Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
physics ch 6
front 1 1) A box of mass m is pulled with a constant acceleration a along a
horizontal frictionless floor by | back 1 B |
front 2  Two objects, each of weight W, hang vertically by spring scales as shown in the figure. The pulleys and the strings attached to the objects have negligible weight, and there is no appreciable friction in the pulleys. The reading in each scale is A) W. | back 2 a |
front 3 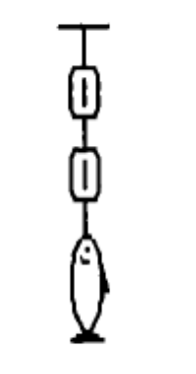 A fish weighing 16 N is weighed using two spring scales, each of
negligible weight, as shown A) The bottom scale will read 16 N, and the top scale will read
zero. | back 3 B |
front 4 Two objects have masses m and 5m, respectively. They both are placed
side by side on a | back 4 E |
front 5 A box slides down a frictionless plane inclined at an angle θ above
the horizontal. The | back 5 D |
front 6 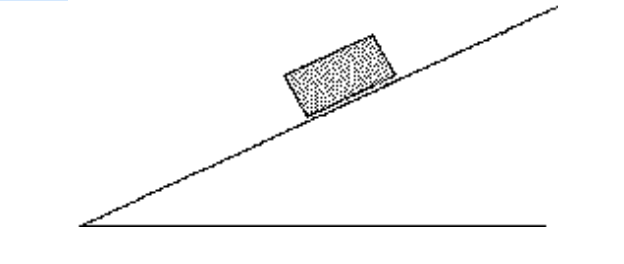 A brick is resting on a rough incline as shown in the figure. The
friction force acting on the A) zero. | back 6 D |
front 7 7) When a parachutist jumps from an airplane, he eventually reaches a
constant speed, called the | back 7 e |
front 8 1) A block lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. A horizontal
force of 100 N is applied to the | back 8 Answer: (a) 33 kg (b) 150 m (c) 30 m/s |
front 9 2) The following four forces act on a 4.00 kg object: | back 9 D |
front 10 3) A 50.0-N box is sliding on a rough horizontal floor, and the only
horizontal force acting on it is | back 10 A |
front 11 A block is on a frictionless horizontal table, on earth. This block
accelerates at 1.9 m/s2 when a | back 11 A |
front 12 5) A block is on a frictionless horizontal table, on earth. This
block accelerates at 3.6 m/s2 when a | back 12 A |
front 13 A 10,000-kg rocket blasts off from earth with a uniform upward
acceleration of 2.00 m/s2 and | back 13 C |
front 14 15) Bumpers on cars are not of much use in a collision. To see why,
calculate the average force | back 14 B |
front 15 8) A box of mass 50 kg is at rest on a horizontal frictionless
surface. A constant horizontal force F | back 15 59N |
front 16 A 1000-kg car is driving toward the north along a straight horizontal
road at a speed of 20.0 | back 16 C |
front 17 A construction worker pulls a box of tools on a smooth horizontal
floor with a force of 100 N | back 17 Answer: (a) The box is acted on by the force of gravity which points
downward toward the |
front 18 A 60.0-kg person rides in an elevator while standing on a scale. The
scale reads 400 N. The | back 18 A |
front 19 A 60.0-kg person rides in elevator while standing on a scale. The
elevator is traveling | back 19 B |
front 20 A block is given a very brief push up a 20.0° frictionless incline to
give it an initial speed of | back 20 (a) 21.5 m (b) 7.16 s |
front 21 A 50.0-kg box rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of
static friction between the box | back 21 (a) 140 N (b) 98.0 N |
front 22 15) In a shuffleboard game, the puck slides a total of 12 m before
coming to rest. If the coefficient | back 22 A |
front 23 A driver in a 1000 kg car traveling at 20 m/s slams on the brakes and
skids to a stop. If the | back 23 A |
front 24 17) Jason takes off from rest across level water on his jet-powered
skis. The combined mass of | back 24 A |
front 25 18) Jason takes off from rest across level water on his jet-powered
skis. The combined mass of | back 25 A |
front 26 19) Kieran takes off from rest down a 50 m high, 10 ° slope on his
jet-powered skis. The skis have a | back 26 A |
front 27 A factory robot drops a 10 kg computer onto a conveyor belt running
at 3.1 m/s. The materials | back 27 A |
front 28 You push downward on a box at an angle 25° below the horizontal with
a force of 750 N. If the | back 28 A |
front 29 A person is dragging a packing crate of mass 100 kg across a rough
horizontal floor where the | back 29 A |
front 30 23) A packing crate rests on a horizontal surface. It is acted on by
three horizontal forces: 600 N to | back 30 A |
front 31 A 6.0 kg box slides down an inclined plane that makes an angle of 39
° with the horizontal. If | back 31 A |
front 32 25) A 200 g hockey puck is launched up a metal ramp that is inclined
at a 30° angle. The | back 32 A |
front 33 A 200 g hockey puck is launched up a metal ramp that is inclined at a
30° angle. The | back 33 A |
front 34 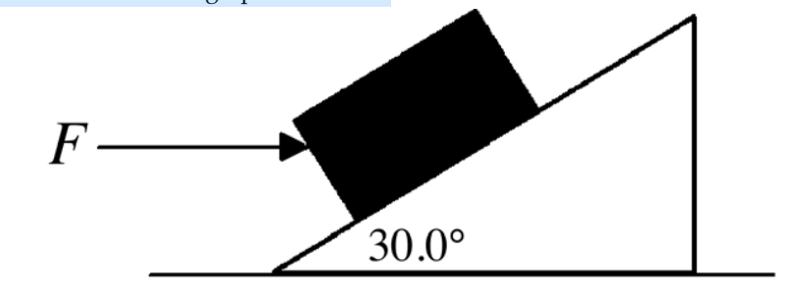 A 4.00-kg block rests on a 30.0° incline as shown in the figure. If
the coefficient of static | back 34 D |
front 35 A box is sliding down an incline tilted at a 12.0° angle above
horizontal. The box is initially | back 35 A |
front 36 29) A 50.0-kg block is being pulled up a 16.0° slope by a force of
250 N which is parallel to the | back 36 C |
front 37 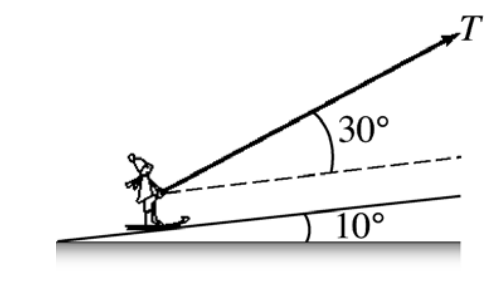 In the figure, a T-bar ski tow pulls a skier up a hill inclined at
10° above horizontal. The skier A) 246 N | back 37 C |
front 38 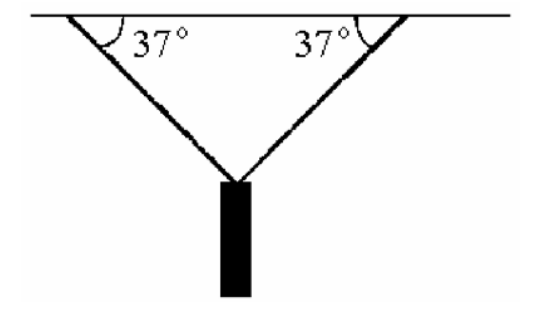 A traffic light weighing 100 N is supported by two ropes as shown in
the figure. The tensions A) 50 N. | back 38 E |
front 39 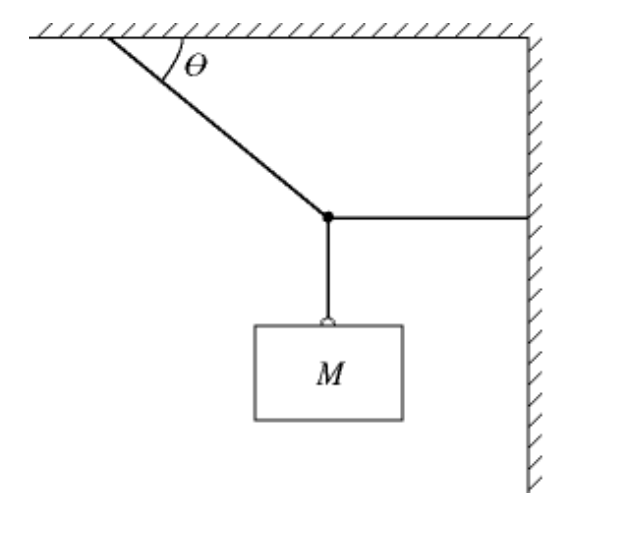 In the figure, a block of mass M hangs at rest. The rope that is
fastened to the wall is horizontal A) 55° | back 39 A |
front 40 34) The magnitude of the drag force of air resistance on a certain
20.0-kg object is proportional to | back 40 D |
front 41 A 30.0-kg object experiences a drag force due to air resistance with
a magnitude proportional | back 41 C |
front 42 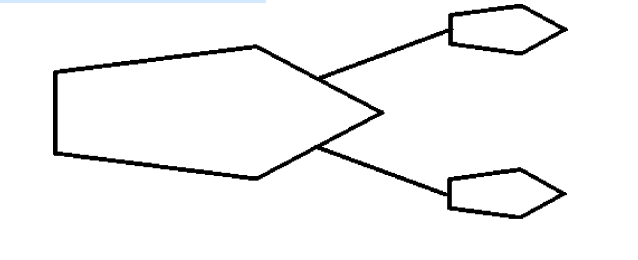 A ship is being pulled through a harbor at constant velocity by two
tugboats as shown in the A) 177 × 105 N | back 42 E |
front 43 37) A 1.20-kg ball is hanging from the end of a rope. The rope hangs
at an angle 25.0° from the | back 43 D |
front 44 38) An 80.0-kg object is falling and experiences a drag force due to
air resistance. The magnitude | back 44 D |
front 45 39) An object weighing 4.00 N falls from rest subject to a frictional
drag force given by Fdrag = | back 45 C |