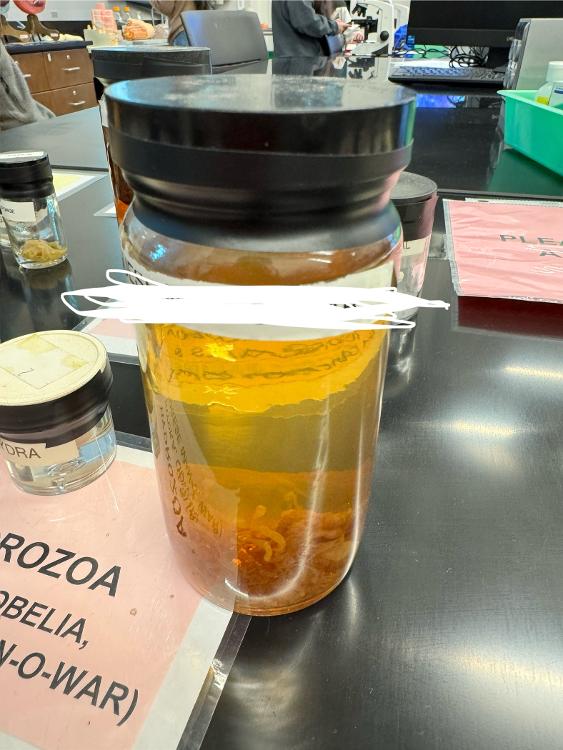

What is this organism?
Portugese man-o-war
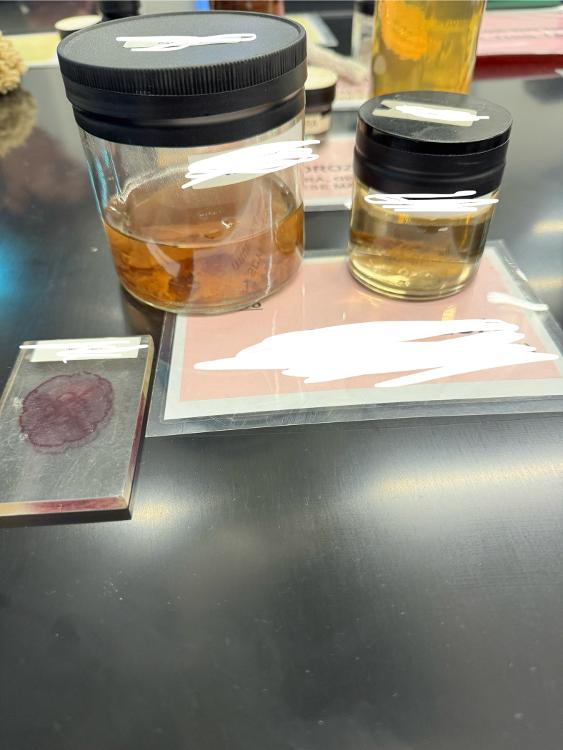

What phylum (and class) are these organisms from?
Cnidaria, class scyphozoa
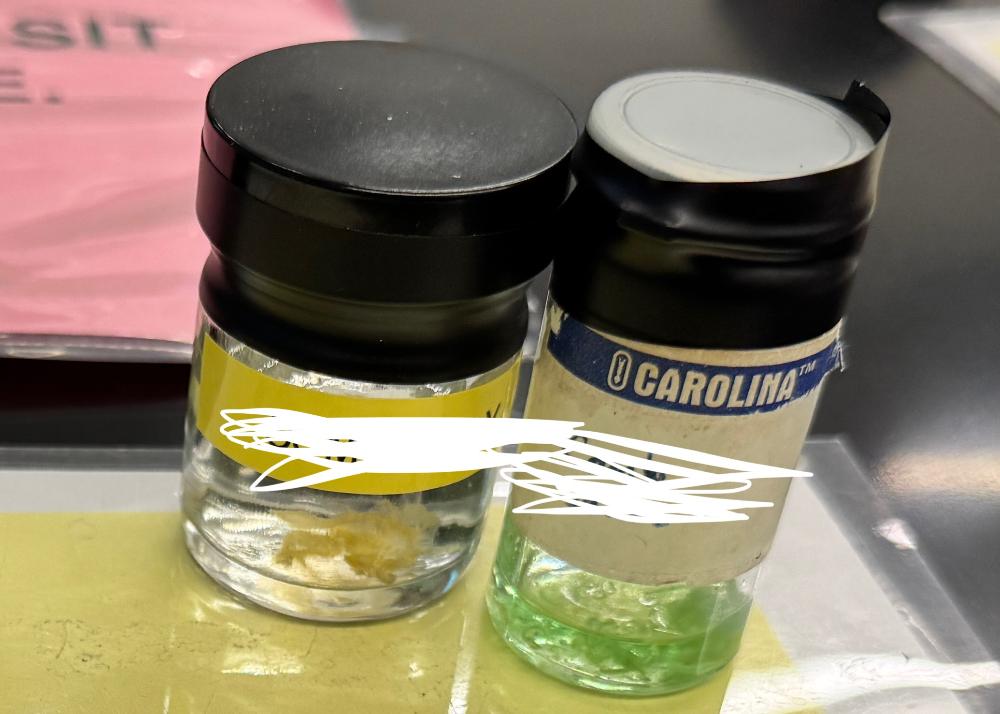

What phylum are these organisms from?
Ctenophora

What organism is this?
Round worm
What type of junction:
Intracellular junctions that are tight enough to block transport of substances through the intercellular space
Tight juncton
What type of junction:
Channels or pores through membranes of two cells and across the intracellular space
Found in areas like the heart where rapid communication is a necessity
Gap junction
What are the four tissue groups?
Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
What are the three arrangement types for epithelial tissue?
Simple, stratified, pseudostratified
What are the three shape terms for epithelial tissue?
squamous, cuboidal, columnar
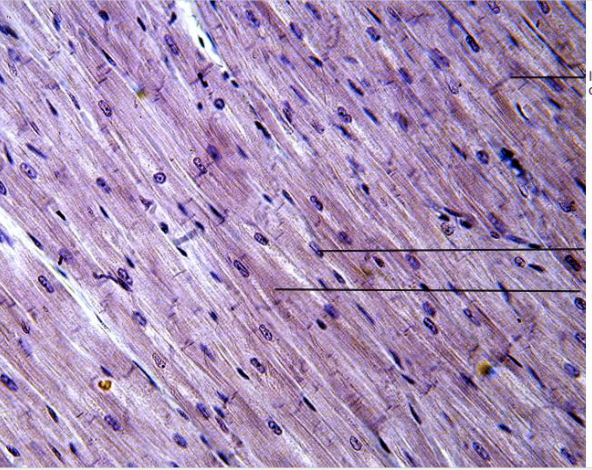
What type of tissue is this?
Cardiac muscle tissue
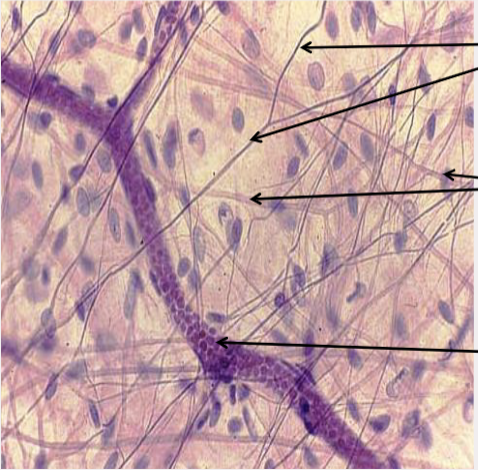
What type of tissue is this?
Loose (areolar) connective tissue
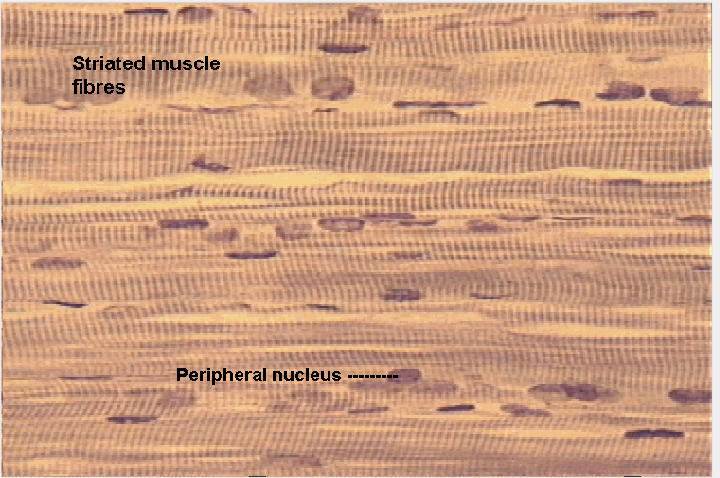
What type of tissue is this?
Skeletal muscle tissue
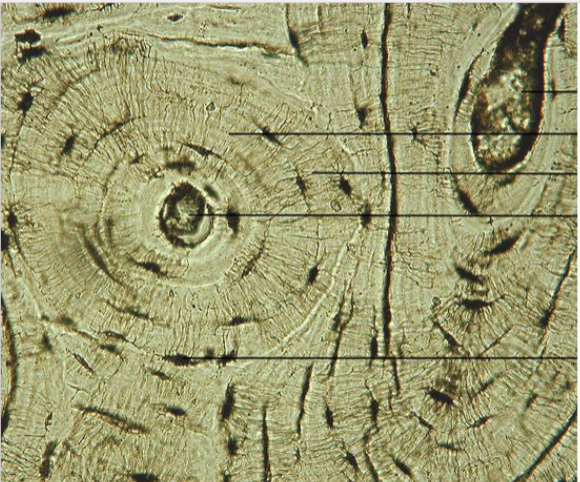

What type of tissue is this?
Bone tissue
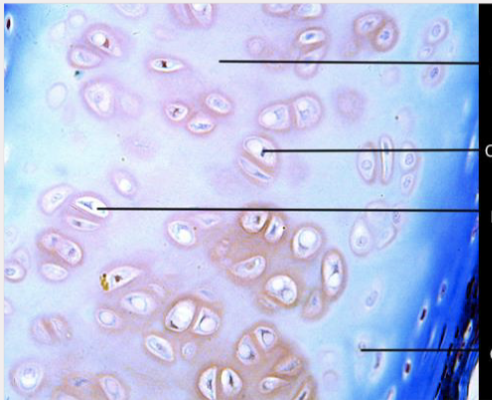
What type of tissue is this?
Hyaline cartilage

What type of tissue is this?
Elastic cartilage
What type of tissue is this?
Dense irregular connective tissue
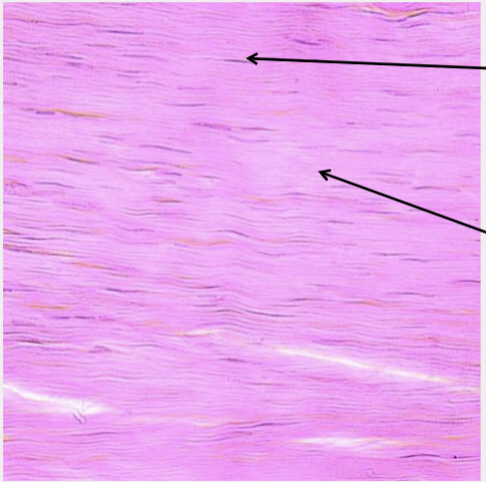
What type of tissue is this?
Dense regular connective tissue
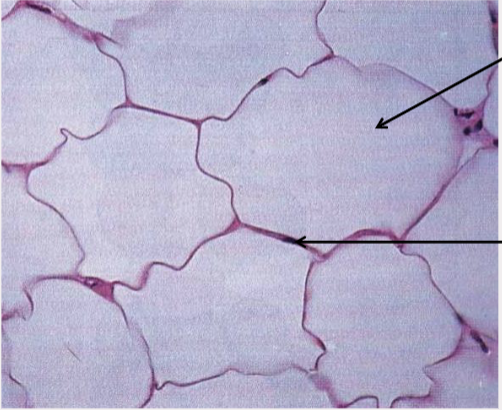
What type of tissue is this?
Adipose (fat) connective tissue
What are the three types of bone tissue cells?
Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes
What is the function of an osteocyte?
maintain bone tissue and reside in the spaces known as lacuna, which are surrounded by the matrix secreted originally by the osteoblasts
What is the function of an osteoclast?
function in bone degradation

What phylum are these organisms within?
Porifera

What phylum is this organism within?
Platyhelminthes
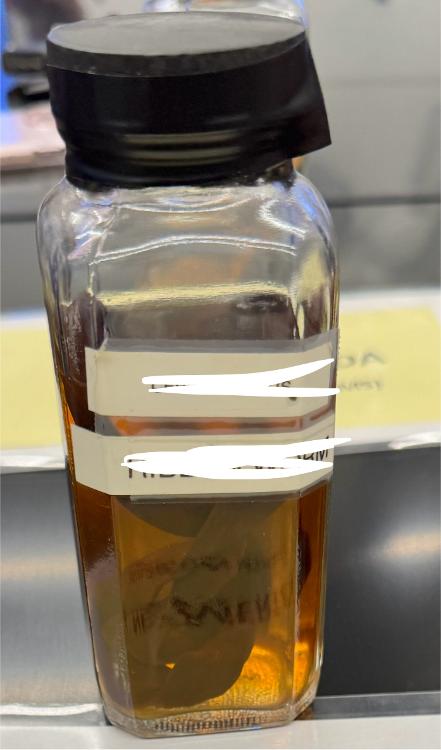

What phylum is this organism within?
nemertea

What phylum is this organism within?
Arthropoda
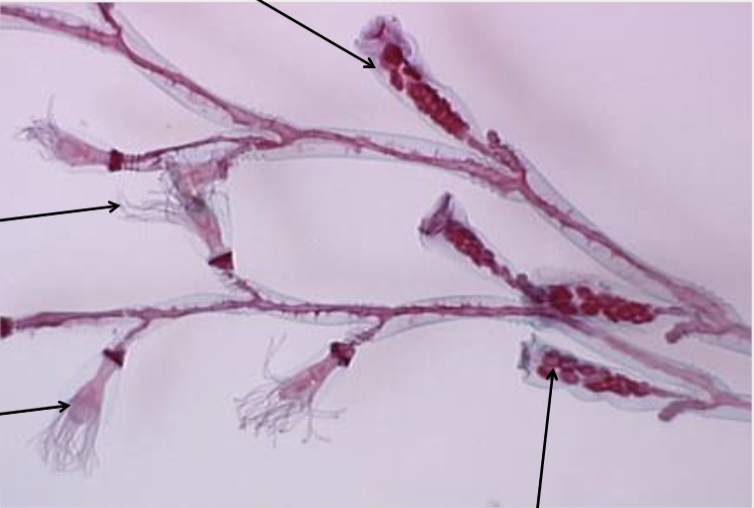
What is the form shown in this picture?
A. Medusa
B. Solitary polyp
C. Colonial polyp
D. Siphonophore
C. Colonial polyp
Does phylum playhelminthes have a tube-in-tube body plan?
No, they are acoelomates
Name the four characteristics of chordates
Dorsal, hollow nerve cord
post-anal tail
notocord
pharangeal gils or slits
Name two characteristics only found in mollusks.
mantle, calcium carbonate shell, visceral mass, radula, muscular foot
Name one animal in clade Grouping Tetrapoda.
...