Anatomy Block III- Popliteal Fossa and Leg
what is the popliteal fossa
junction between thigh and leg, a diamond shaped space in back of the knee

a. semitendinosus
b. semimembranosus
c. medial head of gastrocnemius
d. lateral head of gastrocnemius
e. biceps femoris
where is the popliteal pulse felt from
popliteal artery, knee flexed, palpate posteriorly for pulse
what is the upper medial border of the popliteal fossa
semimebranosus and semitendonosus
what is the upper lateral border of the popliteal fossa
biceps femoris
what are the lower medial and lateral borders of the popliteal fossa
medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius
what is the popliteal fossa covered with? what is that continuous with
covered with popliteal fascia, continuous with fascia latae, which contines down to the fascia of the leg
does the fossa have a lot of fat
yes
what are the contents of the popliteal fossa
sometimes the end of the sciatic nerve
small saphenous vein
tibial nerve
common fibular nerve
popliteal vein
popliteal artery
what does the small saphenous vein drain into
popliteal vein
what part of the leg does the small saphenous vein drain
superficial posterior part of the leg
where is the tibial nerve in the popliteal fossa
medial part of fossa
what is the tibial nerve a branch of
sciatic nerve
what is the fibular nerve a branch of
sciatic nerve
where does the common fibular nerve leave the popliteal fossa
the lateral side of the fossa
where is the popliteal vein in the popliteal fossa
deep in the fossa, more superficial than the artery
where is the popliteal artery in the popliteal artery
deep to popliteal vein
where does the popliteal artery branch from and what does it give off
continuation of the femoral artery, gives off some arteries that supply part of the leg like the tibial arteries
what is another name for the interosseus ligament
interosseus membrane
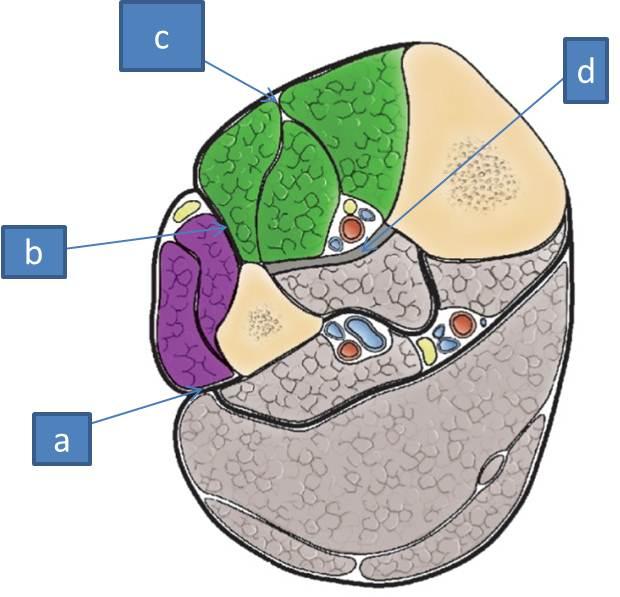
a. posterior intermuscular septum
b. anterior intermuscular septum
c. deep (crural) fascia
d. interosseus membrane
which bone of the leg is more medial and which is more lateral
tibia medial, fibula lateral
what is the structure of the leg like
paired long bones with interosseus membranse in both (thick CT between two bones) and each bone has an interosseus border
what are teh bones of the leg
tibia
fibula
tarsal bones and other bones of the foot discussed later
what is the role of the tibia? what does it articulate with
weight bearing bone, articulates with the femur
what is the role of the fibula
bone for ankle support, also serves as a muscle attachment place and has no femur connection
what are the lateral and medial malleoli
they are the lateral and medial prominences on their respective sides of the ankle, formed by the fibula and tibia respectively
what is the interosseus membrane
CT joining tibia and fibula
what is the functional moving role of the interosseus membrane
allows pivot among the two bones
what does the interosseus membrane do structurally
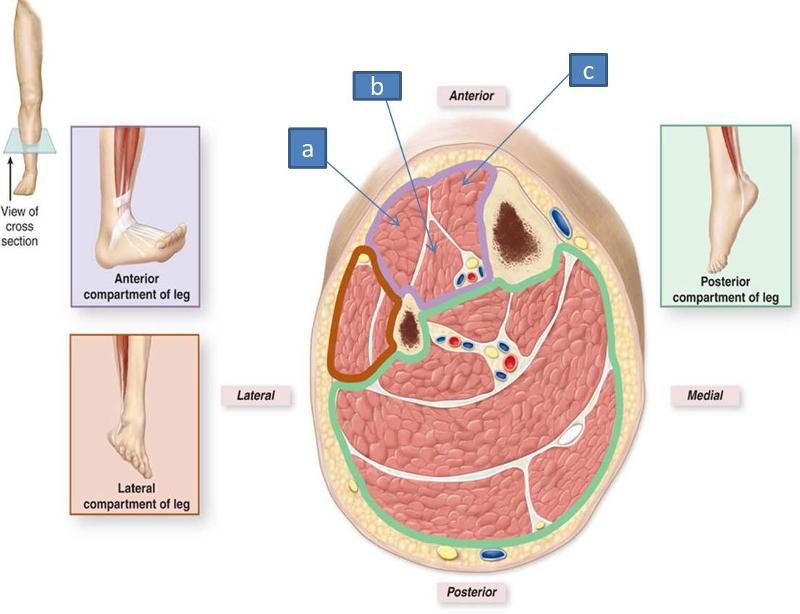
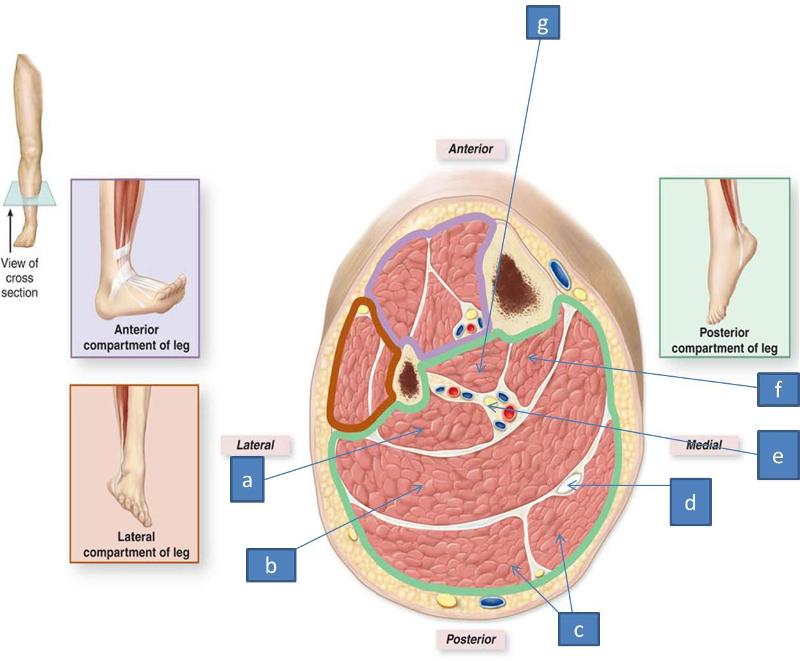
divides anterior and posterior compartments
what is the crural fascia
deep fascia of the leg, goes tibia to tibia
what is the crural fascia continuous with
continuous superiorly with the popliteal fascia and fascia latae
what is the role of the anterior intermuscular septum
divides anterior and lateral compartments
what is the role of the posterior intermuscular septum
divides lateral from posteiror compartments
what is the role of the interosseus membrane structurally
divides anterior and posterior compartments
what do muscles in the same compartment typically share
muscle actions
innervation
blood supply
what is the shared action of muscles in the anterior compartment
dorsiflexion of ankle/foot (pulls toes up)
where is the anterior compartment relative to the tibia
lateral
what is the action of the tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion and ankle inversion (rolls ankle inwards)
where does the tibialis anterior attach?
tarsal bones
what is the action of the extensor hallucis longus
dorsiflexion and extension of the toe
what is the extensor hallucis longus attached to distally
big toe
where is extensor hallucis longus
deep to other anterior muscles, tendon visible
what is the action of the extensor digitorum longus
dorsiflexion and helps extend toes 2-5
what does the extensor digitorum longus connect with
toes 2-5
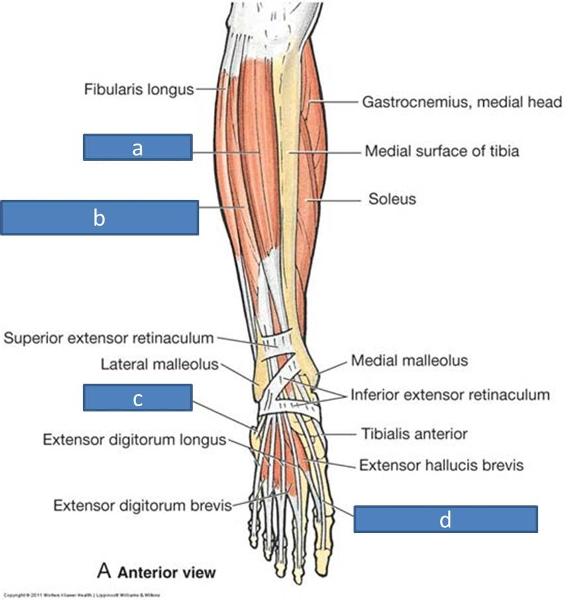
a. tibialis anterior
b. extensor digitorum longus
c. fibularis tertius
d. extensor hallucis longus
where is the extensor digitorum longus
lateral to tibialis anterior
where does the fibularis tertius run
small muscle that wraps around lateral side
what is the action of the fibularis tertius
weak dorsiflexor and helps evert the ankle
what does the anterior tibial artery become within the anterior compartment
dorsalis pedis artery
what anterior rami make up the deep fibular nerve
L4-S1
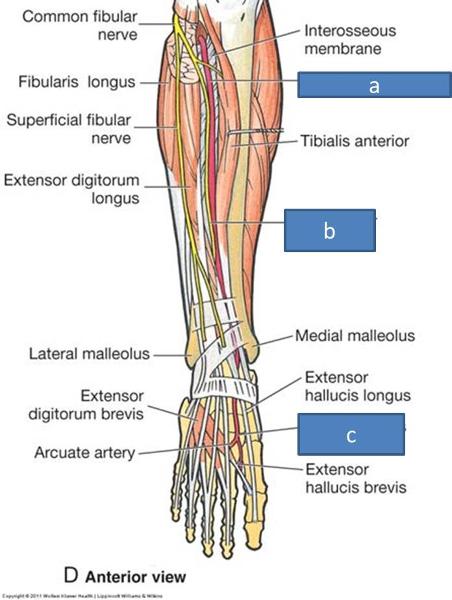
a. anterior tibial artery
b. deep fibular nerve
c. dorsalis pedis artery
a. extensor digitorum longus
b. extensor hallucis longus
c. tibialis anterior
what does the deep fibular nerve supply
(Anterior Compartment Muscles)
tibialis anterior
extensor hallucis longus
extensor digitorum longus
fibularis tertius
what compartment is the tibialis anterior in
anterior
what compartment is the extensor hallucis longus in
anterior
what compartment is the extensor digitorum longus in
anterior
what compartment is the fibularis tertius in
anterior
what is the shared action of the lateral compartment
everts and plantarflexes
where does the lateral compartment insert
behind lateral malleolus of the fibula
where are the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis relative to one another
fibularis longus is superficial to fibularis brevis
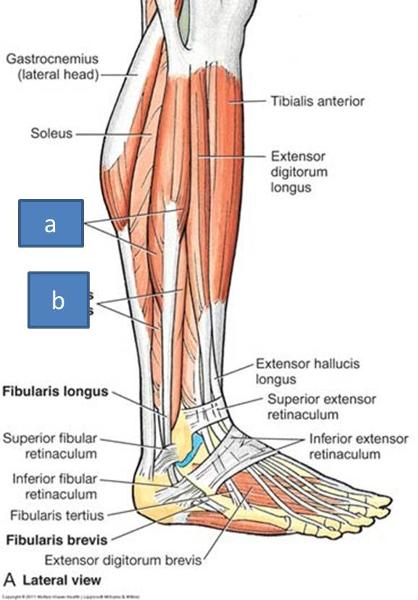
a. fibularis longus
b. fibularis brevis
what is the function of fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
evert the foot (contract to prevent ankle inversion) and plantarflexion
where does the fibular artery come from
posterior compartment
what does the fibular artery give off
perforating branches of the fibular artery
where does the superficial fibular nerve get its innervation from
anterior rami of L5-S2
what muscles does the superficial fibular nerve innervate
fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
what is special about the posterior compartment of the leg compared to the rest
2 layers
what is the shared action of the posterior compartment
plantarflexes
where does the tibial nerve get innervation from
L4-S3
what arteries are in the posterior compartment
posterior tibial artery supplies this compartment
fibular artery is found in this compartment but does not supply it
what vein is in the posterior compartment
tibial vein
what muscles are part of the superficial layer of the posterior compartment
gastrocnemius
soleus
plantaris
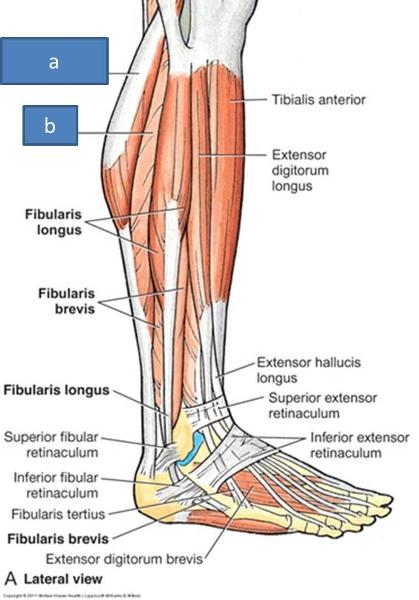
a. lateral head of gastrocnemius
b. soleus
what is the role of the gastrocnemius
flexes knee and plantarflexes
what is interesting about the gastrocnemius
has medial and lateral heads, crosses knee joint and attaches to the femur
what is the power plantarflexor in the posterior compartment
gastrocnemius, important in running/sprinting
where is the soleus
deep to gastrocnemius
what does the soleus look like
large flat muscle
where does the soleus use for attachment (gastrocnemius uses it also)
achilles tendon
what is the function of the soleus
endurance plantarflexor as opposed to the power of the gastrocnemius
what does the plantaris do that is interesting structurally
crosses the knee
where is the tendon for the plantaris go?
between gastrocnemius and soleus
what is the role of plantaris
weak plantarflexor, may be a proprioceptor
which muscle has a long tendon that is called the medical student nerve
plantaris
what is another name for the calcaneal tendon
achilles tendon
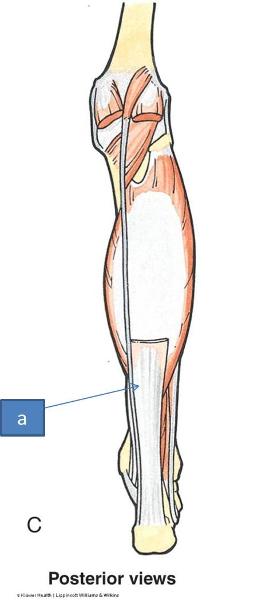
calcaneal tendon/achilles tendon
what do the muscles in the deep posterior layer do
plantarflex, minus one
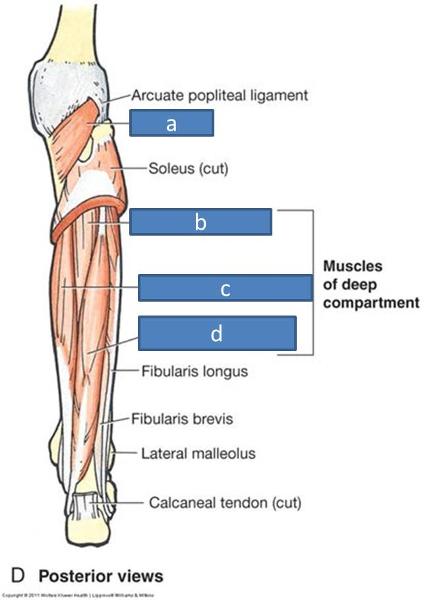
a. popliteus
b. tibialis posterior
c. flexor digitorum longus
d. flexor hallucis longus
which one of the deep posterior compartment muscles does not plantarflex
popliteus
what does the popliteus do
helps unlock keen joint, flexes knee
where is the popliteus located
deep
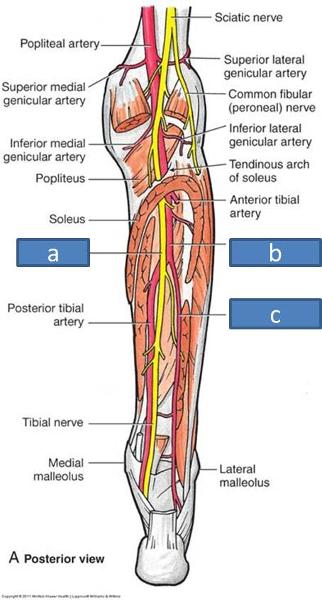
a. tibial nerve
b. posterior tibial artery
c. fibular artery
what innervates the popliteus
tibial nerve L4-S1
what is the action of the flexor hallucis longus
plantarflexion of great toe
where is the flexor hallucis longus located relative to the rest of the muscles in the deep posterior compartment
medial
what is the actino of the flexor digitorum longus
plantarflexes toes 2-5
where is the flexor digitorum longus relative to the deep posterior compartment
lateral
what is the innervation of the flexor hallucis longus
tibial nerve S2, S3
what is the innervation of the flexor digitorum longus
tibial nerve S2, S3
a. tibialis posterior
b. flexor digitorum longus
c. tibial artery
d. tibial nerve
e. flexor hallucis longus
what is the action of the tibialis posterior
plantarflexes and inverts
what muscle does the tibialis posterior invert with?
tibialis anterior
what innervates the tibialis posterior
tibial nerve L4 and L5
what does the artery tree with regard to the popliteal artery, anterior and posterior tibial arteries, and fibular artery look like
popliteal splits into anterior and posterior tibial, posterior tibial gives off fibular
a. flexor hallucis longus
b. soleus
c. gastrocnemius
d. plantaris tendon
e. tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery
f. flexor digitorum longus
g. tibialis posterior
what is compartment syndrome
raised pressure due to infection or inflammation causes there to be a lack of blood delivered to tissues, which can lead to necrosis because of the compartmentalization
how could compartment syndrome develop
acutely from trauma or infection
chronically from inflammation from various sources
what is often done to help in a compartment syndrome
fasciotomy, which relieves the pressure
what is shin splints
minor case of compartment syndrome, typically in the anterior compartment or deep posterior compartment
how can shin splints develop
acute from inflammation from exercise
chronic from overuse
why is the common fibular nerve injury common
due to superficiality of the nerve
what are the most common symptoms from common fibular nerve injury
foot drop and foot flop
what do you typically lose functionally with common fibular nerve injury
dorsiflexion
why is loss of anterior compartment function worse than losing plantarflexion
because lateral and posterior compartment both help with plantarflexion
what is the retinaculum
thickenings of fascia in each compartment
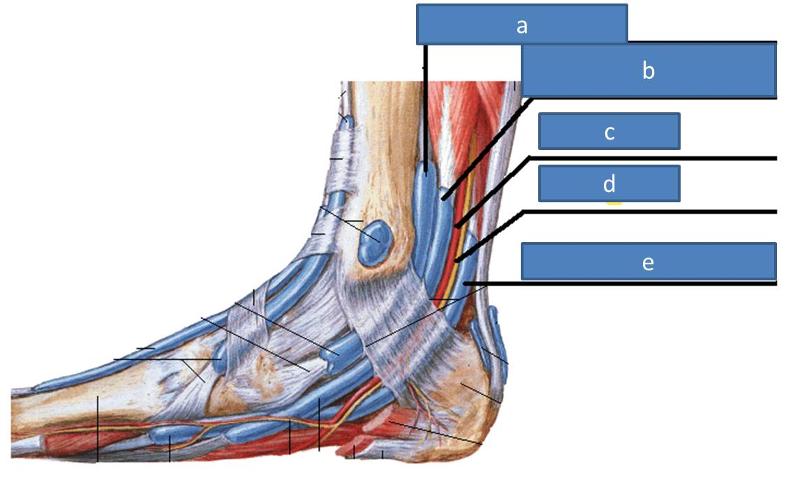
a. extensor retinaculum
b. fibular retinaculum

a. flexor retinaculum
what does the extensor retinaculum do
covers most of extensors from anterior compartment
superior and inferior that cross all the way over, designed to help hold extensor tendons close to bones, keep them from bowing out
what are extensor retinaculum injuries usually from
high ankle sprain
what does the fibular retinaculum cover
lateral compartment tendons (fibularis longus and fibularis brevis)
what does the flexor retinaculum cover
many of posterior compartment muscles (tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis)
what innervates the cutaneous lower posterolateral leg
sural nerve
what innervates the cutaneous upper lateral leg
lateral sural cutaneous nerve
what innervates the cutaneous lower anterolateral leg and dorsum of the foot
superficial fibular nerve
what innervates the medial leg
saphenous nerve
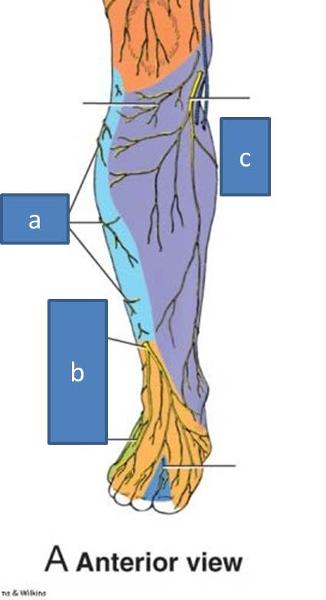
a. lateral sural cutaneous nerves
b. superficial fibular nerves
c. saphenous nerve
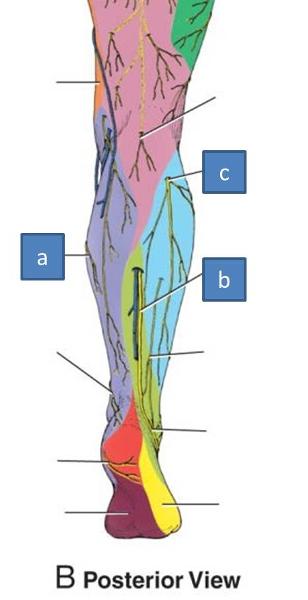
a. saphenous nerve
b. sural nerve
c. lateral sural cutaneous nerve
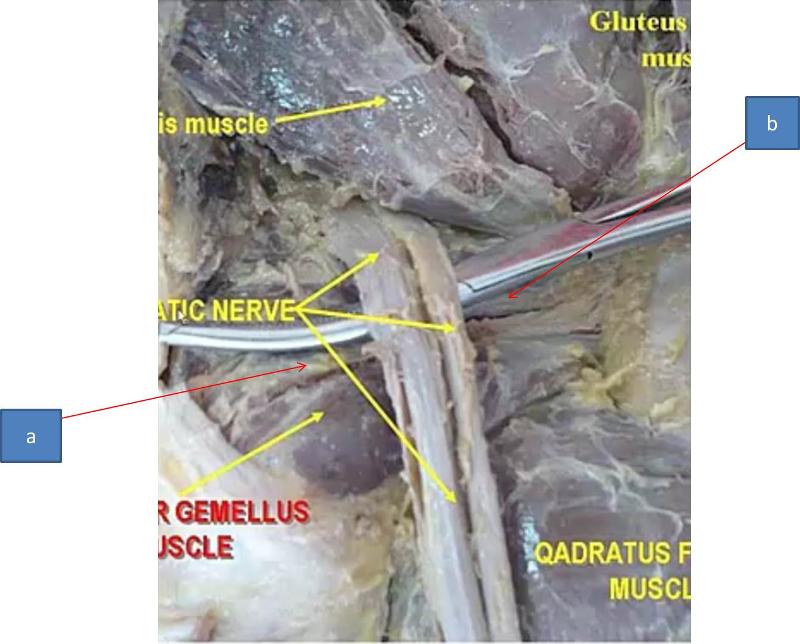
a. lateral sural cutaneous
b. saphehous
c. superificial fibular nerve
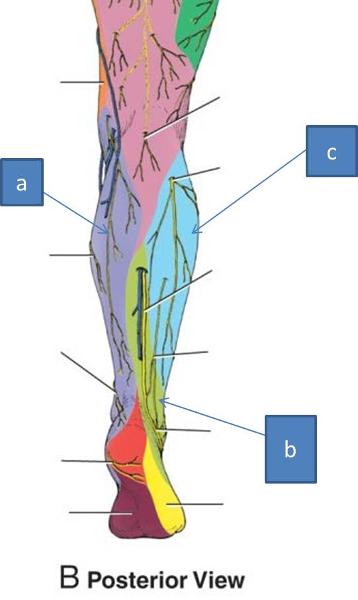
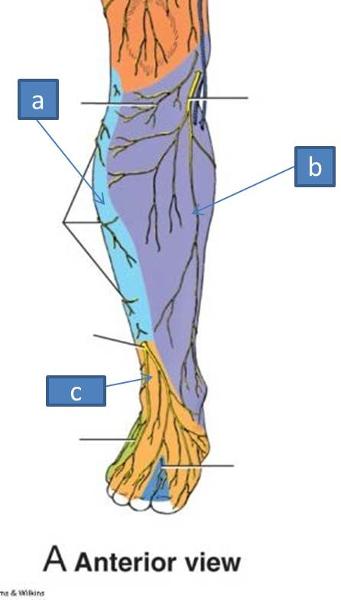
a. saphenous
b. sural nerve
c. lateral sural cutaneous