Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Thorax & Abdomen
front 1 Correct preparation for a patient scheduled for an upper gastrointestinal (GI) series is most likely to be | back 1 NPO after midnight |
front 2  The position shown in Figure A is known as | back 2 left lateral decubitus. |
front 3 Which of the following statements is (are) correct with respect to evaluation criteria for a PA projection of the chest for lungs?
| back 3 1 and 2 only |
front 4 The type of ileus characterized by cessation of peristalsis is termed | back 4 paralytic |
front 5 Which of the following positions is most likely to place the right kidney parallel to the IR? | back 5 LPO |
front 6 Which of the following statements is (are) correct, with respect to a left lateral projection of the chest?
| back 6 1, 2, and 3 |
front 7 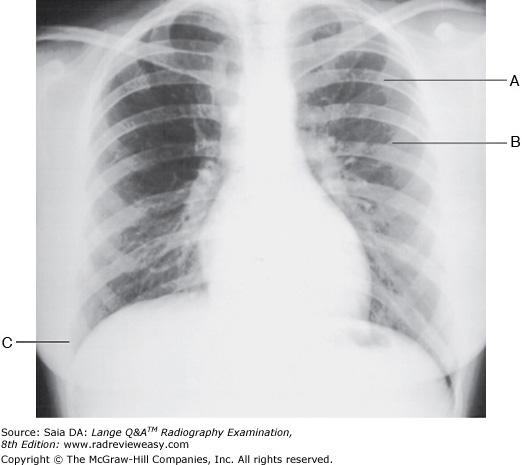 The PA chest radiograph shown in the figure below demonstrates
| back 7 1, 2, and 3 |
front 8 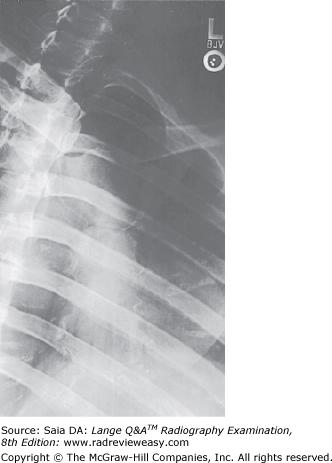 Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the figure below?
| back 8 2 and 3 only |
front 9 Which of the following anatomic structures is best demonstrated in the LPO position, in a positive-contrast exam? | back 9 Hepatic flexure |
front 10
Involuntary motion can be caused by 2. severe pain. 3. heart muscle contraction. | back 10 1, 2, and 3 |
front 11 All the following statements regarding large bowel radiography are true except | back 11 single-contrast studies help to demonstrate intraluminal lesions. |
front 12 Which of the following procedures will best demonstrate the cephalic, basilic, and subclavian veins? | back 12 Upper-limb venogram |
front 13
Which of the following positions will demonstrate the
right axillary ribs? | back 13 2 and 3 only |
front 14 During chest radiography, the act of inspiration | back 14 2 and 3 only |
front 15 Which of the following is (are) part of the bony thorax?
| back 15 1 and 3 only |
front 16
Operative cholangiography may be performed to
2. determine function of the hepatopancreatic ampulla. 3. examine the patency of the biliary tract. | back 16 1, 2, and 3 |
front 17 Free air in the abdominal cavity is best demonstrated in which of the following positions? | back 17 AP projection, left lateral decubitus position |
front 18 Which of the following radiologic examinations can demonstrate ureteral reflux? | back 18 Voiding cystourethrogram |
front 19
What instructions might a patient be given following an
upper GI examination? 2. Take a mild laxative. 3. Increase dietary fiber. | back 19 1, 2, and 3 |
front 20 Widening of the intercostal spaces is characteristic of which of the following conditions? | back 20 Emphysema |
front 21 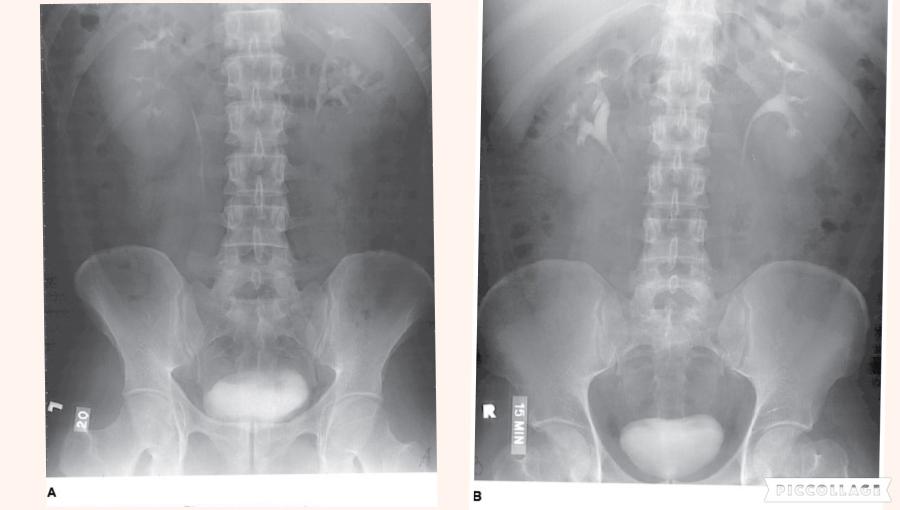 Which of the following statements referring to the images below is (are) correct?
| back 21 2 only |
front 22 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) usually involves
| back 22 1 and 2 only |
front 23 The thoracic cavity is lined by | back 23 parietal pleura. |
front 24 During IV urography, the prone position generally is recommended to demonstrate
| back 24 1 and 2 only |
front 25 All the following positions are likely to be employed for both single- and double-contrast examinations of the large bowel except | back 25 right and left lateral decubitus abdomen. |
front 26 Which of the following positions can be used to demonstrate the
axillary ribs of the right thorax? | back 26 2 and 3 only |
front 27 All of the following statements regarding the RAO position of the sternum are true, except | back 27 a thin thorax requires a lesser degree of obliquity than a thicker thorax. |
front 28 What is the position of the stomach in a hypersthenic patient? | back 28 High and horizontal |
front 29 Which of the following examinations require(s) restriction of a patient's diet?
| back 29 1 and 2 only |
front 30
Free air in the abdominal cavity is demonstrated in
which of the following? 2. Erect AP abdomen 3. Left lateral decubitus abdomen | back 30 2 and 3 only |
front 31 The pyloric canal and duodenal bulb are best demonstrated during an upper GI series in which of the following positions? | back 31 RAO |
front 32 The ridge that marks the bifurcation of the trachea into the right and left primary bronchi is the | back 32 Carina |
front 33 Following the ingestion of a fatty meal, what hormone is secreted by the duodenal mucosa to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder? | back 33 Cholecystokinin |
front 34 Which of the following structures will usually contain air, in the PA recumbent position on a sthenic patient, during a double-contrast upper GI (UGI) examination? | back 34 Gastric fundus |
front 35 Inspiration and expiration projections of the chest are performed to demonstrate
| back 35 1, 2, and 3 |
front 36 Which of the following examinations most likely would be performed to diagnose Wilm's tumor? | back 36 IVU |
front 37 Which of the following structures will be filled with barium in the AP recumbent position of a sthenic patient during an upper GI examination? | back 37 Gastric fundus |
front 38 When the erect position is requested as part of an IVU, it is used to demonstrate | back 38 kidney mobility. |
front 39 The condition in which pulmonary alveoli lose their elasticity and become permanently inflated, causing the patient to consciously exhale, is | back 39 emphysema |
front 40 A patient suffering from orthopnea would experience the least discomfort in which body position? | back 40 Erect |
front 41 To demonstrate the pulmonary apices with the patient in the AP position, the | back 41 central ray is directed 15° to 20° cephalad. |
front 42 The sternoclavicular joints will be best demonstrated in which of the following positions? | back 42 Anterior oblique |
front 43 Which of the following positions will move the fundus of the gallbladder shown in Figure 7–6 away from the superimposed transverse process? | back 43 LAO |
front 44  Which of the following is represented by the number 3 in the figure below? | back 44 Aorta |
front 45 Which of the following will be demonstrated best in the 45-degree right anterior oblique (RAO) position? | back 45 Left axillary ribs |
front 46 A lesion with a stalk projecting from the intestinal mucosa into the lumen is a(n) | back 46 polyp |
front 47 An aspirated foreign body is more likely to enter the lower respiratory tract via the | back 47 right main stem bronchus. |
front 48 Which of the following positions is most likely to offer the best visualization of the pulmonary apices? | back 48 AP axial lordotic |
front 49 The stomach of an asthenic patient is most likely to be located | back 49 low, vertical, and toward the midline. |
front 50 Which of the following positions will most effectively move the gallbladder away from the vertebrae in an asthenic patient? | back 50 LAO |
front 51 An esophagram would most likely be requested for patients with which
of the following esophageal disorders/symptoms? | back 51 1 and 2 only |
front 52 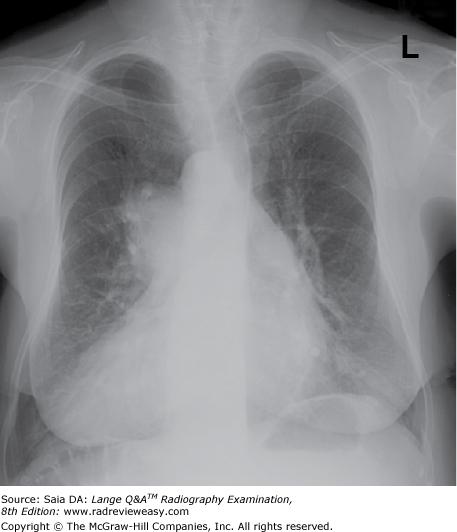 The figure below demonstrates which of the following conditions? | back 52 dextrocardia |
front 53 For the average patient, the CR for a lateral projection of a barium-filled stomach should enter | back 53 midway between the midcoronal line and the anterior abdominal surface |
front 54 Which type of articulation is evaluated in arthrography? | back 54 Diarthrodial |
front 55 Which of the following equipment is mandatory for performance of a myelogram? | back 55 Tilting x-ray table |
front 56 Which of the following positions is required to demonstrate small amounts of air in the peritoneal cavity? | back 56 Lateral decubitus, affected side up |
front 57 To obtain an exact axial projection of the clavicle, place the patient | back 57 in a lordotic position and direct the central ray at right angles to the coronal plane of the clavicle. |
front 58 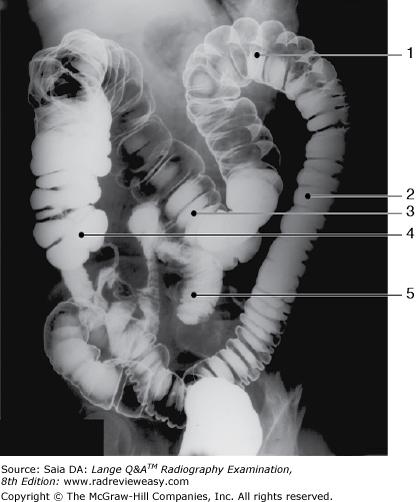 The structure indicated by the number 5 in Figure 6–11 is the | back 58 ileum. |
front 59 Deoxygenated blood from the head and thorax is returned to the heart by the | back 59 superior vena cava |
front 60 Below-diaphragm ribs are better demonstrated when | back 60 the patient is in the recumbent position. |
front 61 In which of the following conditions is a double-contrast BE essential for demonstration of the condition?
| back 61 1 and 2 only |
front 62 A patient is usually required to drink barium sulfate suspension to
demonstrate which of the following structures? 2. Pylorus 3. Ilium | back 62 1 and 2 only |
front 63 Which of the following are mediastinal structures?
| back 63 1, 2, and 3 |
front 64 Which of the following radiologic procedures requires that a contrast medium be injected into the renal pelvis via a catheter placed within the ureter? | back 64 Retrograde urography |
front 65 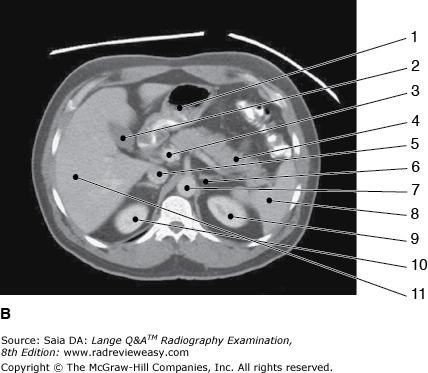 The structure labeled number 2 in Figure 6–3, image B is the | back 65 gallbladder |
front 66
Which of the following conditions would
require an increase in exposure factors? 2. Pleural effusion 3. Emphysema | back 66 1 and 2 only |
front 67 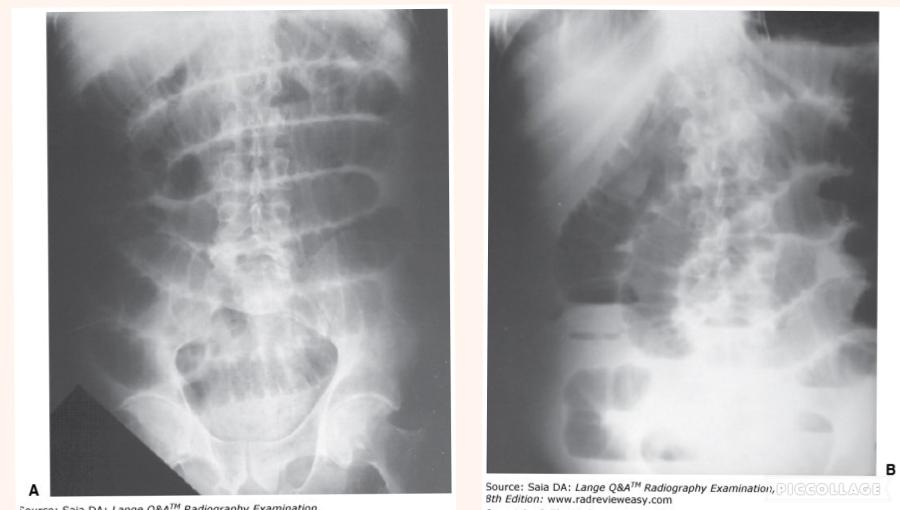 Which of the radiographs shown in Figure 4–5 most likely required the greater exposure? | back 67 Image B |
front 68 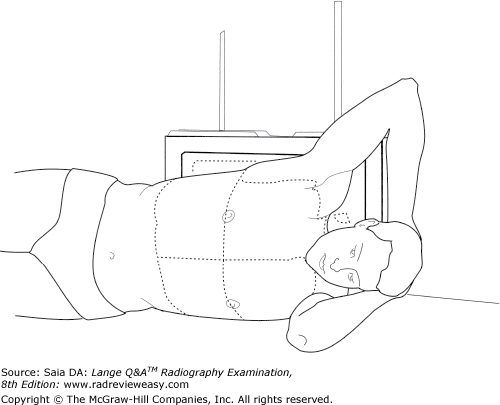 All the following statements regarding the position shown in Figure 2–17 are true except | back 68 the CR is directed vertically to the level of T7. |
front 69 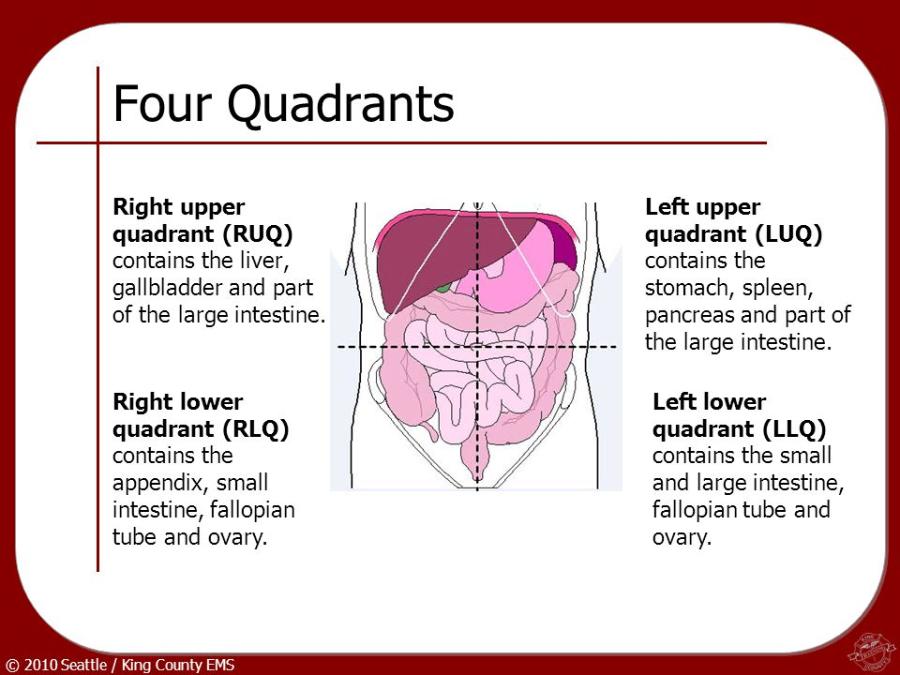 Which of the following structures is (are) located in the right upper
quadrant (RUQ)? | back 69 2 and 3 only |
front 70 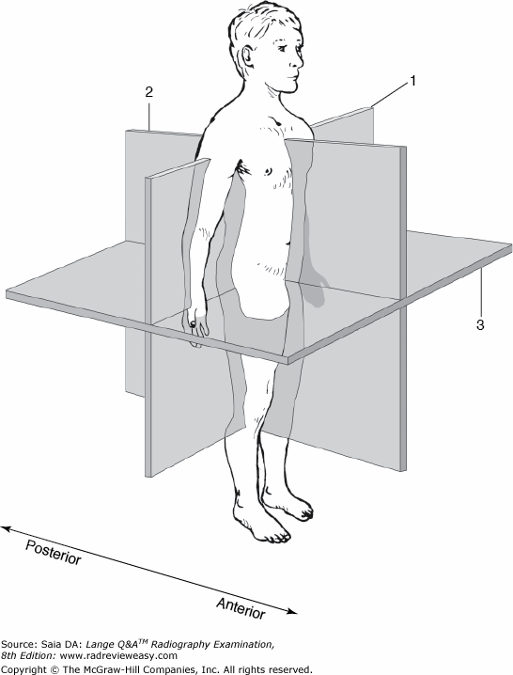 What is the name of the plane indicated by the number 1 in Figure 6–17? | back 70 Midcoronal plane |
front 71 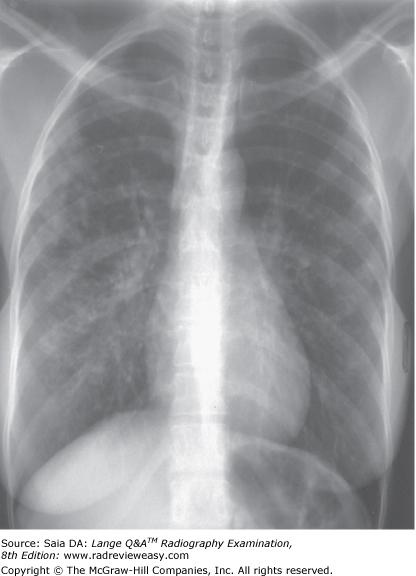 The PA chest image shown in Figure 4–13 exhibits which of the following qualities?
| back 71 1, 2, and 3 |
front 72 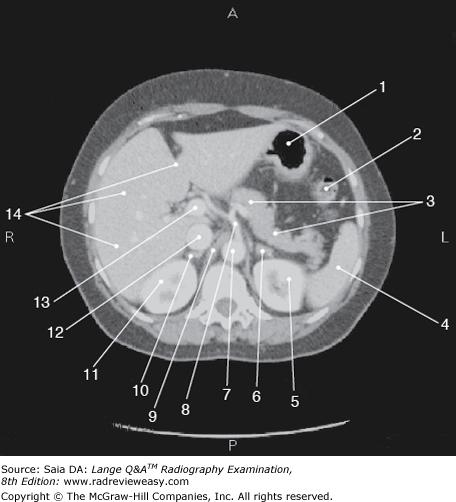 The figure below illustrates a sectional image of the abdomen. Which of the following is represented by the number 13? | back 72 Portal vein |
front 73 Dorsal decubitus projections of the chest are used to evaluate small amounts of
| back 73 1 only |
front 74 Which of the following radiologic examinations requires preparation consisting of a low-residue diet, cathartics, and enemas? | back 74 Barium enema (BE) |
front 75 Which of the following techniques would provide a posteroanterior (PA) projection of the gastroduodenal surfaces of a barium-filled high and transverse stomach? | back 75 Angle the CR 35 to 45 degrees cephalad. |
front 76 Which of the following equipment is necessary for ERCP?
| back 76 1, 2, and 3 |
front 77
Which projection(s) of the abdomen would be used to
demonstrate pneumoperitoneum? 2. Left lateral decubitus 3. Upright | back 77 2 and 3 only |
front 78 Which of the following structures is (are) located in the right upper quadrant (RUQ)?
| back 78 1 and 2 only |
front 79 Moderate hypertension can produce damage to which of the following organs? 1. Lungs 2. Kidneys 3. Brain | back 79 1, 2, and 3 |
front 80 In what order should the following examinations be scheduled?
| back 80 2, 3, 1 |
front 81 Which of the following is the preferred scheduling sequence? | back 81 Abdomen ultrasound, lower GI series, upper GI series |
front 82 During studies of the soft tissue of the neck, the exposure can be
made 2. during Valsalva maneuver. 3. at the height of swallowing motion with opacification. A 1 only | back 82 1, 2, and 3 |
front 83 The body habitus characterized by a long and narrow thoracic cavity and low midline stomach and gallbladder is the | back 83 asthenic |
front 84 Which of the following is (are) evaluation criteria for a PA chest radiograph of the heart and lungs?
| back 84 1 and 2 only |
front 85 In a posteroanterior (PA) projection of the chest being used for cardiac evaluation, the heart measures 14.7 cm between its widest points. If the magnification factor is known to be 1.2, what is the actual diameter of the heart? | back 85 12.25 cm |
front 86 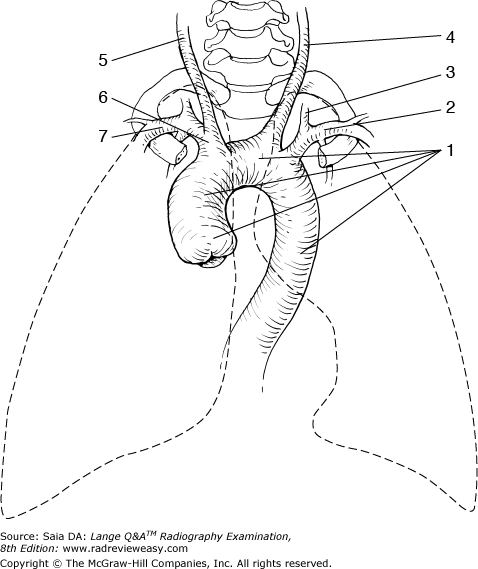 The structure labeled number 6 in Figure 2–39 is the | back 86 brachiocephalic artery |
front 87 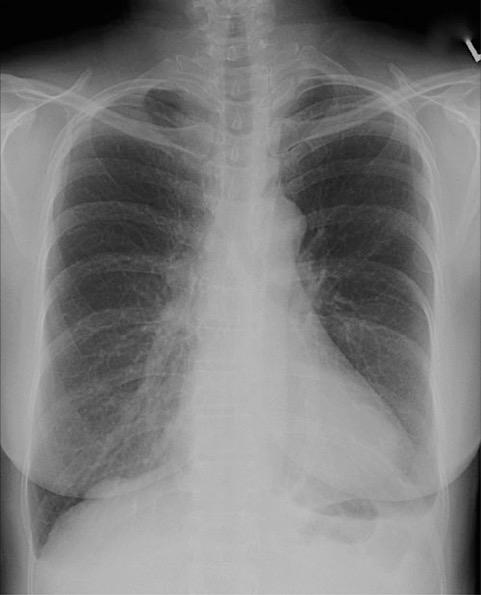 Which of the following statements with respect to the PA chest seen in Figure 2–11 is (are) correct?
| back 87 1, 2, and 3 |
front 88 Double-contrast examinations of the stomach or large bowel are performed to better visualize the | back 88 gastric or bowel mucosa |
front 89 To radiograph an infant for suspected free air within the abdominal cavity, which of the following projections of the abdomen will demonstrate the condition with the least patient exposure? | back 89 Left lateral decubitus without grid |
front 90 In myelography, the contrast medium generally is injected into the | back 90 subarachnoid space between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae |
front 91 Which of the following pathologic conditions probably will require a decrease in exposure factors? | back 91 Osteoporosis |
front 92 The AP axial projection of the pulmonary apices requires the CR to be directed | back 92 15 degrees cephalad |
front 93 Which of the following is the most likely site for a lumbar puncture? | back 93 L3–4 |
front 94 With the patient recumbent on the x-ray table with the head lower than the feet, the patient is said to be in the | back 94 Trendelenburg position |
front 95 Fluoroscopic imaging of the ileocecal valve is generally part of a(n) | back 95 small-bowel series. |
front 96 What is the position of the gallbladder in an asthenic patient? | back 96 Inferior and medial |
front 97 The usual patient preparation for an upper GI examination is | back 97 nothing by mouth (NPO) 8 hours before the examination. |
front 98 The act of expiration will cause the
| back 98 2 and 3 only |
front 99 Routine excretory urography usually includes a postmicturition
radiograph of the bladder. This is done to demonstrate | back 99 1, 2, and 3 |
front 100 During endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) examination, contrast medium is injected into the | back 100 common bile duct |
front 101 Moderate hypertension can produce damage to which of the following organ(s) 1. Lungs 2. Kidneys 3. Brain | back 101 1 2 and 3 |
front 102 How should a chest examination to rule out air–fluid levels be obtained on a patient having traumatic injuries? | back 102 Include a lateral chest examination performed in dorsal decubitus position. |
front 103 A flat and upright abdomen is requested on an acutely ill patient, to demonstrate the presence of air-fluid levels. Because of the patient's condition, the x-ray table can be tilted upright only 70° (rather than the desired 90°). How should the central ray be directed? | back 103 Parallel to the floor |
front 104
What are the positions most commonly employed for a
radiographic examination of the sternum? 2. RAO 3. LAO | back 104 1 and 2 only |
front 105 Which of the following positions is required to demonstrate small amounts of air in the pleural cavity? | back 105 Lateral decubitus, affected side up |
front 106 An increase in exposure factors usually is required in which of the following circumstances?
| back 106 1, 2, and 3 |
front 107 Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the CR image artifact seen in the erect PA projection of the chest shown in Figure 4–31? The object is located within the IP. | back 107 The object is located within the IP. |
front 108 Which of the following is a radiologic procedure that functions to dilate a stenotic vessel? | back 108 Percutaneous angioplasty |
front 109 Place the following anatomic structures in order from anterior to posterior: 1. | back 109 Apex of heart, trachea, esophagus |
front 110 The following instructions should be given to a patient following a
barium sulfate contrast examination: | back 110 1, 2, and 3 |
front 111
During an upper gastrointestinal (GI) examination, the
AP recumbent projection of a stomach of average shape will usually
demonstrate 2. barium-filled fundus. 3. double-contrast body and antral portions. | back 111 2 and 3 only |
front 112 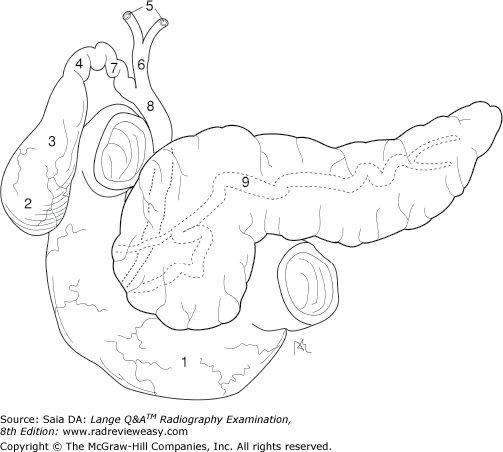 What is the structure indicated by the number 8 in Figure 2–18? | back 112 Common bile duct |
front 113 Which of the following positions may be used to effectively demonstrate the right posterior axillary ribs? | back 113 RPO |
front 114 In which of the following procedures is quiet, shallow breathing recommended during the exposure to obliterate prominent pulmonary vascular markings?
| back 114 1, 2, and 3 |
front 115 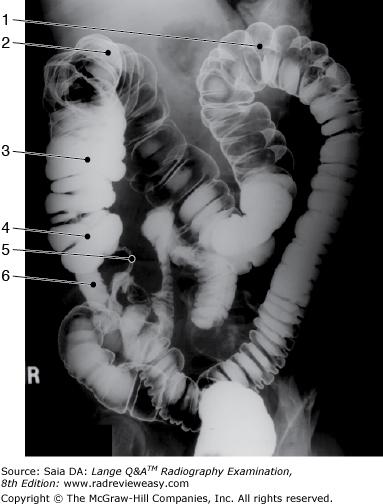 The structure indicated as number 4 in Figure 2–9 is the | back 115 cecum |
front 116 Which of the following sequences correctly describes the path of blood flow as it leaves the left ventricle? | back 116 Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins |
front 117 Which of the following statements regarding the image in Figure 2–4 is correct? | back 117 The left kidney is more parallel to the IR. |
front 118 All the following statements regarding respiratory structures are true except | back 118 the inferior portion of the lung is the apex. |
front 119 During GI radiography, the position of the stomach may vary depending on
| back 119 1, 2, and 3 |
front 120 During an upper gastrointestinal (GI) examination, a stomach of average shape demonstrates a barium-filled fundus and double contrast of the pylorus and duodenal bulb. The position used is most likely | back 120 LPO |
front 121 Differences between body habitus types are likely to affect all the following except | back 121 the degree of bone porosity. |
front 122 Which of the following groups of organs/structures are located in the left upper quadrant? | back 122 Left kidney, left suprarenal gland, and gastric fundus |
front 123 Another name for Hirschsprung's disease, the most common cause of lower GI obstruction in neonates, is | back 123 congenital megacolon. |
front 124 The patient's chin should be elevated during chest radiography to | back 124 avoid superimposition on the apices |
front 125 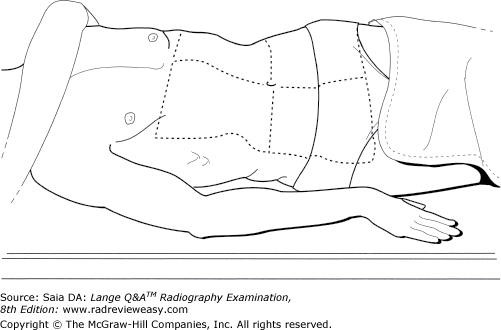 Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the position illustrated in Figure 2–19?
| back 125 2 and 3 only |
front 126 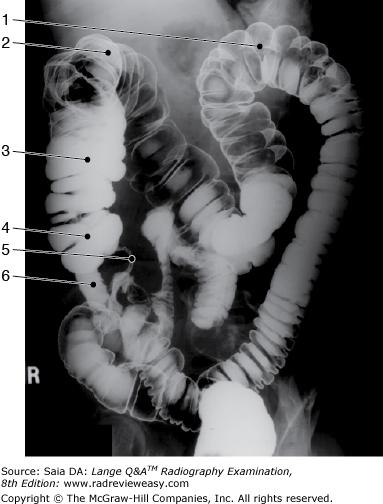 In which of the following positions was the radiograph in Figure 2–9 taken? | back 126 RPO |
front 127 All the following procedures demonstrate renal function except | back 127 retrograde urography |
front 128 Which of the following are characteristics of the hypersthenic body type?
| back 128 1 and 2 only |
front 129 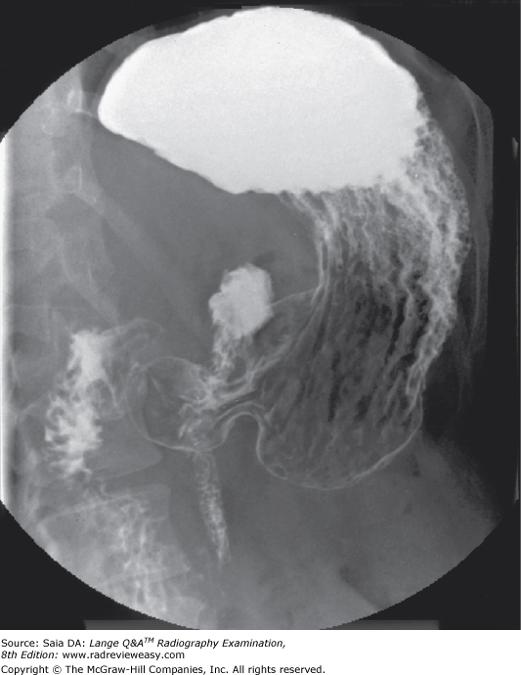 The image shown in Figure 7–4 was made in the following recumbent position | back 129 LPO |
front 130 Abdominal viscera located in the retroperitoneum include the
| back 130 1, 2, and 3 |
front 131 Which of the following conditions require(s) a decrease in technical factors?
| back 131 1 and 2 only |
front 132 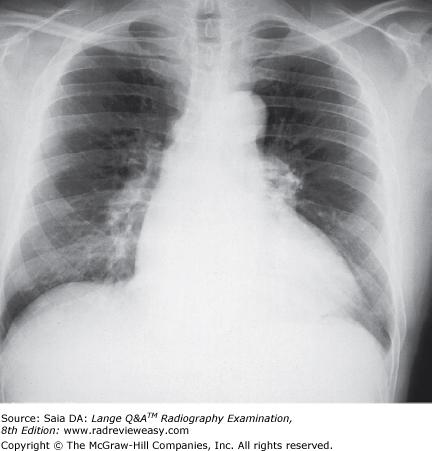 The PA chest analog image shown in the figure below demonstrates
| back 132 2 and 3 only |
front 133 Which of the following radiographic examinations require(s) the patient to be NPO 8–10 hours prior to examination for proper patient preparation?
| back 133 2 and 3 only |
front 134 The patient usually is required to drink barium sulfate suspension in order to demonstrate which of the following structures?
| back 134 1 only |
front 135 Demonstration of which anatomic structures require(s) ingestion of barium sulfate suspension?
| back 135 1 and 2 only |
front 136 Types of inflammatory bowel disease include
| back 136 1 and 2 only |
front 137 All the following positions are used frequently to demonstrate the sternoclavicular articulations except | back 137 weight-bearing |
front 138 Which of the following will best demonstrate the size and shape of the liver and kidneys? | back 138 AP abdomen |
front 139 Which of the following pathologic conditions would require an increase in exposure factors? | back 139 Ascites |
front 140 The pain experienced by an individual whose coronary arteries are not conveying sufficient blood to the heart is called | back 140 angina pectoris. |
front 141 Particulate matter entering the respiratory bronchi can cause | back 141 pneumoconiosis. |
front 142 Abnormal accumulation of air in pulmonary tissues, resulting in overdistention of the alveolar spaces, is | back 142 emphysema |
front 143 Which of the following procedures requires that the patient be placed in the lithotomy position? | back 143 Hysterosalpingography |
front 144 Which of the following positions can be used to effectively demonstrate the left colic flexure during radiographic examination of the large bowel?
| back 144 2 and 3 only |
front 145 Which cholangiographic procedure uses an indwelling drainage tube for contrast medium administration? | back 145 T-tube cholangiography |
front 146 When a GI series has been requested on a patient with a suspected perforated ulcer, the type of contrast medium that should be used is | back 146 water-soluble iodinated media. |
front 147 The esophagus commences at about the level of | back 147 C6 |
front 148 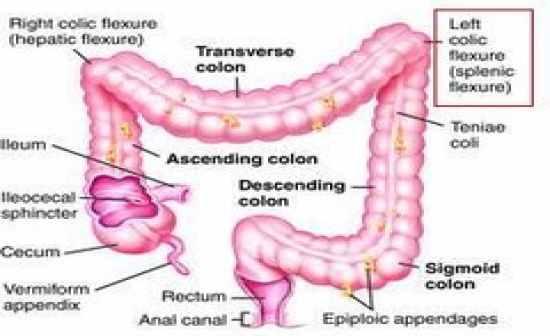
Which of the following positions may be used to
effectively demonstrate the hepatic flexure during radiographic
examination of the large bowel? 2. LAO 3. LPO | back 148 1 and 3 only |
front 149 A patient in a recumbent position with the head lower than the feet is said to be in which of the following positions? | back 149 Trendelenburg |
front 150
Which of the following criteria are used to evaluate a
PA projection of the chest? 2. Sternoclavicular joints should be symmetrical. 3. The scapulae should be lateral to the lung fields. | back 150 1, 2, and 3 |
front 151 In which of the following examinations is exposure on full expiration required? | back 151 Below diaphragm ribs |
front 152 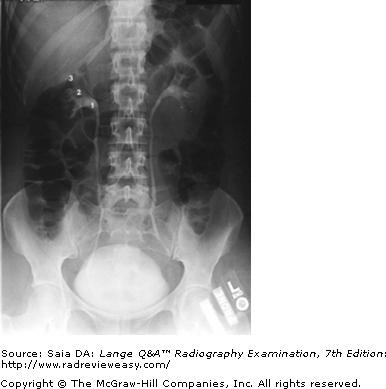 The number 1 in the radiograph in Figure A represents which of the following renal structures? | back 152 Renal pelvis |
front 153 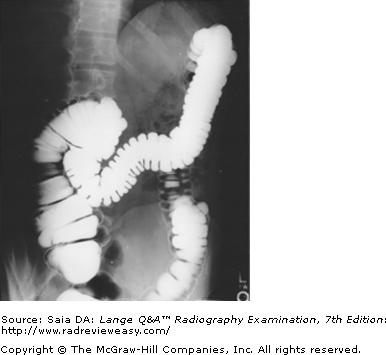 In which of the following positions was the radiograph in Figure A taken? | back 153 LPO |
front 154 An acute infection of the lungs is called | back 154 Pneumonia |
front 155 Compared with that of the hypersthenic and sthenic body types, the gallbladder of an asthenic patient is most likely to be located | back 155 lower and more medial |
front 156 Correct preparation for a patient scheduled for a lower GI series is most likely to be | back 156 cathartics and cleansing enemas. |
front 157 Gas-producing powder or crystals usually are ingested for which of the following examinations? | back 157 Double-contrast gastrointestinal (GI) series |
front 158 Esophageal varices are best demonstrated in which of the following positions? | back 158 Recumbent |
front 159 A near-frontal (AP/PA) view of the sternum is best accomplished in which of the following positions? | back 159 RAO |
front 160 Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the
radiograph shown in Figure 6–16? | back 160 2 only |
front 161 During an air-contrast BE, in what part of the colon is air most likely to be visualized with the body in the AP recumbent position? | back 161 Transverse colon |
front 162 The condition that allows blood to shunt between the right and left ventricles is called | back 162 ventricular septal defect. |
front 163 To demonstrate esophageal varices, the patient must be examined in | back 163 the recumbent position |
front 164 To best visualize the lower ribs, the exposure should be made | back 164 on expiration |
front 165 The AP axial projection of the chest for pulmonary apices
| back 165 1 and 3 only |
front 166
Which of the following projections of the
abdomen may be used to demonstrate air or fluid levels? 2. Lateral decubitus 3. AP Trendelenburg | back 166 1 and 2 only |
front 167 The plane that passes vertically through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior halves, is termed the | back 167 midcoronal plane |
front 168 Which of the following positions is required to demonstrate small amounts of fluid in the pleural cavity? | back 168 Lateral decubitus, affected side down |
front 169 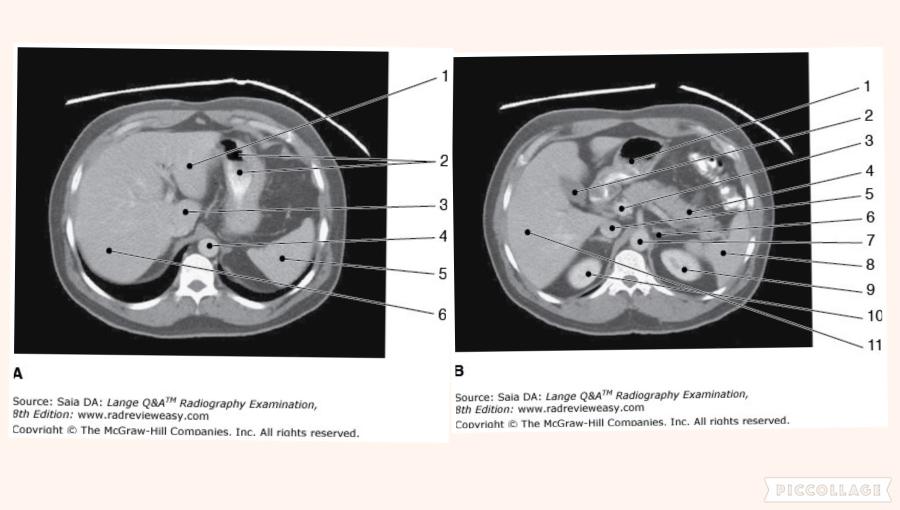 Which of the following statements is (are) true with regard to the two CT images seen below?
| back 169 1 only |
front 170 The sternal angle is at approximately the same level as the | back 170 T5 |
front 171 The uppermost portion of the iliac crest is at approximately the same level as the | back 171 fourth lumbar vertebra |
front 172
Which of the following examinations might require the
use of 120 kVp? 2. Chest radiograph 3. Barium-filled stomach | back 172 2 and 3 only |
front 173 During an intravenous urogram (IVU), the RPO position is used to demonstrate the
| back 173 1 and 3 only |
front 174 Double-contrast examinations of the stomach or large bowel are performed to better visualize the | back 174 gastric or bowel mucosa. |
front 175 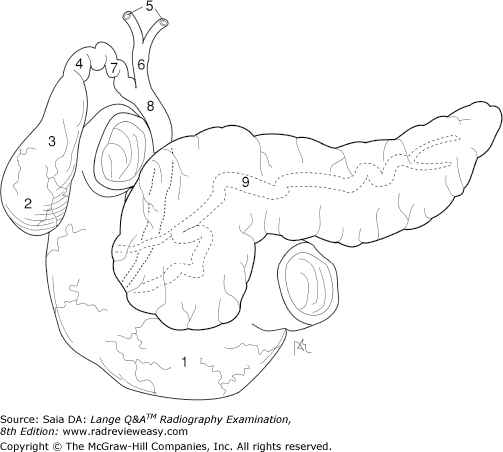 What is the structure indicated by the number 7 in Figure 2–18? | back 175 Cystic duct |
front 176 The manubrial notch is at approximately the same level as the | back 176 T2–3 interspace. |
front 177 The act of inspiration will cause elevation of the | back 177 1 and 2 only |
front 178 Using the PA projection, which of the following tube angle and direction combinations is correct for an axial projection of the clavicle? | back 178 15 to 30 degrees caudad |
front 179  The structure indicated by the number 2 in Figure 6–11 is the | back 179 descending colon. |
front 180 The AP Trendelenburg position is often used during an upper GI examination to demonstrate | back 180 hiatal hernia |
front 181 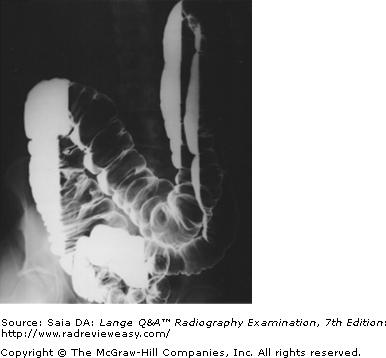 The radiograph pictured in Figure A may be used to evaluate 1. polypoid lesions. 2. the lateral wall of the descending colon. 3. the posterior wall of the rectum. | back 181 1 and 2 only |
front 182 Which of the anatomic structures listed below is seen most anteriorly in a lateral projection of the chest? | back 182 Cardiac apex |
front 183 Blood is returned to the left atrium, from the lungs, via the | back 183 pulmonary veins. |
front 184
High-kilovoltage exposure factors are usually required
for radiographic examinations using 2. a negative contrast agent. 3. barium sulfate. | back 184 3 only |
front 185 Which of the following is a vessel that does not carry oxygenated blood? | back 185 Pulmonary artery |
front 186 Which of the following positions is obtained with the patient lying supine on the radiographic table with the CR directed horizontally to the iliac crest? | back 186 Dorsal decubitus position |
front 187 All of the following statements regarding respiratory structures are true except | back 187 the right lung has two lobes. |
front 188 The ileocecal valve normally is located in which of the following body regions? | back 188 Right iliac |
front 189 Which of the following statements is (are) correct with respect to postoperative cholangiography?
| back 189 1, 2, and 3 |
front 190 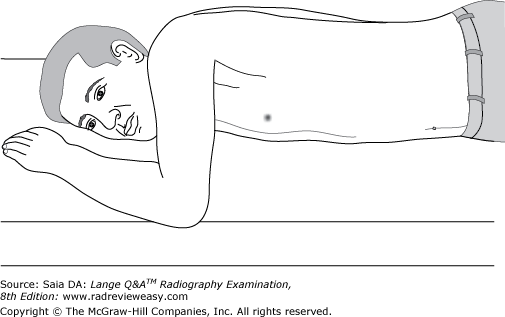 The position illustrated in the figure below can be used successfully to demonstrate the
| back 190 1, 2, and 3 |
front 191 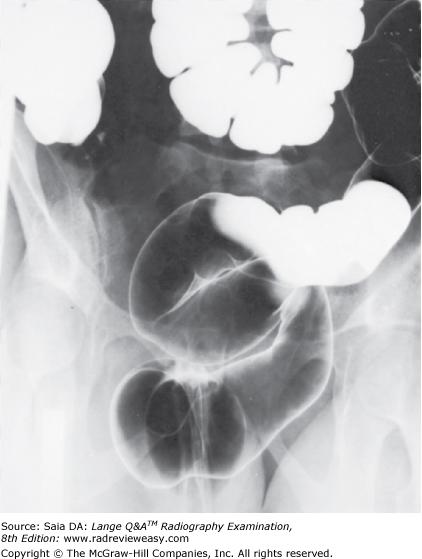 The position illustrated in the radiograph in Figure 2–28 may be obtained with the patient
| back 191 2 and 3 only |
front 192 Ingestion of barium sulfate is contraindicated in which of the following situations?
| back 192 1, 2, and 3 |
front 193 Which of the following statements is/are true regarding Figure A? 1. The radiograph was made in the LAO position. 2. The central ray should enter more inferiorly. 3. The sternum is projected onto the left side of the thorax. | back 193 2 and 3 only |