ch 10 plus some of ch 9
The processes are vital for all life forms
transport
Cells must be able to _____ nutrients and _____waste
import, export
All cells maintain__________of various metabolites across the plasma membrane and other intracellular membranes
concentration gradients
Many transport processes involve the movement of
polar or ions across the hydrophobic interior of a membrane
Transport proteins are
integral membrane proteins
Uniport moves
1 solute downward
Symport moves
2 solutes downward
Antiport moves 2 solutes
in opposite directions (one goes up and other goes down)
What are the four modes of membrane transport?
1. Passive diffusion (-ΔG) (favored)
2. Facilitated diffusion (-ΔG) (favored)
3. Active transport (+ΔG) (opposed)
4. Secondary active transport (+ΔG) (opposed)
Passive diffusion doesn't require proteins and means the transportation of species
moving down its concentration gradient from high to low concentrations
Passive diffusion of uncharged species move across the membrane depending on
the concentration on the two sides
Passive diffusion of a charged species also depends on the concentration and
the charge of the particle
allow transport of charged molecules such as protons across the bilayer down its concentration
Hydrophobic ionophores
The proteins "facilitate" transport, increasing the rate of transport
facilitated diffusion
Two important distinguishing features of facilitated diffusion
1. solute flows only in the favored direction
2. Transport displays saturation kinetics: there is an upper limit to how solutes can influence the rate of transport
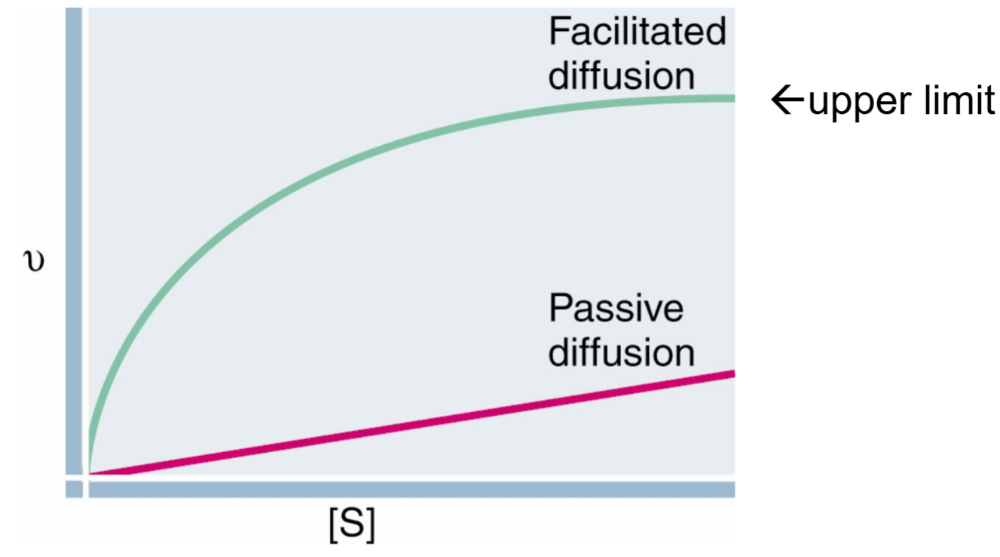
Facilitated diffusion displays saturation
Single channels can be formed from
dimers, trimers, tetramers, or pentamers of protein subunits
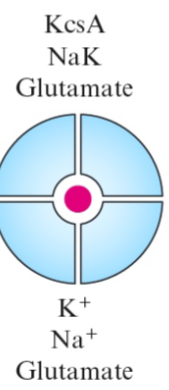
Multimeric assemblies in which each subunit
has its own pore as known
Potassium channels combine
high selectivity with high conduction rates
Active transport is used to transport
against the thermodynamic potential of solutes
Active transport directly uses
ATP (hydrolysis)
Another way to refer to the sodium-potassium pump
Na,K-ATPase
Na,K-ATP maintains intracellular Na+ ____ and K+______ and it is crucial for organs ____ and_____
low, high
brain, neural tissue
Drives Na+ out and K+ in
ATP hydrolysis
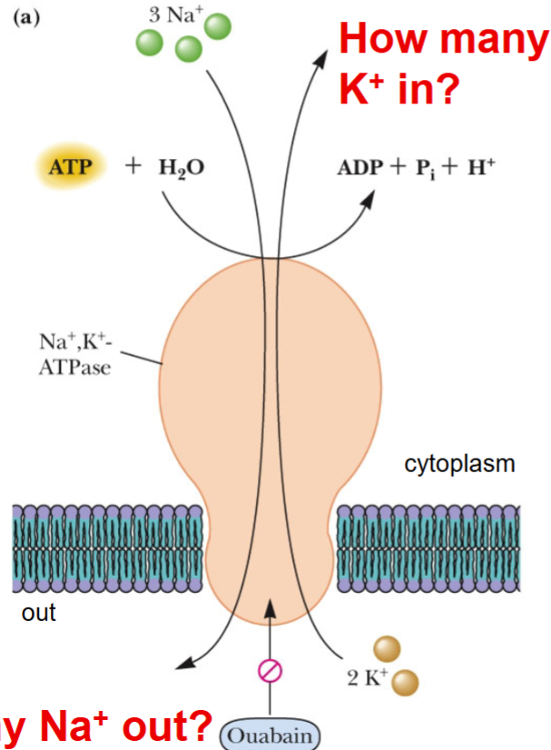
how much ATP is used?
How many K+ goes from high to low?
How many Na+ goes from low to high concentration?
- 1 ATP
- 2 K+
- 3 Na+
Inhibit by binding to outside part of the transporter
cardiac glycosides(ouabain)
Secondary active transport is not directly driven by
ATP
In secondary active transport, the gradient of H+, Na+ and other cations and anions previously established by ATPase
can be used for secondary active transport against their concentration gradient
Many of these are symports with the ion and the transported
amino acids or sugar moving in the same direction
AcrB is an example of
secondary transport system
AcrB is a major multi-drug resistance transporter in
E.coli
As protons flow spontaneously inward through AcrB in the E.coli inner membrane,
drug molecules are driven outward
Both lipids and proteins of the membrane exhibit
lateral and transverse asymmetry
Proteins can associate and cluster in the plane of the membrane -They are not uniformly distributed
Lateral asymmetry of proteins
Lipids can cluster in the plane of the membrane-they are not uniformly distributed
lateral asymmetry of lipds
Mark Bretscher shows that N-terminus of glycophorin is extracellular whereas C-terminus is intracellular
Transverse asymmetry of proteins
In most cell membranes, including those of intracellular organelles, the composition of the outer monolayer is quite different from that of the inner monolayer
transverse asymmetry of lipids
Dynamic means
motion
Lipids and proteins undergo lots of movements in the membrane and these motions
support a variety of cell functions
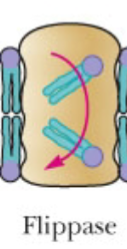
Move PS from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet
ATP dependent flipase (flip in)
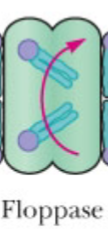
Moves lipids including cholesterol, PC, and sphingomyelin from the inner leaflet to the outer leaflet of the membrane
ATP dependent flopase (flop out)
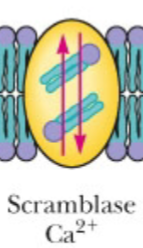
Randomize lipids across the membrane and thereby degrade membrane lipid asymmetry
Scramblases ( Ca^2+ activated but ATP dependent)
At low tempertures , bilayer lipids are highly ordered, forming a gel, with acyl chains extended,nearly
perpendicular to the membrane plane
So, solid ordered state
the lipid chains are tightly packed and undergo relatively little motion
Characteristics of So, solid ordered state,
1. lipid chains are in their fully extended conformation
2. surface area per liquid is minimal
3. bilayer thickness is maximal
At higher temperatures, acyl chains undergo much more motion and acyl chain C-C bonds result in bending of the acyl chains
Ld, liquid- disordered state
Characteristics of Ld, liquid- disordered state
1. surface area per lipid increases
2. lipid chains are more likely to be bent at any one time
3. bilayer thickness decrease by 10-15%
Transition from gel phase to liquid crystalline is a true
phase transition
The temperature at which this occurs is the transition temperature
Melting temp. Tm
If Tm is increasing,
the chain length would increase
-lipids can influence curvature
- integral membrane proteins with conical shapes can induce curvature
- scaffolding proteins can influence membrane shape in many ways
Membrane remodeling and curvature
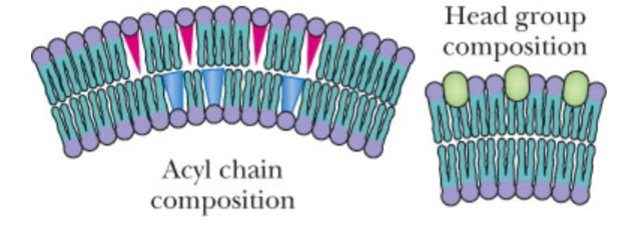
What type of bending is this?
lipid composition
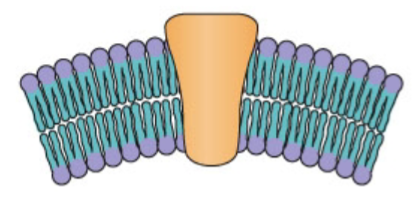
What type of bending is this?
membrane proteins
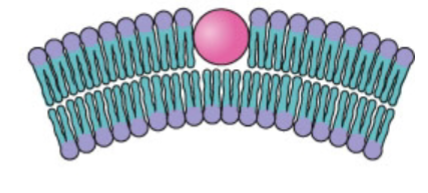
What type of bending is this?
amphipathic helix insertion
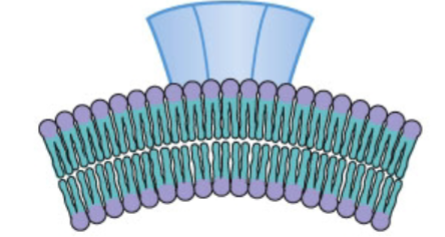
What type of bending is this?
scaffolding
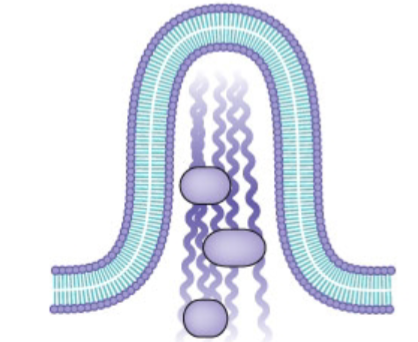
What type of bending is this?
cytoskeleton
Membranes fusion requires proteins that _____opposite membranes and ____ them together
pierce, pull