Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Dissection of blood vessels of cat
front 1 Aorta | back 1 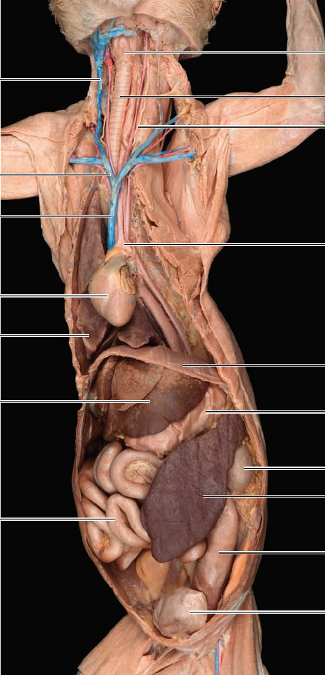 largest artery in body; issuing from left ventricle |
front 2 superior vena cava | back 2  precava; largest, dark-colored vessel entering the base of the heart |
front 3 inferior vena cava | back 3 post cava; enters right atrium |
front 4 coronary arteries | back 4  supply myocardium; can be seen on surface of heart |
front 5 heart | back 5  in mediastinum enclosed by pericardium |
front 6 lungs | back 6  flanking the heart |
front 7 thymus | back 7 superior to and partially covering the heart; large in young cats & replaced by fat in older cats |
front 8 liver | back 8  posterior to diaphragm |
front 9 stomach | back 9  dorsally located and to the left of liver |
front 10 spleen | back 10  flattened, brown organ curving around the lateral aspect of the stomach |
front 11 small intestine | back 11  continues posteriorly from stomach |
front 12 large intestine | back 12  takes a U-shaped course around small intestine and terminates in rectum |
front 13 aortic arch | back 13  gives off two large vessels: left subclavian artery and brachiocephalic artery |
front 14 brachiocephalic artery | back 14  has three major branches: Right subclavian artery, and right/left common carotid arteries |
front 15 Difference between origin of left common carotid arteries in humans & cats | back 15  In humans, the left common carotid artery & left subclavian artery are direct braches off aortic arch |
front 16 right common carotid artery | back 16  gives off branches to neck muscles, thyroid gland, and trachea branches to form external/internal carotid arteries |
front 17 right subclavian artery | back 17  gives off four branches: vertebral artery, costocervical trunk, thyrocervical trunk, and internal thoracic artery |
front 18 vertebral artery | back 18  along with internal carotid artery supplies the arterial circulation of the brain |
front 19 costocervical trunk | back 19  branches to the costal and cervical regions |
front 20 thyrocervical trunk | back 20  branches to the shoulder |
front 21 internal thoracic (mammary) artery | back 21  serving the ventral thoracic artery |
front 22 axillary artery | back 22  when subclavian passes in front of first rib, it becomes this artery. Branches of this artery include: ventral thoracic artery, long thoracic artery, and subscapular artery which supply the trunk and shoulder muscles |
front 23 ventral thoracic artery | back 23  to the pectoral muscles |
front 24 long thoracic artery | back 24  to pectoral muscles and latissimus dorsi |
front 25 subscapular artery | back 25  to trunk muscles |
front 26 brachial artery | back 26  as axillary artery enters the arm, it becomes this artery which branches at the elbow to produce the radial and ulnar arteries |
front 27 radial and ulnar arteries | back 27  serve the forearm and hand |
front 28 celiac trunk | back 28  supplies the stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and the spleen |
front 29 superior mesenteric artery | back 29  immediately posterior to celiac trunk supplies the small intestine and most of large intestine |
front 30 adrenolumnar arteries | back 30  paired arteries diverging from aorta slightly posterior to superior mesenteric artery supply the muscles of the body wall and adrenal glands |
front 31 renal arteries | back 31  paired arteries supplying kidneys |
front 32 gonadal arteries | back 32  ovarian or testicular arteries that supply gonads |
front 33 inferior mesenteric artery | back 33  unpaired; thin vessel arising from ventral surface of aorta posterior to the gonadal arteries supplies the second half of large intestines |
front 34 iliolumbar arteries | back 34  paired, rather large arteries that supply the body musculature in iliolumbar region |
front 35 external iliac arteries | back 35  paired arteries which continue through the body wall & pass under the inguinal ligament to hindlimb |
front 36 internal iliac arteries | back 36  two arteries which supply the pelvic viscera |
front 37 Difference between iliac arteries in cat and humans | back 37  there is NO COMMON ILIAC ARTERY in cat |
front 38 median sacral artery | back 38  descending abdominal aorta divides into the two internal iliac arteries and ___________ |
front 39 caudal artery | back 39  as median sacral artery enters tail, it becomes this artery |
front 40 femoral artery | back 40  courses through thigh and gives off branches to thigh muscles |
front 41 saphenous artery | back 41  branches off femoral artery to supply medial portion of the leg |
front 42 popliteal artery | back 42  descends deep to knee to become this artery which gives off two branches: sural artery and posterior tibial artery |
front 43 sural, posterior tibial, and anterior tibial arteries | back 43  supply the leg and foot |
front 44 Aygos vein | back 44  passing directly into tits dorsal surface drains the thoracic intercostal muscles |
front 45 internal thoracic (mammary) vein | back 45  drains chest and abdominal wall |
front 46 right vertebral vein | back 46  drains spinal cord and brain |
front 47 right and left brachiocephalic veins | back 47  form the precava by their union |
front 48 Difference in formation of brachiocephalic veins in humans and cats | back 48 Humans: brachiocephalic vein is formed by union of internal jugular vein and subclavian veins Cats: formed by union of external jugular vein and subclavian veins |
front 49 external jugular vein | back 49 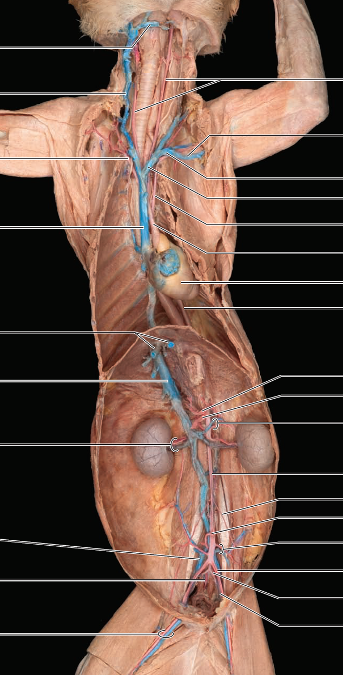 courses anteriorly along side of neck to point where its joined on medial surface by internal jugular vein |
front 50 Difference in cat & human jugular veins | back 50 Human: internal jugular vein is considerably larger & drains into subclavian vein Cat: External jugular vein is larger & internal jugular vein drains into it |
front 51 subclavian vein | back 51  moves laterally toward the arm; becomes axillary vein |
front 52 axillary vein | back 52  becomes this vein as it passes in front of first rib and runs through brachial plexus giving off subscapular vein |
front 53 subscapular vein | back 53  drains the proximal part of the arm and shoulder |
front 54 brachial vein | back 54  axillary vein becomes this vein as it enters the arm; receives radial/ulnar vein at the inner bend of elbow |
front 55 radial and ulnar veins | back 55  drain the forelimb |
front 56 cephalic vein | back 56  on dorsal side of the arm; communicates with brachial vein via median cubital vein in elbow then enters transverse scapular vein in shoulder |
front 57 hepatic veins | back 57  entering postcava from liver |
front 58 adrenolumbar veins | back 58  empty into postcava and drain adrenal glands and body wall |
front 59 renal veins | back 59  drain the kidneys & empties into postcava (common to find two right renal veins) |
front 60 gonadal veins | back 60  testicular or ovarian veins left vein of this venous pair enters the left renal vein anteriorly |
front 61 Iliolumbar veins | back 61  drain muscles of the back & empties into postcava |
front 62 common iliac veins | back 62  unite to form postcava |
front 63 internal and external iliac veins | back 63  unite to form common iliac veins |
front 64 internal iliac veins | back 64  receive branches from pelvic organs and gluteal region |
front 65 external iliac veins | back 65  receives venous drainage from lower limb |
front 66 deep femoral vein | back 66  drains the thigh and external genital region |
front 67 femoral vein | back 67  receives blood from the thigh, leg, and foot formed by union of great saphenous vein and popliteal vein |
front 68 great saphenous vein | back 68  superficial vein that courses up inner aspect of calf & across inferior portion o gracilis muscle to enter femoral vein |
front 69 popliteal vein | back 69  located deep in the thigh beneath the semimembranosus and semitendinosus muscles in popliteal spaces accompanying popliteal artery |
front 70 posterior and anterior tibial veins | back 70  drain the leg |
front 71 hepatic portal vein | back 71 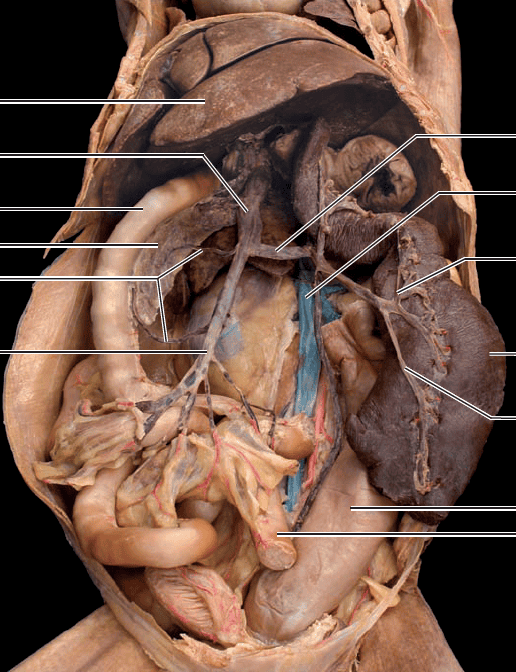 formed by the union of the gastrosplenic and superior mesenteric veins |
front 72 Difference between formation of hepatic portal vein in cats and humans | back 72  Humans: formed by union of splenic and superior mesenteric veins Cat: formed by union of gastrosplenic and superior mesenteric veins |
front 73 Gastrosplenic vein | back 73 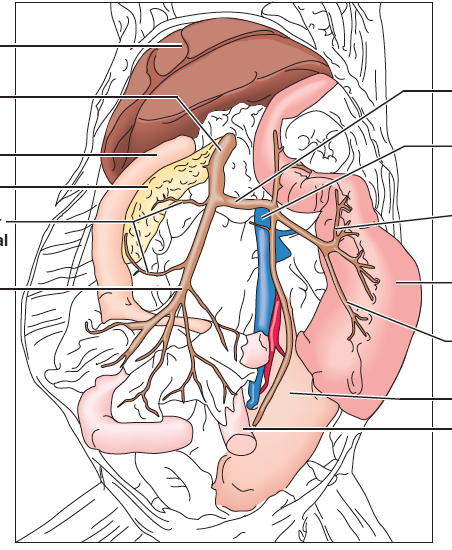 carries blood from spleen and stomach located dorsal to stomach |
front 74 superior mesenteric vein | back 74  large vein draining small and large intestine and pancreas |
front 75 inferior mesenteric vein | back 75  parallels course of inferior mesenteric artery empties into superior mesenteric vein |
front 76 pancreaticoduodenal vein | back 76  anterior branch empties into hepatic portal vein posterior branch empties into superior mesenteric vein |