Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Amino acids and proteins
front 1 Which functional group is LEAST important in biochemistry? A. Amine B. Ester C. Aromatic D. Hydroxyl E. Amide | back 1 C. Aromatic |
front 2 All of the following are examples of fibrous proteins except: A. Fingernails B. Insulin C. Skin D. Bones E. Wool | back 2 B. Insulin |
front 3 Collagen is an example of a (an): A. Storage protein B. Structural protein C. Hormone D. Enzyme E. Transport protein | back 3 B. Structural protein |
front 4 Which amino acid is not chiral? A. Phenylalanine B. Alanine C. Arginine D. Cysteine E. Glycine | back 4 E. Glycine |
front 5 Which type of interaction is not directly involved in maintaining tertiary structure? A. Hydrophobic interactions B. Disulfide bridges C. Peptide bonds D. Salt bridges E. Hydrogen bonding | back 5 C. Peptide bonds |
front 6 All of the following are major functions of proteins except: A. Transport of necessary chemicals B. Storage of energy C. Control of biochemical reactions D. Support for organs or tissue E. Protection against foreign substances | back 6 B. Storage of energy |
front 7 The peptide bond joining amino acids into proteins is a specific example of an _______ bond. A. Amide B. Ester C. Glycosidic D. Hydrogen E. Carbonyl | back 7 A. Amide |
front 8 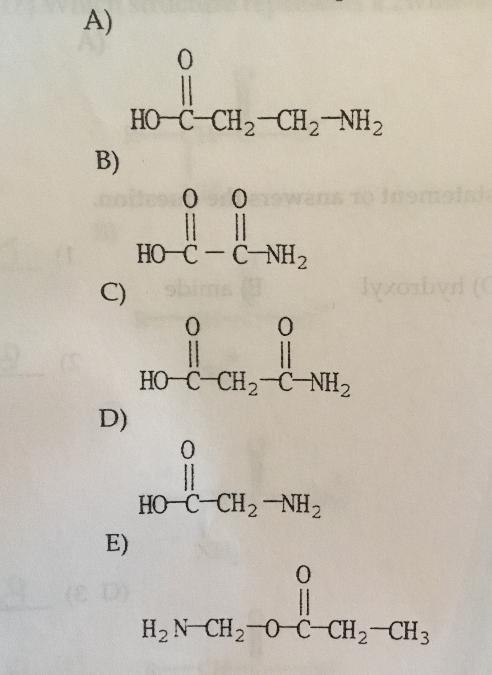 Which molecule is an alpha amino acid? | back 8 D. |
front 9 Which amino acid can form covalent sulfur-sulfur bonds? A. Phenylalanine B. Proline C. Cysteine D. Methionine E. Glycine | back 9 C. Cysteine |
front 10 All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except: A. Nuclei acids B. Lipids C. Carbohydrates D. Proteins E. All are biomolecules | back 10 E. All are biomolecules |
front 11 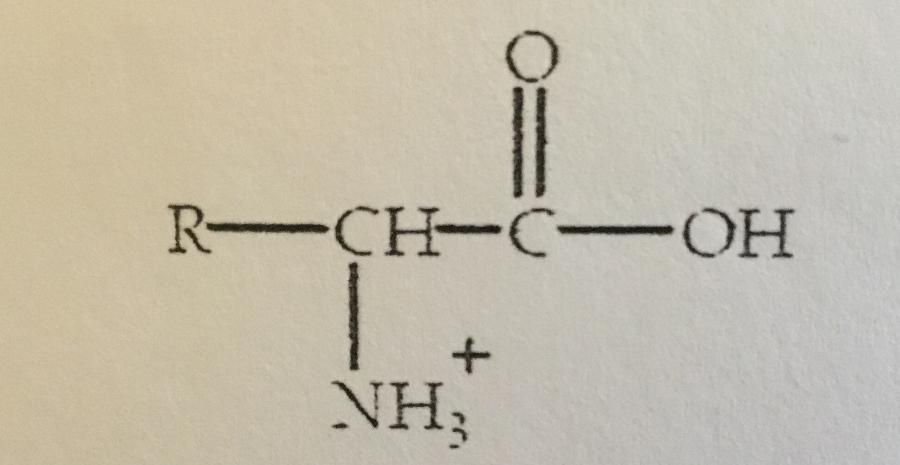 An amino acid will have the form shown at: A. Any pH other than 7.0 B. A pH less than its isoelectric point C. A pH grater than its isoelectric point D. A pH of 7.0 E. Its isoelectric point | back 11 B. A pH less than its isoelectric point. |
front 12 Polar R groups, along with acidic and basic R groups, are said to be ______ because they are attracted to water molecules. A. Unreactive B. Hydrophobic C. Ionized D. Hydrophilic E. None of the above | back 12 D. Hydrophilic |
front 13 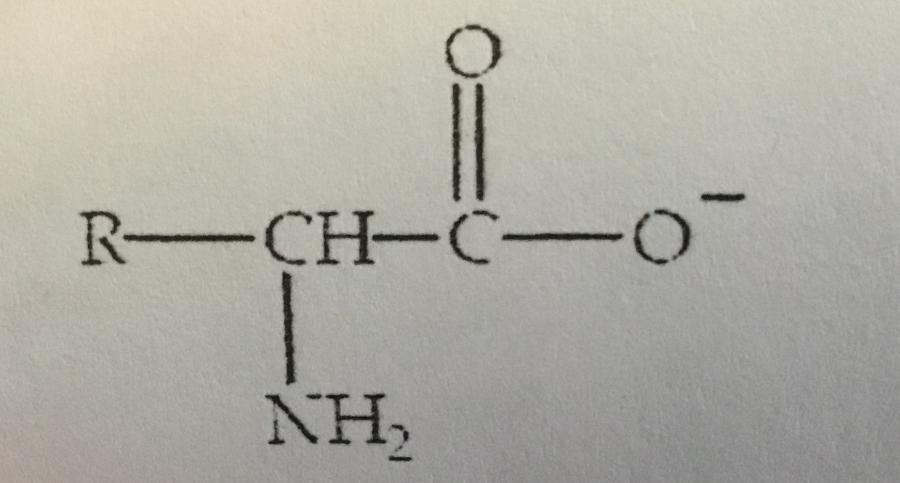 An amino acid has the form shown at, A. A pH grater than its isoelectric point B. A pH less than its isoelectric point C. A pH of 7.0 D. It’s isoelectric point. E. Any pH other than 7.0 | back 13 A. A pH greater than its isoelectric point |
front 14 Serum albumin is an example of a (an) A. Enzyme B. Transport protein C. Structural protein D. Storage protein E. Protective protein | back 14 B. Transport protein |
front 15 The C-terminal amino acid in the peptide, Ala-Leu-Gly-His-Pro is, A. Proline B. Leucine C. Glycine D. Histidine E. Alanine | back 15 A. Proline |
front 16 The N-terminal amino acid in the peptide, Ala-Leu-Gly-His-Pro is, A. Glycine B. Proline C. Leucine D. Alanine E. Histidine | back 16 D. Alanine |