Exam 2 BICH: TCA CYCLE
TCA cycle is a central pathway for___ ____ from several metabolic pathways when acetyl CoA can be generated
-recovering energy
Acetyl CoA is oxidized in the TCA cycle, where intermediates are
utilized in a circular pathway
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplam and doesnt require energy. Meanwhile, the TCA cycle occurs in the
mitochondria
The TCA cycle allows for the oxidation of pyruvate to CO2 under_____conditions, and yields about ______ATP
-aerobic
-36
Do the electrons from glucose oxidation feed into the electron transport pathway, driving synthesis of ATP?
YES
What is Acetyl CoA oxidized to?
CO2
Electrons stored as NADH and FADH2 are delivered to a________ to
the
final electron acceptor O2.
-membrane-associated electron-transport chain
Electron transfer is coupled
to a proton gradient across the
membrane to drive the
synthesis of ATP in a process known as____
-oxidative phosphorylation.
How many electrons are removed when a complete oxidation of glucose to CO2 occurs?
-24 electrons
How many total electrons are in PDHC?
-4 electrons total in 2 pyr-> acetyl-CoA
How many total electrons are in TCA cycle?
-8 electrons for each acetyl CoA (16 total)
These electrons are stored as ___ and ___ used to fuel oxidative phosphorylation.
-NADH
-FADH2
Flavin coenzymes can exist in three oxidation states
FAD, FMN, and riboflavin
The three oxidation states allows for flavin coenzymes to participate in
one-electron or two-electron transfer reactions.
Catalyze many reactions in biological systems and work with many electron donors and acceptors
Flavoproteins
FADH2 can transfer either __ or __ e- at a time
-1
-2
FADH, FAD, FADH2 are made form the vitamin
riboflavin
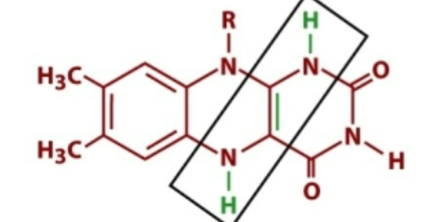
What structure is this?
FADH2
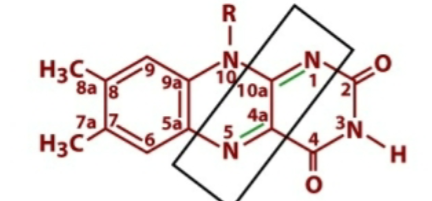
What structure is this?
FAD
What is the source of acetyl CoA?
pyruvate
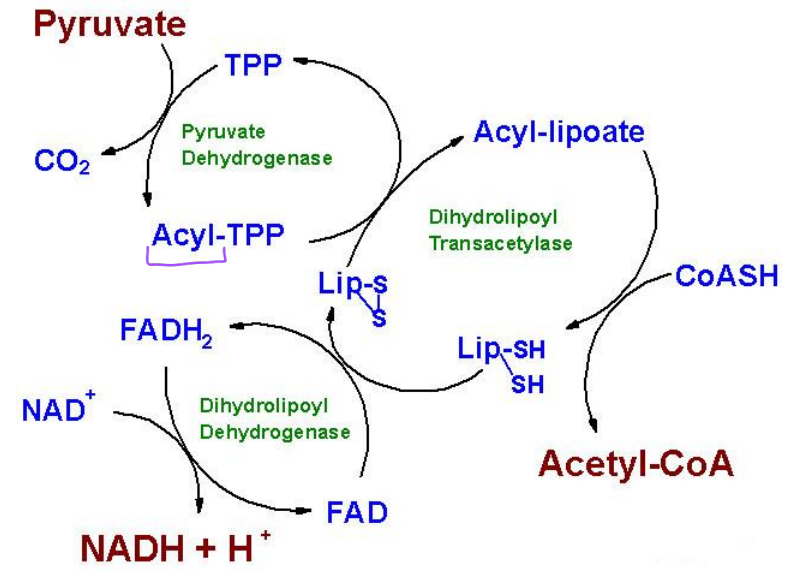
The reaction that converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA is catalyzed by the
-pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC or PDHC)
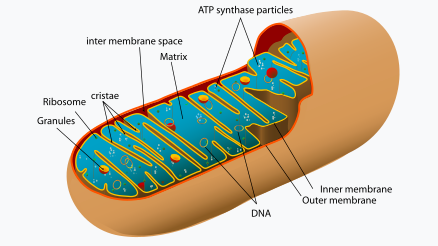
permeable to anything smaller than 5 kD
Outer membrane
permeable only to O2, H2O, and CO2
Inner membrane
How does pyruvate make its way into the mitochondrial matrix?
-it travels through a channel in the outer membrane and an H+/pyruvate symporter in the inner membrane
From pyruvate to Acetyl CoA:
oxidation by NAD+ and formation of a thioester
What is the function of CoA?
-a carrier of acetyl and other acyl groups
What is the reaction of a pyruvate DH complex?
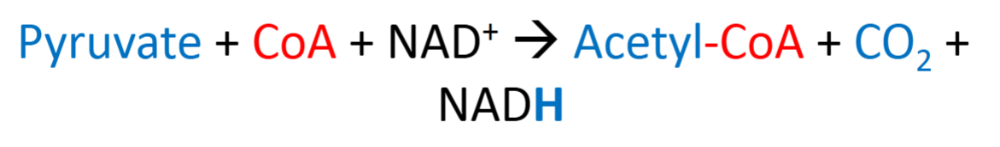
What three enzymes is pyruvate dehydrogenase made of?
_pyruvate dehydrogenase(E1)
-Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2)
-Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3)
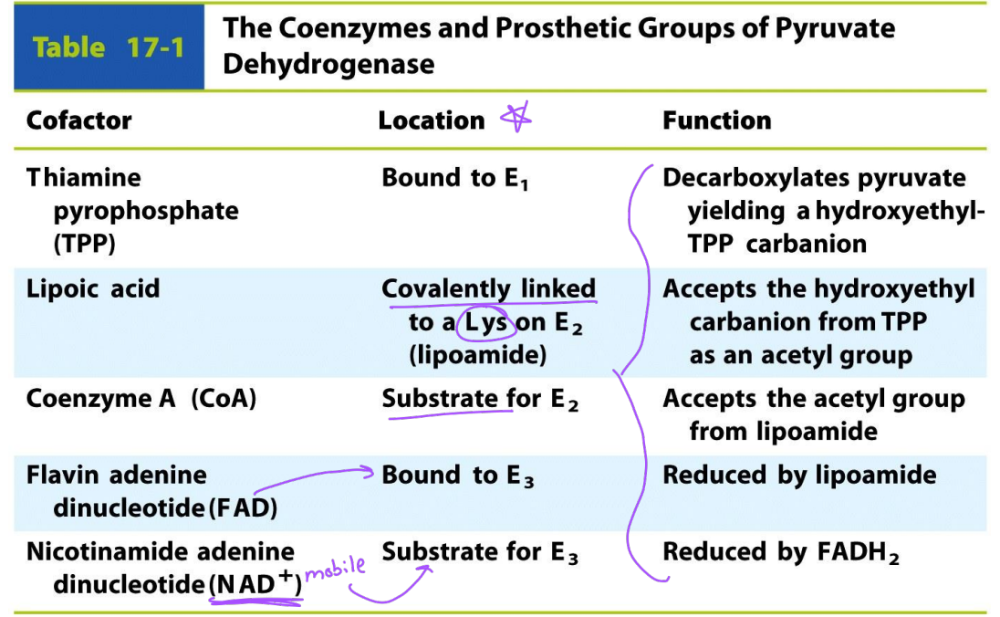
What are the 5 cofactors of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
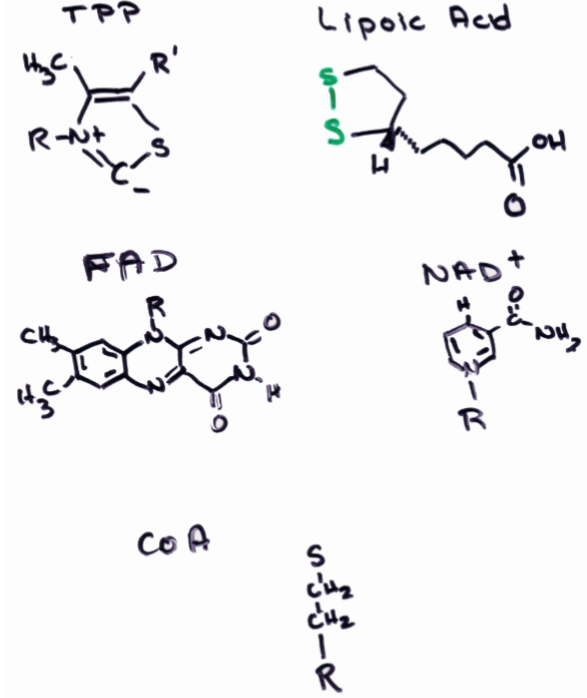
-TPP
-NAD
-FAD
-Lipoic Acid
-CoA
Pyruvate conversion to Acetly CoA
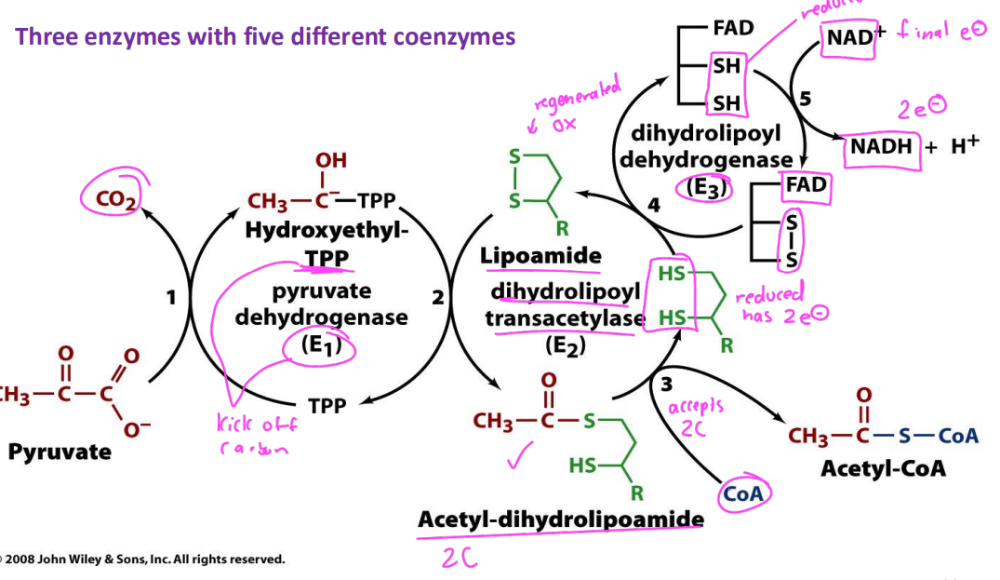
What is the purpose of TPP cofactor?
facilitates decarboxylation
What is the purpose of lipoic acid?
-bound to a lysyl residue to form lipoamide that is reduced to from dihydrolipoamide
-serves as a swinging arm to transfer intermediates from E1, E2, E3
Arsenic poisoning is a toxic compound that binds to
sulfhydryl compounds
The inactivation of lipoamide-containing compounds such as pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase__-
halts respiration
Arsenic compounds are more toxic to______ and was used to treat ___,___,___
-microorganisms
-syphilis, bacteria, and parasitic diseases
TPP( vitamin B1/thiamine) deficiency results in
pain, paralysis, wasting, and heart failure
TPP being used in pyruvate DH
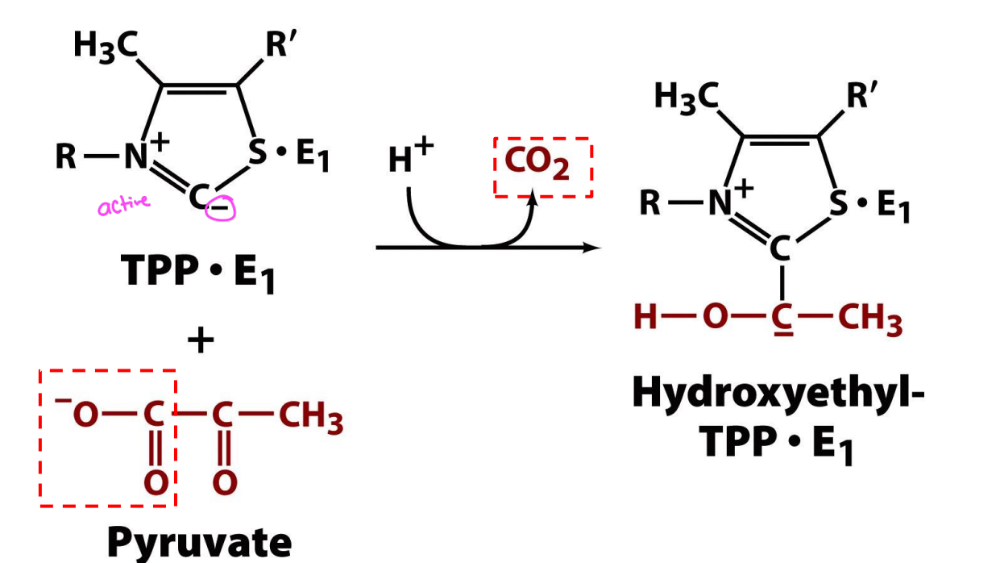
In pyruvate decarboxylase, hydrooxyethyl-TPP is
cleaved to release acetaldehyde +TPP
In pyruvate DH reaction, hydroxyethyl-TPP transfers H3C-(C=O)- to_____ and ____occurs producing dihydrolipoate
-lipoic acid
-oxidation
T or F: Humans can make lipoic acid (it is a vitamin)
false
The nucleophilic attack by CoA at carbonyl carbon results in transfer of acetyl group to CoA generating
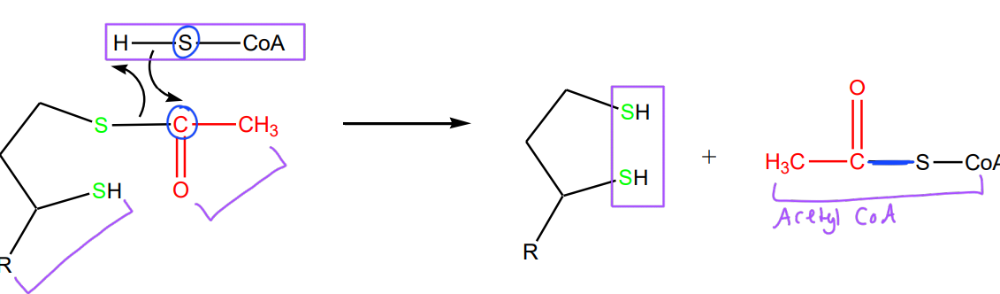
acetyl CoA
When the acetyl group is transferred to CoA, FAD and NAD+ are used to
reclose (oxidize) S-S of lipoic acid
E2 is a proper
oxidation state
PDHC mechanism
KNOW THIS TABLE
Thiamine is a vitamin in B1 and can be found in
nuts, meats, and whole grains
Lipoic acid is made from fatty acid precursors in animals and can be found in
spinach, broccoli, yeast, rice bran, red organic meat
CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine pantothenate and ATP and is
lesser known than vit. B5 because all foods are a source of B5
FAD/FMN is synthesized from_____ and can be found in_____-
-riboflavin
-eggs, organ meats, low-fat milk, cereals, bread, and grain products
NAD+ biosynthesized from____, but relies on salvage pathways that use______
-tryptophan
-niacin
A long lasting drop or rise of ΔΨmvs normal levels may
induce unwanted loss of cell viability and be a cause of various pathologies
ΔΨmvs drives inward transport of____ and outward transport of _____
-cations
-anions
ΔΨmvs is an important factor in selection of
non-functional mitochondria
1. Entry of new carbon units into the TCA cycle is from pyruvate or oxidation of fatty acids
2. Transfer of the 2-C acetyl CoA to 4C OAA yields citrate
3. A dehydration-rearrangement yields isocitrate
4. two successive decarboxylation produce alpha-KG and then succinyl CoA
5. Multiple rearrangements to regenerate OAA
The chemical logic of the TCA cycle
reaction where 2C unit of acetyl CoA is introduced into the TCA cycle by addition to the 4C unit OAA to from citrate
1. Citrate synthase
The Cα of the acetyl group in acetyl-CoA is acidic and can be deprotonated to form a
carbanion
The carbanion is a strong ______that can attack the α-carbonyl of ______
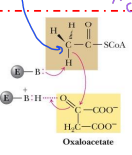
-nucleophile
-oxaloacetate
Due to citrates poor oxidation, the enzyme___ catalyzes an isomerization reaction
2. aconitase
Aconitase uses an_____ to achieve stereospecificity
iron-sulfur cluster
Is a hydride removal followed by a decarboxylation and is a link to the electron transport pathway because it makes NADH
3. Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase produces the 1st NADH and the CO2 released came from the
end of OXAL
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase catalyzes the_________of the TCA cycle
2nd oxidative decarboxylation
Enzyme is nearly identical to pyruvate dehydrogenase and the 2nd NADH is produced
4. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Uses 5 coenzymes: TPP, CoASH, lipoic acid, NAD+, and FAD
α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is a very __, _____ reaction
-exergonic
-irreversible
The 60 subunits are made up of:
-pyruvate dehydrogenase: 24(E1)
-dihydrolipoyl transacetylase: 24(E2)
-dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase:12(E3)
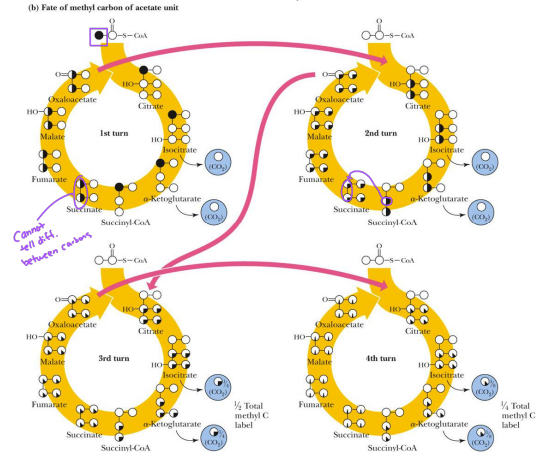
Harvest "high energy" thioester bond to make GTP. Since succinate is symmetric, we can no longer distinguish which carbons came from acetyl coA
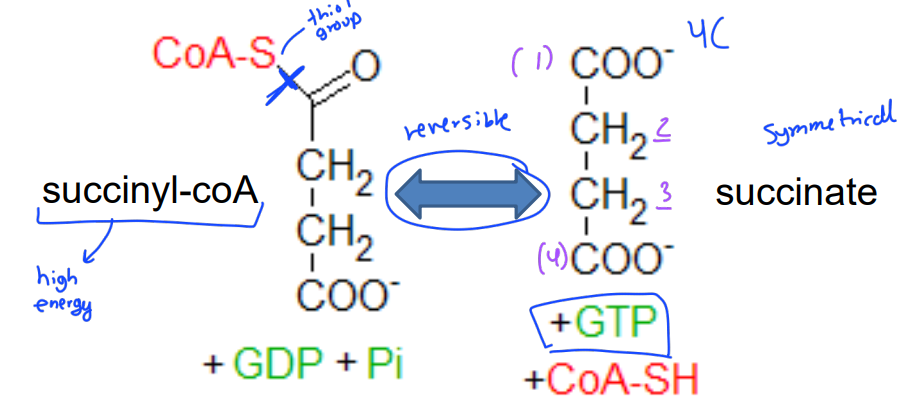
5. Succinyl-CoA synthetase
It is considered to be the substrate-level phosphorylation
Succinyl-CoA synthetase reaction
During Succinyl-CoA synthetase the mechanism involves formation of a ________to produce_____
-phosphohistidine
-succinate
A____is made after succinyl-CoA synthetase
nucleoside triphosphate
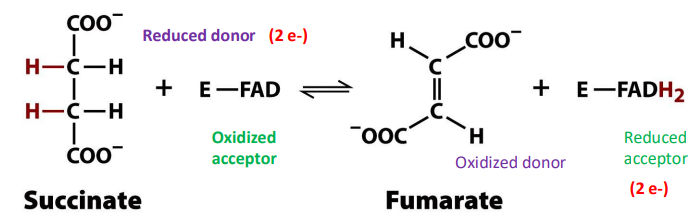
It is near equilibrium. DH->FADH2 rather than NADH
6. Succinate dehydrogenase
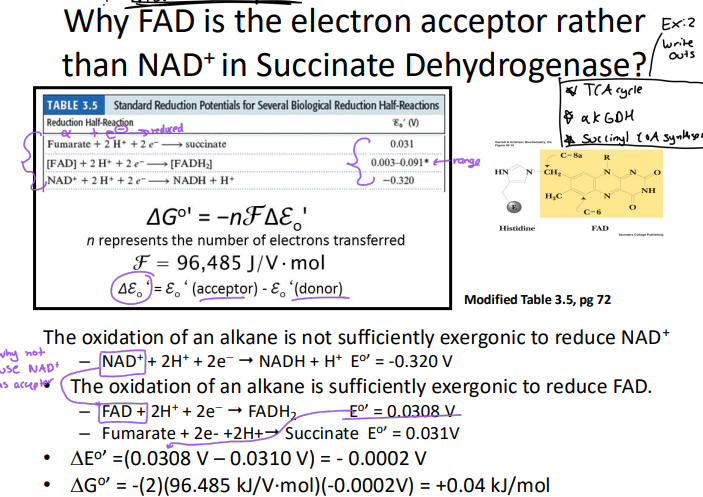
(Δℰo‘= ℰo‘ (acceptor) - ℰo‘(donor))
Remember this!!
Reduction potential
Practice this math question
Succinate dehydrogenase contains three types of Fe-S centers:
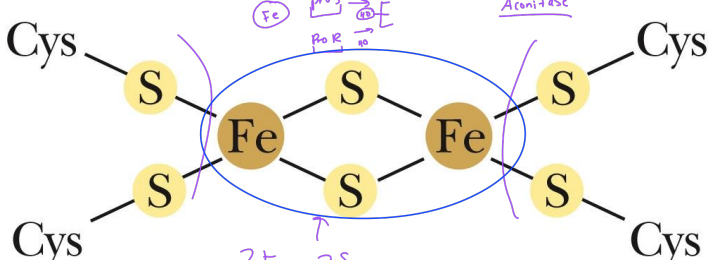
a 4Fe-4S center, a 3Fe-4S, and a 2Fe-2S center
Succinate DH involves hydride removal by ____. This enzyme is part of the electron transport pathways in the inner _____
-FAD
-mitochondrial membrane
The electrons transferred from succinate to FAD(to form FADH2) are passed to____in electron transport pathway
ubiquinone
Fumarase converts fumarate->malate by
adding water
Fumarase causes the
hydration across the double bond
Malate DH _____malate-> OAA
reversibly oxidizes
The carbon that gets oxidized received an OH group in the previous reaction. Is NAD+-dependent oxidation
8. Malate oxidation
The carbon atoms of Acetyl-CoA have diff. fates
Electrons stored as NADH and FADH2 are delivered to a membrane associated ETC to the final electron acceptor O2. Electron transfer is coupled to a proton gradient across the membrane to drive the synthesis of ATP in a process known as
oxidative phosphorylation