Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Review Ch. 3 Abdomen
front 1 What 6 organs are part of the digestive system? | back 1 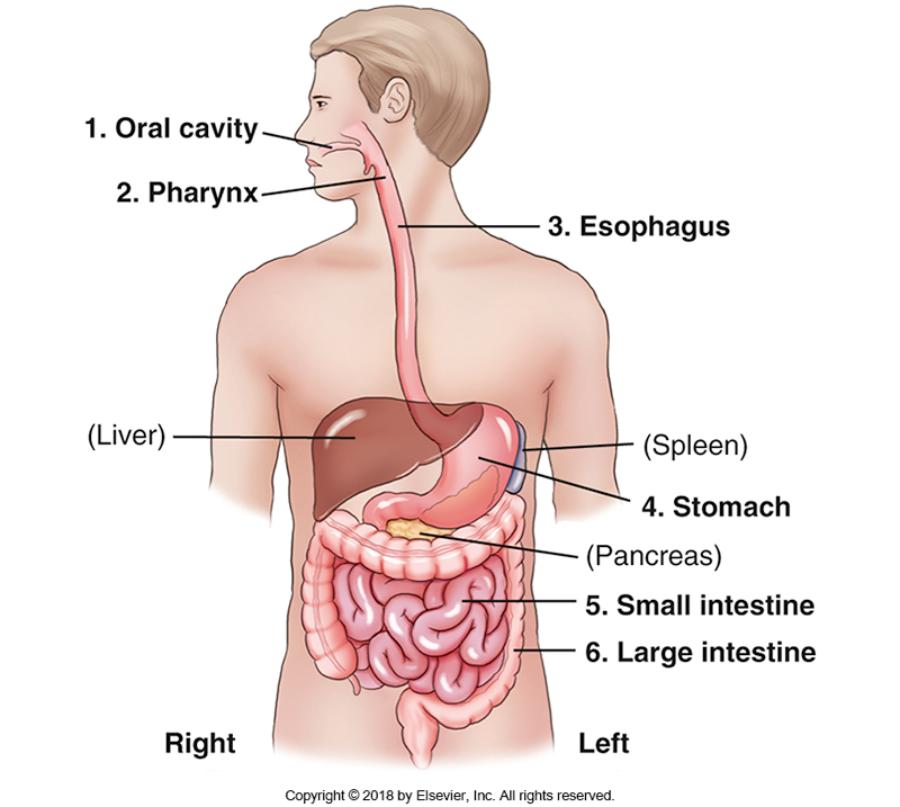 OPES Si Li = Oral Cavity, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestinte |
front 2 What is KUB | back 2 Kidney, ureters, bladder |
front 3 What else does KUB refer to? | back 3 Abdomen supine. When shooting an abdomen supine x-ray we can demonstrate the borders of the psoas major muscles. |
front 4 What are 3 abdominal muscles? | back 4 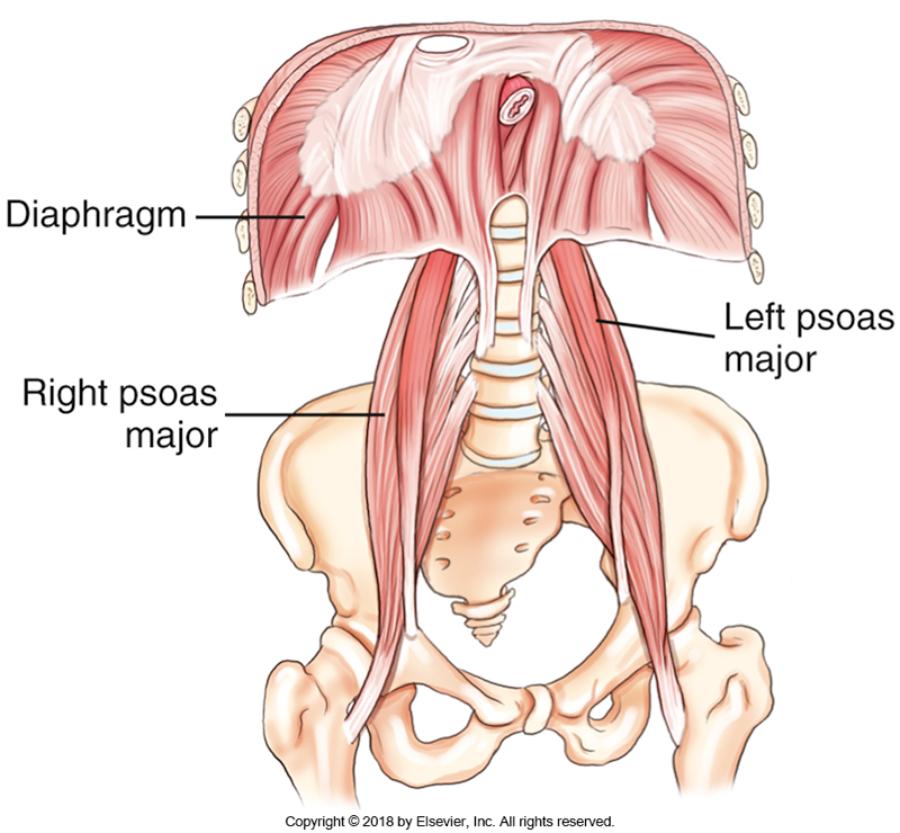 Diaphragm, R psoas major, L psoas major |
front 5 Where does the psoas major muscle originate? | back 5 at the transverse process of L1 |
front 6 Where does the psoas major muscle insert? | back 6 at the lesser trochanter of the femur. |
front 7 Psoas major muscle | back 7 Is one of the major flexor muscles of the trunk. It allows us to bend waist down. |
front 8 Diaphragm | back 8 an inspiration muscle which separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity |
front 9 Which organs are a part of the digestive tract? | back 9 Oral cavity, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, and Large intestine |
front 10 What are the accessory organs? | back 10 Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas |
front 11 cholelithiasis | back 11 is the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder |
front 12 What are the functions of the accessory organs? | back 12 They are involved in the digestion and break down of food particles. |
front 13 Spleen | back 13 is a part of the lymphatic system located in the abdomen |
front 14 stomach | back 14 first organ of the digestive system located in the abdominal cavity. Size and shape depends on the body habitus and contents of the stomach. |
front 15 What connects the stomach to the duodenum? | back 15 Pylorus |
front 16 How long is the small intestine? | back 16 15 to 18 feet |
front 17 What parts are in the small intestine? | back 17 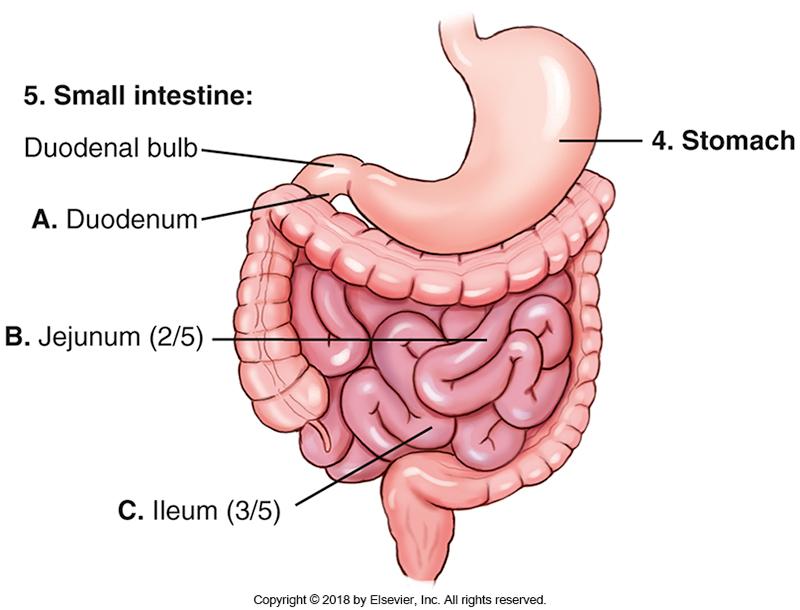 Duodenum (10 inches or 25cm in length), Jejunum (2/5), Ileum (3/5) |
front 18 Where does the ileum end? | back 18 RLQ |
front 19 Where is the ileocecal valve located? | back 19 at the conjunction where the ileum meets the cecum |
front 20 Which organ is the last organ of the digestion system | back 20 large intestine |
front 21 How long is the large intestine? | back 21 about 1.5 meters |
front 22 What parts are in the large intestine? | back 22 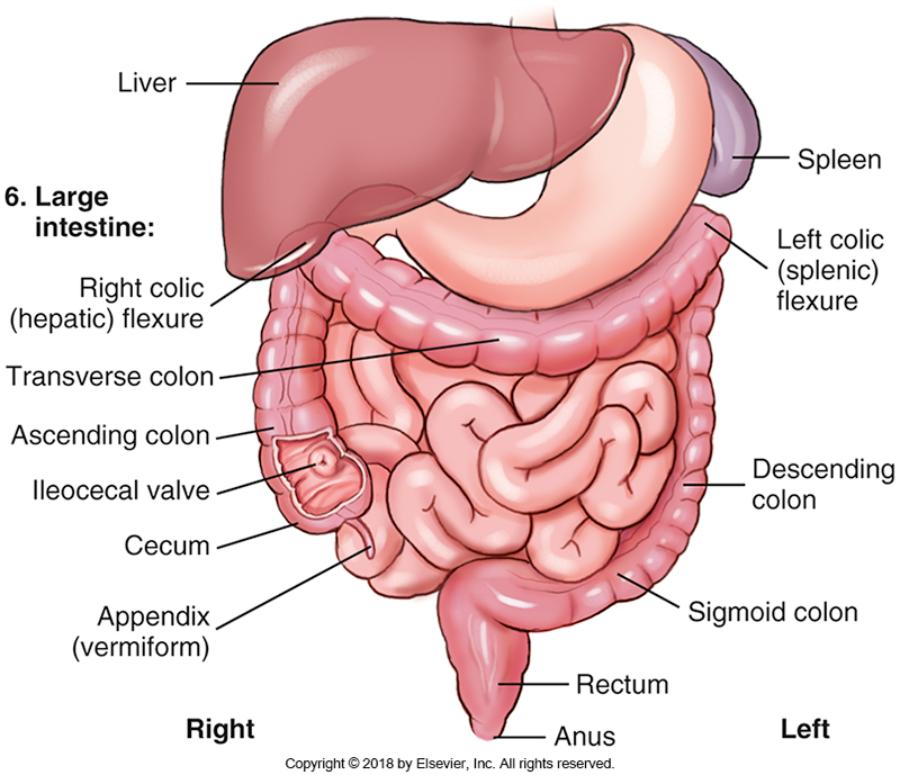 Ileocecal valve, Appendix (Vermiform), Cecum, Ascending Colon,Right colic (hepatic) flexure, Transverse colon, Left colic (splenic) flexure, Descending colon, Sigmoid colon, Rectum, Anus |
front 23 What is the main function of the Ileocecal valve? | back 23 Prevents back flow of bowel movements. |
front 24 What are the 9 abdominal regions? | back 24 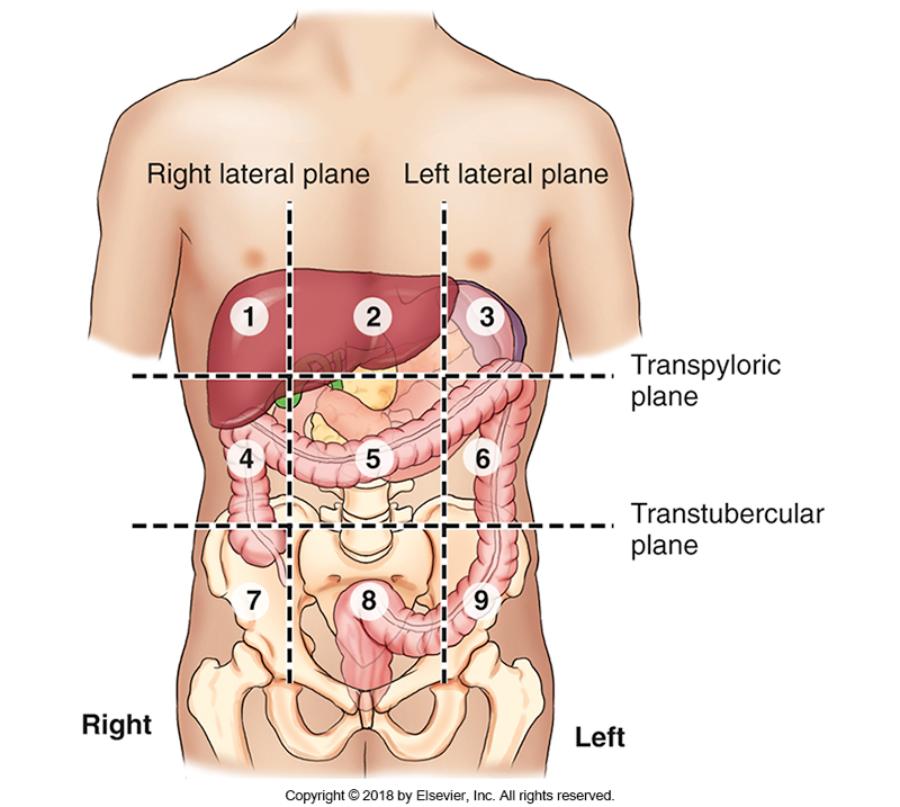
|
front 25 What are considerations about Gonadal shielding for abdomen imaging? | back 25 Males always shield. Physician must decide if female may be shielded. |
front 26 What are the 7 landmarks? Which 3 are most commonly used? | back 26 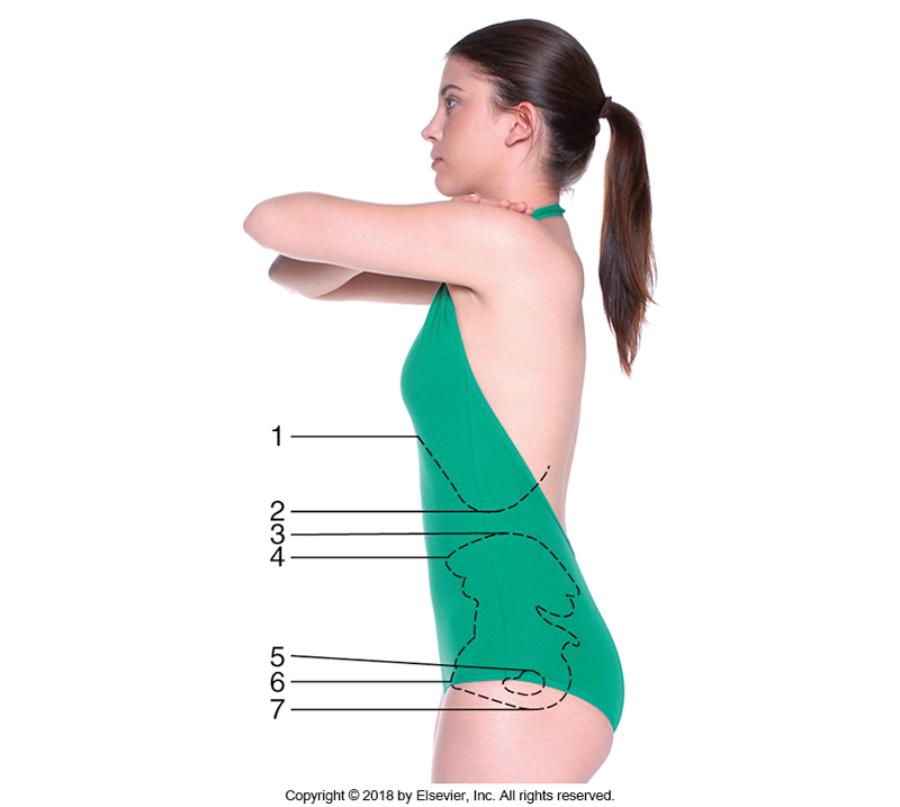
Most used 1. Iliac crest 2. ASIS 3. Greater trochanter |
front 27 What are abdominal positioning considerations? | back 27
|
front 28 What are abdominal exposure factors to consider? | back 28
|
front 29 What does Pneumoperitonium refer to? | back 29 Free air or gas in the peritoneal cavity. |
front 30 What is Intussusception? | back 30 When the distal small intestine, loops over itself and creates an obstruction. Needs to be treated within 48 hours before necrosis (tissue death). Most common in kids. |
front 31 The largest solid organ in the abdomen | back 31 Liver |
front 32 True or false? The stomach is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen? | back 32 True |
front 33 The membrane covering the abdominal organs is termed | back 33 Visceral peritoneum |
front 34 In which region or compartment of the abdomen is the pancreas located? | back 34 Retroperitoneal |
front 35 The spleen is located in which quadrant? | back 35 LUQ |
front 36 In which abdominal region is the majority of the transverse colon located in a person with a sthenic body type? | back 36 Umbilical region |
front 37 Which segment of the large intestine is located in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen? | back 37 Cecum |
front 38 In which region or compartment of the abdomen is the urinary bladder located? | back 38 Infraperitoneal |
front 39 Which topographic landmark corresponds to the level of L2/L3? | back 39 Inferior costal margin |
front 40 What is the greater trochanter is part of? | back 40 Proximal femur |
front 41 A properly exposed radiograph of the abdomen should demonstrate
the: | back 41 1 and 2 only |
front 42 What is the best method of reducing involuntary motion during an abdomen projection? | back 42 Short exposure time |
front 43 Neoplasms of the abdominal organs can be evaluated with: | back 43 1, 2 and 3 |
front 44 An abnormal collection of free air or gas within the peritoneal cavity is termed: | back 44 Pneumoperitoneum |
front 45 Which pathologic condition is most common in young children? | back 45 Intussusception |
front 46 Which one of the following structures must be demonstrated on a KUB projection?
| back 46 Symphysis pubis |
front 47 Two AP projections in the supine position with the IR oriented crosswise may be needed for patients who have a body type that is:
| back 47 Hypersthenic |
front 48 The AP projection of the abdomen is a better choice than a PA projection when the kidneys are of primary interest due to:
| back 48 Less magnification of the kidneys |
front 49 Which projection or position of the abdomen will best demonstrate an umbilical hernia?
| back 49 Dorsal decubitus position |
front 50 Where is the CR directed for a left lateral decubitus position of the abdomen?
| back 50 2 inches (5 cm) above iliac crests |
front 51 What is the optimal amount of time a patient should lie on his side prior to a left lateral decubitus projection?
| back 51 10 to 20 min |
front 52 An acute abdominal series includes AP projections in the: | back 52 1 and 2 only |
front 53 Which projection is performed to demonstrate free air or gas in the abdominal cavity when the patient is unable to stand?
| back 53 Left lateral decubitus |
front 54 Clinical indications for an acute abdominal series include: | back 54 1 and 2 only |
front 55 Which positioning error is classified as a repeatable error for an AP supine-KUB projection?
| back 55 Symphysis pubis not included on radiograph |
front 56 Which structure is evaluated to determine rotation on an AP radiograph of the abdomen?
| back 56 Iliac wings |
front 57 What is the specific positioning error if the right iliac wing is wider in appearance as compared to the left as seen on an AP supine abdomen radiograph?
| back 57 Rotation of the right side of the body toward the IR (right rotation) |
front 58 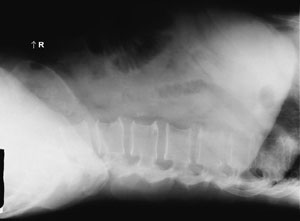 The position demonstrated in the abdomen image below is the:
| back 58 Dorsal decubitus |
front 59 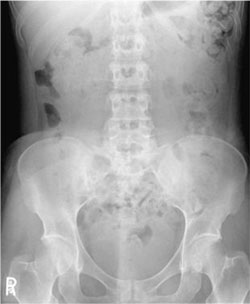 The abdomen image below could be improved by:
| back 59 1 only |
front 60 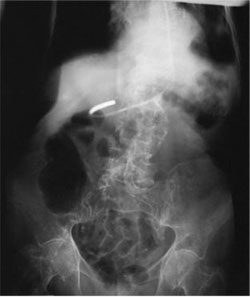 The abdomen image below could be improved by:
| back 60 1, 2, and 3 |