Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
BICH EXAM 2: Electron transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
front 1 Electron transport is when electrons are carried by reduced coenzyme (NADH and FADH2) are passed through a _______ and conenzymes to drive the generation of a proton gradient across the _________ | back 1 -chain of proteins - inner mitochondrial membrane |
front 2 The proton gradient drives the synthesis of ATP | back 2 Oxidative phosphorylation |
front 3 The complexes allow for the flow of | back 3 electrons through these complexes |
front 4 (Δℰo‘ = ℰo‘ (acceptor) - ℰo‘(donor)) . | back 4 -Acceptors are located above the chart and accept electrons (more + numbers) - Donors are located below the chart and donate electrons (more - numbers) |
front 5 Complex 1 makes | back 5 4 H+ |
front 6 Complex 3 makes | back 6 4 H+ |
front 7 Complex 4 makes | back 7 2 H+ |
front 8 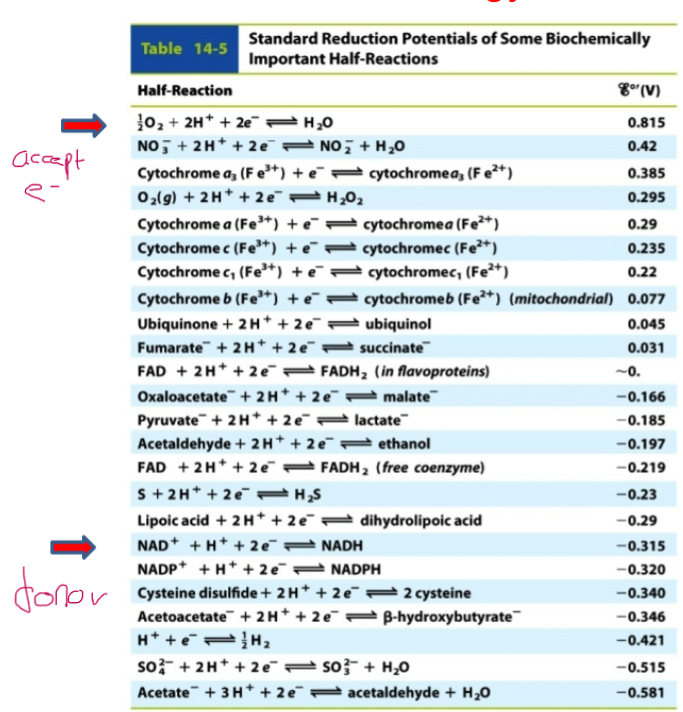 Learn this chart | back 8 PLZZZ |
front 9 Complex I: NADH-UQ reductase NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase pumps | back 9 4 H+ across mitochondria inner membrane |
front 10 Complex 1 is reduced by_____, and oxidized by______ | back 10 - NADH -Coenyme Q |
front 11 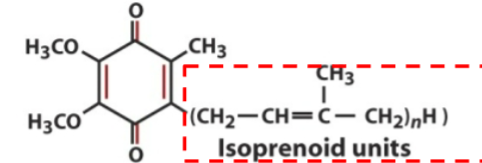 Ubiquinone contains no | back 11 electrons |
front 12 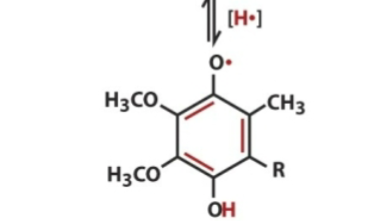 Ubisemiquinone contains | back 12 1 electron |
front 13 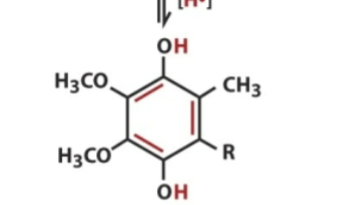 Ubiquinol contains | back 13 all 2 electrons |
front 14 Complex 1 transports H+ from | back 14 matrix to cytosol |
front 15 __H+ are transported from the matrix across the _____membrane to the cytosolic side | back 15 -4 -inner |
front 16 Is a component of e- transport complex 2 | back 16 Succinate DH |
front 17 Complex 2 utilized Fe-S clusters and hemes to move electrons from | back 17 reduced FADH2 to W, forming QH2 |
front 18 No proton transport occurs at complex 2 as electrons are | back 18 passed from succinate to QH2 |
front 19 Starts at coenzyme Q and ends at cytochrome C oxidoreductase | back 19 -complex 3 |
front 20 Complex 3 results in QH2 is _____, and ______by Cyt C. | back 20 -reduced -oxidized |
front 21 In complex 3, QH2_____electrons, and Cyt C_____electrons from complex 3. | back 21 -bringing -taking |
front 22 CoQ passes electrons to cyt c in a redox cycle known as | back 22 Q cycle |
front 23 The principle transmembrane in complex 3 is the | back 23 b cytochromes- with heme bL and bH |
front 24 The path electrons take through complex 3 | back 24 Q cycle |
front 25 1. UQH2-> Rieske Fe-S-> Cyt C (release 2H+, leaves UQ) 2. 1e- transferred from UQ. to bL heme then to bH heme | back 25 Oxidation process occurs in these 2 steps (first half) |
front 26 1. 2nd UQH2 is oxidized same way as first half 2. However after electron is transferred to bh heme, it is transferred to QH.- to reform UQH2 (release 2 H+ | back 26 second half of q-cycle |
front 27 Cytochrome c is a | back 27 mobile e- carrier |
front 28 Cytochrome c is the only mitochondrial cytochrome that is _____soluable, important because it shuttles electrons from complex 3 to complex 4 by _____associating with the inner mitochondrial membrane | back 28 -water -loosely |
front 29 Complex 4 cytochrome C oxidase pumps | back 29 2H+ across mitochondrial inner membrane |
front 30 Complex 4 is reduced by____ and oxidized by______. Electron carriers are ______ and______ | back 30 -Cyt C -O2 -cytochromes and Cu |
front 31 Free radicals are | back 31 dangerous |
front 32 .OH (hydroyl) and O2.- (superoxide radicals) | back 32 Extremely reactive free radicals |
front 33 Complex 4 transfers electrons in ________. This shields the rest of the cell from____ | back 33 -batches of 4 -reactive intermediates |
front 34 What is the result of the oxidation of NADH and FADH2? | back 34 -NADH-10H+ are pumped out of matrix into IMS -FADH2-6H+ are pumped out of matrix into IMS |
front 35 This mechanism stores the energy of electron transport in an electrochemical potential: pH rises and matrix becomes | back 35 negatively charged as compare to cytosol |
front 36 Protons are highly attracted back to the interior of the matrix and the energetically favorable electrochemical | back 36 gradient drives synthesis of ATP |
front 37 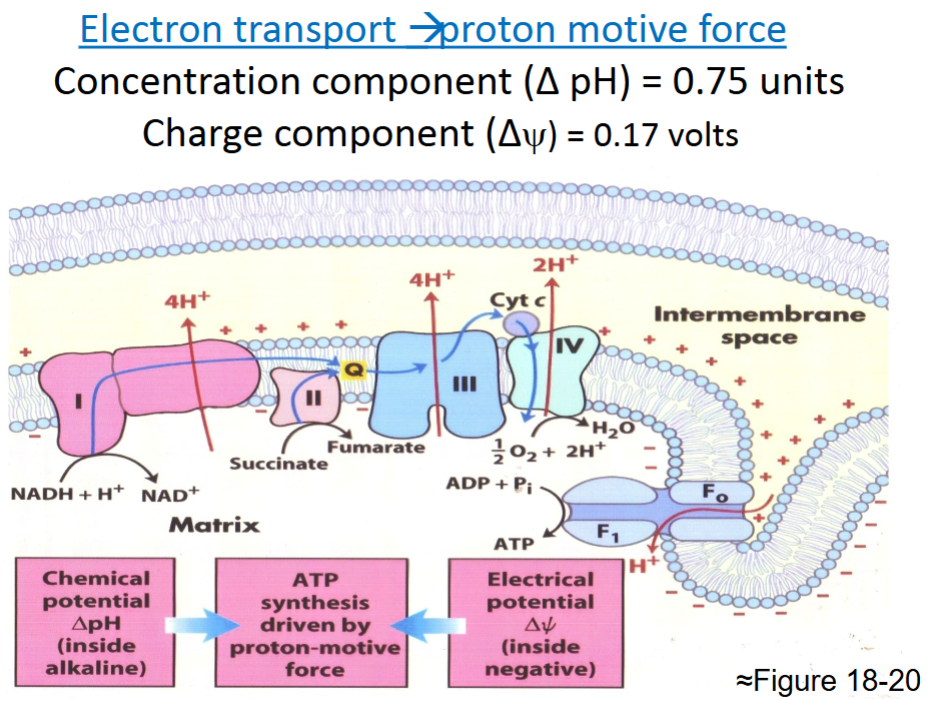 | back 37 Good summary |
front 38 NADH has ___ATP transport of H+ | back 38 2.5 |
front 39 FADH2 has _____ATP transport of H+ | back 39 1.5 |
front 40 H+ will be pumped from matrix to IMS if rotating | back 40 clockwise direction |
front 41 Rotation of the c-ring delivers protons to the outlet | back 41 half channel in the a-subunit |
front 42 Flow of protons through structure turns the rotor and drives cycle of conformational changes in | back 42 B that synthesize ATP |
front 43 Aspartic acid is buried in a ______ core, where proton cannot be released. | back 43 hydrophobic |
front 44 Each 120 degree rotation equal | back 44 1 ATP |
front 45 Each 3x120 degrees so, | back 45 3 ATPs are made |
front 46 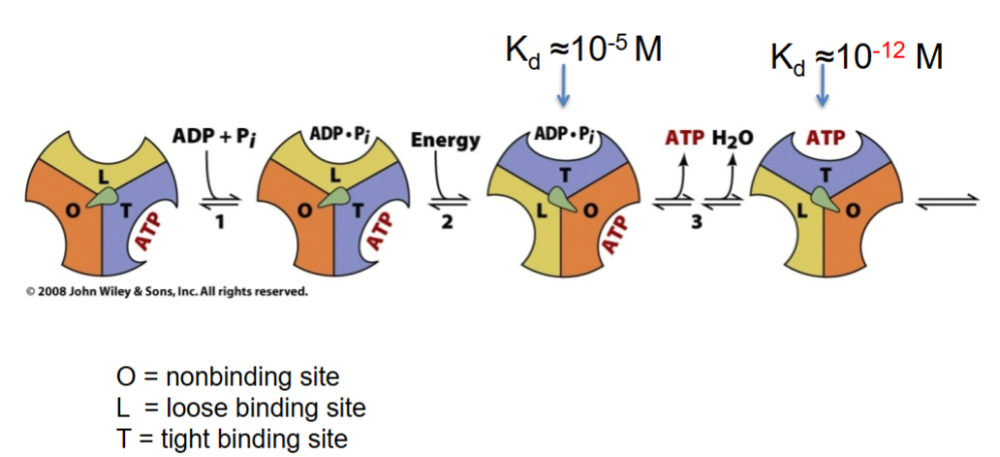 KNow thissss | back 46 ..... |
front 47 ATP must be transported out of | back 47 the mitochondria |
front 48 ATP is ____ and ADP is ___ in translocase | back 48 -out -in |
front 49 ATP movement out is favored because the cytosol is + relative to the | back 49 - matrix |
front 50 So every ATP transported costs | back 50 one H+ |
front 51 1ATP= | back 51 4H+ |
front 52 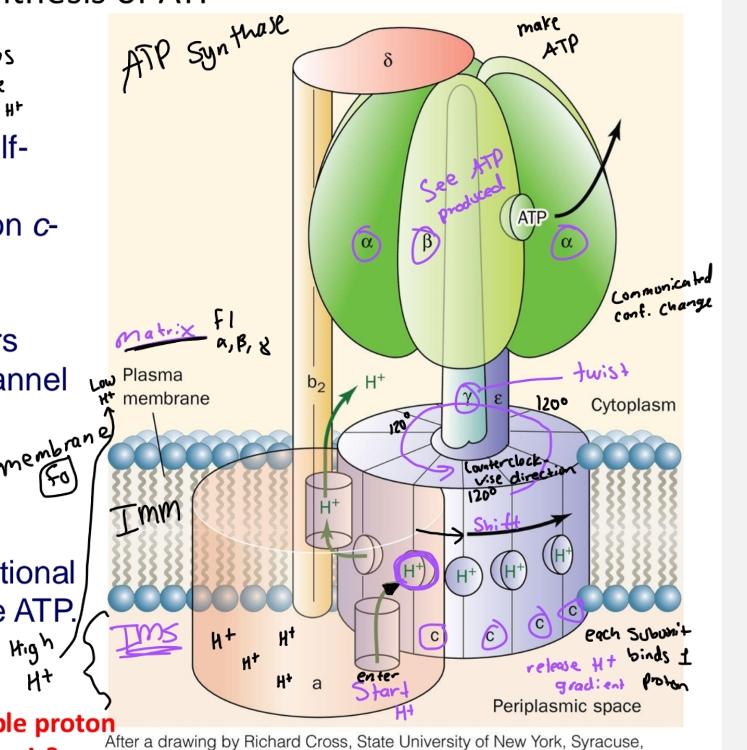 | back 52 ATP synthesis diagram |
front 53 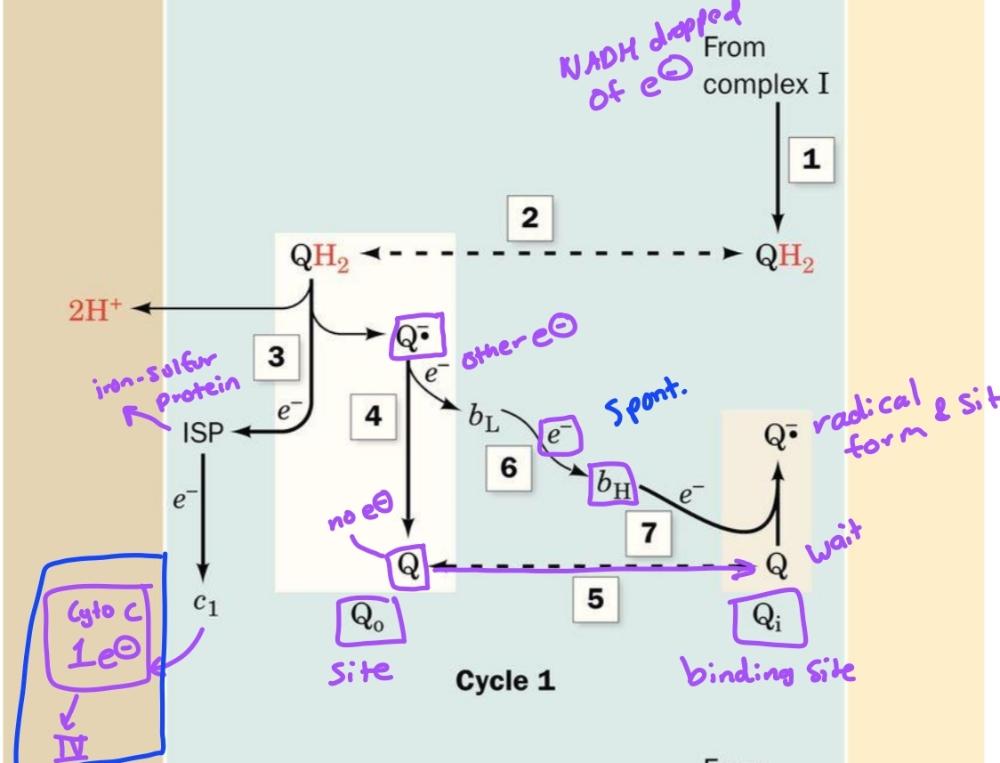 | back 53 Cycle 1 of Q-cycle |
front 54 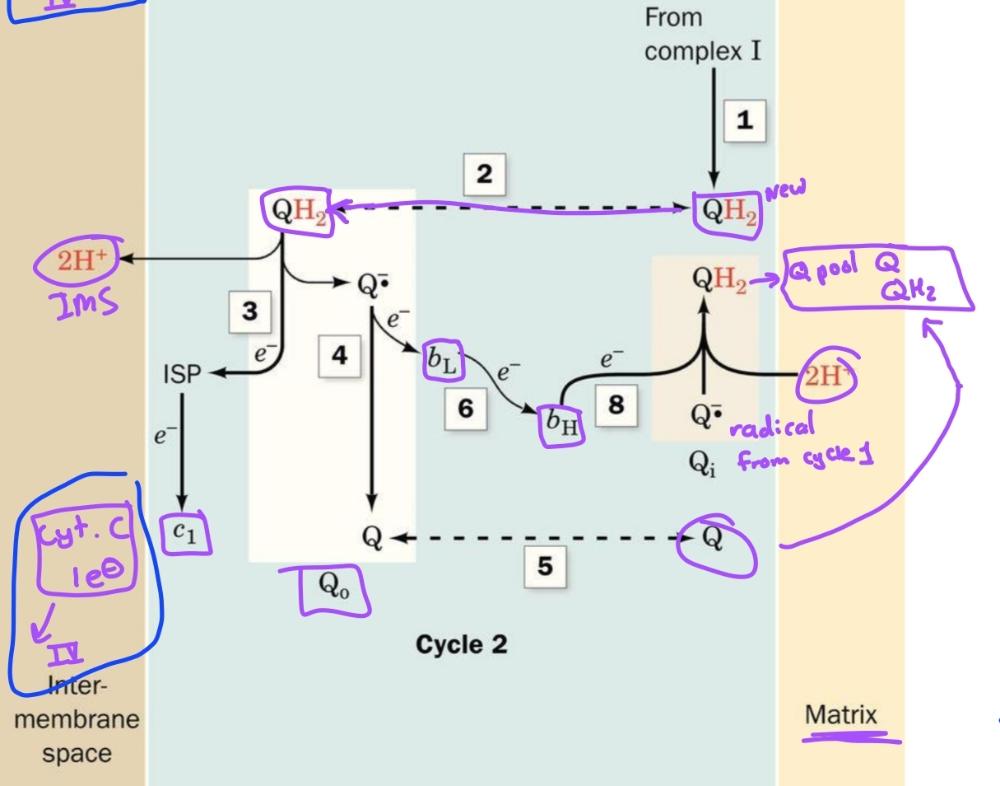 | back 54 Cycle 2 of Q cycle |
front 55 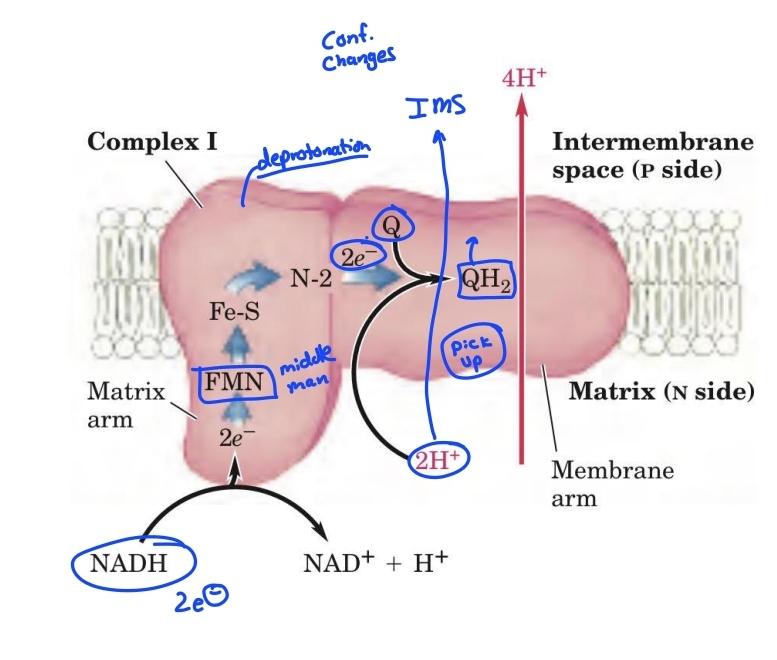 | back 55 Complex 1 diagram |
front 56 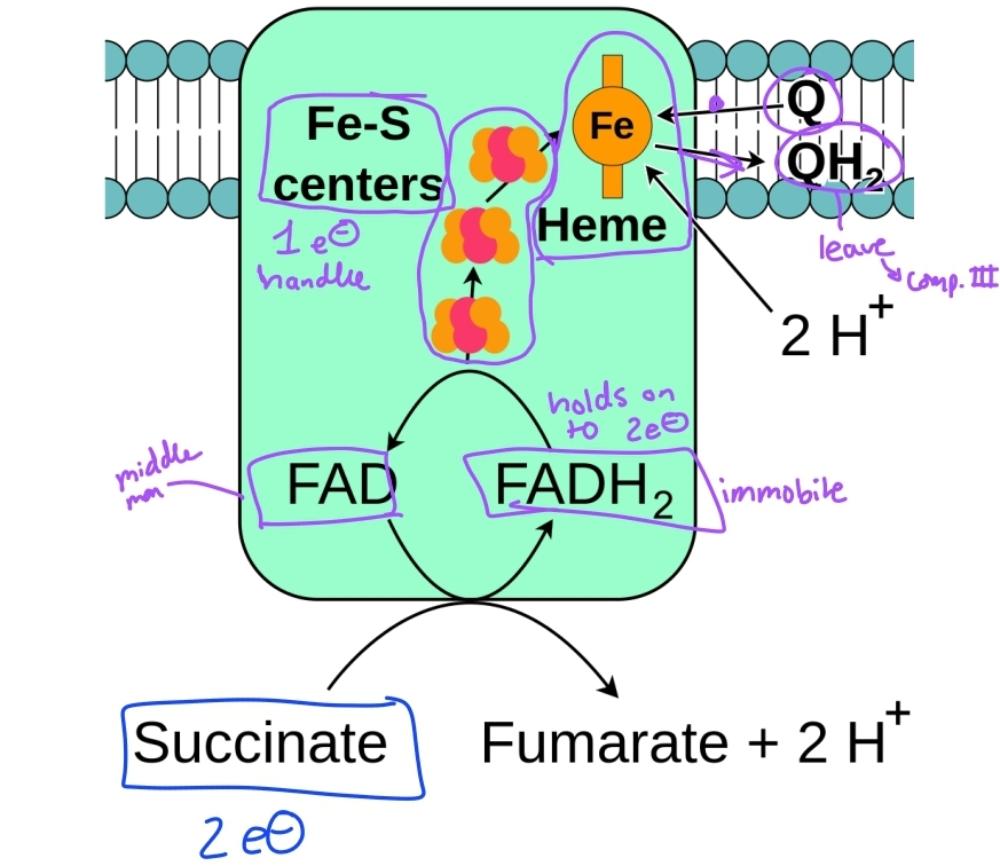 | back 56 Complex 2 diagram |
front 57 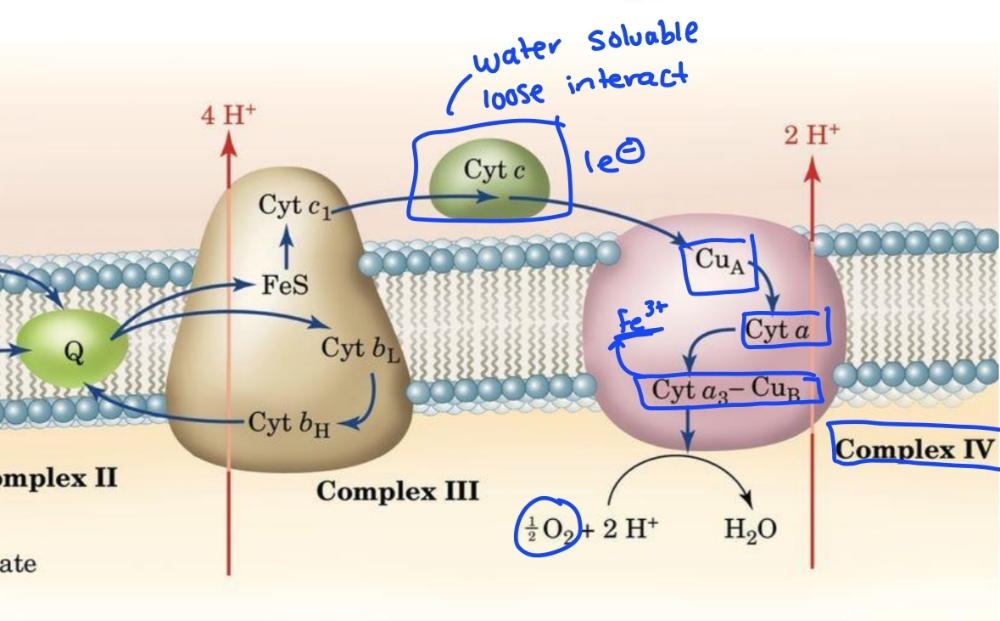 | back 57 Complex 3 and 4 diagram |