BICH EXAM 2: Electron transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
Electron transport is when electrons are carried by reduced coenzyme (NADH and FADH2) are passed through a _______ and conenzymes to drive the generation of a proton gradient across the _________
-chain of proteins
- inner mitochondrial membrane
The proton gradient drives the synthesis of ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation
The complexes allow for the flow of
electrons through these complexes
(Δℰo‘ = ℰo‘ (acceptor) - ℰo‘(donor)) .
-Acceptors are located above the chart and accept electrons (more + numbers)
- Donors are located below the chart and donate electrons
(more - numbers)
Complex 1 makes
4 H+
Complex 3 makes
4 H+
Complex 4 makes
2 H+
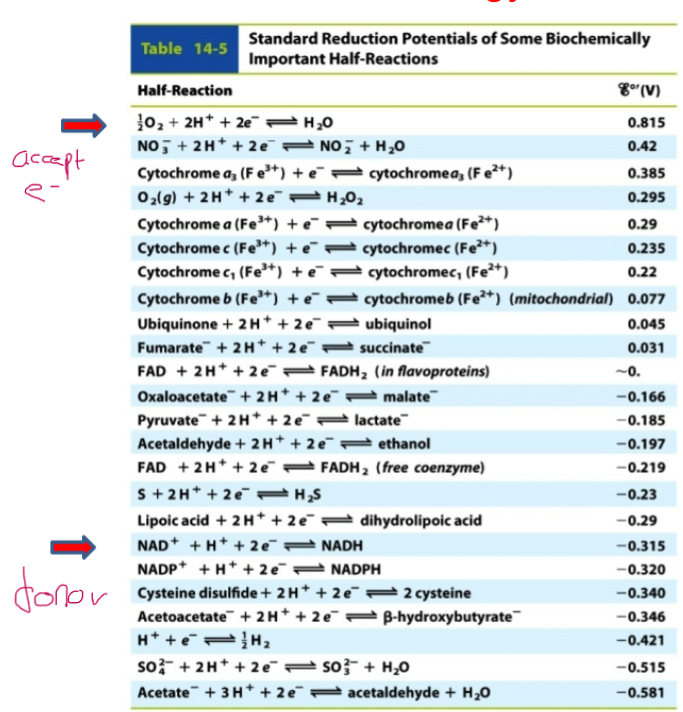
Learn this chart
PLZZZ
Complex I: NADH-UQ reductase
NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase pumps
4 H+ across mitochondria inner membrane
Complex 1 is reduced by_____, and oxidized by______
- NADH
-Coenyme Q
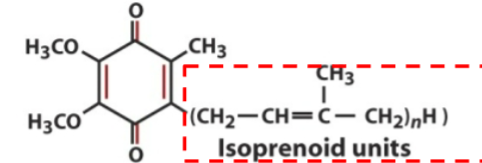
Ubiquinone contains no
electrons
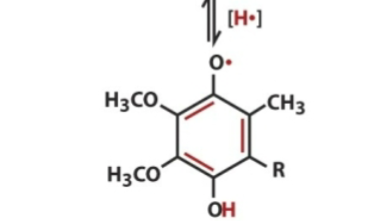
Ubisemiquinone contains
1 electron
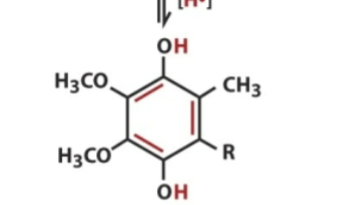
Ubiquinol contains
all 2 electrons
Complex 1 transports H+ from
matrix to cytosol
__H+ are transported from the matrix across the _____membrane to the cytosolic side
-4
-inner
Is a component of e- transport complex 2
Succinate DH
Complex 2 utilized Fe-S clusters and hemes to move electrons from
reduced FADH2 to W, forming QH2
No proton transport occurs at complex 2 as electrons are
passed from succinate to QH2
Starts at coenzyme Q and ends at cytochrome C oxidoreductase
-complex 3
Complex 3 results in QH2 is _____, and ______by Cyt C.
-reduced
-oxidized
In complex 3, QH2_____electrons, and Cyt C_____electrons from complex 3.
-bringing
-taking
CoQ passes electrons to cyt c in a redox cycle known as
Q cycle
The principle transmembrane in complex 3 is the
b cytochromes- with heme bL and bH
The path electrons take through complex 3
Q cycle
1. UQH2-> Rieske Fe-S-> Cyt C (release 2H+, leaves UQ)
2. 1e- transferred from UQ. to bL heme then to bH heme
Oxidation process occurs in these 2 steps (first half)
1. 2nd UQH2 is oxidized same way as first half
2. However after electron is transferred to bh heme, it is transferred to QH.- to reform UQH2 (release 2 H+
second half of q-cycle
Cytochrome c is a
mobile e- carrier
Cytochrome c is the only mitochondrial cytochrome that is _____soluable, important because it shuttles electrons from complex 3 to complex 4 by _____associating with the inner mitochondrial membrane
-water
-loosely
Complex 4 cytochrome C oxidase pumps
2H+ across mitochondrial inner membrane
Complex 4 is reduced by____ and oxidized by______. Electron carriers are ______ and______
-Cyt C
-O2
-cytochromes and Cu
Free radicals are
dangerous
.OH (hydroyl) and O2.- (superoxide radicals)
Extremely reactive free radicals
Complex 4 transfers electrons in ________. This shields the rest of the cell from____
-batches of 4
-reactive intermediates
What is the result of the oxidation of NADH and FADH2?
-NADH-10H+ are pumped out of matrix into IMS
-FADH2-6H+ are pumped out of matrix into IMS
This mechanism stores the energy of electron transport in an electrochemical potential: pH rises and matrix becomes
negatively charged as compare to cytosol
Protons are highly attracted back to the interior of the matrix and the energetically favorable electrochemical
gradient drives synthesis of ATP
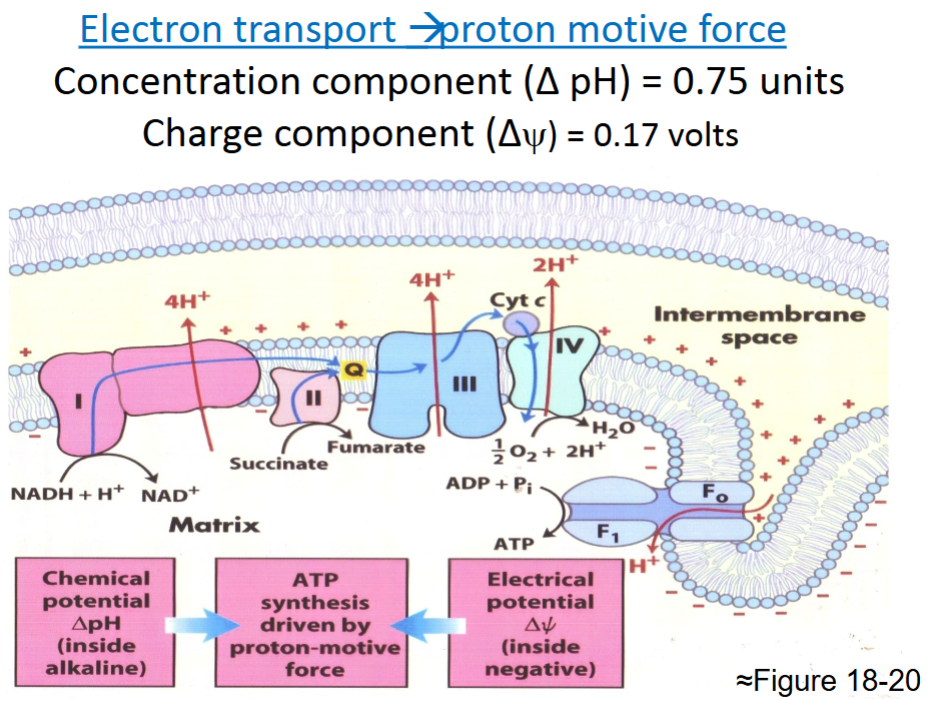
Good summary
NADH has ___ATP transport of H+
2.5
FADH2 has _____ATP transport of H+
1.5
H+ will be pumped from matrix to IMS if rotating
clockwise direction
Rotation of the c-ring delivers protons to the outlet
half channel in the a-subunit
Flow of protons through structure turns the rotor and drives cycle of conformational changes in
B that synthesize ATP
Aspartic acid is buried in a ______ core, where proton cannot be released.
hydrophobic
Each 120 degree rotation equal
1 ATP
Each 3x120 degrees so,
3 ATPs are made
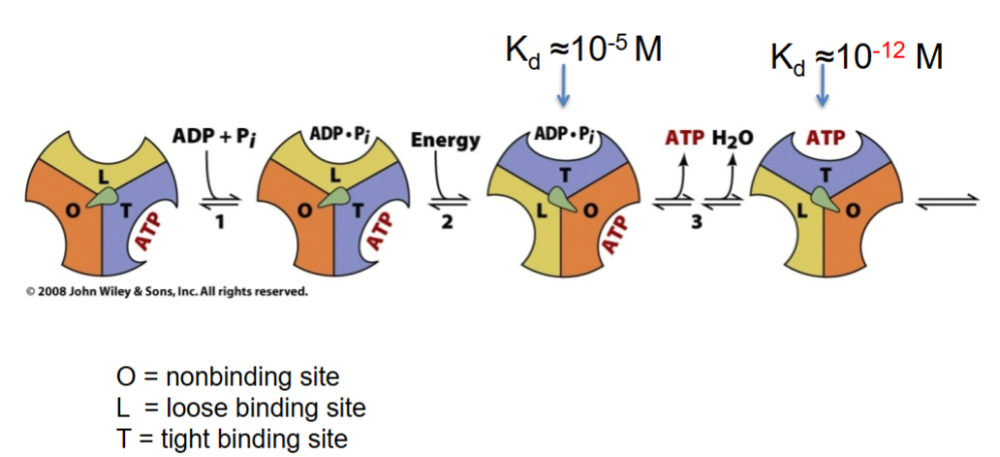
KNow thissss
.....
ATP must be transported out of
the mitochondria
ATP is ____ and ADP is ___ in translocase
-out
-in
ATP movement out is favored because the cytosol is + relative to the
- matrix
So every ATP transported costs
one H+
1ATP=
4H+
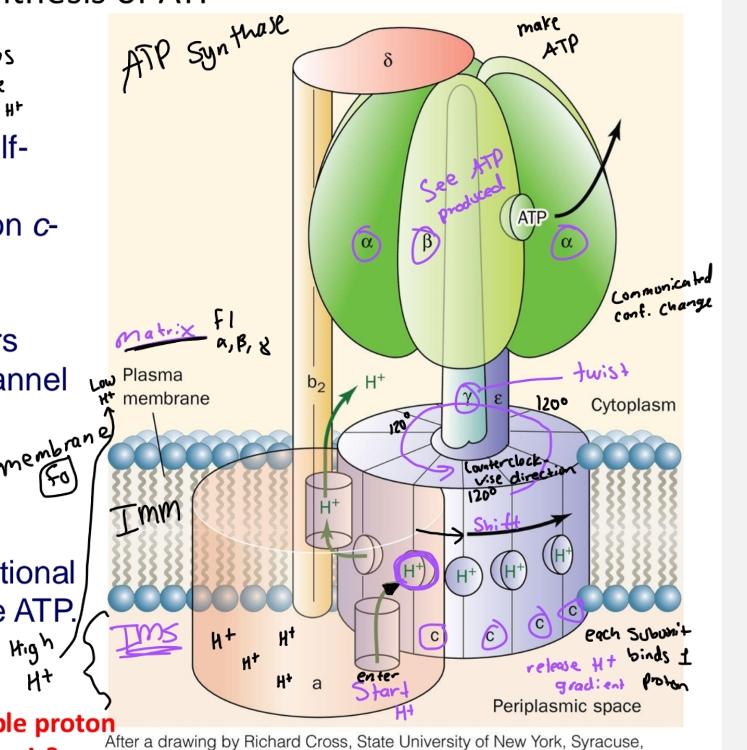
ATP synthesis diagram
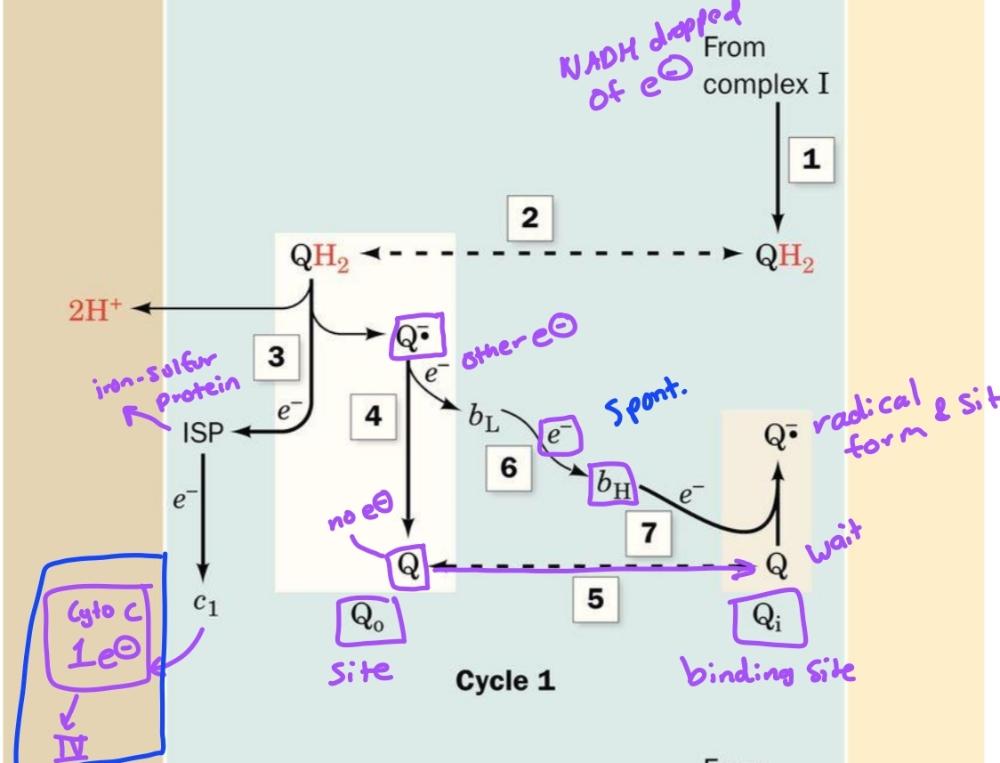
Cycle 1 of Q-cycle
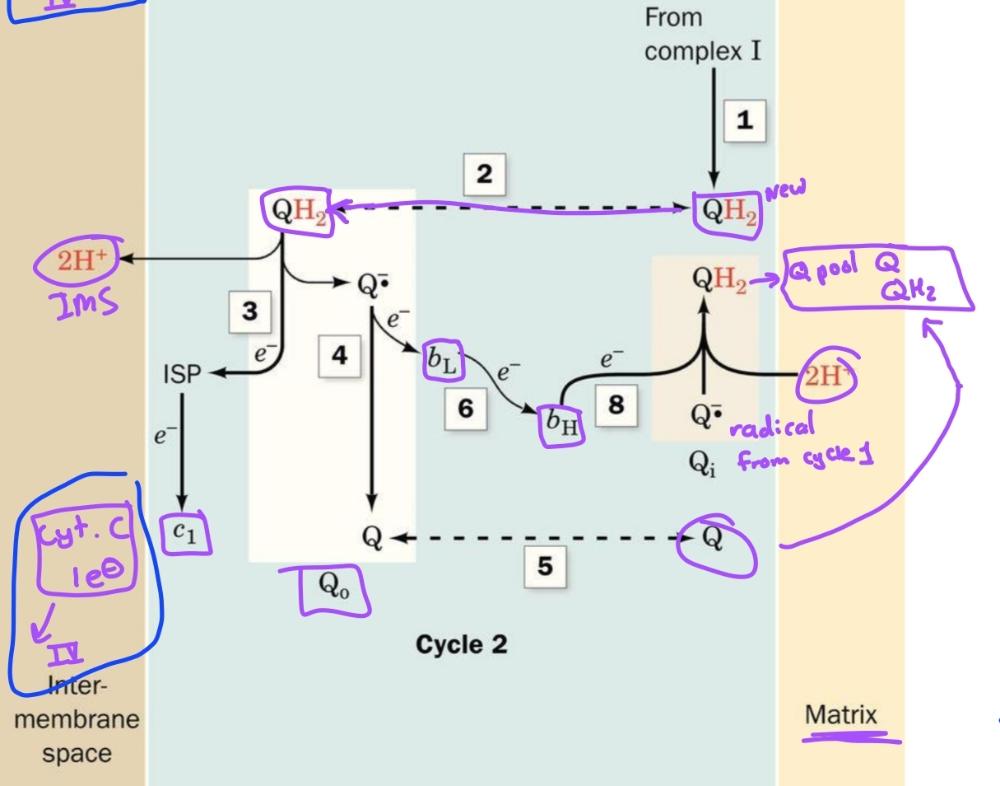
Cycle 2 of Q cycle
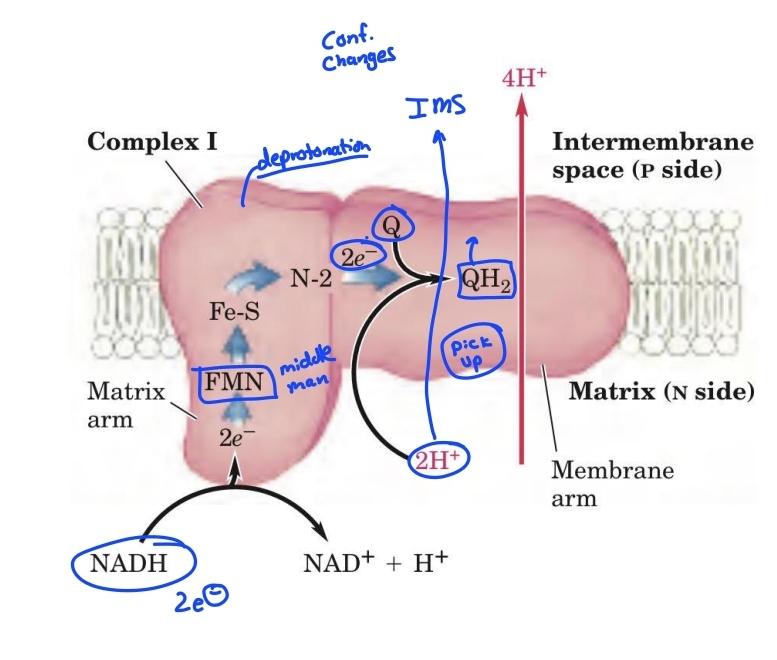
Complex 1 diagram
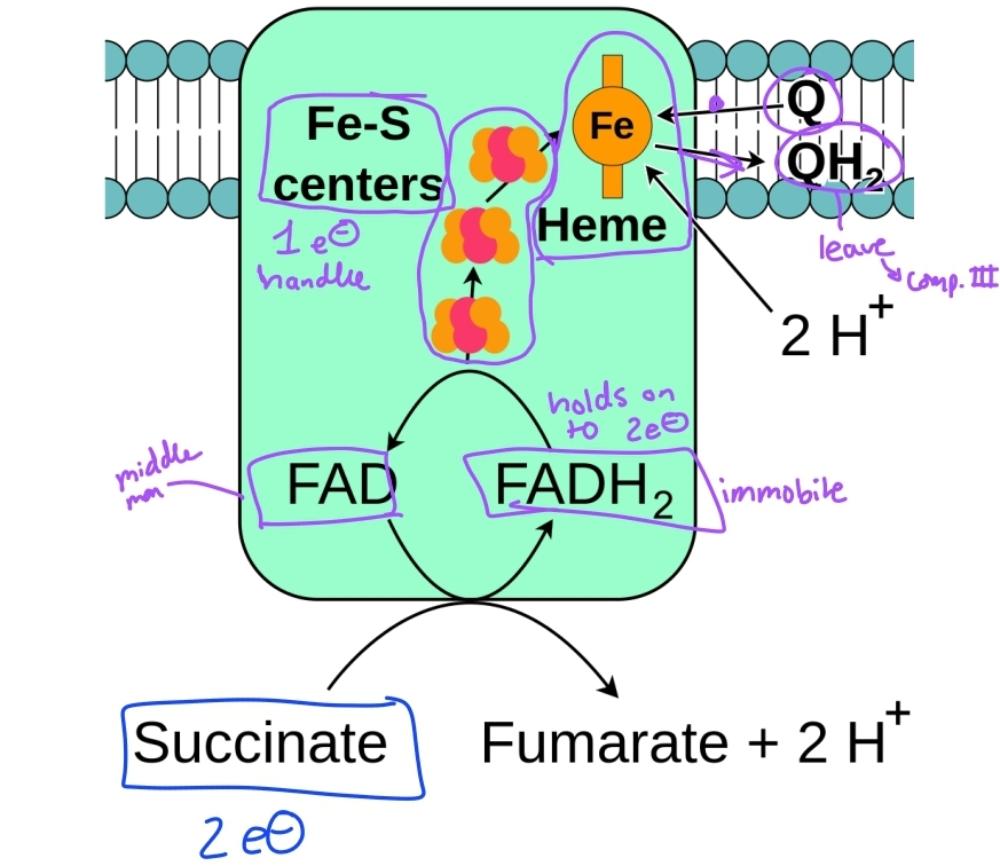
Complex 2 diagram
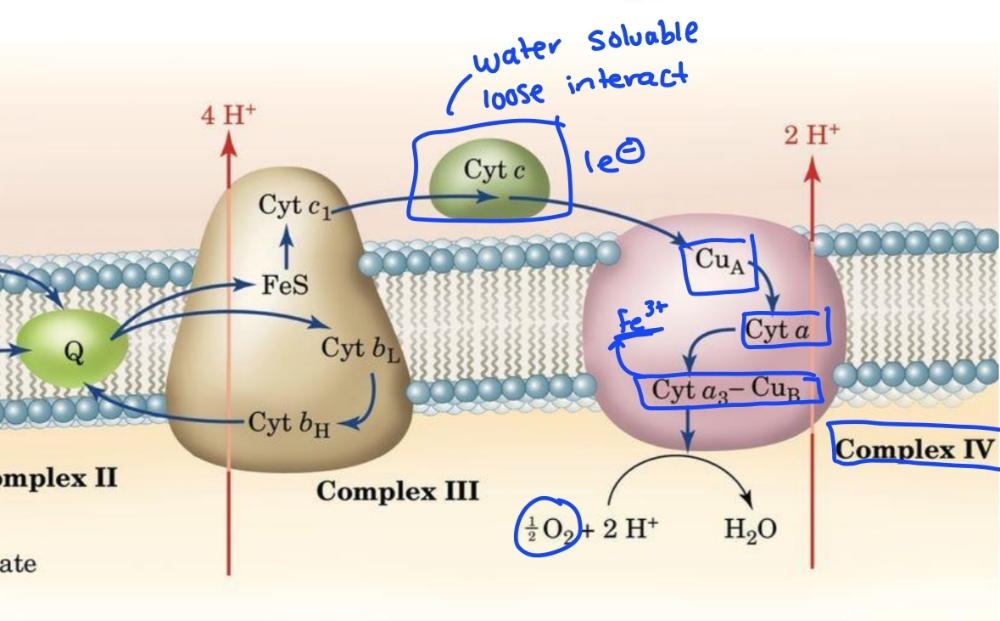
Complex 3 and 4 diagram