Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
2-Development-Embryonic Period
front 1 Cleavage | back 1 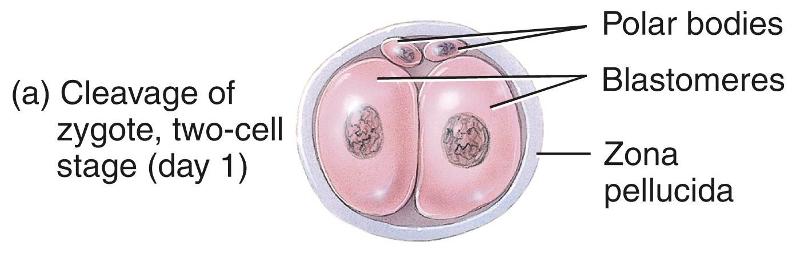 The rapid mitotic division of the zygote, starting the first week of development |
front 2 Blastomeres | back 2 Progressively smaller cells produced by cleavage |
front 3 Morula | back 3 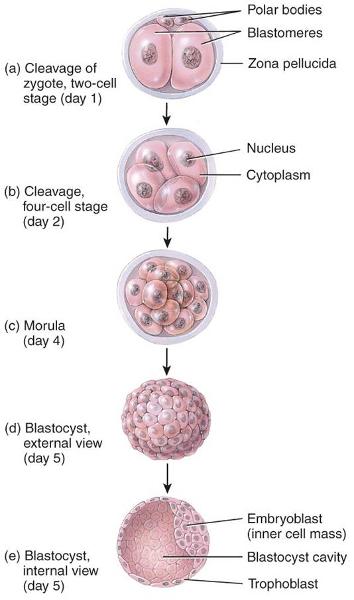 A solid ball of cells formed 3-4 days after fertilization |
front 4 Blastocyst | back 4
|
front 5 Implantation | back 5 The attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrium 6–8 days after fertilization |
front 6 Inner cell mass | back 6 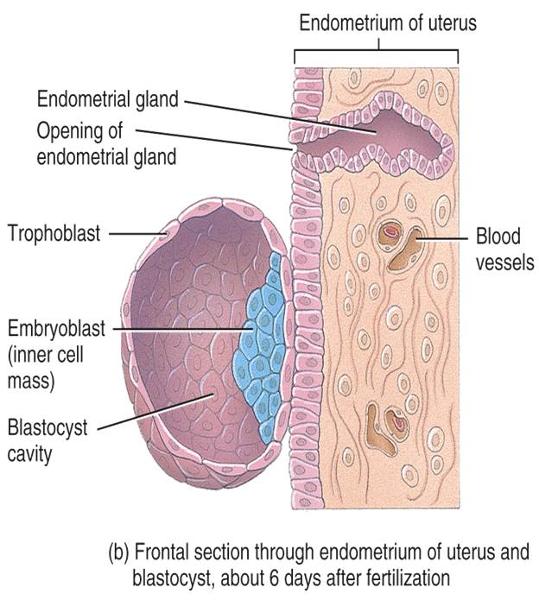
|
front 7 How does the endometrium respond to the blastocyst | back 7
|
front 8 Decidua | back 8 The portion of the endometrium that is modified after implantation |
front 9 Week One - 12-24 hours after ovulation | back 9 Fertilization |
front 10 Week One - 30 hours after fertilation | back 10 Cleavage |
front 11 Week One - 3-4 Days after fertilization | back 11 Morula |
front 12 Week One - 4 1/2 - 5 days after fertilization | back 12 Blastocyst enters uterine cavity |
front 13 Week One - 6 days after fertilization | back 13 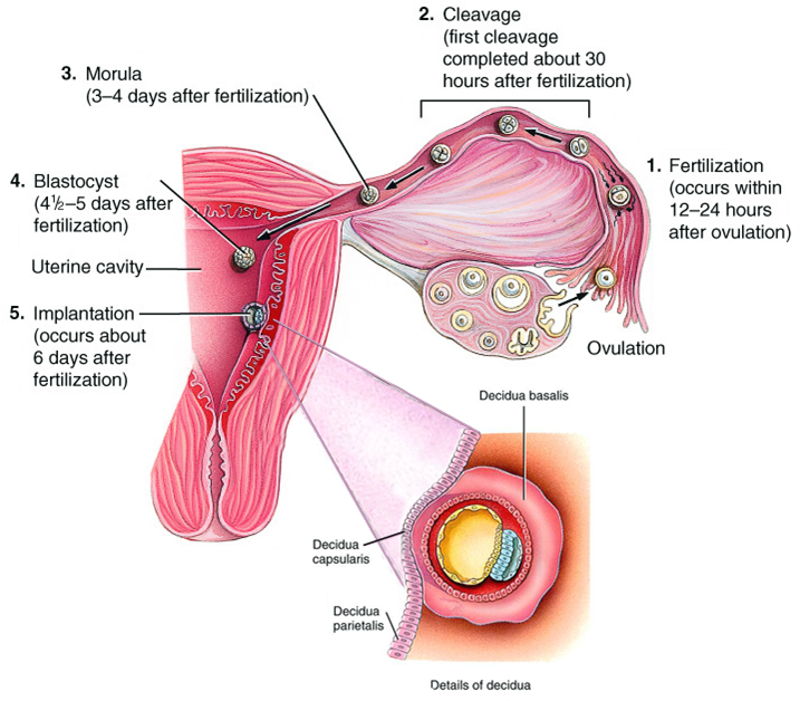 Implantation |
front 14 Trilaminar embryonic disc | back 14 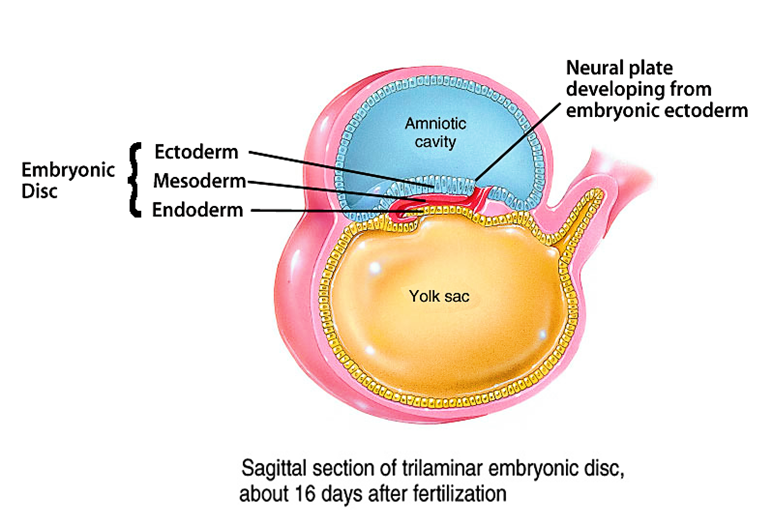
|
front 15 Three primary germ layers of Trilaminar embryonic disc | back 15 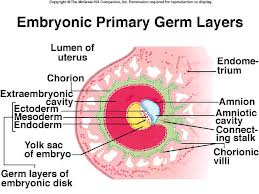
|
front 16 Ectoderm | back 16
|
front 17 Mesoderm | back 17
|
front 18 Endoderm | back 18
|
front 19 Extraembryonic membranes | back 19 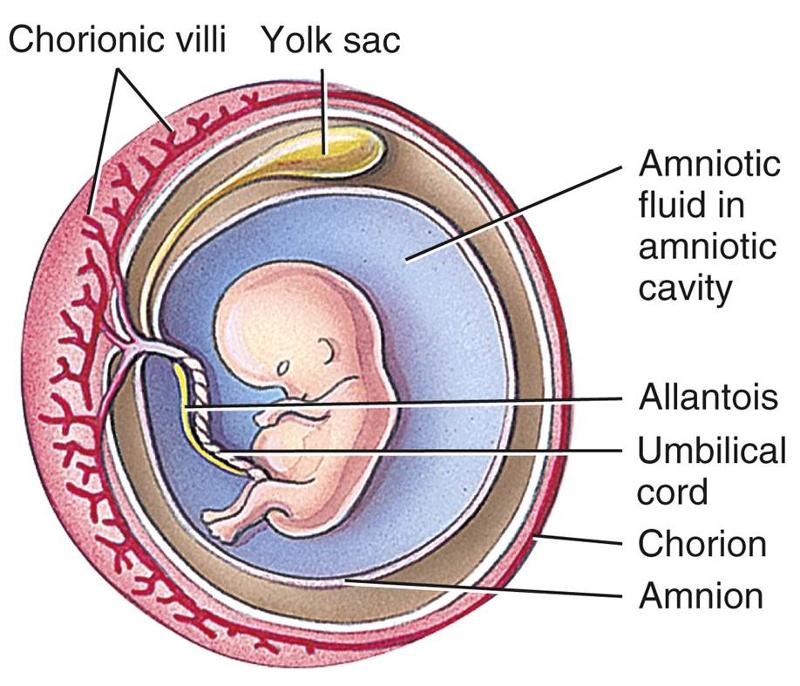 Formed during growth of developing embryo
|
front 20 Amnion | back 20
|
front 21 Yolk sac | back 21
|
front 22 Allantois | back 22
|
front 23 Chorion | back 23
|
front 24 Where does the placenta develop from | back 24 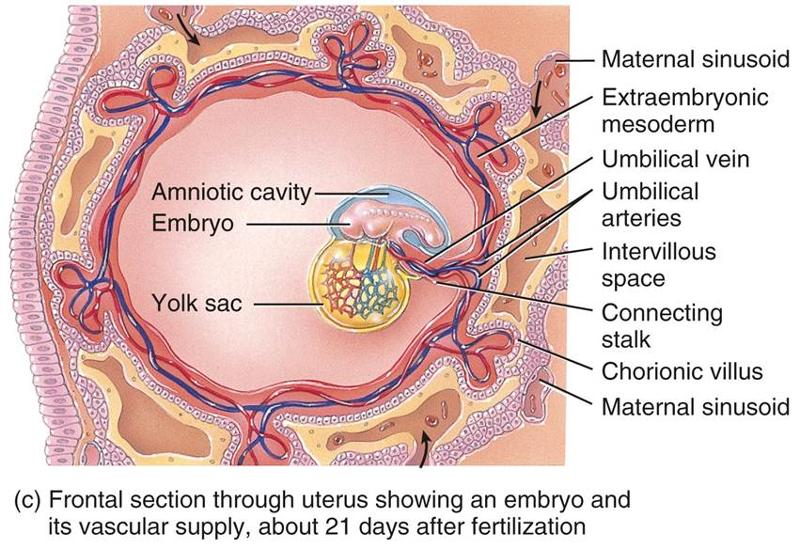 The chorionic villi of the embryo and endometrium of the mother |
front 25 What is managed in the placenta | back 25
|
front 26 What hormone secretion is taken over by the placenta | back 26 Occurs as the corpus luteum in the ovary gradually atrophies.
|
front 27 Organogenesis | back 27 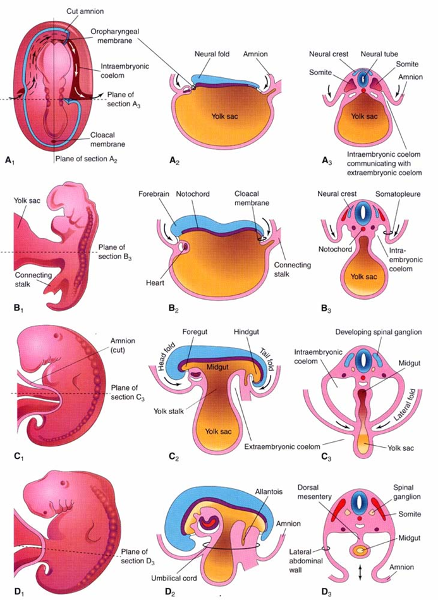 The 4th-8th weeks of development |
front 28 When does embryonic folding occurs (head, laterals, tail) | back 28 During week 4 |
front 29 When have all major body systems started to develop | back 29 By the end of week 8 |