A&P II Chapters 16 and 17 Attendance Quiz 2 and 3 Unit Test 2
Which of the following statements does not describe blood?
blood carries body cells to injured areas for repair.
The special type of hemoglobin present in fetal red blood cells is ________.
hemoglobin F
No visible cytoplasmic granules are present in ___________.
monocytes
Which blood type is generally called the universal donor?
O
Which of the following is not a cause of bleeding disorders?
excess secretion of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Which of the following is characteristic of all leukocytes?
they are nucleated
An individual who is blood type AB negative can ________.
receive any blood type in moderate amounts except that with the Rh antigen
The plasma protein that is the major contributor to osmotic pressure is ________.
albumin
All of the following can be expected with polycythemia except ________.
low blood viscosity
Which of the following hormones suppresses appetite and increases energy expenditure?
leptin
A man has been told that he is NOT synthesizing enough follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and for this reason he may be unable to father a child. Choose the correct statement to explain this problem.
FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes
Which of the following is NOT a change typically produced by a hormonal stimulus?
stimulates production of an action potential
Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference?
It does not require a second messenger to cause a response.
Fred's blood was determined to be AB positive. What does this mean?
There are no antibodies to A, to B, or to Rh antigens in the plasma.
Which of the statements below is an incorrect or false statement?
Blood typing for the Kell, Lewis, and Duffy factors is always done before a blood transfusion.
A lack of intrinsic factor, leading to a deficiency of vitamin B12 and causing an appearance of large pale cells called macrocytes, is characteristic of ________.
pernicious anemia
All of the following conditions impair coagulation except ________.
vascular spasm
Which of the following would not be a possible cause of sickling of red blood cells in someone with sickle-cell anemia?
sleeping in a well-ventilated room
What organ in the body regulates erythrocyte production?
kidney
The slowest step in the clotting process is ________.
formation of prothrombin activator
Which of the following is not a functional characteristic of WBCs?
granulosis
Select the incorrect statement regarding blood cell formation.
Platelets are formed from myeloblasts.
Thromboembolic disorders ________.
include embolus formation, a clot moving within the circulatory system
Which of the following is a protective function of blood?
prevention of blood loss
Which of the following is not a structural characteristic that contributes to erythrocyte gas transport functions?
mitotically active
Which of the following is not a phase of hemostasis?
fibrinolysis
Blood volume restorers include all of the following except ________.
packed cells
When neither anti-A serum nor anti-B serum clot on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is type ________.
O
Blood is a ________.
suspension
James has a hemoglobin measurement of 16 g/100 ml blood. This is ________.
within the normal range
Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis?
hypoxia of EPO-producing cells
What is the average normal pH range of blood?
7.35-7.45
Which of the choices below is the parent cell for all formed elements of blood?
hemocytoblast
When can erythroblastosis fetalis not possibly happen in the child of an Rh negative mother?
if the father is Rh-
Which sequence is correct for the following events?
1.
fibrinogen → fibrin
2. clot retraction
3. formation of
thromboplastin
4. prothrombin → thrombin
3, 4, 1, 2
Which of the following is not a distribution function of blood?
transport of salts to maintain blood volume
Several hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the anterior pituitary gland. The mechanism of transportation from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland is through the ________.
hypophyseal portal system
Which of the following is not a cardinal sign of diabetes mellitus?
polycythemia
The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract ________.
is partly contained within the infundibulum
What ion is sometimes used as a second messenger of amino acid based hormones?
Calcium
Which organ does not produce hormones?
spleen
Which of the following is not a type of hormone interaction?
feedback
Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular ________.
second messengers
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on ________.
the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
Eicosanoids do not include ________.
hydrocortisones
Leptin is secreted by ________.
adipocytes
Which of the choices below is not a factor required for target cell activation by hormone receptor interaction?
type of hormone
Which of the following is not a steroid-based hormone?
epinephrine
Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells in a manner similar to ________.
steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells
Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids and that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called ________.
hormones
When it becomes necessary to enlist the fight-or-flight response, a hormone that is released during the alarm phase of the general adaptation syndrome is ________.
epinephrine
Regulating hormones from the hypothalamus ________.
first enter into the hypophyseal portal system
ACTH ________.
secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic regulatory hormone
Aldosterone ________.
functions to increase sodium reabsorption
In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the target organ. This is known as ________.
up-regulation
The most important mineralcorticoid regulator of electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is ________.
aldosterone
The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________.
binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP.
Which of the following is not a parathyroid gland mechanism to maintain adequate levels of blood calcium?
inhibition of calcitonin synthesis
Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus?
enzyme
The major targets of growth hormone are ________.
bones and skeletal muscles
Oxytocin ________.
release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism
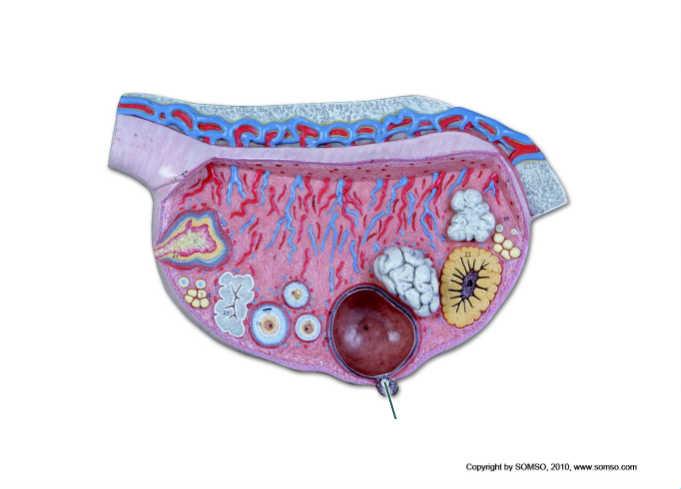
Which structure is highlighted?
oocyte
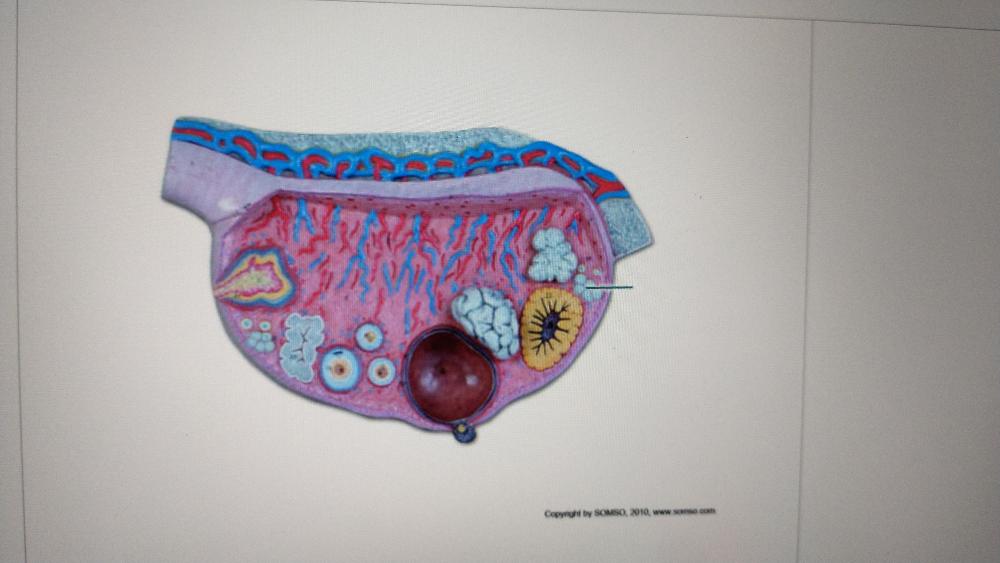
Which follicles are highlighted?
primordial
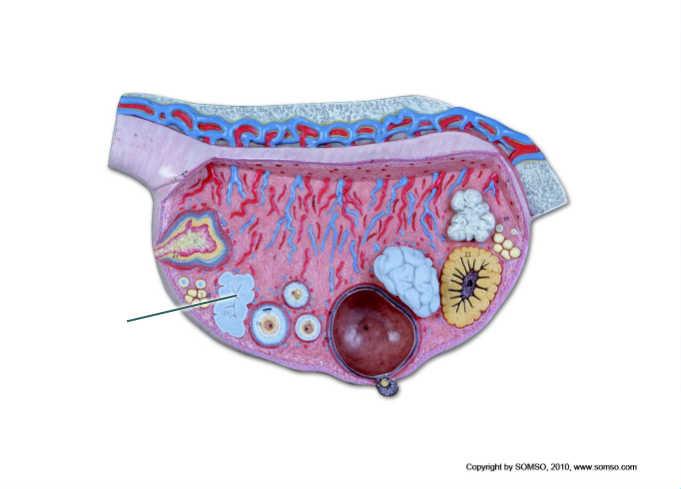
Which structure is highlighted?
corpus albicans
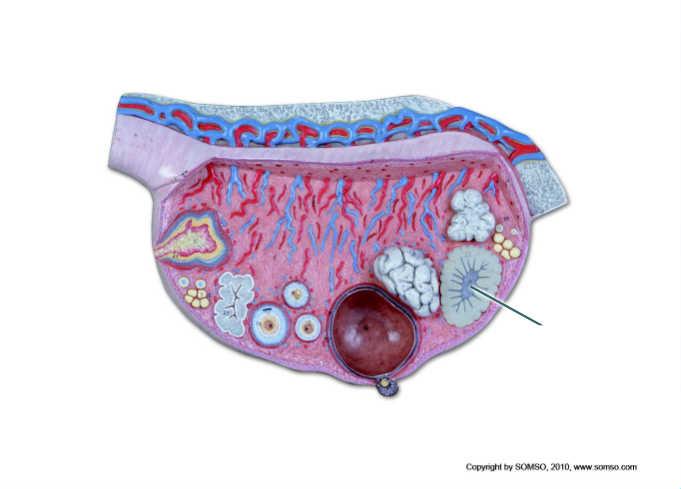
What is the function of the hormones secreted by the highlighted structure?
to prepare the uterus for implantation
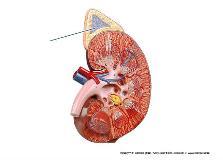
What is the result of secretions from the highlighted region?
increase blood pressure and heart rate
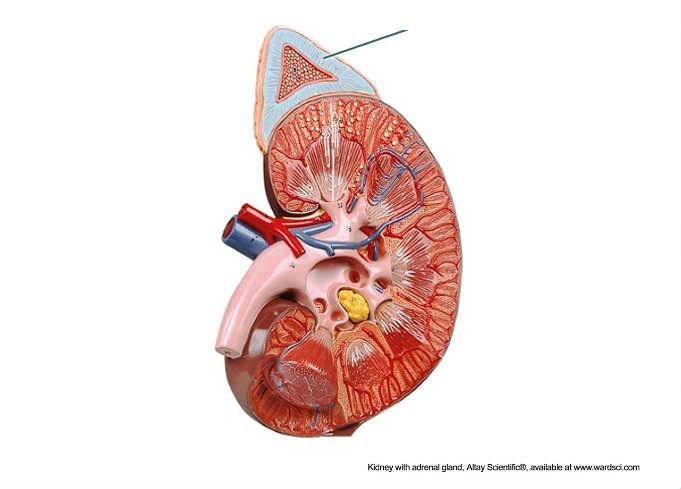
Which structure is highlighted?
adrenal cortex
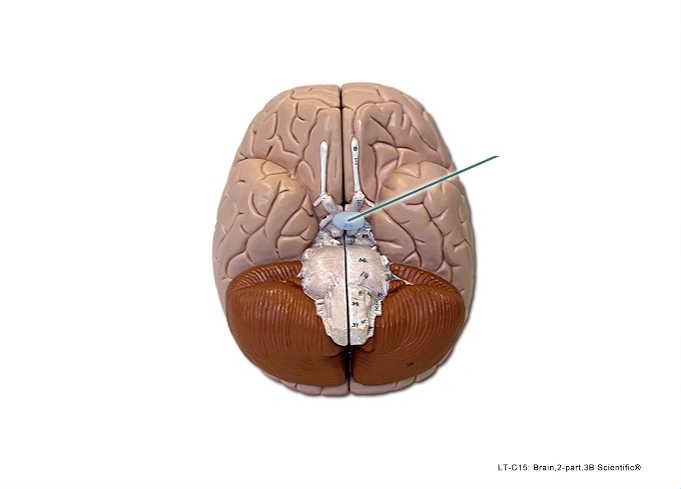
Which structure is highlighted?
pituitary gland
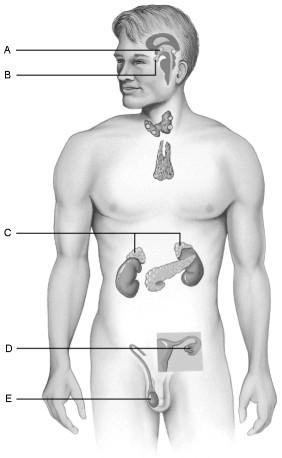
Produces the hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
D

Produces the hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics.
E
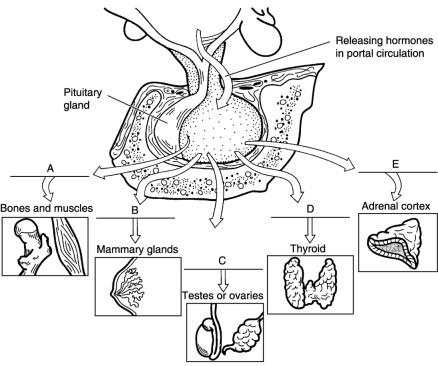
Follicle stimulating hormone
C
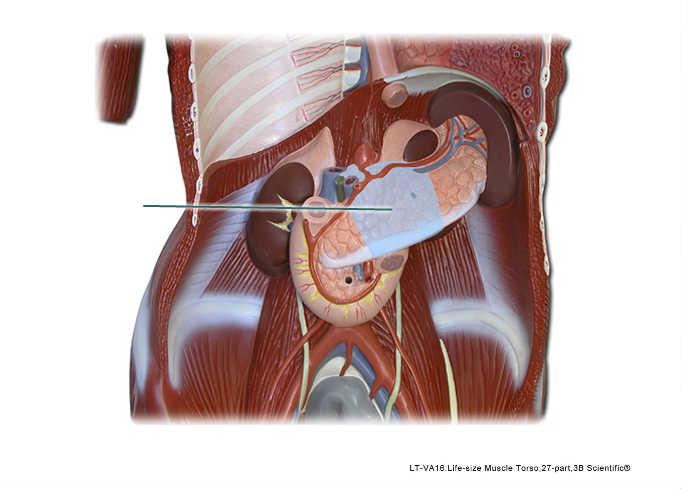
Which structure is highlighted?
body of pancreas
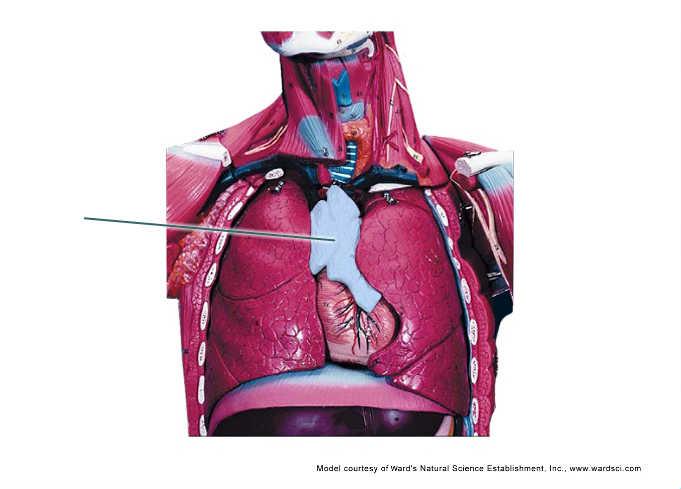
Which gland is highlighted?
thymus

Which structure is highlighted?
parathyroid glands
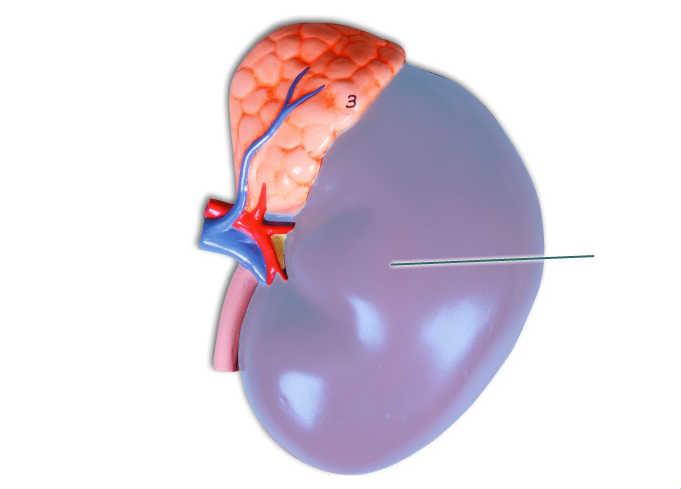
Which structure is highlighted?
kidney
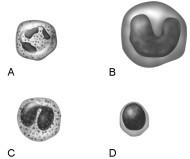
Lymphocyte.
D

Monocyte
B

Eosinophil.
C

Neutrophil.
A
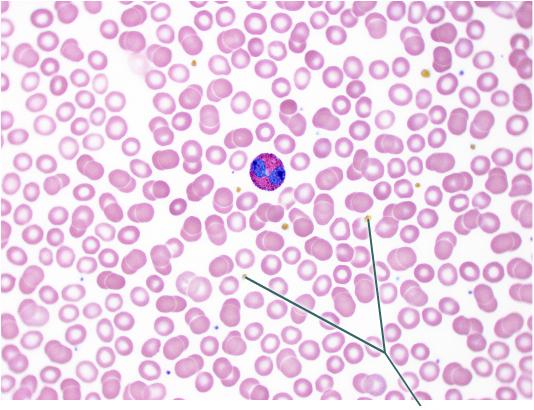
Which formed elements are highlighted?
platelets
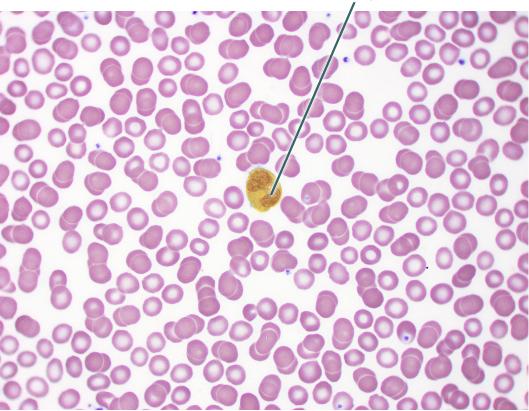
Which of the following is a function of the highlighted cell?
phagocytosis
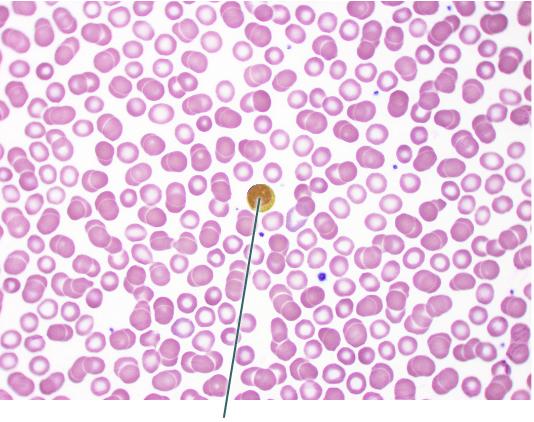
Which cell is highlighted?
lymphocyte
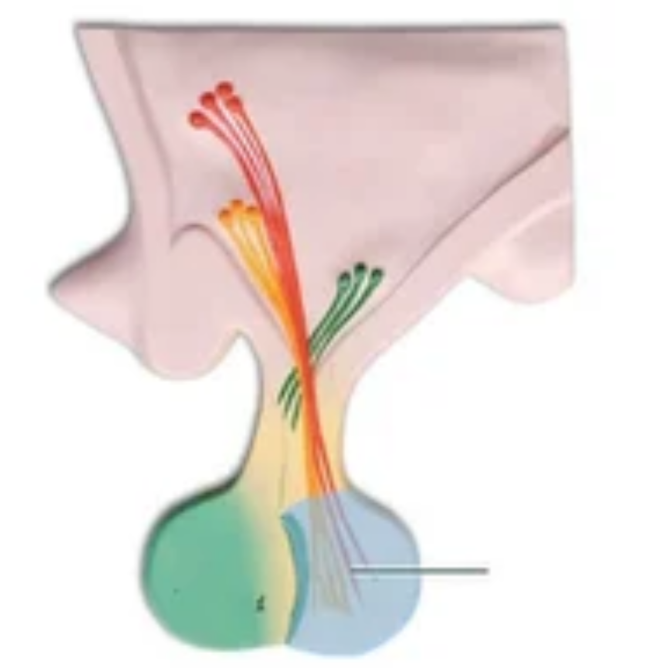
What primary tissue type comprises the highlighted structure?
nervous