Chapter 2 - Acids and Bases

Label the Bronsted Lowry acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.

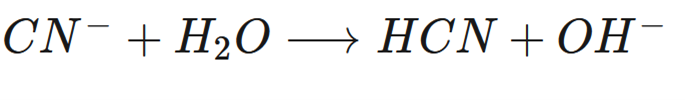
Label the Bronsted Lowry acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.
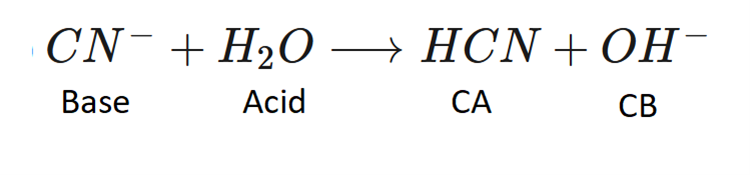
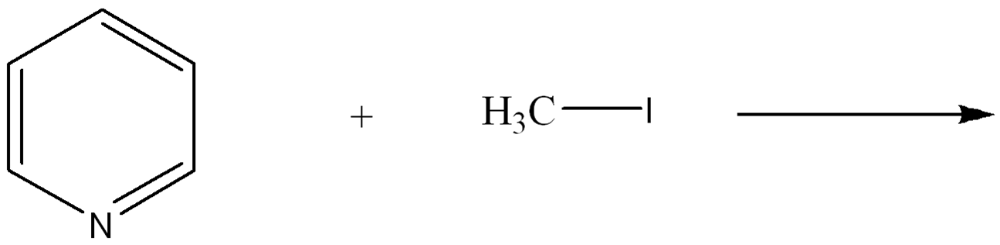
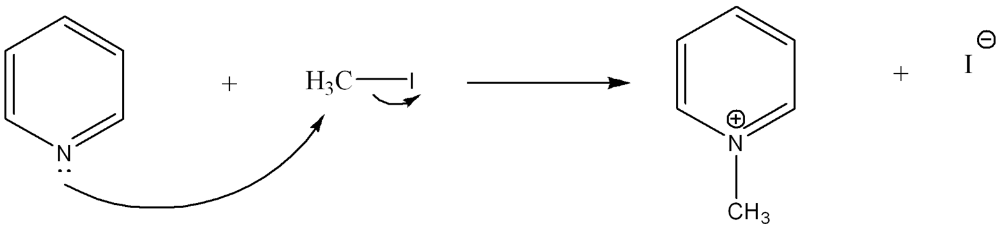
Use curved arrow notation to show the movement of electrons in the Lewis Acid-Base Reaction
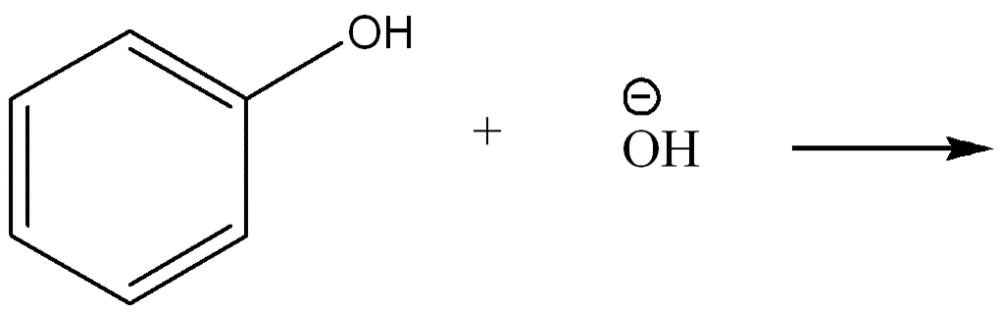
Use curved arrow notation to show the movement of electrons in the Bronsted Lowry Acid-Base Reaction
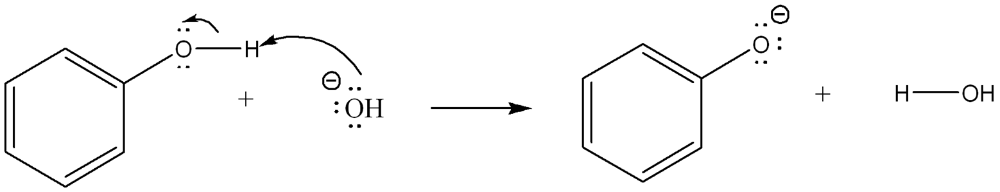
Label the Bronsted Lowry acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base. Then determine in which direction equilibrium is favored.
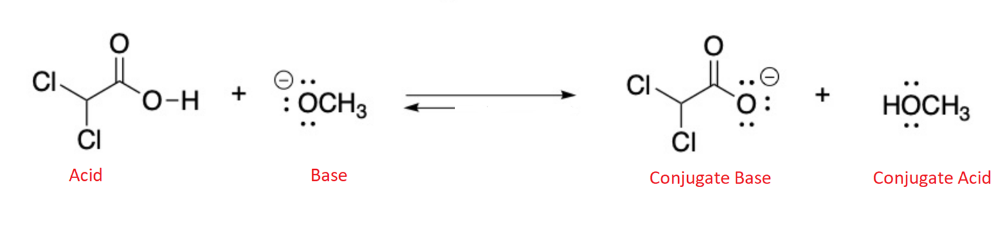
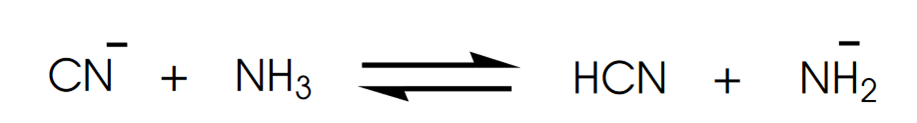
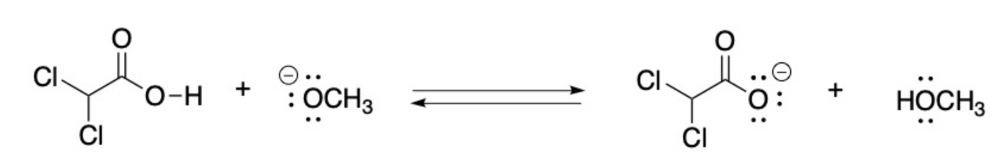
Determine in which direction equilibrium is favored.
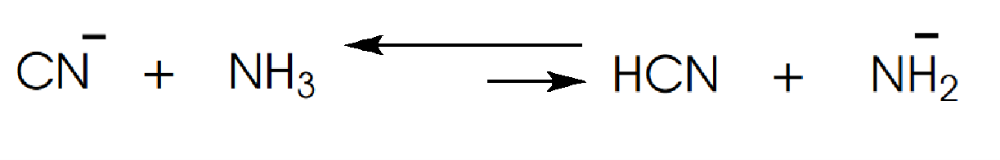
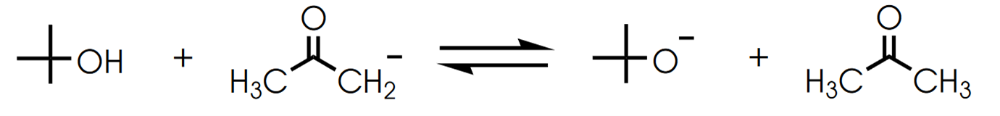
Determine in which direction equilibrium is favored.
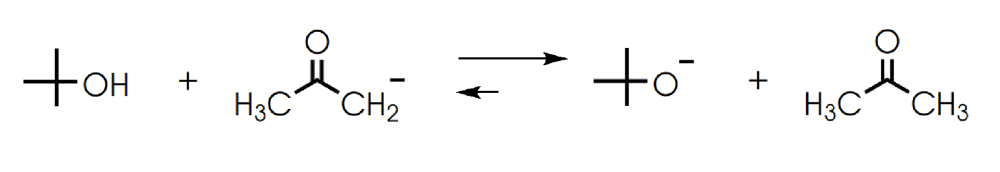
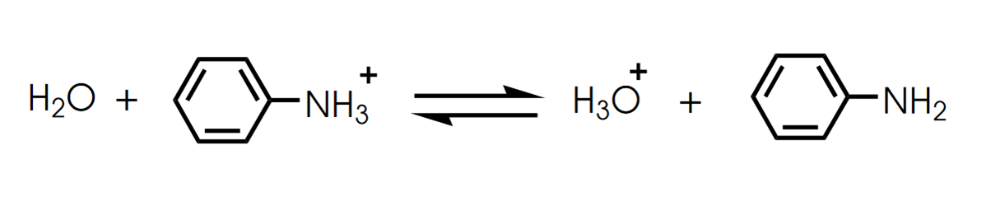
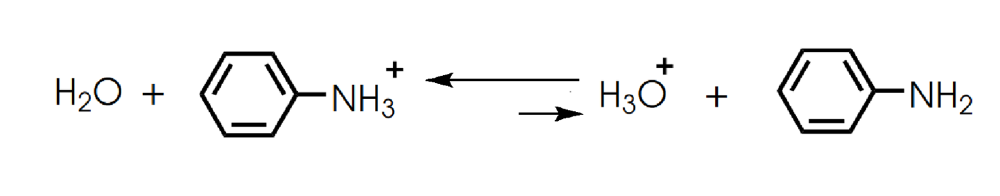
Determine in which direction equilibrium is favored.
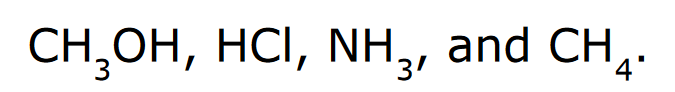
Rank the following in order of increasing acidity
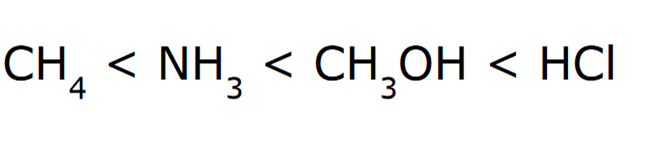
*Elemental Effect
Electronegativity when comparing CH4, NH3, and CH3OH
Polarizability when comparing CH3OH and HCl
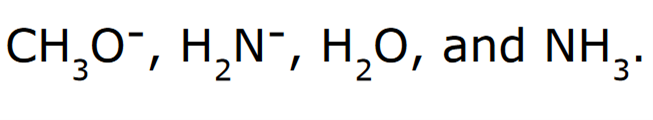
Rank the following in order of increasing basicity
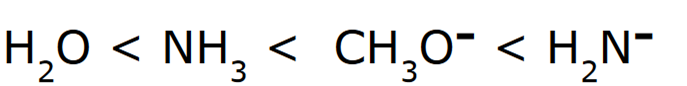
Negatively charged ions are stronger bases compared to their neutral counterparts
When comparing H2O and NH3, H2O is a stronger acid, because the conjugate base (OH-) is more stable than (NH2-) because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen. Since OH- is the more stable conjugate base, it is a stronger acid, and thereby the weakest base.

Rank these compounds in order of increasing acidity
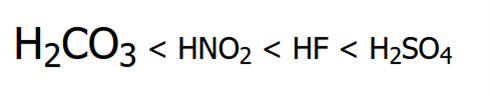
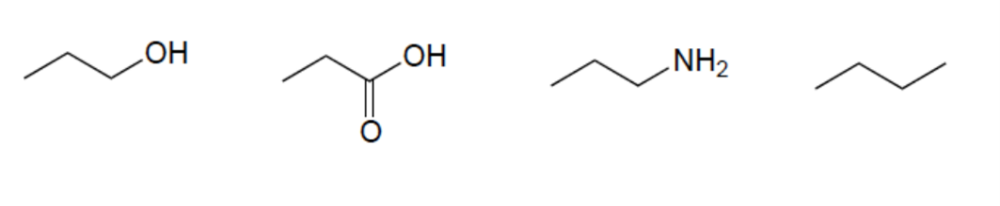
Rank these compounds in order of increasing acidity
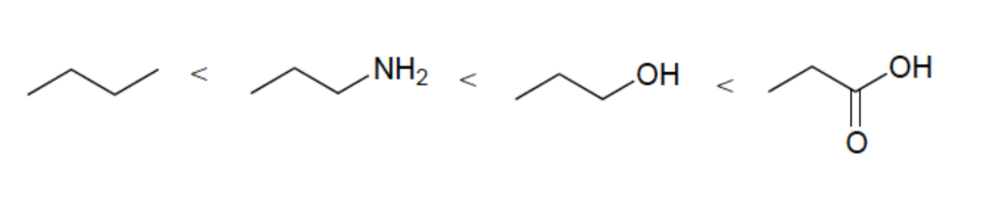
Elemental Effect (CH3 vs NH2)
Elemental Effect (NH2 vs OH)
Resonance Effect (OH vs. CO2H)
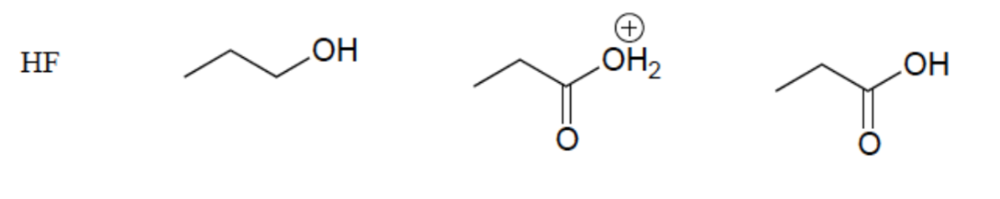
Rank these compounds in order of increasing acidity
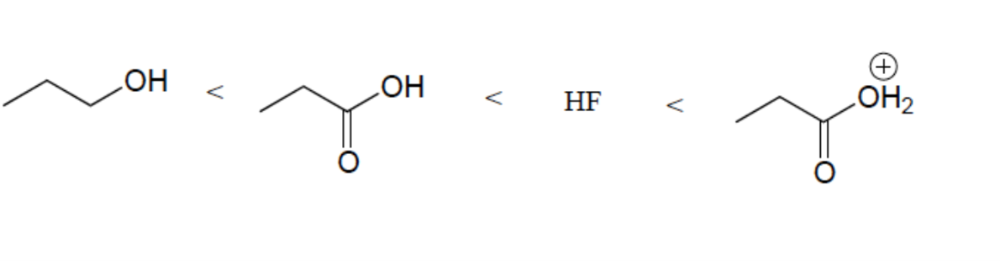
Resonance Effect (OH vs CO2H)
Elemental Effect (CO2H vs HF)
Positively charged ions are stronger acids than neutral counterparts
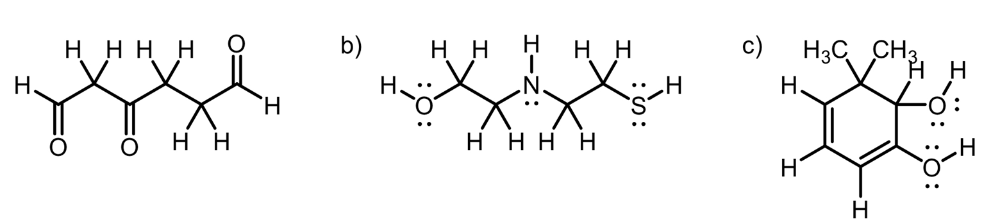
Circle the most acidic proton on each compound
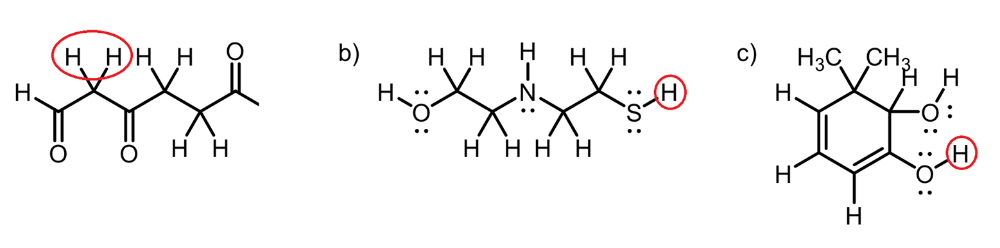
A. Inductive Effect
B. Elemental Effect (Eliminates C-H and N-H), (Sulfur is more polarizable than Oxygen)
C. Elemental Effect (Eliminates C-H), Resonance Effect (Eliminates O-H group)
Circle the most acidic proton on each compound
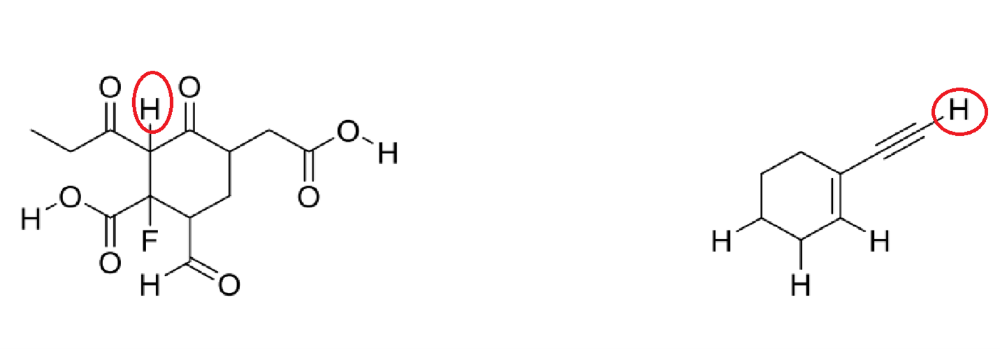
A. Elemental Effect (Fluorine electronegativity)
B. Hybridization Effect (increase percent s character, closer to the nucleus, more stable)

Draw the products for the Lewis Acid and Base Reaction. Identify the electrophile and nucleophile
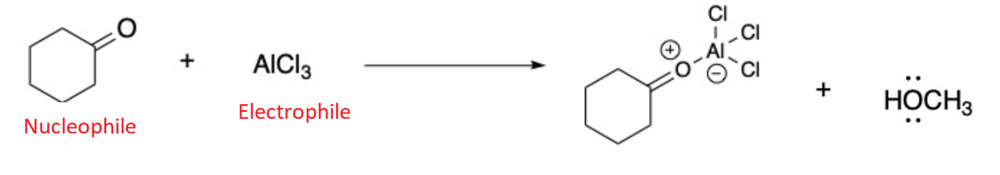
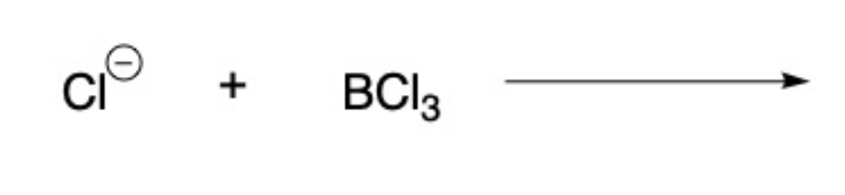
Draw the products for the Lewis Acid and Base Reaction. Identify the electrophile and nucleophile
