Anatomy Block III- Foot
what is the plantar
part of foot contacting the ground
what is the dorsum
dorsal (superior) surface of the foot
what is the heel
sole of foot under calcaneous
what is the ball of the foot
some of foot under medial two metatarsals
what is the last part of the foot contacting the ground when walking
ball of the foot
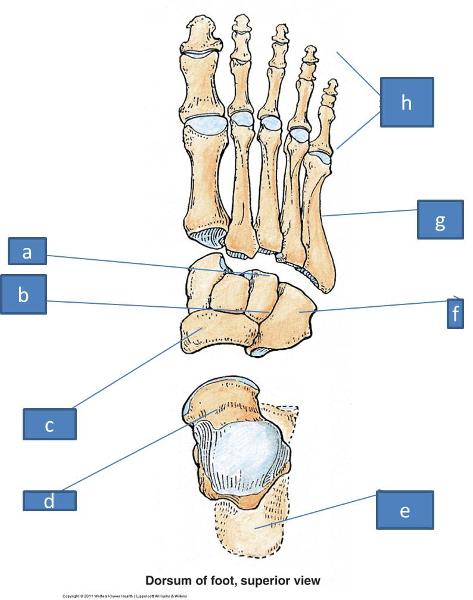
a to b. medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bones
c. navicular bone
d. talus bone
e. calcaneus bone
f. cuboid bone
g. metatarsals
h. proximal, intermediate, distal phalanges
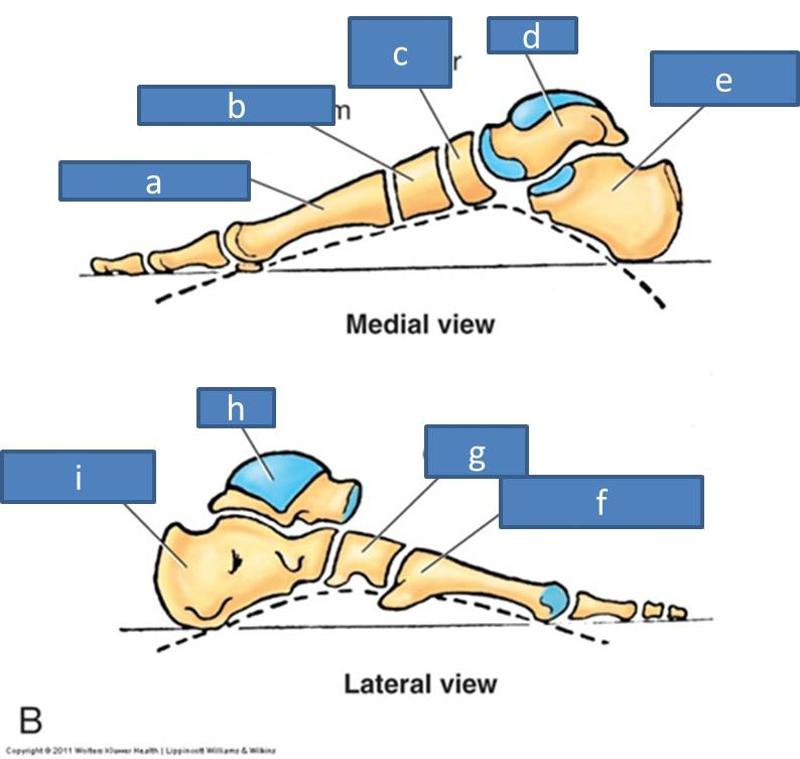
a. metatarsals
b. medial cuneiform
c. navicular
d. talus
e. calcaneus
f. metatarsal
g. cuboid
h. talus
calcaneus
what are the orders of the toe numbers
1st toe big, great toe
toes 2-5, fifth toe is pinky toe
what are the general categories of bones of the foot
tarsals
metatarsals
phalanges
sesamoid bones
what are the tarsal bones
calcaneous
talus
navicular
cuboid
cuneiform (medial, intermediate, lateral)
what bones make up the hindfoot and midfoot
tarsals
what bones make up the ankle joints
tarsals
what bone forms large bony protrusion posteriorly
calcaneous
what does the calcaneal tendon attach to (tarsal bone)
calcaneous
what is the domed superior tarsal bone
talus
what bone wedges between tibia and fibula
talus
what tarsal makes up the large portion of the ankle joint
talus
what bone articulates with the talus
navicular
what tarsal is a crescent shaped bone
navicular
what bone is proximal to the cuneiform
navicular
what is the most lateral tarsal
cuboid
where is the cuneiform relative to the navicular
distal to the navicular
what are the different cuneiform bones
medial (first)
intermediate (second)
lateral (third)
how many metatarsals are there
five
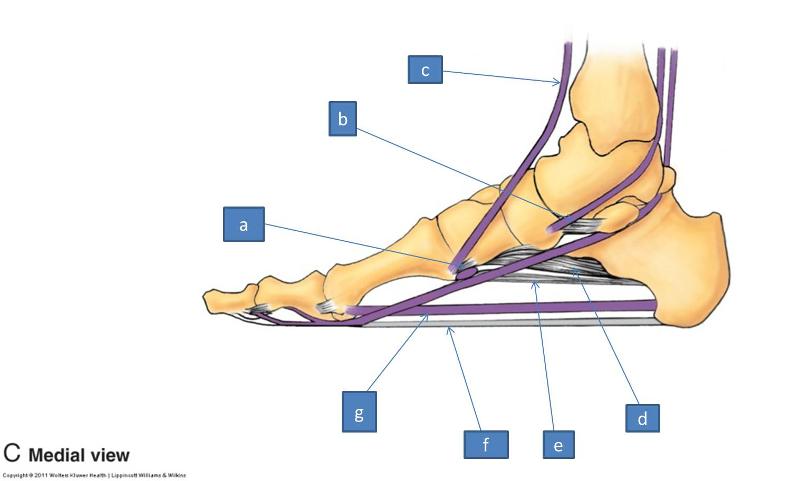
a. fibularis longus
b. tibialis posterior
- plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is ligament behind it
c. tibialis anterior
d. short plantar ligament
e. long plantar ligament
f. plantar aponeurosis
g. intrinsic plantar muscles
- flexor hallucis longus is muscle that wraps around ankle and goes to toe
what are the long boes that make up the arch/body of the foot
metatarsals
how many phalanges are tehre
14
two off big toe, three off each of the rest
what are the phalanges
proximal and distal of big toe
proximal intermediate distal off the rest of the toes 2-5
what are the two odd bones in the muscle tendon at the head of the first metatarsal on plantar surface
sesamoid bones
what bones are buried in tendons of flexor hallucis brevis tendons
sesamoid bones
what is the purpose of the sesamoid bones
general frictional forces and change up the angle that flexor hallucis brevis inserts on big toe, giving it more of a mechanical advantage
what is important about the foot's general role
major supportive structure that bears weight whenever we stand up or use locomotion
what is the support function of the foot based on
three arches
what do the arches of the foot do?
act as shock absorbers
help support/distribute body weight
protect BVs
propel body when moving
why do people with flat feet have problems
nerves and arteries bothered and pinched
what are the arches of the foot
medial longitudinal arch
lateral longitudinal arch
transverse arch
where is the medial longitudinal arch
runs on medial longitudinal border of the foot
which arch of the foot does not make a footprint
medial longitudinal arch
where is the lateral longitudinal arch
on lateral longitudinal border of the foot, not as high as medial longitudinal arch so it makes a footprint
where is the transverse arch of the foot
arrangement of the metatarsal bones themselves
how do the bones of the arch provide passive support
due to how they are shaped and interlock structurally
what are the layers of fibrous tissue that provide passive support to the arches of the feet
plantar aponeurosis
long plantar ligament
short plantar ligament
plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
what is the function of the plantar aponeurosis
protects underlying tendons, muscles, nerves, BVs
has arch support function
what is the plantar aponeurosis
thickened portion of plantar fascia
functions to provide firm attachment for skin and thus improve grip
where does plantar aponeurosis run
calcaneus to heads of metatarsals and base of proximal phalanx
where does the long plantar ligament run
from calcaneous to metatarsals
what arches does the long plantar ligament support
both longitudinal arches
what layer of the fibrous tissue runs deep to the long plantar ligament
short plantar ligament
what layer of fibrous tissue runs from the calcaneous to cuboid tarsal bones
short plantar ligaments
what is plantar fasciitis
inflammation of plantar fascia that makes weight bearing difficult
where does pain in plantar fasciitis usually originate
close to calcaneus
what can sometimes develop in plantar fasciitis
heel spur
how can plantar fasciitis be helped
exercise and stretching of gastroc and soleus
severe cases: corticosteroids but this can wear it away too so be careful
what layer of fibrous tissue provides the main support to the medial longitudinal arch
plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
which ligament is considered the spring ligament
plantar calcaneonavicular
which layer of fibrous tissue are stretched out over the course of the day
what provides dynamic support to the arch
intrinsice muscles
active contractions of muscles
which muscles actively contract to support the arch
tibialis anterior
fibularis longus
what is the function of the tibialis anterior relative to the dynamic support of the arch
supports medial longitudinal arch
what is the function of the fibularis longus relative to dynamic support of the arch
cuts across transverse arch and wraps under plantar aspect of foot and supports that transverse arch
what are two types of foot shapes
pes planus
pes cavus
what is pes planus
flat feet
is pes planus common?
yes, one reason that people are exempt from army
what are two types of pes planus
supple
rigid
what is supple pes planus like
when foot not weight bearing, their arch looks normal; when weight bearing it flattens out as passive and active supports give way
what is rigid pes planus due to
bone alignment fitting a certain way
what is pes cavus and what is it from
abnormally high arch
due to tight dynamic support
where do problems in the feet often manifest themselves
pain in other joints/muscles that usually do not bear stress
what do the muscles on the dorsum of the foot do
extend the toes
what are the muscles of the dorsum of the foot innervated by
deep fibular nerve
what artery supplies the dorsum of the foot
dorsalis pedis artery
what eventually becomes the dorsalis pedis artery
femoral to popliteal to anterior tibial to dorsalis pedis artery
what is the action of the extensor hallucis brevis
big toe extensor
what is the action of the extensor digitorum brevis
extensor of toes 2-5
what is an important division line on the plantar side of the foot
central axis of the foot, bisects 2nd toe and goes to calcaneus
what are two terminal branches of the tibial nerve
medial and lateral plantar nerve
what nerves supply the plantar side of the food
medial and lateral plantar nerves
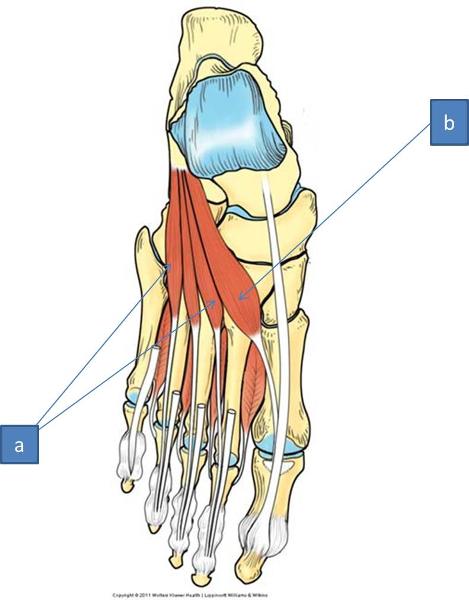
a. extensor digitorum brevis
b. extensor hallucis brevis
what is in the first (superficial) layer of muscles of the plantar side of the foot made of
two abductors and a flexor
what is included in the first layer of muscles on the plantar side of the foot
abductor hallucis
flexor digitorum brevis
abductor digiti minimi
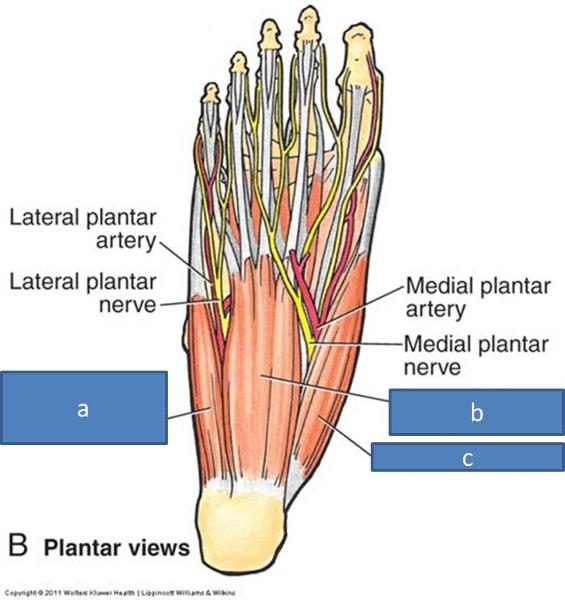
a. abductor digiti minimi
b. flexor digitorum brevis
c. abductor hallucis
what innervates the abductor hallucis
medial plantar nerve
what innnervates the flexor digitorum brevis
medial plantar nerve
what innervates the abductor digiti minimi
lateral plantar nerves
what is between the first and second layer of plantar muscles
plantar nerves and plantar BVs
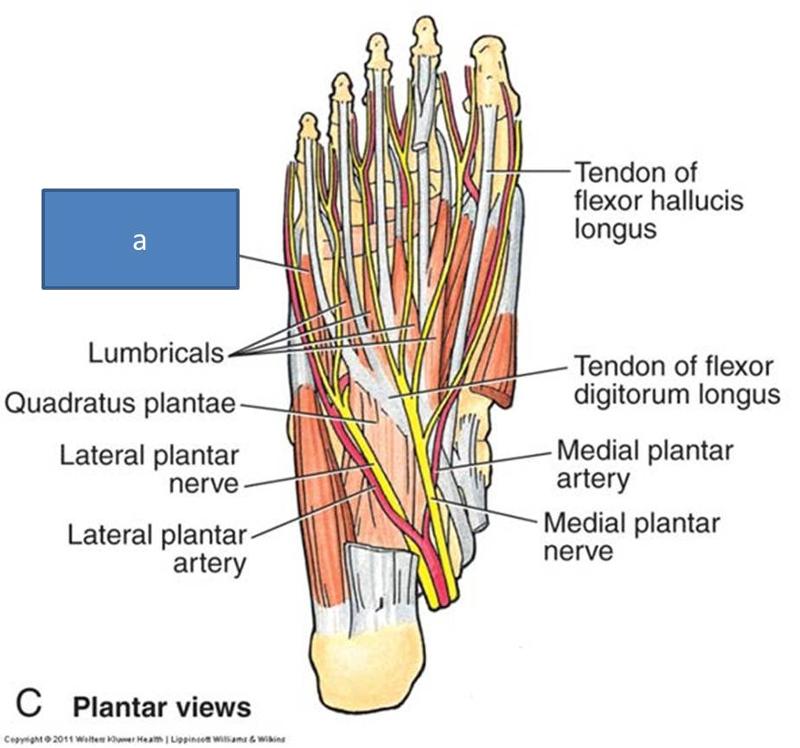
what is within the second layer of plantar side foot muscles
two muscles, two tendons
what muscles are within the second layer of plantar side foot muscles
quadratus plantae
lumbricals
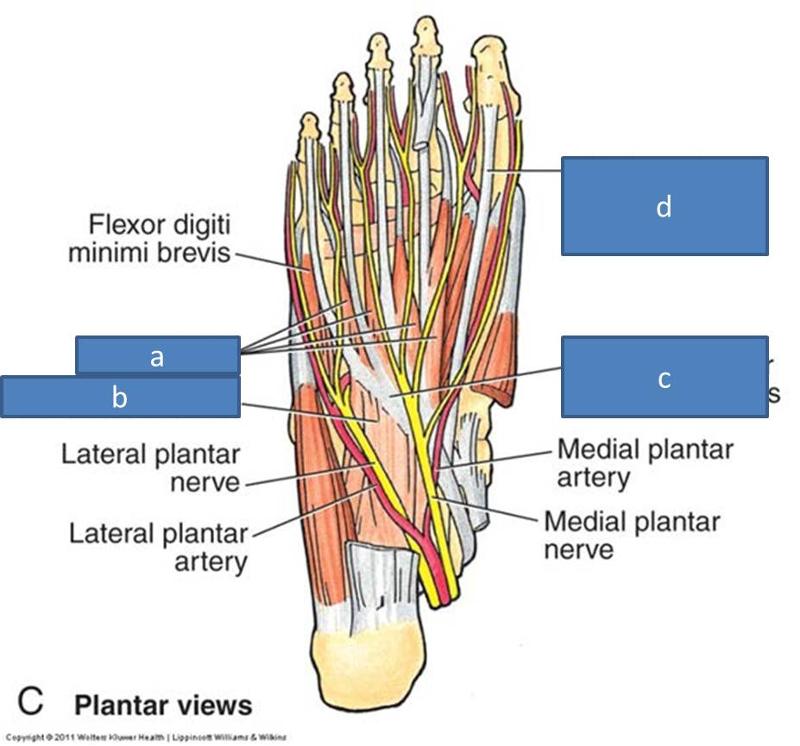
a. lumbricals
b. quadratus plantae
c. tendon of flexor digitorum longus
d. tendon of flexor hallucis longus
flexor digiti minimi (3rd layer, looks out of place)
what tendons are within the second layer of plantar side foot muscles
tendon of flexor hallucis longus
tendon for flexor digitorum longus
what innervates the quadratus plantae
LPN
what innervates the first lumbrical
MPN
what innervates the 2-5 lumbricals
LPN
what do the lumbricals do
flex proximal phalanges and extend intermediate and distal phalanges
where does the quadratus plantae run
from heel to tendons of flexor hallucis longus
what is interesting abuot quadratus plantae
only in lower limb because quadratus plantae pulls on toes so that they don't curl at an angle but straightforward
what do the lumbricals attach to
flexor digitorum tendons, run to digits
what do lumbricals mean
wormlike
where are the tendon of flexor hallucis longus and tendon of flexor digitorum longus from
from leg
what is in the third layer of plantar muscles of the foot
one adductor, two flexors
what are teh msucles in the third layer of plantar muscles in the foot
flexor hallucis brevis
adductor hallucis
flexor digiti minimi brevis
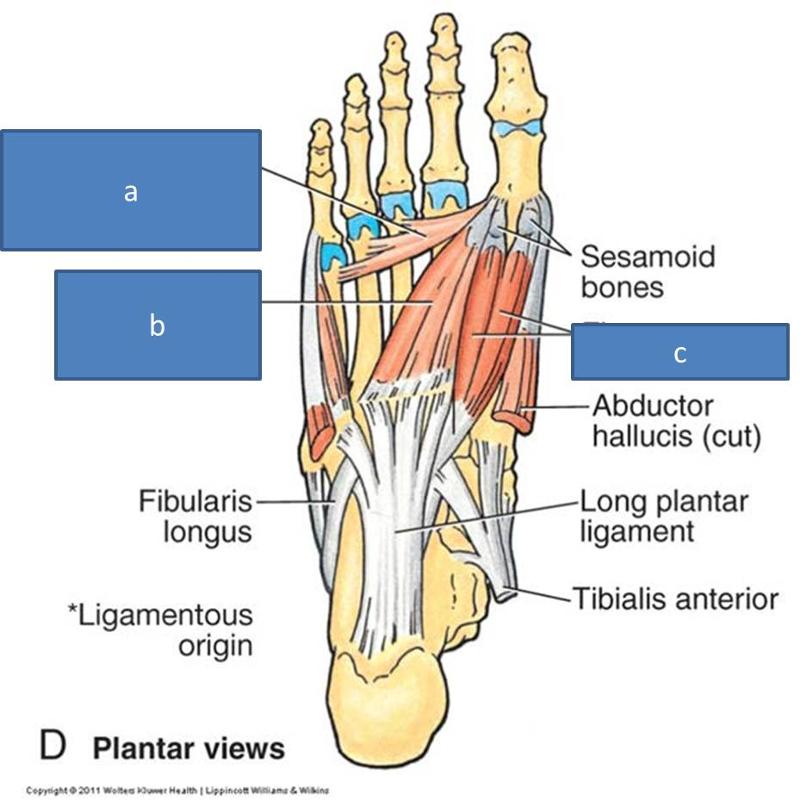
a. transverse head of adductor hallucis
b. oblique head of adductor hallucis
c. flexor hallucis brevis
what is the role of the flexor hallucis brevis
flexes proximal phalanx of first toe
what is the action of the adductor hallucis
active during pushoff phase of gait
pulls toes 2-5 and holds transverse arch stable
where does the flexor hallucis brevis insert
two sesamoid bones
what innervates the flexor hallucis brevis
MPN
what is interesting about the adductor hallucis
has two muscle heads, looks like a 7
what innervates the adductor hallucis
LPN
what innervates the flexor digiti minimi brevis
LPN
what is included in the fourth layer of the plantar side of the foot
many short muscles and two tendons
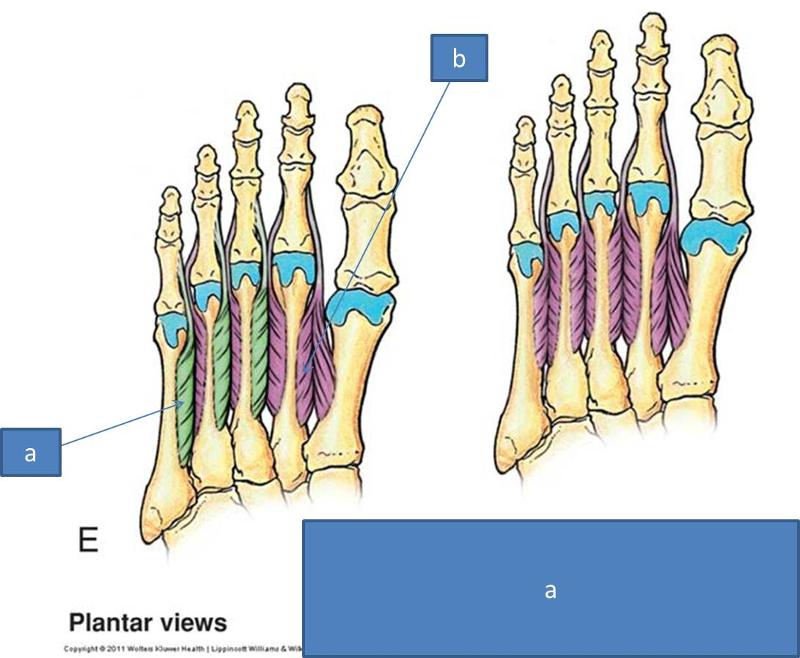
a. plantar interossei
b. dorsal interossei
what is the action of the plantar interossei
adduction of toes
how many plantar interossei are there
3
are the plantar interossei unipennate or dipennate
unipennate
whta is the actin of the dorsal interossei
abduction of toes
how many dorsal interossei are tehre
4
are dorsal interossei unipennate or dipennate
bipennate
what are the short muscles that run in between the metatarsals
interossei
how many plantar interossei are there
three
how mnay dorsal interossei are there
four
what are the two tendons of fourth layer of the plantar side of the foot
tendon of fibularis longus
tendon of tibialis posterior
what are the muscles that are in the fourth layer of the plantar side of the foot
plantar and dorsal interossei
what artery supplies the dorsum of the foot
dorsalis pedis artery
what areter does the dorsalis pedis artery give off distally
arcuate artery
what does the dorsalis pedis artery come off of
anterior tibial artery
what comes off the arcuate artery
deep plantar artery that passes to plantar aspect of foot and small digital branches
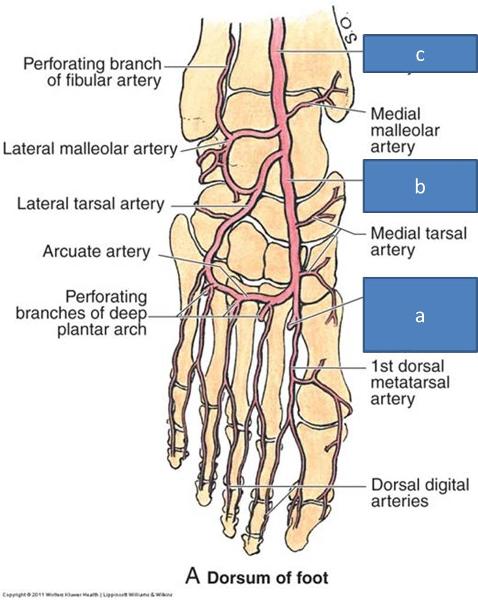
a. deep plantar artery
b. dorsalis pedis artery
c. anterior tibial artery
what is the path of the deep plantar artery
goes between toes 1 and 2
where is the dorsalis pedis artery from
anterior tibial artery
what is the course of the dorsalis pedis artery
sends branch to plantar side of foot, anastamoses with some plantar BVs and terminates between first and second toe
where is the palpable dorsalis pedis pulse
distal to extensor retinaculum and just laeral to tendon for extensor hallucis longus
what is the dorsalis pedis artery checked for
arterial insufficiency
how much of the populatin have a weak or absent dorsalis pedis artery
10%
what is the smaller branch of the posterior tibial artery
medial plantar artery
what does the medial plantar artery supply
medial plantar side of foot
what is the larger branch of the posterior tibial artery
lateral plantar artery
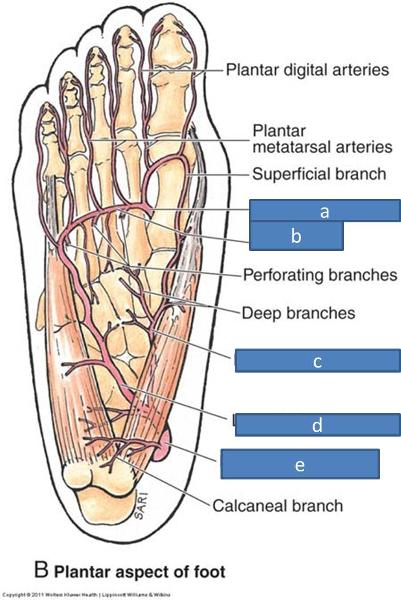
a. deep plantar artery
b. plantar arch
c. medial plantar artery
d. lateral plantar artery
e. posterior tibial artery
what supplies most of the plantar side of the foot
lateral plantar artery
what is the plantar arterial arch a union of
lateral plantar artery and deep plantar artery (from dorsalis pedis)
what gives off the digital arteries
plantar arterial arch
does the cutaneous information of the foot follow the central axis rule
nope
what does the saphenous nerve supply
medial side of dorsum to first metatarsal
what does the superficial fibular nerve supply
dorsum of foot and parts of digits
what does the deep fibular nerve supply
between first and second digits
what does the medial plantar nerve supply
medial plantar side of foot and first 3.5 digits
what does the lateral plantar nerve supply
lateral plantar side of foot and last 1.5 digits
what does the sural nerve supply
very lateral side of foot
what does the tibial nerve supply
skin of heel
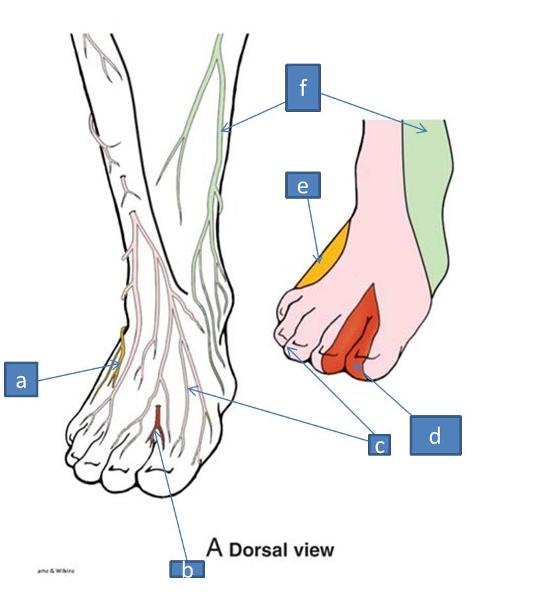
a. sural nerve
b. deep fibular nerve
c. superficial fibular nerve
d. deep fibular nerve
e. sural nerve
f. saphenous nerve
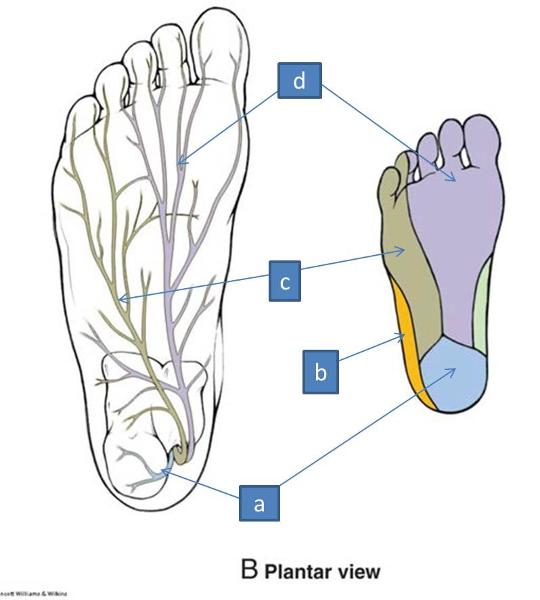
a. tibial nerve
b. sural nerve
c. lateral plantar nerve
d. medial plantar nerve