Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
AP Bio Review 1.5
front 1 In the cross AaBb x AaBb, how many different kinds of genotypes can result in the progeny if the A and B genes are independently assorting? | back 1 9 |
front 2 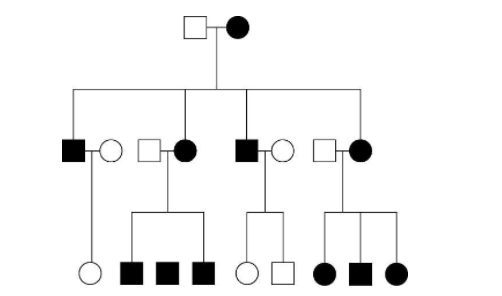 The pedigree in the figure above shows the transmission of a trait in a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait is most likely _____. A) mitochondrial B) sex-linked dominant C) sex-linked recessive D) autosomal dominant | back 2 A |
front 3 Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents? A) XnXn and XnY B) XNXN and XnY C) XNXN and XNY D) XNXn and XNY | back 3 D |
front 4 A couple has 5 children, all sons. If the women gives birth to the sixth child what is the probability it will be a son | back 4 1/2 |
front 5 What organelle modifies and packages for secretion the material produced by the ribosomes | back 5 the golgi apparatus |
front 6 How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE? a. 4 b. 8 c. 16 d. 32 e. 64 | back 6 8 |
front 7 Assume that the alleles referred to all assort independently.
| back 7 D |
front 8 Assume that the alleles referred to all assort independently.
| back 8 B |
front 9 Assume that the alleles referred to all assort independently.
| back 9 D |
front 10 Assume that the alleles referred to all assort independently.
| back 10 C |
front 11 .In sheep, eye color is controlled by a single gene with two alleles.
When a homozygous brown-eyed sheep is crossed with a homozygous
green-eyed sheep, blue eyes offspring are produced. If the blue eyed
sheep are mated with each other, what percent of their offspring will
most likely have brown eyes? | back 11 B |
front 12 1) Chromosomes and genes share all of the following characteristics
except that | back 12 E |
front 13 14) The reason that linked genes are inherited together is that
| back 13 A |
front 14 16) There is good evidence for linkage when | back 14 D |
front 15 In a species that has five different alleles for a gene at a
particular locus....?how many different alleles may be present in the
somatic cels of one diploid individual? | back 15 2 |
front 16 Questions 102-103 refer to the birth of a child with blood type
A | back 16 D |
front 17 103. If the father has blood type AB, which of the
following | back 17 B |
front 18 Questions 114-116 refer to an experiment in which a dialysis-tubing
bag is filled with a mixture of 3% starch and 3% | back 18 B |
front 19 Questions 114-116 refer to an experiment in which a dialysis-tubing
bag is filled with a mixture of 3% starch and 3% | back 19 A |
front 20 Questions 114-116 refer to an experiment in which a dialysis-tubing
bag is filled with a mixture of 3% starch and 3% | back 20 A |
front 21 Questions 111-113 refer to an experiment that was performed to
separate DNA fragments from four samples | back 21 C |
front 22 Questions 111-113 refer to an experiment that was performed to
separate DNA fragments from four samples | back 22 D |
front 23 Questions 111-113 refer to an experiment that was performed to
separate DNA fragments from four samples | back 23 B |
front 24 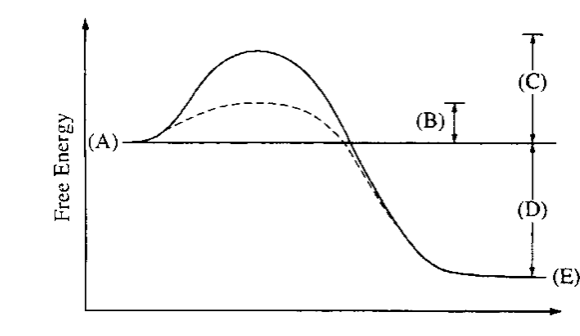
| back 24 D |
front 25 
| back 25 B |
front 26 
| back 26 A |
front 27 
| back 27 E |
front 28  Represents the energy state of the products of the enzyme catalyzed path way | back 28 E |
front 29 8) Synaptic signaling between adjacent neurons is like hormone
signaling in which of the following ways? | back 29 D |
front 30 6) The process of transduction usually begins | back 30 B |
front 31 Which of the following describes cell communication systems? | back 31 E |
front 32 Which of the following would be inhibited by a drug that specifically
blocks the addition of phosphate groups to proteins? | back 32 E |
front 33 a molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, often a larger one | back 33 ligand |
front 34 the general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein | back 34 protein kinase |
front 35 special proteins which control which genes are turned on - that is, which genes are transcribed into mRNA - in a particular cell at a particular time | back 35 transcription factors |
front 36 The mechanism of action of many common medications involves interfering with the normal pathways that cells use to respond to hormone signals. Which of the following best describes a drug interaction that directly interferes with a signal transduction pathway? A. A medication interrupts the transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. B. A medication enters the target cell and inhibits an enzyme that normally synthesizes a second messenger. C. A medication causes the cell to absorb more of a particular mineral, eventually poisoning the cell. D. A medication enters the target cell's cytoplasm and acts as a mutagen. | back 36 B |
front 37 Is an allergy (to pollen, bees, peanuts, etc) a normal body function or a disruption of body function? A. An allergy is a normal body function that returns the immune system to homeostasis. B. An allergy is a disruption of normal body function when the immune system overreacts to a particular antigen. C. An allergy is a disruption of normal body function when the immune system is inactivated and cannot fight a particular antigen. D. An allergy is a disruption of normal body function when the immune system identifies a foreign antigen as one of the body’s own self proteins. | back 37 B |
front 38 Most nerve cells communicate with others by means of: A. electrical signals that pass across synapses. B. chemical signals that pass across synapses. C. bursts of pressure that bump the postsynaptic cell membrane. D. sodium ions as they are released from one cell and enter the next. | back 38 B |
front 39 The process of transduction usually begins a.when the chemical signal is released from the alpha cell. b.when the signal molecule changes the receptor protein in some way. c.after the target cell divides. d.after the third stage of cell signaling is completed. e.when the hormone is released from the gland into the blood. | back 39 B |
front 40 The signal transduction pathway in animal cells that use
epinephrine | back 40 A |
front 41 When a cell releases a signal molecule into the environment and a
number of cells in the immediate vicinity respond, this | back 41 C |
front 42 Of the following, a receptor protein in a membrane that recognizes a
chemical signal is most similar to | back 42 A |
front 43 A small molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, usually
a larger one | back 43 B |
front 44 A plant deficient in calcium could experience several problems,
including | back 44 A |
front 45 Which of the following provides the best evidence that cell-signaling
pathways evolved early in the history of life? | back 45 C |
front 46 Which of the following is true of synaptic signaling and hormonal signaling? A) Hormonal signaling occurs in animals only. B) Hormonal signaling is important between cells that are at greater distances apart than in synaptic signaling. C) Both act on target cells by a G-protein-signaling pathway. D) Only A and B are true. E) A , B, and C are true. | back 46 B |