Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
final exam biology
front 1 Which of the following is a major difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? A) Prokaryotic cells are generally larger than eukaryotic cells. B) Eukaryotic cells have flagella, while prokaryotic cells do not. C) Prokaryotic cells have cell walls, while eukaryotic cells do not. D) Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not. | back 1 correct answer : D Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not. |
front 2 Which of the following will have the greatest ratio of surface area to volume? A) A box that is 1×1×1. B) A box that is 2×2×2. C) A box that is 1×1×2. D) A box that is 2×2×1. | back 2 correct answer : A A box that is 1×1×1. |
front 3 Which domains of life are classified as prokaryotes? A) Archaea and Fungi B) Bacteria and Archaea C) Bacteria and Protista D) Bacteria and Eukarya | back 3 correct answer : B Bacteria and Archaea |
front 4 Which structure is common to plant and animal cells? A) central vacuole B) chloroplast C) mitochondrion D) centriole | back 4 correct answer : C mitochondrion |
front 5 Which of the following are found in plant, animal, and bacterial cells? A) mitochondria B) ribosomes C) endoplasmic reticulum D) chloroplasts | back 5 correct answer : B ribosomes |
front 6 Beginning within the nucleus, the first step leading to the synthesis of a polypeptide is _____. A) linking of nucleotides to form a polypeptide B) translation of an RNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids C) transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA D) removal of introns from RNA and the stitching together of exons E) translation of a DNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids | back 6 correct answer : C transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA |
front 7 What is the function of the nuclear pore complex found in eukaryotes? A) It synthesizes secreted proteins. B) It synthesizes the proteins required to copy DNA and make mRNA. C) It regulates the movement of proteins and RNAs into and out of the nucleus. D) It assembles ribosomes from raw materials that are synthesized in the nucleus. | back 7 correct answer : C It regulates the movement of proteins and RNAs into and out of the nucleus. |
front 8 Which of the following macromolecules leaves the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell through pores in the nuclear membrane? A) phospholipids B) mRNA C) DNA D) amino acids | back 8 correct answer : B mRNA |
front 9 Which organelle plays a role in intracellular digestion? A) chloroplast B) Golgi apparatus C) ribosome D) lysosome E) plasmodesma | back 9 correct answer : D lysosome |
front 10 A cell with a predominance of rough endoplasmic reticulum is most likely ________. A) producing large quantities of proteins for secretion B) producing large quantities of carbohydrates for storage in the vacuole C) producing large quantities of proteins in the cytosol D) producing large quantities of carbohydrates to assemble an extensive cell wall matrix | back 10 correct answer : A producing large quantities of proteins for secretion |
front 11 Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large, complex, undigested lipids. Which cellular organelle is most likely defective in this condition? A) the Golgi apparatus B) the lysosome C) the smooth endoplasmic reticulum D) the rough endoplasmic reticulum | back 11 correct answer : B the lysosome |
front 12 The liver is involved in detoxification of many poisons and drugs. Which of the following structures is primarily involved in this process and, therefore, abundant in liver cells? A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum B) nuclear envelope C) rough endoplasmic D) reticulum E) Golgi apparatus | back 12 correct answer : A smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
front 13 Which of the following is the most common pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein that will be secreted by a cell? A) rough ER → Golgi → transport vesicle → plasma membrane B) rough ER → lysosome → transport vesicle → plasma membrane C) Golgi → rough ER → lysosome → transport vesicle → plasma membrane D) rough ER → Golgi → transport vesicle → nucleus | back 13 correct answer : A rough ER → Golgi → transport vesicle → plasma membrane |
front 14 Asbestos is a material that was once used extensively in construction. One risk from working in a building that contains asbestos is the development of asbestosis caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers. Cells will take up asbestos by phagocytosis, but are not able to degrade it. As a result, asbestos fibers accumulate in ________. A) lysosomes B) peroxisomes C) nuclei D) the Golgi apparatus | back 14 correct answer : A lysosomes |
front 15 The evolution of eukaryotic cells most likely involved ________. A) evolution of an endomembrane system and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum B) endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic archaeal cell in a larger bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic archaea evolved into chloroplasts C) endosymbiosis of an oxygen-using bacterium in a larger bacterial host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into chloroplasts D) endosymbiosis of an oxygen-using bacterium in a larger bacterial host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria | back 15 correct answer : D endosymbiosis of an oxygen-using bacterium in a larger bacterial host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria |
front 16 Cyanide binds with at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the bound cyanide is likely to be localized within the ________. A) mitochondria B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum C) peroxisomes D) lysosome | back 16 correct answer : A mitochondria |
front 17 Suppose a young boy is always tired and fatigued, suffering from a metabolic disease. Which of the following organelles is most likely malfunctioning in this disease? A) smooth endoplasmic reticulum B) lysosomes C) Golgi apparatus D) mitochondria | back 17 correct answer : D mitochondria |
front 18 Motor proteins provide for molecular motion in cells by interacting with what types of cellular structures? A) free ribosomes and ribosomes attached to the ER B) cellulose fibers in the cell wall C) components of the cytoskeleton D) membrane proteins of the inner nuclear envelope | back 18 correct answer : C components of the cytoskeleton |
front 19 A cell has formed a food vacuole as it ingested a food particle. Which of the following events is associated with the breakdown of that food particle? A) Enzymes for the breakdown of the food are delivered to the food vacuole from the cytosol. B) The membrane of the food vacuole is derived from the cell wall. C) Digestion of the food particle occurs in a vesicle enclosed by a membrane that separates the digestion from the cytoplasm. D) Proteins for digestion of the food are made by ribosomes in the Golgi apparatus. E) Proteins for digestion of the food particle were initially processed in mitochondria. | back 19 correct answer : C Digestion of the food particle occurs in a vesicle enclosed by a membrane that separates the digestion from the cytoplasm. |
front 20 A cell with a predominance of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is likely specialized to ________. A) Import and export large quantities of protein B) synthesize large quantities of lipids C) actively secrete large quantities of protein D) store large quantities of water | back 20 correct answer : B synthesize large quantities of lipids |
front 21 Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells? A) peroxisome B) lysosome C) mitochondrion D) Golgi apparatus | back 21 correct answer : C mitochondrion |
front 22 Which of the following functions is NOT associated with the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells? A) the contraction of muscle cells in animals B) maintaining the position of the nucleus in the cell C) the beating of cilia or flagella D) determining the shape of animal cells E) Movement of RNA molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm | back 22 correct answer : E Movement of RNA molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm |
front 23 Vinblastine, a drug that inhibits microtubule polymerization, is used to treat some forms of cancer. Cancer cells given vinblastine would be unable to _____. A) migrate by amoeboid movement B) form cleavage furrows during cell division C) maintain the shape of the nucleus D) separate chromosomes during cell division | back 23 correct answer : D separate chromosomes during cell division |
front 24 Amoebae move by crawling over a surface (cell crawling), which involves ________. A) assembly of microtubule extensions that vesicles can follow in the direction of movement B) localized contractions driven by myosin and microtubules C) reinforcement of the pseudopod with intermediate filaments D) growth of actin filaments to form bulges in the plasma membrane | back 24 correct answer : D growth of actin filaments to form bulges in the plasma membrane |
front 25 Researchers investigating the mechanism of vesicular transport assembled a cell-free system that included microtubule tracks, vesicles, and ATP. However, they observed no movement of transport of vesicles in this system. What were they missing? A) an axon B) intermediate filaments C) contractile microfilaments D) motor proteins | back 25 correct answer: D motor proteins |
front 26 Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is true? A) Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other. B) Although microtubules are common within a cell, actin filaments are rarely found outside of the nucleus. C) The cytoskeleton of eukaryotes is a static structure most resembling scaffolding used at construction sites. D) Chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would have little effect on a cell's response to external stimuli. | back 26 correct answer : A Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other. |
front 27 What is another name for a condensation reaction? A) dehydration B) water formation C) hydrolysis D) catabolism E) monomerization | back 27 correct answer: A dehydration |
front 28 What is the name of the process during which a bond between two monomers is broken? A) combustion B) dehydration C) hydrolysis D) condensation | back 28 correct answer : C hydrolysis |
front 29 How many molecules of water are released during the polymerization of a 20 monomer-long cellulose molecule? A) 40 B) 20 C) 10 D) 19 | back 29 correct answer : D 19 |
front 30 Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis? A) Dehydration reactions and hydrolysis reactions assemble polymers from monomers. B) Dehydration reactions eliminate water from membranes; hydrolysis reactions add water to membranes. C) Hydrolysis reactions create polymers and dehydration reactions create monomers. D) Dehydration reactions assemble polymers; hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart. | back 30 correct answer : D Dehydration reactions assemble polymers; hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart. |
front 31 Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because ________. A) starch monomers are joined by covalent bonds, and cellulose monomers are joined by ionic bonds B) the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is galactose C) humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α-glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β-glycosidic linkages of cellulose D) Starch is softer than cellulose | back 31 correct answer : C humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the α-glycosidic linkages of starch but not the β-glycosidic linkages of cellulose |
front 32 Which molecule is not a carbohydrate? A) Cellulose B) Lipid C) Starch D) Glycogen | back 32 correct answer : B Lipid |
front 33 Which of the following statements about monosaccharide structure is true? A) A six-carbon sugar is called a pentose. B) Monosaccharides can be classified according to the spatial arrangement of their atoms. C) All monosaccharides contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. D) Aldoses and ketoses differ in the position of their hydroxyl groups. | back 33 correct answer : B Monosaccharides can be classified according to the spatial arrangement of their atoms. |
front 34 True or false? Peptidoglycan is a polysaccharide found only in bacteria. A) True B) False | back 34 correct answer : A true |
front 35 Which complex carbohydrate contains only a-1,4-glycosidic linkages? A) Amylopectin B) Amylose C) Cellulose D) Glycogen | back 35 correct answer : B Amylose |
front 36 Which of the following complex carbohydrates is listed with its correct function? A) Amylose: main component of plant starch B) Chitin: constituent of bacterial cell walls C) Cellulose: structural component of plant cell walls D) Starch: primary energy-storage molecule in animals | back 36 correct answer : C Cellulose: structural component of plant cell walls |
front 37 Which polysaccharide contains a modified monosaccharide? A) Peptidoglycan B) Starch C) Cellulose D) Glycogen | back 37 correct answer : A Peptidoglycan |
front 38 Glycogen is _____. A) the form in which plants store sugars B) a source of saturated fat C) a polysaccharide found in plant cell walls D) a transport protein that carries oxygen E) a polysaccharide found in animals | back 38 correct answer : E a polysaccharide found in animals |
front 39 glucose + glucose —> _____ by _____. A) maltose + water ... dehydration synthesis B) sucrose + water ... dehydration synthesis C) cellulose + water ... hydrolysis D) lactose + water ... hydrolysis E) starch + water ... dehydration synthesis | back 39 correct answer : A maltose + water ... dehydration synthesis |
front 40 Which of these is a source of lactose? A) starch B) potatoes C) milk D) sugar beets E) sugar cane | back 40 correct answer : C milk |
front 41 Which of these is a polysaccharide? A) cellulose B) lactose C) galactose D) glucose E) sucrose | back 41 correct answer : A cellulose |
front 42 _____ is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. A) Glycogen B) Lactose C) Cellulose D) Glucose E) Starch | back 42 correct answer : C Cellulose |
front 43 Starch and cellulose ________. A) are polymers of glucose B) are structural components of the plant cell wall C) are used for energy storage in plants and animals D) are cis and trans isomers of each other | back 43 correct answer : A are polymers of glucose |
front 44 People who are lactose intolerant cannot extract energy from milk because ________. A) milk is fermented to a by-product, which cannot be digested B) lactose is too big to be digested by the enzymes C) they are missing an enzyme D) they are missing the bacteria that can digest lactose | back 44 correct answer : C they are missing an enzyme |
front 45 The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? A) C18H36O18 B) C18H32O16 C) C6H10O5 D) C18H30O15 | back 45 correct answer : B C18H32O16 |
front 46 What does the term insoluble fiber refer to on food packages? A) cellulose B) amylopectin C) starch D) polypeptides | back 46 correct answer : A cellulose |
front 47 A molecule with the chemical formula C6H12O6 is probably a _____. A) polysaccharide B) monosaccharide C) nucleic acid D) fatty acid | back 47 correct answer : B monosaccharide |
front 48 Which of these is NOT a lipid? A) wax B) phospholipid C) cholesterol D) RNA E) steroids | back 48 Correct answer : D RNA |
front 49 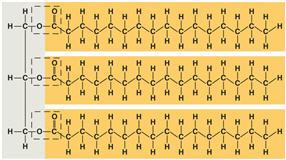 This figure is an example of a(n) _____. A) nucleic acid B) steroid C) saturated fat D) protein E) unsaturated fat | back 49 correct answer : C saturated fat |
front 50 Which of these is rich in unsaturated fats? A) Lard B) olive oil C) beef fat D) a fat that is solid at room temperature E) butter | back 50 correct answer : B olive oil |
front 51 A function of cholesterol that does not harm health is its role _____. A) as a component of animal cell membranes B) the most abundant male sex hormone C) All of cholesterol's effects cause the body harm. D) as the primary female sex hormone E) in calcium and phosphate metabolism | back 51 correct answer : A as a component of animal cell membranes |
front 52 What makes lipids/fats hydrophobic? A) their long carbon skeleton B) presence of relatively nonpolar CH bonds C) the glycerol moiety D) the carboxyl group at one end of the molecule | back 52 correct answer : B presence of relatively nonpolar CH bonds |
front 53 For lipids to be fluid at room temperature, they should have ________. A) a higher number of cis double bonds B) a higher number of glycerol molecules C) a longer carbon chain D) single bonds only | back 53 correct answer : A a higher number of cis double bonds |
front 54 How do phospholipids interact with water molecules? A) Phospholipids do not interact with water because water is polar and lipids are nonpolar. B) The polar heads avoid water; the nonpolar tails attract water (because water is polar and opposites attract). C) Phospholipids dissolve in water. D) The polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not. | back 54 correct answer : D The polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not. |
front 55 Phospholipids and triglycerides both _____. A) contain serine or some other organic compound B) have three fatty acids C) have a phosphate D) have a glycerol backbone | back 55 correct answer : D have a glycerol backbone |
front 56 Which of the following could be responsible for atherosclerosis and should be eliminated from diet for health reasons? A) butter B) olive oil C) lard D) butter and lard | back 56 correct answer : D butter and lard |
front 57 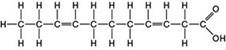 The molecule illustrated in the figure ________. A) is a saturated fatty acid B) is a carbohydrate C) stores genetic information D) will be liquid at room temperature | back 57 correct answer : D is a saturated fatty acidis a carbohydratestores genetic informationwill be liquid at room temperature |
front 58 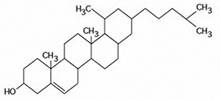 The molecule shown the figure is a ________. A) steroid B) fatty acid C) phospholipid D) triacylglycerol | back 58 correct answer: A steroid |
front 59 In fat synthesis,________and fatty acids combine to make fats plus________. A) glycerol; water B) glucose; phosphate C) esters; water D) esters; phosphate E) phosphate; glycerol | back 59 correct answer : A glycerol; water |
front 60 In the reaction that builds a fat,________ groups react with ________ groups. A) hydroxyl; carboxyl B) sulfhydryl; carboxyl C) phosphate; amino D) carboxyl; amino E) hydroxyl; phosphate | back 60 correct answer : A hydroxyl; carboxyl |
front 61 A food company hydrogenated a barrel of fat. The treatment ... A) made the fat less fluid. B) made the fat less saturated. C) lengthened the fat tails. D) put more bends (kinks) in the fat tails. E) Both (a) and (d). | back 61 correct answer : A made the fat less fluid. |
front 62 The most unsaturated fats have ... A) the shortest hydrocarbon tails. B) the highest ratio of H to C. C) the fewest double bonds. D) the most double bonds. E) the longest hydrocarbon tails. | back 62 correct answer : D the most double bonds. |
front 63 What do DNA, proteins, and fats have in common? A) They contain carbonyl groups. B) They contain phosphorus. C) They are polymers. D) They are polar. E) They contain nitrogen. | back 63 correct answer : A They contain carbonyl groups. |
front 64 A dehydration reaction (or condensation reaction) is the process in which _____. A) water molecules are attracted to each other B) water molecules are used as a source of raw material to break down polymers to monomers C) the bonds between the individual monomers of a polymer are broken by the addition of water molecules D) water molecules are produced as a polymer is formed from monomers E) None of the choices is correct. | back 64 correct answer : D water molecules are produced as a polymer is formed from monomers |
front 65 Which of the following is not a polymer? A) RNA B) glucose C) starch D) DNA | back 65 correct answer : B glucose |
front 66 Which of the following shows the flow of genetic information? A) DNA to RNA to ribosomes B) protein to RNA to DNA C) DNA to RNA to protein D) RNA to DNA to protein | back 66 correct answer : C DNA to RNA to protein |
front 67 Which of the following clues would tell you if a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic? A) whether or not the cell is compartmentalized by internal membranes B) the presence or absence of ribosomes C) whether the cell contains DNA or RNA D) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall | back 67 correct answer : A whether or not the cell is compartmentalized by internal membranes |
front 68 The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is? A) changeable, depending on the amino acid that attaches to the tRNA. B) complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. C) the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid. D) complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA. E) catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme. | back 68 correct answer : B complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. |
front 69 Which of the following DNA mutations is most likely to damage the protein it specifies? A) an addition of three nucleotides B) a substitution in the last base of a codon C) a codon deletion D) a base-pair deletion | back 69 correct answer : D a base-pair deletion |
front 70 How might a single base substitution in the sequence of a gene affect the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by the gene? A) The amino acid sequence would be substantially altered, because the reading frame would change with a single base substitution. B) All amino acids following the substitution would be affected, because the reading frame would be shifted. C) It is not possible for a single base substitution to affect protein structure, because each codon is three bases long. D) Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame would be unaffected. | back 70 correct answer : D Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame would be unaffected. |
front 71 Which of the following statements correctly describes the effect a nonsense mutation would have on a gene? A) It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA. B) It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein. C) It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein. D) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA. | back 71 correct answer: A It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA. |
front 72 Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product? A) a deletion of two nucleotides B) a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon C) a deletion of a codon D) a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon | back 72 correct answer: A a deletion of two nucleotides |
front 73 Where does translation take place? A) Ribosome B) Golgi apparatus C) Endoplasmic reticulum D) Nucleus | back 73 correct answer : A Ribosome |
front 74 Which nucleic acid is translated to make a protein? A) rRNA B) tRNA C) mRNA D) DNA | back 74 correct answer : C mRNA |
front 75 Which of the following processes is an example of a post-translational modification? A) Phosphorylation B) Initiation C) Peptide bond formation D) Elongation | back 75 correct answer : A Phosphorylation |
front 76 Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation? A) The large ribosomal subunit joins the complex. B) The small subunit of the ribosome binds to the 5’ cap on the mRNA. C) A peptide bond is formed between two adjacent amino acids. D) An aminoacyl tRNA binds to the start codon | back 76 correct answer : A The large ribosomal subunit joins the complex. |
front 77 At which site do new aminoacyl tRNAs enter the ribosome during elongation? A) P-site B) A-site C) B-site D) E-site | back 77 correct answer : B A-site |
front 78 What is meant by translocation? A) The two ribosomal subunits are joined in a complex. B) The completed polypeptide is released from the ribosome. C) The ribosome slides one codon down the mRNA. D) The polypeptide chain grows by one amino acid. | back 78 correct answer : C The ribosome slides one codon down the mRNA. |
front 79 True or false. A tRNA with an anticodon complementary to the stop codon catalyzes the reaction by which translation is terminated. A) true B) false | back 79 correct answer : B false |
front 80 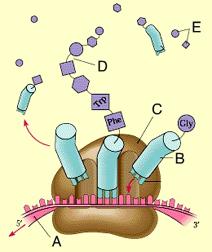 Which of these is a tRNA? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E | back 80 correct answer : B B |
front 81 What enzyme catalyzes the attachment of an amino acid to tRNA? A) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase B) rubisco C) dextrinase D) arginino E) succinate lyase nuclease | back 81 correct answer : A aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase |
front 82 The tRNA anticodon, GAC, is complementary to the mRNA codon with the sequence _____. A) CAG B) CTG C) GAC D) CUG E) TCG | back 82 correct answer : D CUG |
front 83 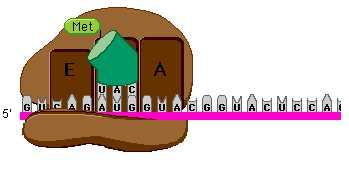 What is the name of the process shown in the diagram? A) initiation (of transcription) B) RNA processing C) initiation (of translation) D) elongation E) termination (of translation) | back 83 correct answer : C initiation (of translation) |
front 84 The initiator tRNA attaches at the ribosome's _____ site. A) A B) translocation C) E D) P E) Q | back 84 correct answer : D P |
front 85 A particular triplet of bases in the coding strand of DNA is AAA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds this mRNA codon is _____. A) UUU B) TTT C) UUA D) AAA | back 85 correct answer : A UUU |
front 86 Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on specificity in the _____. A) binding of the anticodon to small subunit of the ribosome B) attachment of amino acids to rRNAs C) binding of ribosomes to mRNA D) binding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs | back 86 correct answer : D binding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs |
front 87 What is the function of the release factor during translation in eukaryotes? A) It releases the ribosome from the ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol. B) It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA. C) It supplies a source of energy for termination of translation. D) It releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form a peptide bond. | back 87 correct answer : B It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA |
front 88 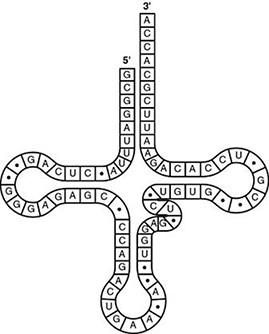 What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule shown in the figure? A) peptide bonding between amino acids B) hydrogen bonding between base pairs C) van der Waals interactions between hydrogen atoms D) ionic bonding between phosphates | back 88 correct answer : B hydrogen bonding between base pairs |
front 89 The flow of information in a cell proceeds in what sequence? A) from DNA to RNA to protein B) from RNA to DNA to protein C) from RNA to protein to DNA D) from protein to RNA to DNA E) from DNA to protein to RNA | back 89 correct answer : A from DNA to RNA to protein |
front 90 A codon consists of _____ bases and specifies which _____ will be inserted into the polypeptide chain. A) two ... nucleotide B) four ... fatty acid C) three ... nucleotide D) three ... amino acid E) four ... amino acid | back 90 correct answer : D three ... amino acid |
front 91 The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume which of the following statements to be true? A) DNA was the first genetic material. B) The same codons in different organisms translate into different amino acids. C) Different organisms have different types of amino acids. D) A gene from an organism can theoretically be expressed by any other organism. | back 91 correct answer : D A gene from an organism can theoretically be expressed by any other organism |
front 92 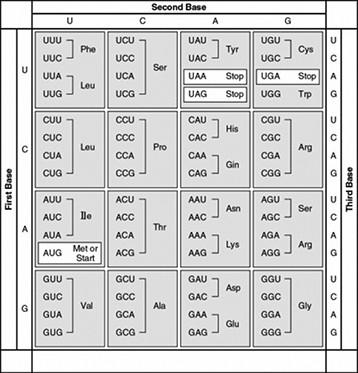 What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following
mRNA codon sequence? A) Met-Arg-Glu-Arg-Glu-Arg B) Met-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser C) Met-Glu-Arg-Arg-Glu-Leu D) Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu | back 92 correct answer : D Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu |
front 93 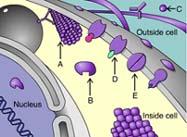 Arrow A is indicating a(n) _____ protein. A) transport B) enzyme C) signal D) receptor E) structural | back 93 correct answer : E structural |
front 94  Arrow D is indicating a _____ protein. A) receptor B) defensive C) transport D) gene regulatory E) storage | back 94 correct answer : A receptor |
front 95 Which of these does NOT contain a structural protein? A) muscles B) ovalbumin C) spider silk D) tendons E) ligaments | back 95 correct answer : B ovalbumin |
front 96 Defensive proteins are manufactured by the _____ system. A) cardiovascular B) integumentary C) immune D) nervous E) digestive | back 96 correct answer : C immune |
front 97 Proteins are polymers of _____. A) amino acids B) hydrocarbons C) CH2O units D) nucleotides E) glycerol | back 97 correct answer : A amino acids |
front 98 What type of bond joins the monomers in a protein's primary structure? A) peptide B) hydrophobic C) S - S D) ionic E) hydrogen | back 98 correct answer : A peptide |
front 99 The secondary structure of a protein results from _____. A) hydrophobic interactions B) hydrogen bonds C) peptide bonds D) ionic bonds E) bonds between sulfur atoms | back 99 correct answer : B hydrogen bonds |
front 100 Tertiary structure is NOT directly dependent on _____. A) hydrophobic interactions B) hydrogen bonds C) bonds between sulfur atoms D) ionic bonds E) peptide bonds | back 100 correct answer : E peptide bonds |
front 101 What component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids? A) the presence of a central C atom B) the glycerol molecule that forms the backbone of the amino acid C) the long carbon-hydrogen tails of the molecule D) the components of the R group | back 101 correct answer : D the components of the R group |
front 102 You disrupt all hydrogen bonds in a protein. What level of structure will be preserved? A) primary structure B) secondary structure C) tertiary structure D) quaternary structure | back 102 correct answer : A primary structure |
front 103 You have just sequenced a new protein found in mice and observe that sulfur-containing cysteine residues occur at regular intervals. What is the significance of this finding? A) Cysteine residues are involved in disulfide bridges that help form tertiary structure. B) Cysteine causes bends, or angles, to occur in the tertiary structure of proteins. C) Cysteine residues are required for the formation of α-helices and β-pleated sheets. D) It will be important to include cysteine in the diet of the mice | back 103 correct answer : A Cysteine residues are involved in disulfide bridges that help form tertiary structur |
front 104 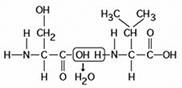 The chemical reaction illustrated ________. A) joins two fatty acids together B) is a hydrolysis reaction C) results in a peptide bond D) links two polymers to form a monomer | back 104 correct answer : C results in a peptide bond |
front 105 Which of the following provides the information necessary to stipulate a protein's 3-D shape? A)sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain B) peptide bonds between different amino acids C) number of water molecules in the vicinity D) side chains of various amino acids | back 105 correct answer : A sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain |
front 106 Which feature of large biological molecules explains their great diversity? A) The many classes of large biological molecules B) The many ways that monomers of each class of biological molecule can be combined into polymers C) The diversity of elements found in large biological molecules | back 106 correct answer : B The many ways that monomers of each class of biological molecule can be combined into polymers |
front 107 Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides? A) a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine B) a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar C) a nitrogenous base and a sugar D) a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group | back 107 correct answer : B a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar |
front 108 Which of the following statements about the 5 end of a polynucleotide strand of RNA is correct? A) The 5 end has phosphate attached to the number 5 carbon of the nitrogenous base. B) The 5 end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. C) The 5 end has a hydroxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. D) The 5 end has a carboxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. | back 108 correct answer : B The 5 end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. |
front 109 Which molecule is a nucleotide? A) Deoxyribose B) ATP C) The amino acid glycine | back 109 correct answer : B ATP |
front 110 When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid _____. A) a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second B) hydrogen bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides C) covalent bonds form between the bases of two nucleotides D) a hydrogen bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second | back 110 correct answer : A a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second |
front 111 Which of the following is a major difference between RNA and DNA? A) type of phosphate B) type of purines C) type of glycosidic bond D) type of sugar | back 111 correct answer : D type of sugar |
front 112 If a strand of DNA has the nitrogen base sequence 5'-ATTTGC-3', what will be the sequence of the matching strand? A) 3'-TUUUCG-5' B) 3'-GCAAAT-5' C) 3'-TAAACG-5' D) 3'-ATTTGC-5' E) 3'-UAAACG-5' | back 112 correct answer : C 3'-TAAACG-5' |
front 113 If a DNA double helix is 100 nucleotide pairs long and contains 25 adenine bases, how many guanine bases does it contain? A) 150 B) 25 C) 75 D) 200 E) 50 | back 113 correct answer : C 75 |
front 114 The two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ that form between pairs of nitrogenous bases. A) hydrogen bonds B) S—S bonds C) hydrophilic interactions D) ionic bonds E) covalent bonds | back 114 correct answer : A hydrogen bonds |
front 115 A nucleotide is composed of a(n) _____. A) glycerol, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar B) sulfhydryl group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar C) amino group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar D) phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a hydrocarbon E) phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar | back 115 correct answer : E phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and a five-carbon sugar |
front 116 Some regions of a polypeptide may coil or fold back on themselves. This is called _____, and the coils or folds are held in place by _____. A) secondary structure ... peptide bonds B) tertiary structure ... covalent bonds C) secondary structure ... hydrogen bonds D) primary structure ... covalent bonds E) tertiary structure ... hydrogen bonds | back 116 correct answer : C secondary structure ... hydrogen bonds |
front 117 A hydrophobic amino acid R group (side group) would be found where in a protein? A) forming hydrogen bonds with other R groups B) on the inside of the folded chain, away from water C) only at one end of a protein chain D) forming a peptide bond with the next amino acid in the polypeptide chain E) on the outside of the folded chain, in the water | back 117 correct answer : B on the inside of the folded chain, away from water |
front 118 Which parts of the amino acids X and Y are involved in the formation
of a peptide bond? A) carboxyl group of X and side chain of Y B) side chains of both X and Y C) carboxyl group of X and amino group of Y D) amino group of X and carboxyl group of Y | back 118 correct answer : C carboxyl group of X and amino group of Y |
front 119 A tripeptide has ________. A) three amino acids and three peptide bonds B) three amino acids and two peptide bonds C) two amino acids and three peptide bonds D) four amino acids and three peptide bonds | back 119 correct answer : B three amino acids and two peptide bonds |
front 120 Which of the following statements is true about proteins? A) Denaturation is always irreversible B) Final folded structure can reveal the steps of protein folding C) Denaturation leads to bond disruption, and the molecule turns into liquid D) Some proteins form a complete 3-D structure only when they interact with their targets | back 120 correct answer : D Some proteins form a complete 3-D structure only when they interact with their targets |
front 121 In sickle-cell disease, as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant hemoglobin tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibers. Based on this information alone, we can conclude that sickle-cell hemoglobin exhibits ________. A) only altered quaternary structure B) only altered primary structure C) only altered tertiary structure D) altered primary structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary structures may or may not be altered | back 121 correct answer : D altered primary structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary structures may or may not be altered |
front 122 Misfolding of polypeptides is a serious problem in cells. Which of the following diseases are associated with an accumulation of misfolded polypeptides? A) Parkinson's B) Alzheimer's C) diabetes mellitus D) Alzheimer's and Parkinson's | back 122 correct answer : D Alzheimer's and Parkinson's |
front 123 Homo sapiens have 23 pairs of chromosomes. This implies that ________. A) 23 single-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell B) 23 double-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell C) several hundreds of genes are present on DNA but not on the chromosomes D) 46 double-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell | back 123 correct answer : D 46 double-stranded DNA molecules are present in each somatic cell |
front 124 The flow of genetic information in a cell goes from _____. A) protein to RNA to DNA B) DNA to lipid to protein C) DNA to RNA to protein D) DNA to RNA to glucose E) DNA to ribosomes to RNA | back 124 correct answer : C DNA to RNA to protein |
front 125 The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called _____. A) DNA and RNA B) polysaccharides C) fatty acids D) pyrimidines and purines E) nucleotides | back 125 correct answer : E nucleotides |
front 126 One of the primary functions of RNA molecules is to _____. A) transmit genetic information to offspring B) function in the synthesis of proteins C) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity D) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA | back 126 correct answer : B function in the synthesis of proteins |
front 127 If 14C-labeled uracil is added to the growth medium of cells, what macromolecules will be labeled? A) both DNA and RNA B) RNA C) polypeptides D) DNA | back 127 correct answer : B RNA |
front 128 In an RNA sample, ________. A) the number of purine may or may not equal the number of and pyrimidine B) the number of thymine may or may not equal the number of adenine C) the number of thymine always equals the number of uracil D) the number of purine always equals the number of pyrimidine | back 128 correct answer : A the number of purine may or may not equal the number of and pyrimidine |