Lab Practical 2 A&P II LAB
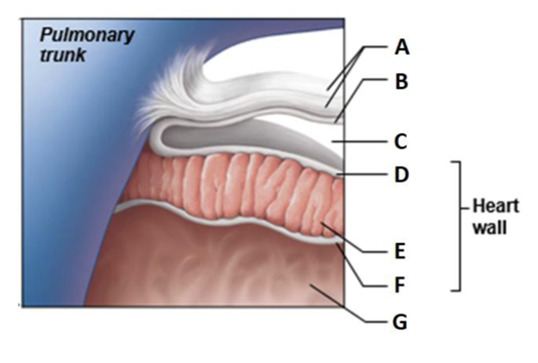
Label A
Fibrous pericardium

Label B
Parietal layer of serous pericardium

Label C
Pericardial cavity

Label D
Epicardium (visceral layer of serous pericardium)

Label E
Myocardium

Label F
Endocardium

Label G
Heart chamber
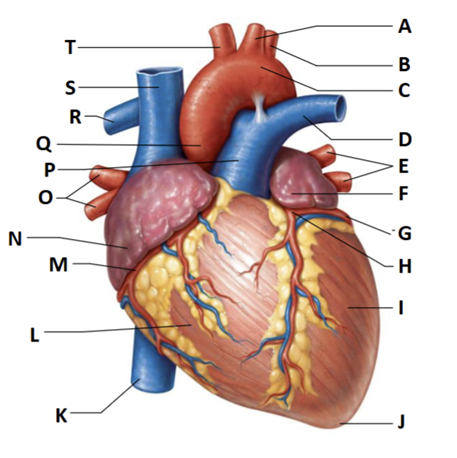
Label A
left common carotid artery

Label B
left subclavian artery

Label C
Aortic arch

Label D
Left pulmonary trunk

Label E
left pulmonary veins

Label F
auricle of left atrium

Label G
circumflex artery

Label H
left coronary artery (in coronary sulcus)

Label I
left ventricle

Label J
apex

Label K
inferior vena cava

Label L
right ventricle

Label M
right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus)

Label N
right atrium

Label O
right pulmonary veins

Label P
pulmonary trunk

Label Q
ascending aorta

Label R
right pulmonary artery

Label S
superior vena cava

Label T
brachiocephalic trunk

Label A
Superior vena cava

Label B
right pulmonary artery

Label C
pulmonary trunk

Label D
right atrium

Label E
right pulmonary veins

Label F
fossa ovalis

Label G
pectinate muscles

Label H
tricuspid valve

Label I
right ventricle

Label J
chordae tendineae

Label K
trabeculae carneae

Label L
inferior vena cava

Label M
interventricular septum

Label N
papillary muscle

Label O
left ventricle

Label P
pulmonary valve

Label Q
aortic valve

Label R
mitral (bicuspid) valve

Label S
left pulmonary vein

Label T
left atrium

Label U
left pulmonary artery

Label V
aorta
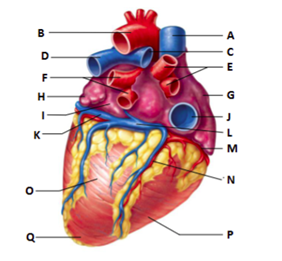
Label A
superior vena cava

Label C
right pulmonary artery

Label E
right pulmonary veins

Label G
right atrium

Label J
inferior vena cava

Label M
right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus)

Label N
posterior interventricular artery (in posterior interventricular sulcus)

Label P
right ventricle

Label L
coronary sinus

Label B
aorta

Label D
left pulmonary artery

Label F
left pulmonary veins

Label H
auricle of left atrium

Label I
left atrium

Label K
great cardiac vein

Label O
left ventricle

Label Q
apex
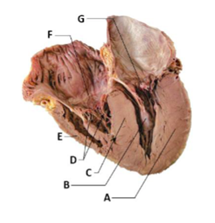
Label A
myocardium of left ventricle

Label B
papillary muscle

Label C
interventricular septum

Label D
chordae tendineae

Label E
myocardium of right ventricle

Label F
tricuspid valve

Label G
mitral valve
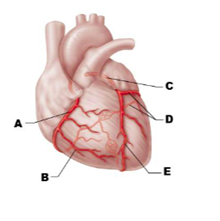
Label A
right coronary artery

Label B
right marginal artery

Label C
left coronary artery

Label D
circumflex artery

Label E
anterior interventricular artery
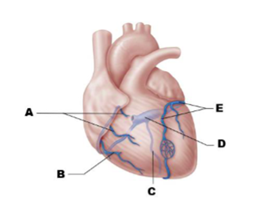
Label A
anterior cardiac veins

Label B
small cardiac vein

Label C
middle cardiac vein

Label D
coronary sinus

Label E
great cardiac vein
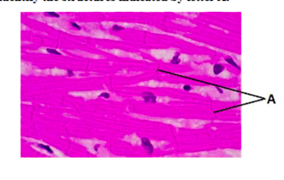
Identify A
Intercalated discs
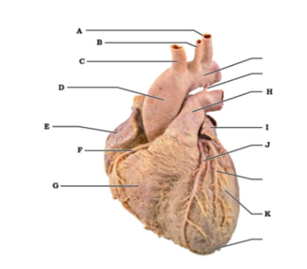
Label A
left subclavian artery

Label B
left common carotid artery

Label C
brachiocephalic trunk

Label D
ascending aorta

Label E
right atrium

Label F
right coronary artery (in coronary sulcus)

Label G
right ventricle

Label H
pulmonary trunk

Label I
auricle of left atrium

Label J
anterior interventricular artery (in anterior interventricular sulcus)

Label K
left ventricle
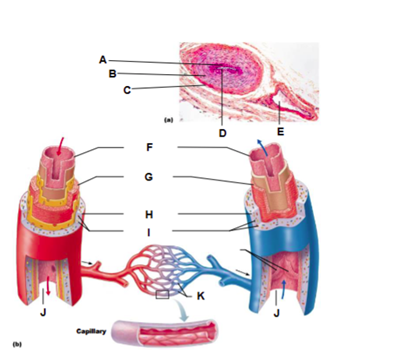
Label A
tunica intima

Label B
tunica media

Label C
tunica externa

Label D
artery

Label E
vein

Label F
tunica intima

Label G
tunica media

Label H
tunica externa

Label I
vasa vasorum

Label K
capillary network

Label J
Lumen
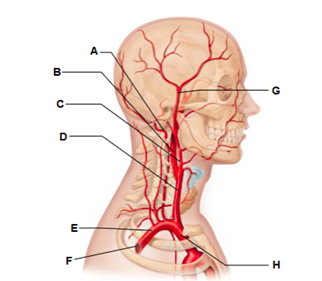
Label A
vertebral artery

Label B
internal carotid artery

Label C
external carotid artery

Label D
common carotid artery

Label E
subclavian artery

Label F
axillary artery

Label G
superficial temporal artery

Label H
brachiocephalic trunk
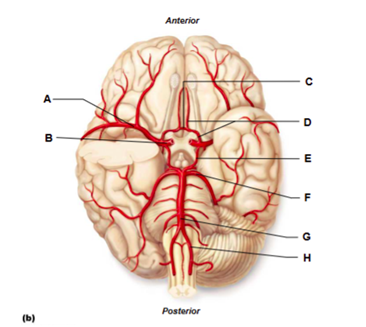
Label A
middle cerebral artery

Label B
internal carotid artery

Label C
anterior communicating artery

Label D
anterior cerebral artery

Label E
posterior communicating artery

Label F
posterior cerebral artery

Label G
basilar artery

Label H
vertebral artery
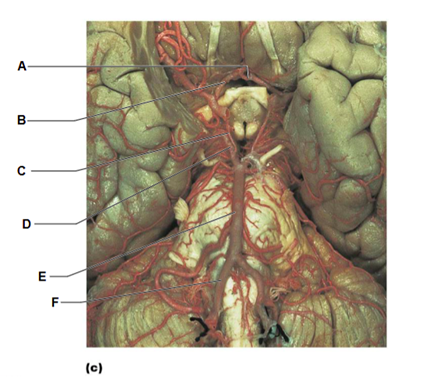
Label A
anterior communicating artery

Label B
anterior cerebral artery

Label C
posterior communicating artery

Label D
posterior cerebral artery

Label E
basilar artery

Label F
vertebral artery
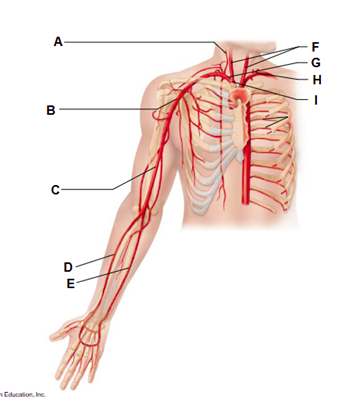
Label A
vertebral artery

Label B
axillary artery

Label C
brachial artery

Label D
radial artery

Label E
ulnar artery

Label F
common carotid arteries

Label G
right subclavian artery

Label H
left subclavian artery

Label I
brachiocephalic trunk
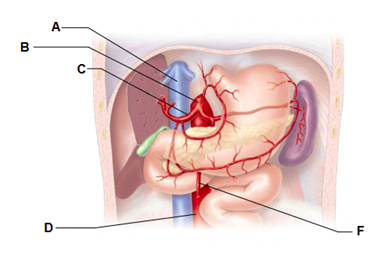
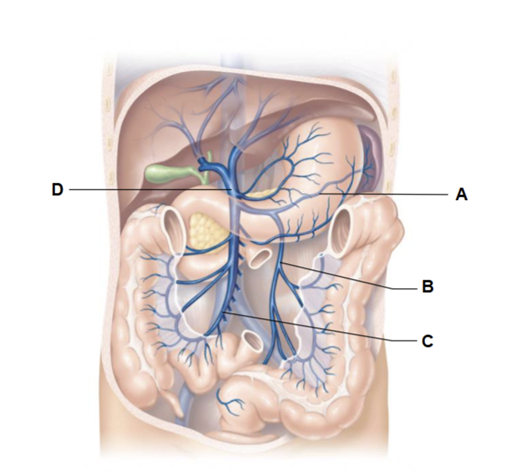
Label A
inferior vena cava

Label B
celiac trunk

Label C
common hepatic artery

Label D
abdominal aorta

Label F
superior mesenteric artery
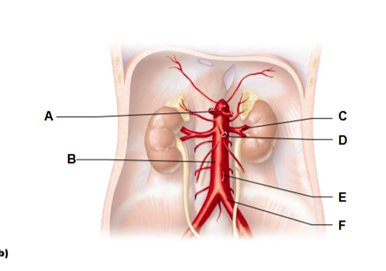
Label A
celiac trunk

Label B
abdominal aorta

Label C
renal artery

Label D
superior mesenteric artery

Label E
inferior mesenteric artery

Label F
common iliac artery
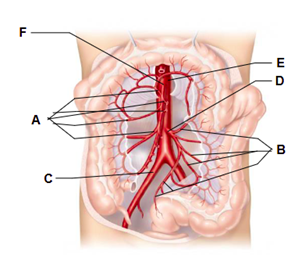
Label A
branches of the superior mesenteric artery

Label B
branches of the inferior mesenteric artery

Label C
right common iliac artery

Label D
inferior mesenteric artery

Label E
abdominal aorta

Label F
superior mesenteric artery
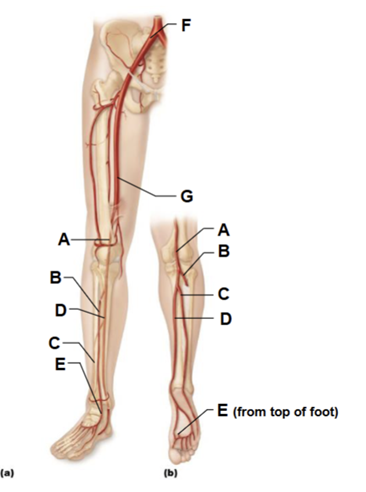
Label A
popliteal artery

Label B
anterior tibial artery

Label C
fibular artery

Label D
posterior tibial artery

Label E
dorsalis pedis artery (from top of foot)

Label F
common iliac artery

Label G
femoral artery
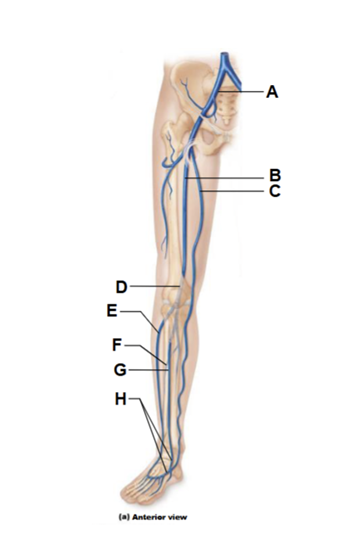
Label A
common iliac vein

Label B
femoral vein

Label C
great saphenous vein (superficial)

Label D
popliteal vein

Label E
small saphenous vein

Label F
fibular vein

Label G
anterior tibial vein

Label H
dorsalis pedis vein
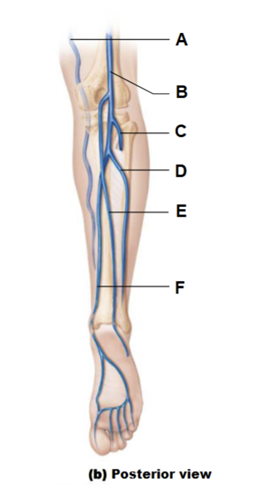
Label A
great saphenous vein

Label B
popliteal vein

Label C
anterior tibial vein

Label D
fibular vein

Label E
small saphenous vein (superficial)

Label F
posterior tibial vein
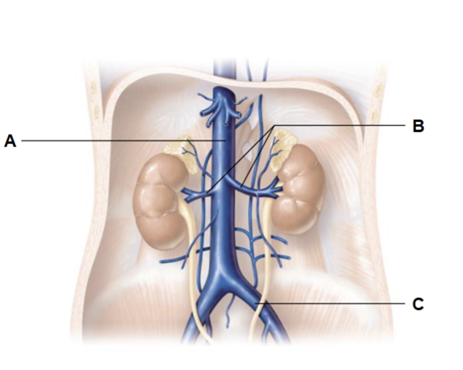
Label A
inferior vena cava

Label B
renal veins

Label C
common iliac vein
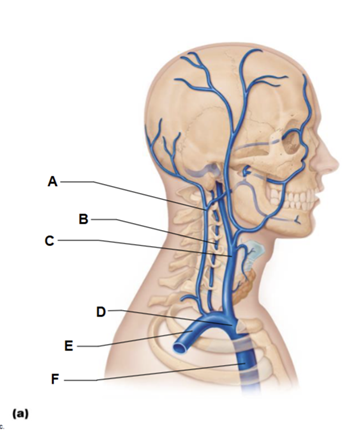
Label A
external jugular vein

Label B
vertebral vein

Label C
internal jugular vein

Label D
brachiocephalic vein

Label E
subclavian vein

Label F
superior vena cava
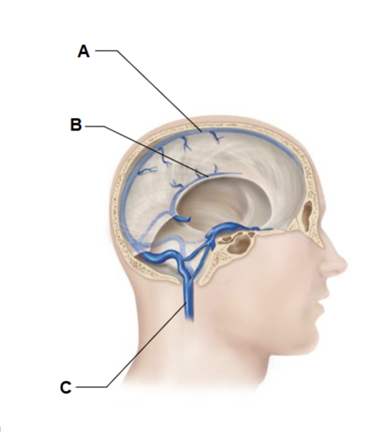
Label A
superior sagittal sinus

Label B
inferior sagittal sinus

Label C
internal jugular vein
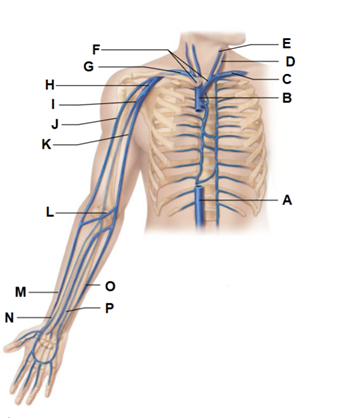
Label A
inferior vena cava

Label B
superior vena cava

Label C
left subclavian vein

Label D
external jugular vein

Label E
Internal jugular vein

Label F
brachiocephalic veins

Label G
right subclavian vein

Label H
axillary vein

Label I
brachial vein

Label J
cephalic vein

Label K
basilic vein

Label L
median cubital vein

Label M
cephalic vein

Label N
radial vein

Label O
basilic vein

Label P
ulnar vein
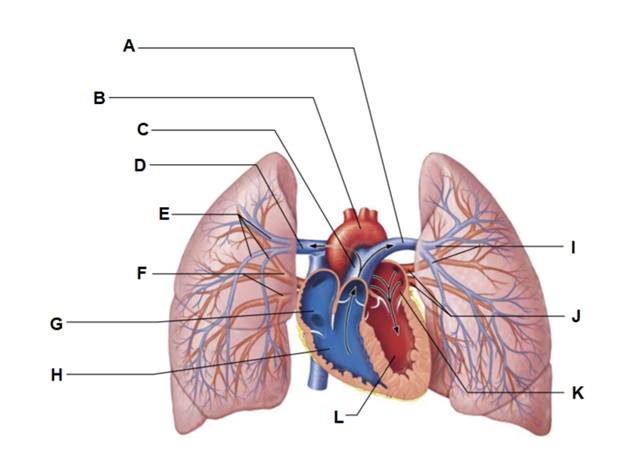
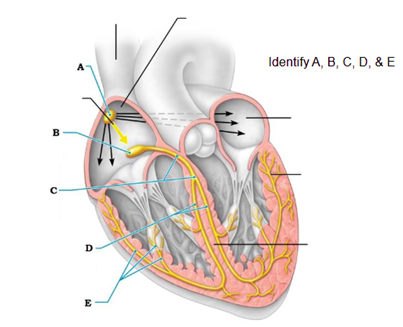
Label A
left pulmonary artery

Label B
aortic arch

Label C
pulmonary trunk

Label D
right pulmonary artery

Label E
three lobar arteries to right lung

Label F
right pulmonary veins

Label G
right atrium

Label H
right ventricle

Label I
two lobar arteries to left lung

Label J
left pulmonary veins

Label K
left atrium

Label L
left ventricle

Label A
aortic arch

Label B
Superior vena cava

Label C
ductus arteriosus

Label D
ligamentum arteriosum

Label E
pulmonary artery

Label F
pulmonary veins

Label G
heart

Label H
lung

Label I
foramen ovale

Label J
fossa ovalis

Label K
liver

Labal L
ductus venosus

Label M
ligamentum venosum

Label N
hepatic portal vein

Label O
umbilical vein

Label P
ligamentum teres

Label Q
inferior vena cava

Label R
umbilicus

Label S
abdominal aorta

Label T
common iliac artery

Label U
umbilical arteries

Lable V
medial umbilical ligaments

Label W
urinary bladder

Label X
umbilical cord

Label Y
placenta
Label A
splenic vein

Label B
inferior mesenteric vein

Label C
superior mesenteric vein

Label D
hepatic portal vein
List the elements of the intrinsic conduction system in
order,
starting from the beginning
SA node → AV node → AV bundle (bundle of His) → left and right bundle
branches
→ subendocardial conducting network (Purkinje fibers)
Label A
the sinoatrial (SA) node pacemaker generates impulses

Label B
the impulses pause (0.1 sec) at the atrioventricular (AV) node

Label C
the atrioventricular (AV) bundle conducts the impulses to the bundle branches

Label D
the bundle branches conduct the impulses through the interventricular septum

Label E
the subendocardial conducting network depolarizes the contractile cells of both ventricles
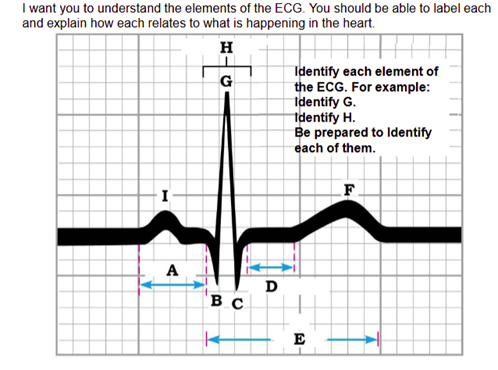
Label A
P-R interval

Label B
Q wave

Label C
S wave

Label D
S-T segment

Label E
Q-T interval

Label F
T wave

Label G
R wave

Label H
QRS complex

Label I
P wave
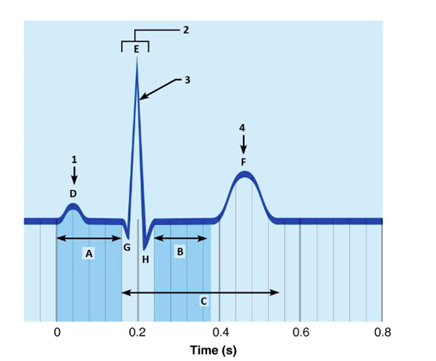
Label A
P-R interval

Label B
S-T segment

Label C
Q-T interval

Label D
P wave

Label E
R wave

Label F
T wave

Label G
Q wave

Label H
S wave

What is happening at 1
atrial depolarization

What is 2
QRS complex

What is happening at 3
ventricular depolarization

What is happening at 4
ventricular repolarization
immediately before the P wave:
The heart is in diastole
during the P wave:
Depolarization of the atria
immediately after the P wave:
Contraction of the atria.
during the QRS complex:
Depolarization of the ventricles and
repolarization of the atria.
immediately after the QRS complex (S-T segment):
Contraction of the ventricles
during the T wave:
Repolarization of the ventricles.
Enlarged R wave
enlarged ventricles
prolonged P-R interval
First-degree heart block
Prolonged Q-T interval
increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
S-T segment elevated from baseline
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
WHAT IS 1
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
lub-dup
WHAT IS 2
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
atrioventricular
WHAT IS 3
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
aortic and pulmonary (semilunar)
WHAT IS 4
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
ventricles
WHAT IS 5
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
atria
WHAT IS 6
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
atria
WHAT IS 7
Complete the following statements.
The two monosyllables
describing the
heart sounds are 1 . The first heart sound
is
a result of closure of the 2 valves,
whereas the second is a
result of closure
of the 3 valves. The heart chambers
that
have just been filled when you hear the
first heart
sound are the 4 , and the
chambers that have just emptied are
the
5 . Immediately after the second heart
sound, both the 6
and 7 are filling
with blood
ventricles
Define pulse
Pressure surges in an artery occurring during each
contraction
and relaxation of the left ventricle.
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points
listed.
at the wrist:
radial
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed. on the dorsum of the foot:
dorsalis pedis
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed. in front of the ear:
temporal
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed. at the side of the neck:
carotid
When you were palpating the various pulse or pressure points, which
appeared to
have the greatest amplitude or tension?
_______________ Why do you think this
was so?
carotid artery, The carotid arteries are the major arteries that deliver blood to the brain and they are closest to the heart.
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is
hemorrhaging badly.
What pressure point would you compress to
help stop bleeding from each of the
following areas THE THIGH
femoral artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is
hemorrhaging badly.
What pressure point would you compress to
help stop bleeding from each of the
following areas THE CALF
popliteal artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is
hemorrhaging badly.
What pressure point would you compress to
help stop bleeding from each of the
following areas THE FOREARM
brachial artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is
hemorrhaging badly.
What pressure point would you compress to
help stop bleeding from each of the
following areas THE THUMB
radial artery
How could you tell by simple observation whether bleeding is arterial or venous?
If it spurts, it is arterial. It will flow evenly if it is venous blood
Define blood pressure.
Pressure exerted by blood against the walls of the blood
vessels.
Identify the phase of the cardiac cycle to which each of the following applies: systolic pressure
systole (ventricular contraction)
Identify the phase of the cardiac cycle to which each of the following applies: diastolic pressure
diastole (relaxation)
What are the sounds of Korotkoff?
Sounds that can be auscultated over a partially
occluded artery
What causes the systolic sound?
Sound of turbulent blood flow as it first begins to
move through
the constricted artery
What causes the disappearance of the sound?
Blood is flowing freely; the artery is no longer constricted
Define pulse pressure.
Why is this measurement important?
Systolic pressure minus diastolic pressure
It indicates the actual working pressure (actual amount of blood forced out of the heart during systole)
Explain why pulse pressure is different from pulse rate.
Pulse pressure is what generates the pulse felt calculated as the systolic pressure minus the diastolic pressure; pulse rate is the number of pulsations per minute
How do venous pressures compare to arterial pressures? Why?
Venous pressures are lower.
Veins are far removed from the pumping action of the heart
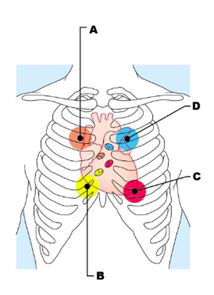
Label A
aortic valve sounds are heard in 2nd intercostal space at right sternal margin

Label B
tricuspid valve sounds are heard in right sternal margin of 5th intercostal space variations include over sternum or over left sternal margin in 5th intercostal space

Label C
mitral valve sounds are heard over heart apex, in 5th intercostal space in line with middle of clavicle

Label D
pulmonary valve sounds are heard in 2nd intercostal space at left sternal margin
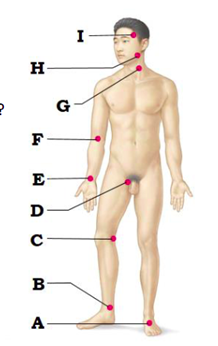
Label A
dorsalis pedis artery

Label B
posterior tibial artery

Label C
popliteal artery

Label D
femoral artery

Label E
radial artery

Label F
brachial artery

Label G
common carotid artery

Label H
facial artery

Label I
superficial temporal artery