Principles of Eco (Lec 5)
Large organisms heat and cool less quickly than
smaller organisms
Heat content is a function of
Heat exchange is a function of
volume
surface area
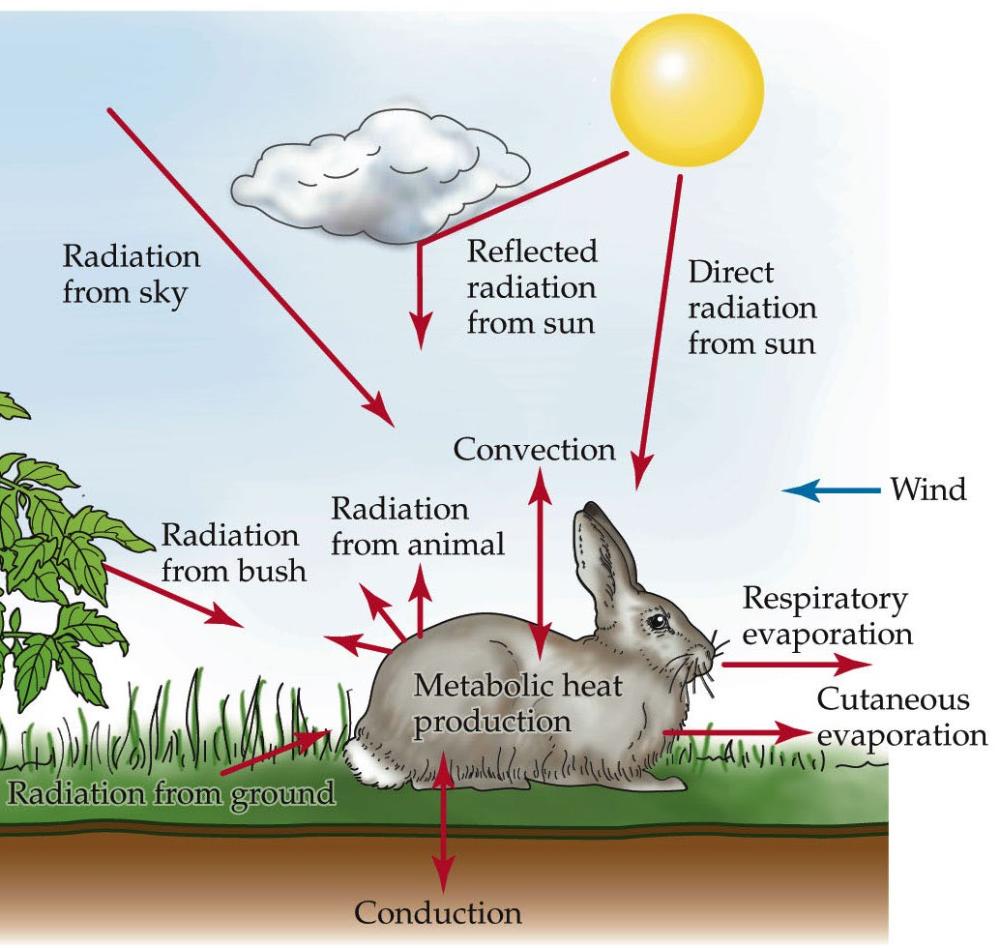
Temp. of organisms is determined by exchanges of
thermal energy(heat) with the external environment
*heat produced by metabolims
Heat Balance Equation: Generalized Equation
H= SR + IRin - IRout +/- Hconv +/- Hcond - Hevap + Hmet
Plant Balance Equation:
H= SR + IRin - IRout +/- Hconv +/- Hcond - Hevap
Organisms influence their temp. by modifying gains and losses via
1. Acute responses occurs within individual plants
2. Phenotypic acclimatization within individual plants
3. Evolutionary adaptation occurs across generations
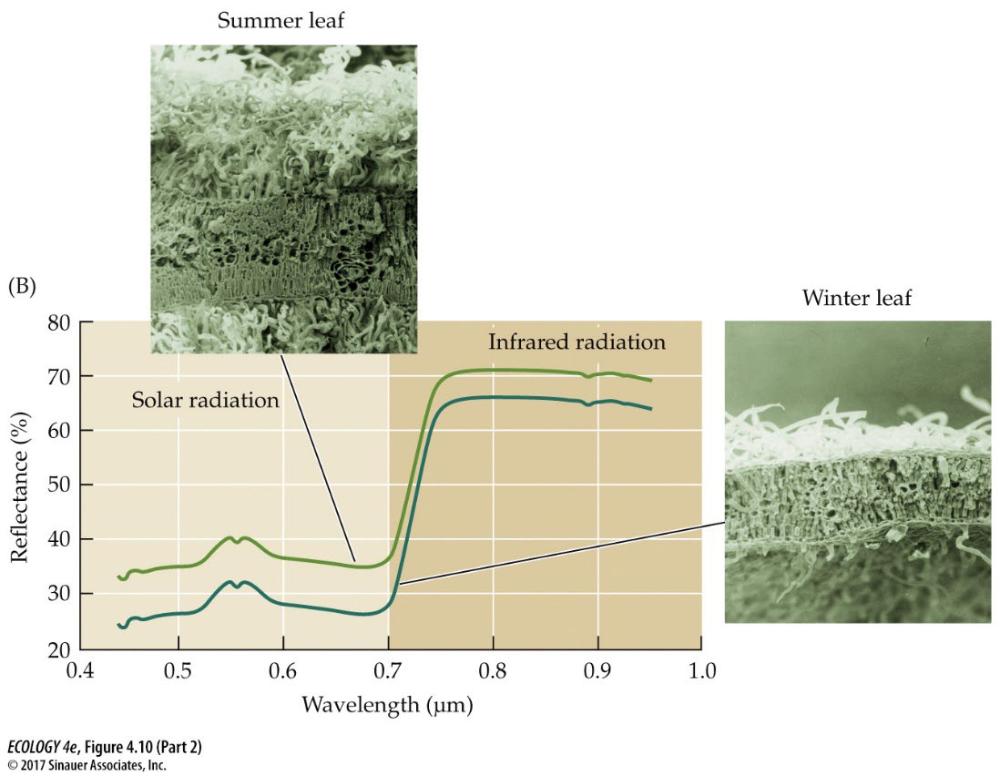
Plants can alter
- evapotranspirational water loss
- leaf surface reflective properties
- leaf orientation to the sun
- leaf surface roughness
Thermal Adaptation
Thermal Acclimatization
Plants used: Brittlebush
Endothermy
*sources of heat
organism to maintain a stable body temperature through metabolic processes.
* predominant source of heat
Ectothermy
*sources of heat
regulate their body temperature using external sources, such as sunlight or ambient temperature
* outside env is their heat
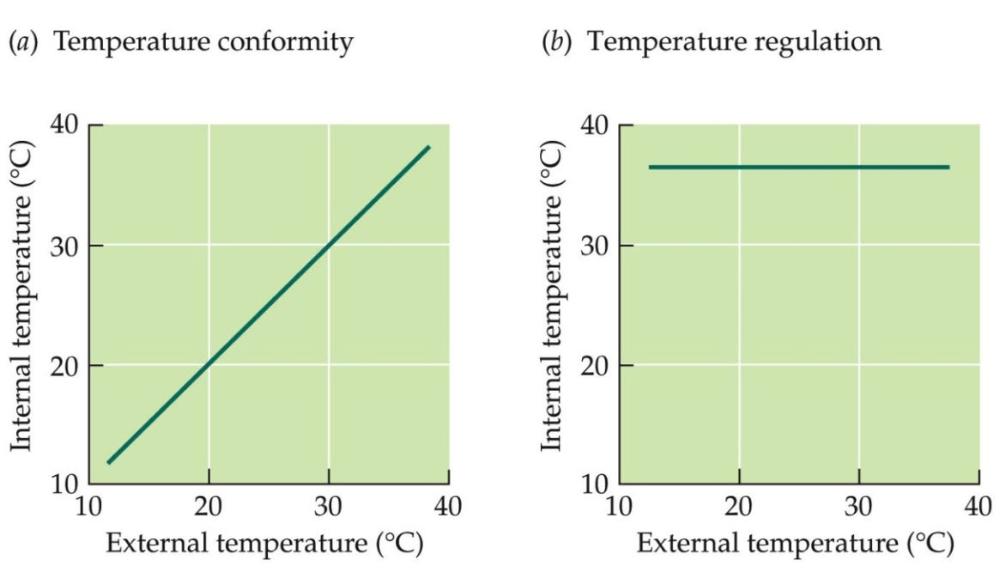
Homeothermy
*body temp
maintain a stable internal body temperature, even when the external temperature varies
to sustain: heat must be lost in the same rate it is gained
Poikilothermy
*body temp
organism that cannot regulate its body temperature except by behavioral means such as basking or burrowing.
Most Fish: Generalized Equation
H= - Hconv +/- Hcond
Terrestrial Ectotherms
H= SR + IRin - IRout +/- Hconv +/- Hcond - Hevap
Hmet dropped due to not producing heat fast enough
Terrestrial Endotherms
H= SR + IRin - IRout +/- Hconv +/- Hcond - Hevap + Hmet
Endotherms can maintain high and constant body temps but
Endothermic homeothermy has a high energetic price
Temp regulation and thermal ecology are inseparable from energy metabolism
Ectotherms can not use what to thermoregulate?
metabolism
Endo and ectothermy are not
strict alternatives
Skipjack tuna use muscle activity and heat exchange to
maintain a body temp 14 C
Terrestrial ectotherms can move between heat sources and heat sinks using
Ex. Lizards
behavioral thermoregulation
Insects have a high concentration of glycerol, a chemical that
*similar to antifreeze proteins that fishes have as well
lowers the freezing point of body fluids
Wood frogs (Rana Sylvatica) and some other species of frogs tolerate
tolerate freezing
Metabolic rate depends on
external temp & S/V ratio
Heat loss is faster in the
cold
* endothermy is non-sustainable due to this and may enter torpor under cold conditions
Benefits of enedothermy
_ independence from env temp
- range expansion to high latitude and alitude
- high capacity to sustain physical activity
Characteristics of Endothermy
- Thermoneutral zone
_ Low critical temp
Thermoneutral zone
a constant basal metabolic rate can be maintained
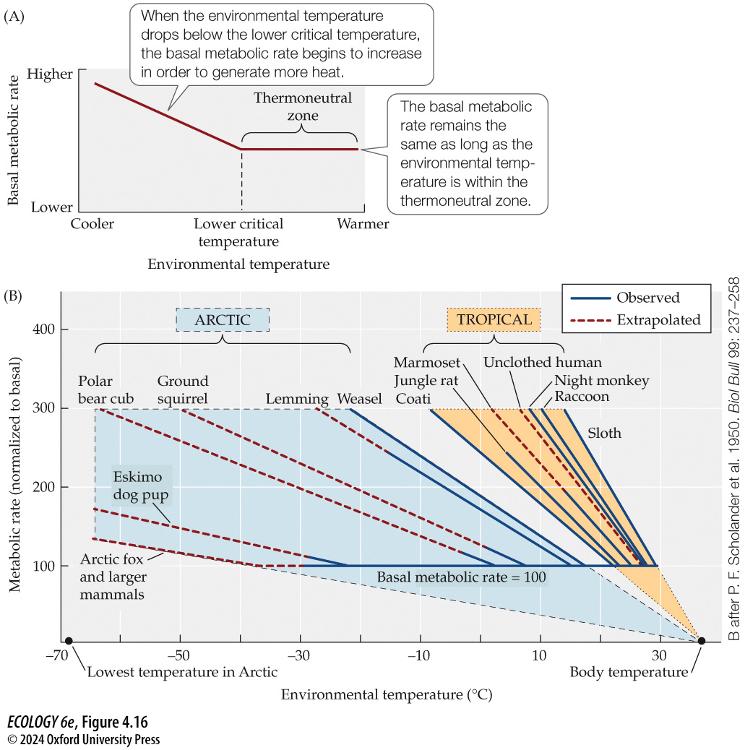
Lower critical temp
* lower in Arctic mammals than tropical mammals
heat loss > metabolic production; body temp drops and heat increases
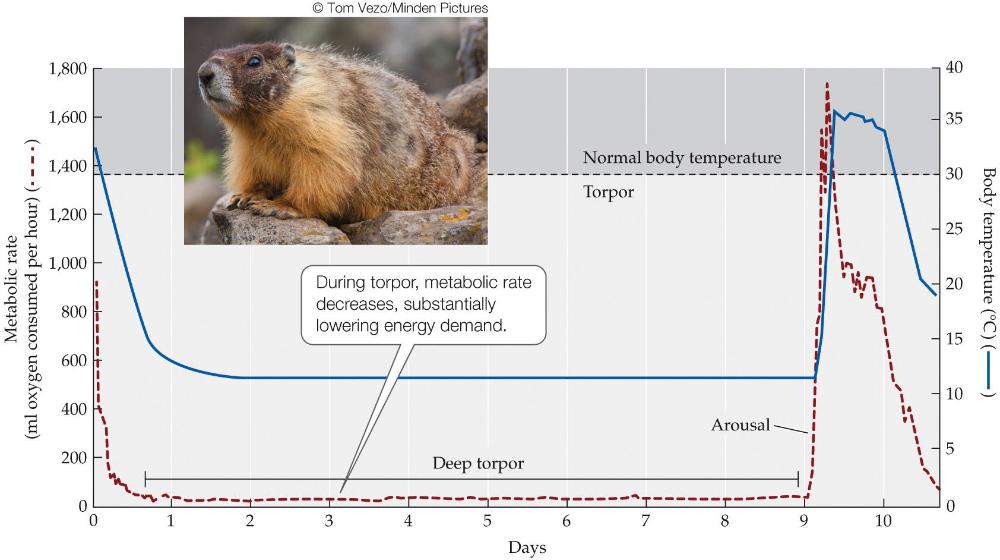
Torpor
* long periods are possible for animals that can store enough energy
* also related to hiberation
state of physical or mental inactivity; lethargy.
Small endothemrs undego daily torpor to
survive cold nights