Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab Exam 2
front 1 Which part of the neuron sends electrical impulses to the next neuron? | back 1 Axon |
front 2 T/F: Binding of O2 to hemoglobin is irreversible. | back 2 False |
front 3 What type of cellular junction is found in the lining of the intestinal wall and blocks transport through the intercellular space? | back 3 tight junction |
front 4 Which leukocyte fights parasitic worm infections? | back 4 Eosinophil |
front 5 Which leukocyte is the "memory bank" of the immune system? | back 5 Lymphocyte |
front 6 Which leukocyte transforms into wandering macrophages? | back 6 Monocyte |
front 7 Which leukocyte is responsible for allergic reactions by releasing histamine? | back 7 Basophil |
front 8 What is the function of osteoblasts in bone tissue? | back 8 generate or build up bone tissue |
front 9 What is the cell shape of skeletal muscle? | back 9 Cylindrical |
front 10 What type of control is true of skeletal muscle> | back 10 Voluntary |
front 11 Name one function of adipose connective tissue. | back 11 Insulation |
front 12 What type of gland secretes products directly into the bloodstream? | back 12 endocrine |
front 13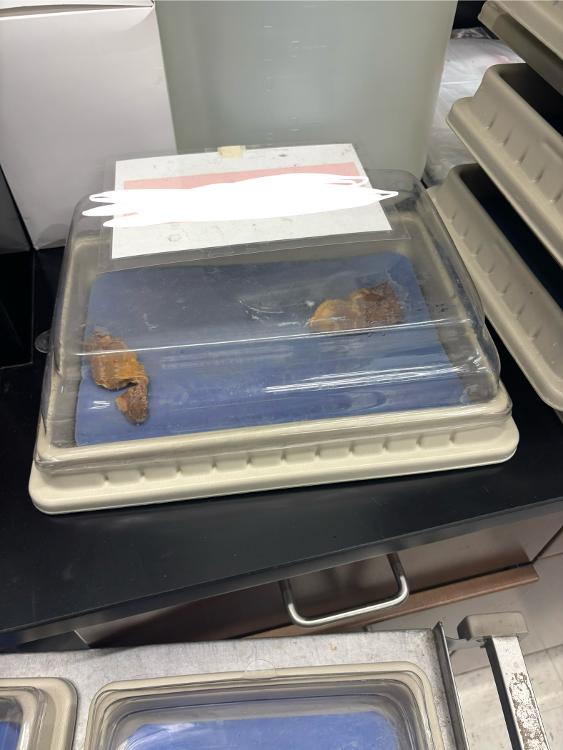  What is this organ? | back 13 pancreas |
front 14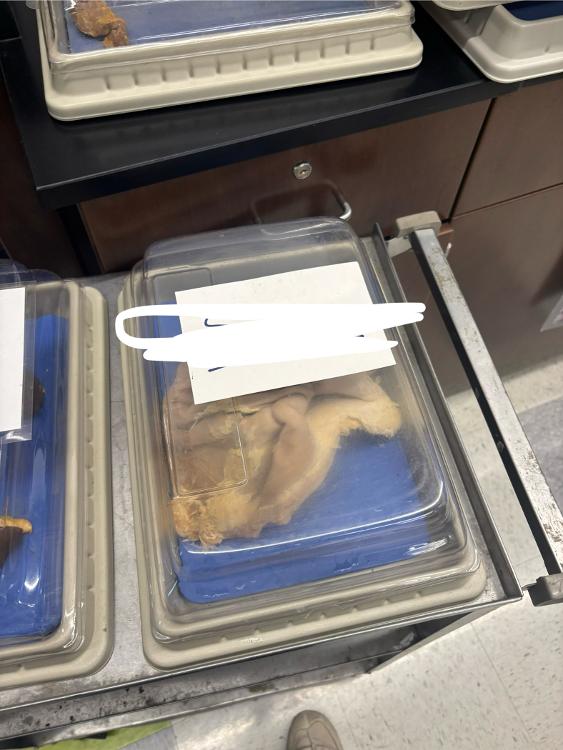  What is this organ? | back 14 Stomach |
front 15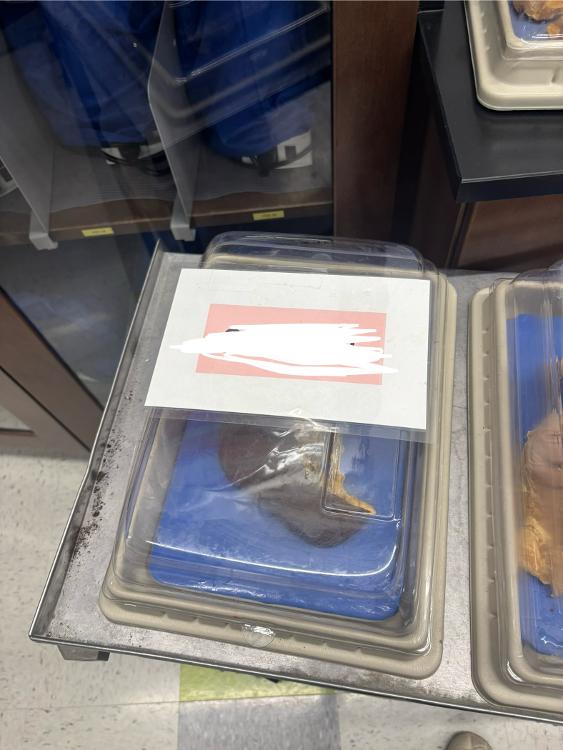  What is this organ? | back 15 Spleen |
front 16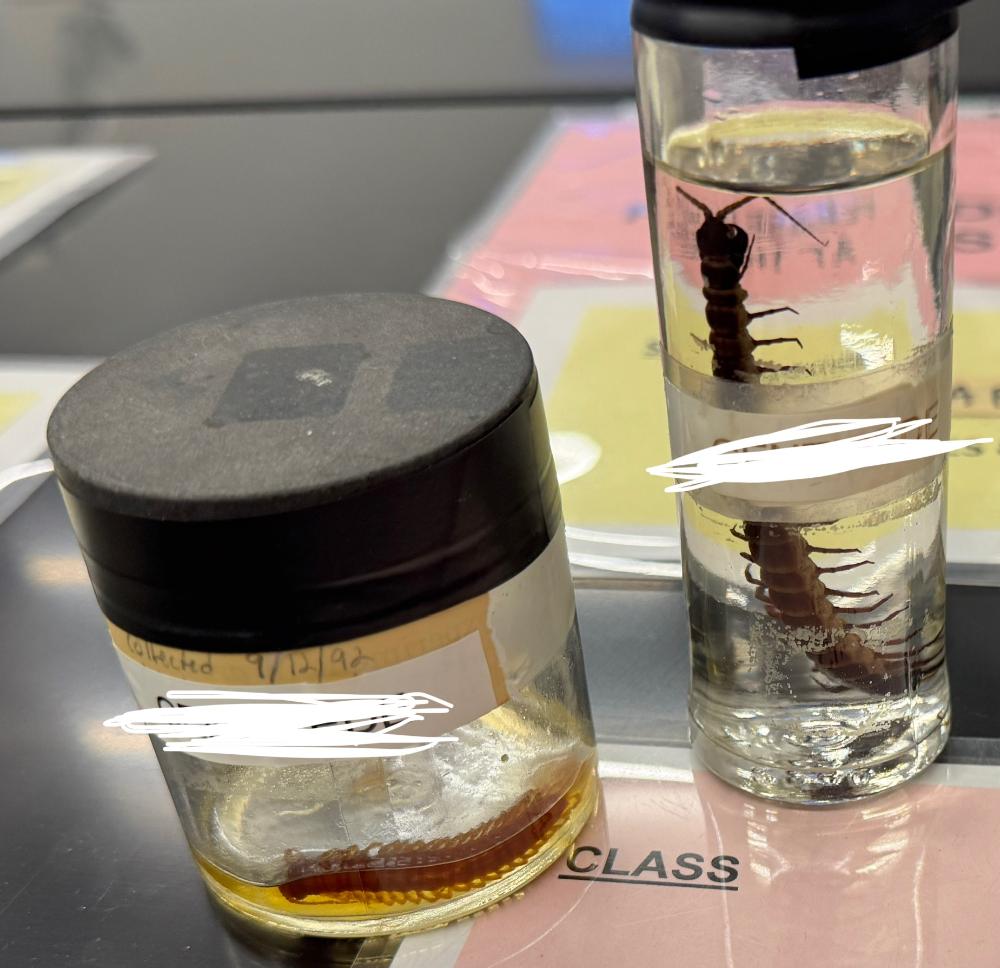  What class is this organism from? | back 16 Chilopoda (centipedes) |
front 17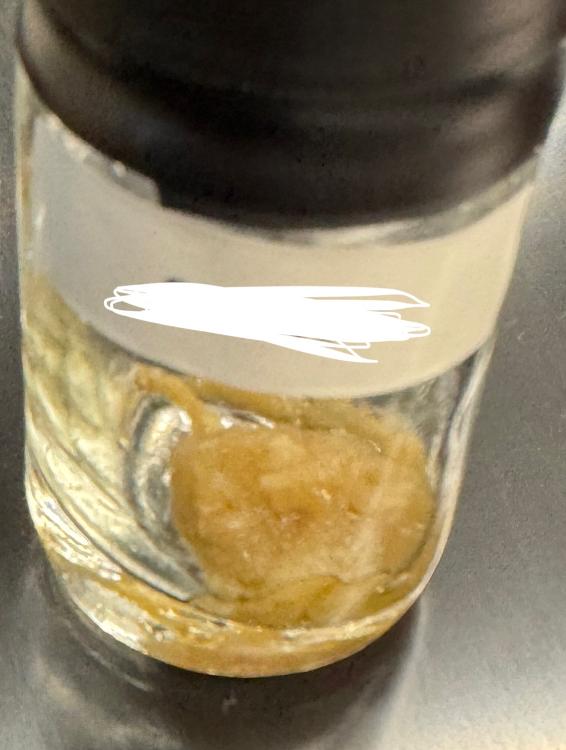  What is this organism? | back 17 Sponge |
front 18 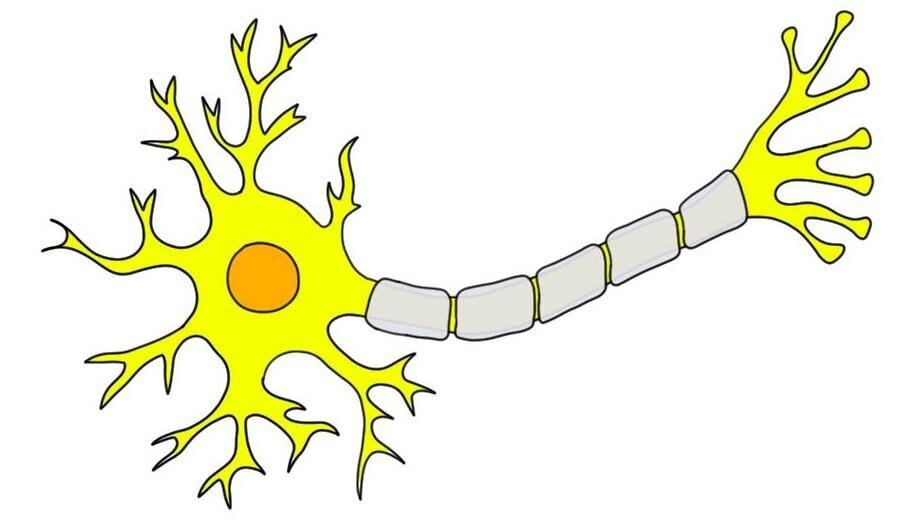 Identify the three components of a neuron. | back 18 Axon, dendrite, soma |
front 19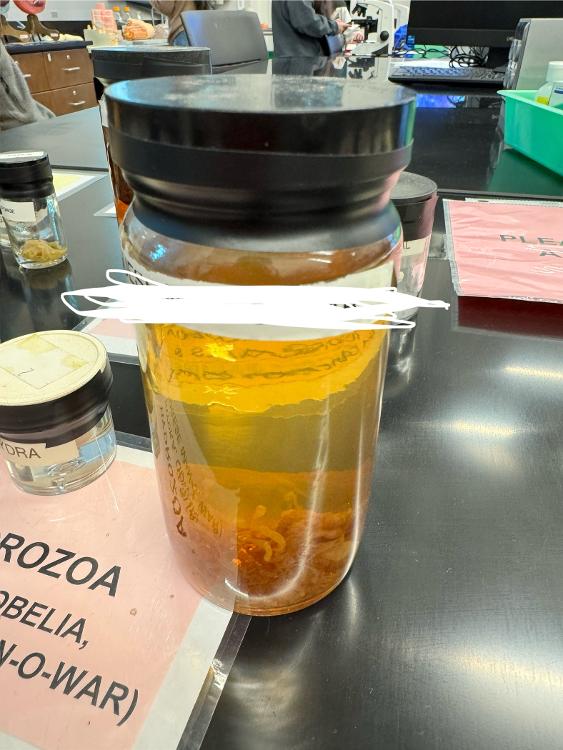  What is this organism? | back 19 Portugese man-o-war |
front 20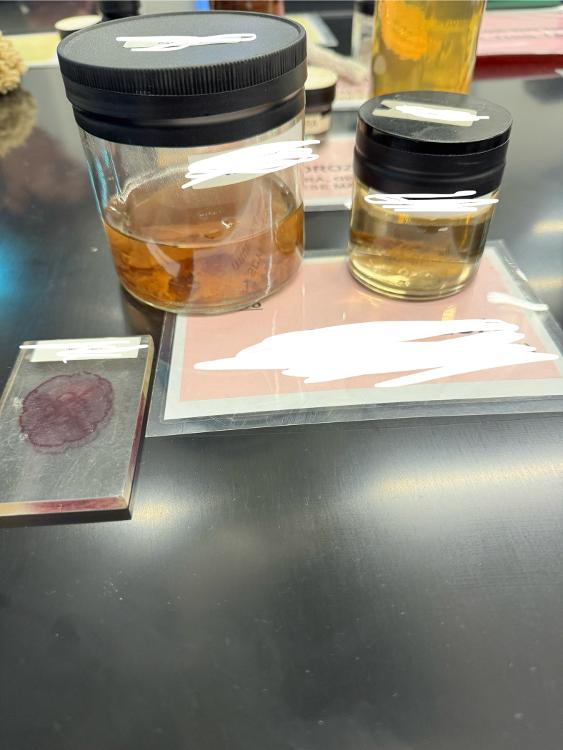  What phylum (and class) are these organisms from? | back 20 Cnidaria, class scyphozoa |
front 21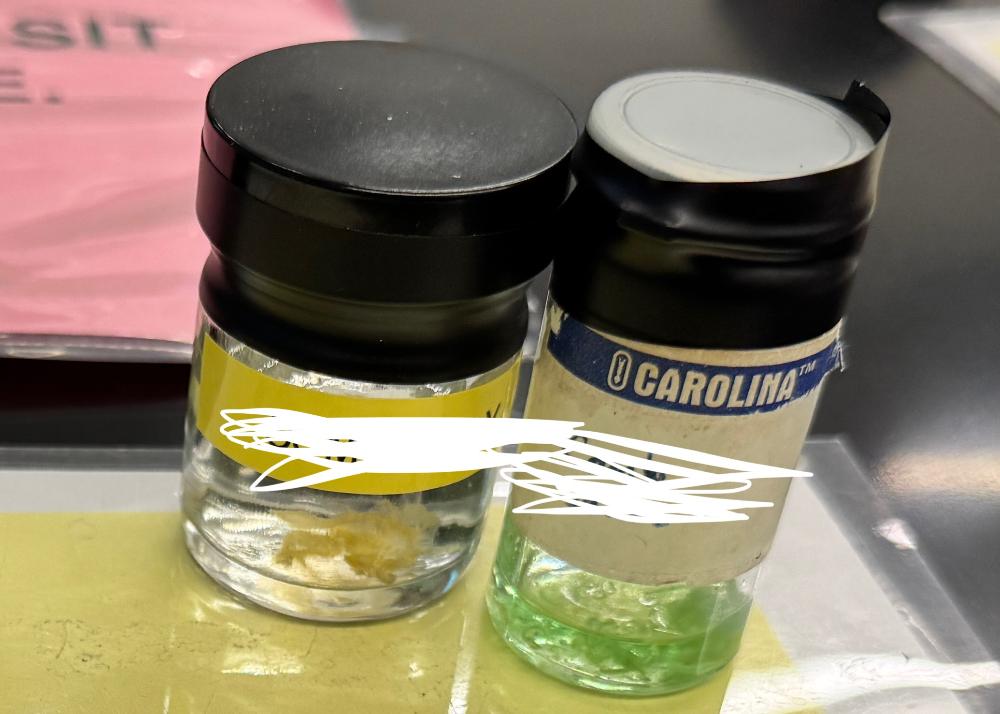  What phylum are these organisms from? | back 21 Ctenophora |
front 22  What organism is this? | back 22 Round worm |
front 23 What type of junction: Intracellular junctions that are tight enough to block transport of substances through the intercellular space | back 23 Tight juncton |
front 24 What type of junction: Channels or pores through membranes of two cells and across the intracellular space Found in areas like the heart where rapid communication is a necessity | back 24 Gap junction |
front 25 What are the four tissue groups? | back 25 Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous |
front 26 What are the three arrangement types for epithelial tissue? | back 26 Simple, stratified, pseudostratified |
front 27 What are the three shape terms for epithelial tissue? | back 27 squamous, cuboidal, columnar |
front 28 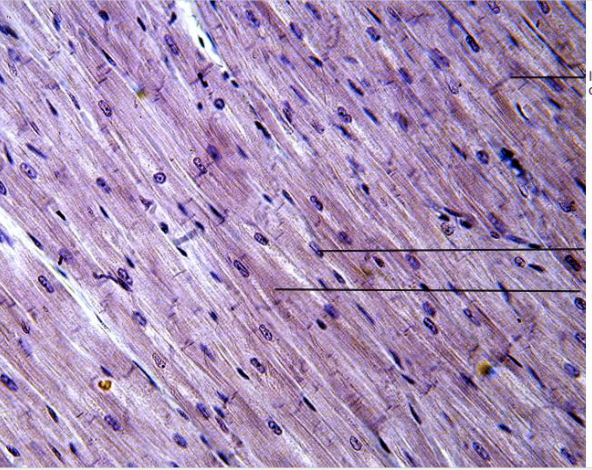 What type of tissue is this? | back 28 Cardiac muscle tissue |
front 29 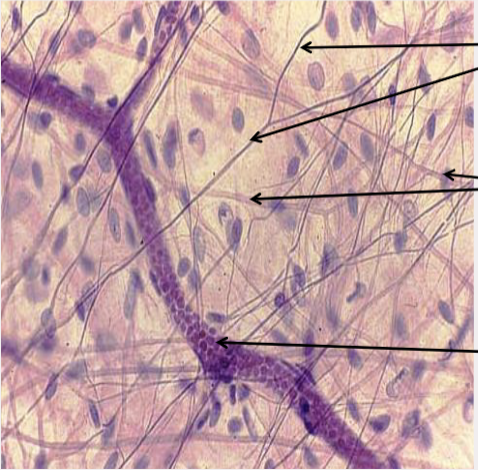 What type of tissue is this? | back 29 Loose (areolar) connective tissue |
front 30 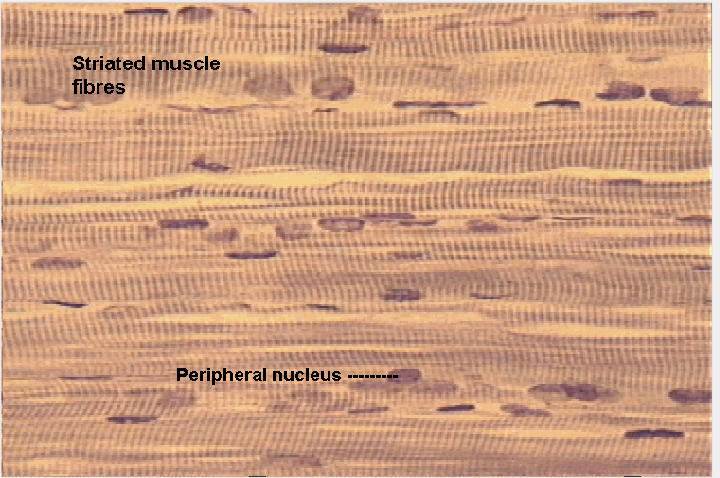 What type of tissue is this? | back 30 Skeletal muscle tissue |
front 31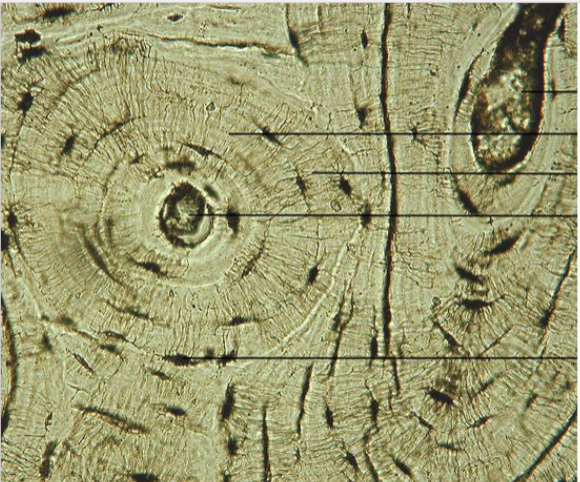  What type of tissue is this? | back 31 Bone tissue |
front 32 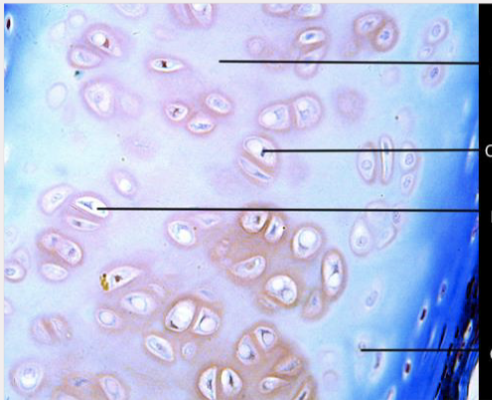 What type of tissue is this? | back 32 Hyaline cartilage |
front 33  What type of tissue is this? | back 33 Elastic cartilage |
front 34  What type of tissue is this? | back 34 Dense irregular connective tissue |
front 35 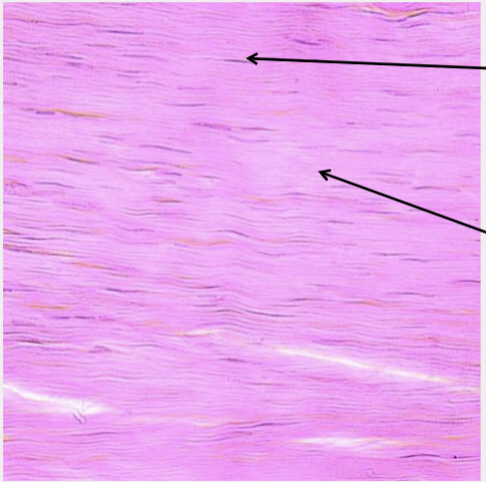 What type of tissue is this? | back 35 Dense regular connective tissue |
front 36 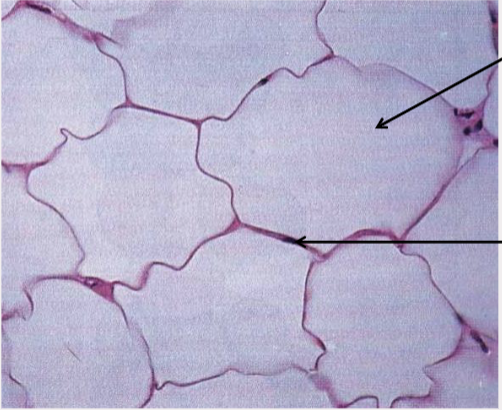 What type of tissue is this? | back 36 Adipose (fat) connective tissue |
front 37 What are the three types of bone tissue cells? | back 37 Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes |
front 38 What is the function of an osteocyte? | back 38 maintain bone tissue and reside in the spaces known as lacuna, which are surrounded by the matrix secreted originally by the osteoblasts |
front 39 What is the function of an osteoclast? | back 39 function in bone degradation |
front 40  What phylum are these organisms within? | back 40 Porifera |
front 41  What phylum is this organism within? | back 41 Platyhelminthes |
front 42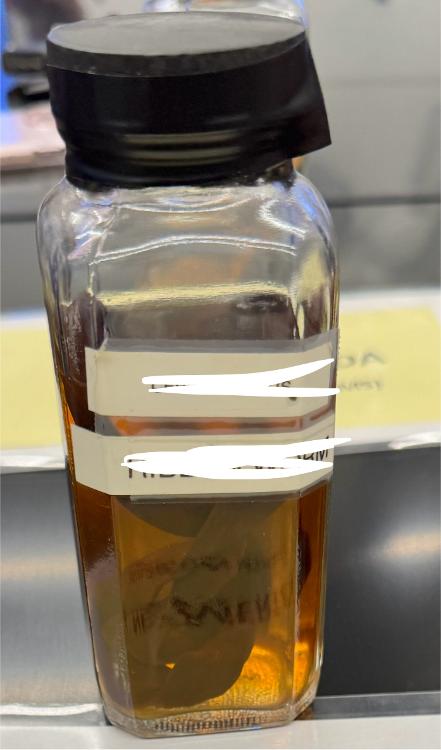  What phylum is this organism within? | back 42 nemertea |
front 43  What phylum is this organism within? | back 43 Arthropoda |
front 44 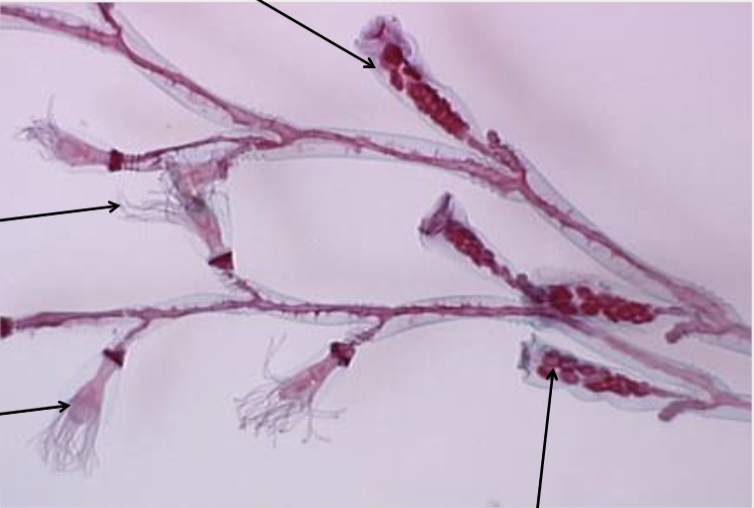 What is the form shown in this picture? A. Medusa B. Solitary polyp C. Colonial polyp D. Siphonophore | back 44 C. Colonial polyp |
front 45 Does phylum playhelminthes have a tube-in-tube body plan? | back 45 No, they are acoelomates |
front 46 Name the four characteristics of chordates | back 46 Dorsal, hollow nerve cord post-anal tail notocord pharangeal gils or slits |
front 47 Name two characteristics only found in mollusks. | back 47 mantle, calcium carbonate shell, visceral mass, radula, muscular foot |
front 48 Name one animal in clade Grouping Tetrapoda. | back 48 ... |