Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
HESI
front 1 What is the best strategy for communicating health care information to a patient who is completely deaf? | back 1 Call for an interpreter certified in sign language |
front 2 Identify the proper medical record documentation of medication administration. | back 2 5 mcg/min, Epinephrine, IV, 11/12/2007, 0940 date, time, drug name, dosage, and route of administration |
front 3 Which guideline is recommended for safely lifting a patient from a seated position? | back 3 Stand with feet apart to establish a wide base of support |
front 4 Which guideline is most effective for reducing the number of nosocomial infections? | back 4 Position urinary catheter bags below the level of the patients bladder |
front 5 Which value represents a normal respiratory rate for a pediatric patient? | back 5 25 breaths per minute |
front 6 According to the American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines, which is the correct rate of chest compressions when administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to a 6-month-old patient? | back 6 At least 100 per minute |
front 7 Which is the most appropriate response to a patient who asks what the term "peritonitis" means? | back 7 peritonitis is an inflammation of the abdomen |
front 8 What route of transmission is responsible for transmitting a disease to a patient through an improperly cleaned x-ray table? | back 8 fomite |
front 9 According to the ARRT Standards of Ethics, a radiographer may be subject to sanctions including revocation of certification for which actions? (Select the three that apply.) | back 9
|
front 10 Which is the best way to control severe bleeding from a deep laceration of the upper arm? | back 10 apply direct pressure to the wound and raise the patients arm above the level of the heart |
front 11 Consider the contrast media label shown here. What does the "Not for parenteral use" warning mean? | back 11 It must be administered orally of rectally |
front 12 A patient is slumped over in his wheelchair and is non-responsive. After easing the patient to the floor, the radiographer finds no carotid pulse. The patient is experiencing which condition? | back 12 Cardiac Arrest. Cardiac arrest is the complete cessation of heart function. Myocardial infarction is the death of heart tissue due to lack of blood supply. |
front 13 Which general guideline is the most appropriate for determining when to use standard precautions? | back 13 When performing exams on all patients |
front 14 Which guideline represents the best approach for examining patients who are mentally impaired? | back 14 assess each patients ability to follow instructions prior to the exam |
front 15 When obtaining a blood pressure reading, systolic and diastolic values are determined by monitoring which pulse point? | back 15 brachial Radial and carotid points are commonly used to assess the rate and quality of a patient's pulse. |
front 16 A trauma patient arrives to the emergency department unconscious with tachycardia and hypotension. The patient has lost a significant volume of blood. The patient is experiencing which condition? | back 16 Hypovolemic shock |
front 17 Which is considered a major contraindication for intravenous urography? | back 17 hypersensitivity to contrast media |
front 18 When transferring a patient with hemiparalysis from a wheelchair to the x-ray table, in which position should the wheelchair be placed? | back 18 parallel to the x-ray table, with the patients strong side closest to the table |
front 19 What are the six right of drug administration that radiographers should follow? | back 19
|
front 20 Washing hands with soap and water disrupts the chain of infection by which process? | back 20 decreasing the number of pathogens present |
front 21 What is the most appropriate response if a patient asks about the risks of radiation exposure from a CT exam? | back 21 A CT results in a much higher radiation dose than x-ray, but your physician believes the benefits outweigh the risks |
front 22 This image is a medical record entry lacking important information. Place the cursor on the portion of this entry that is incorrect and left click. | back 22 All medical record entries must include the printed name and
credentials of the radiographer. |
front 23 What precautions should a radiographer take when entering the room of a patient with varicella virus? | back 23 Wear a particulate respirator mask, gloves, and gown Varicella is chickenpox, so airborne and contact precautions |
front 24 Place the cursor on the contrast media that should be administered for an intravenous urogram and left click. | back 24 Isovue |
front 25 Which condition requires a patient to be placed in a negative pressure room, and healthcare workers to wear respiratory protection when entering? | back 25 Tuberculosis |
front 26 Which example of nonverbal communication is most effective fr helping a patient overcome anxiety and apprehension prior to an exam? | back 26 maintain direct but appropriate eye contact with the patient |
front 27 During a routine radiographic examination, a patient complains of dizziness and appears anxious and diaphoretic. while checking the patients vital signs, the radiographer note a rapid heart rate, shaky hands, and clammy skin. Which is the most likely explanation for this presentation? | back 27 hypoglycemia |
front 28 during the medical history assessment prior to an upper GI study, the patient reports he is taking an AC inhibitor, Vasotec. This suggests the patient is being treated for which condition? | back 28 hypertension |
front 29 Which item must be discarded in a biohazard bag? | back 29 bed sheet saturated with blood |
front 30 What type of shock is caused by a reaction to contrast media? | back 30 vasogenic |
front 31 When a radiographer asks a patient to lie down on the imaging table and the patient complies, which type of consent has the patient given? | back 31 Simple consent |
front 32 Which describes the proper technique for needle insertion during venipunture? | back 32 Insert needle into vein at a 15-degree angle with bevel facing upward |
front 33 Which practices are considered violations of HIPAA? (two) | back 33
|
front 34 Which is the most likely result if an exposure is made without the use of a focusing cup? | back 34 Increased off focus radiation |
front 35 Which term refers to the removal of an electron from the orbital shell of an atom? | back 35 ionization |
front 36 How is the process of thermionic emission described? | back 36 electrons are released when the filament is heated |
front 37 which type of interaction results in the production of bremsstrahlung -rays? | back 37 a projectile electron slows down near the nucleus of the target atom |
front 38 Which term is used to describe the intensity of the x-ray beam? | back 38 quantity Quantity refers to the intensity, or total number of x-ray photons in the primary beam. |
front 39 what is the primary controlling factor for x-ray beam quality? | back 39 kVp |
front 40 Which type of radiation is produced when an outer shell electron fills an inner shell vacancy? | back 40 Characteristic |
front 41 What is the minimum recommended filtration for general diagnostic x-ray units? | back 41 2.5 mm Al |
front 42 In which position should the patient be placed in order to demonstrate the right intervertebral foramina of the cervical spine while minimizing radiation dose to the thyroid gland? | back 42 RAO |
front 43 What is the advantage of using high kVp, low mAs technique with DR systems? | back 43 patient exposure decreases |
front 44 With all other factors remaining the same, a decrease in kVp with cause an increase in which x-ray beam characteristic? | back 44 wavelength |
front 45 Which fluoroscopic mode results in the lowest patient dose? | back 45 Digital pulsed progressive |
front 46 A six year old pediatric patient arrives in the radiology suite for a radiograph of the abdomen. Which st of technical factors provides the best radiation protection? | back 46 82 kVp, 7.5 mAs |
front 47 What is the maximum allowable tabletop intensity in high level control (HLC) fluoroscopic procedures? | back 47 20 R/min |
front 48 A radiographer performs an abdomen examination with a mobile DR system. In order to reduce the likelihood of a repeat exposure, he decides to increase the technical factors slightly more than necessary. Which term refers to this undesirable practice? | back 48 Dose creep |
front 49 Which is the required amount of inherent filtration for general purpose x-ray tubes? | back 49 0.5 mm AL equivalent |
front 50 According to the FDA, what is the maximum air kerma rate for fixed fluoroscopic units? | back 50 10 cGy/min |
front 51 A radiographer stands six feet from the x-ray source when performing a portable chest exam and receives an exposure of 2 mGy. If the radiographer performs a repeat exam using the same technical factors standing at a distance of three feet from the source, how much exposure will be received? | back 51 8 mGy According the inverse square law, when the distance is halved, the exposure increases by a factor of four. In this scenario, the radiographer will receive 8 mGy at a distance of three feet, compared to 2 mGy at a distance of six feet. The equation is old intensity/new intensity equals the square of the new distance/old distance. The other answers result from incorrect application of the inverse square law. |
front 52 Which factors will impact the radiation barrier calculations for an x-ray room? (3) | back 52
|
front 53 Which procedures should imaging personnel perform in order to reduce exposure time during fluoroscopic procedures? (3) | back 53
|
front 54 Which organ has the highest tissue weighting factor? | back 54 gonads The gonads are the most radiosensitive organ, with a weighting factor of 0.20. The weighting factor for both the thyroid and breast is .05. The weighting factor for lung tissue is .12. |
front 55 Which minimum thickness of lead shielding is required to cover the bucky slot during fluoroscopic exams? | back 55 0.25 mm |
front 56 Which value represents the annual maximum dose limit for exposure to the extremities in medical imaging personnel? | back 56 500 mSv |
front 57 Which is the maximum allowable exposure to the embryo or fetus each month? | back 57 0.5 mSv |
front 58 A 14 year old female patient arrives in the radiology department for a scoliosis series. Which option provides both the bst image quality and lowest radiation dose for this patient? | back 58 Employ shadow shields |
front 59 For which lumbar spine projections should a shaped contact shield be applied to provide protection for the gonads of a male patient? (3) | back 59
|
front 60 How will dose area product (DAP) be affected during a 4 Roentgen exposure is the collimated field is reduced from 8 X 8 cm to 4 X 4 cm? | back 60 DAP will be 1/4 of the original |
front 61 Which statement correctly describes the amount of kinetic energy required for a photon to remove an inner shell electron from its orbit? | back 61 The same or greater than the electron binding energy |
front 62 In the diagnostic energy range, which substances possesses the greatest ability to absorb radiant energy through the process of photoelectric absorption? | back 62 bone |
front 63 Which are by-products of photoelectric absorption? | back 63 photoelectric and characteristic photon |
front 64 Which interaction with matter contributes to the majority of occupational exposure? | back 64 compton scattering |
front 65 Which describes the relationship between LT and RBE? | back 65 As LET increases, RBE increases |
front 66 Which describes a linear, non-threshold dose-response relationship? | back 66 No dose may be considered completely safe |
front 67 Which term is an alternate name for the prodromal stage of ARS? | back 67 Initial stage |
front 68 Which whole body dose most closely approximates the LD 50/30 for humans? | back 68 300 rad The LD 50/30 refers to the whole-body dose that can be lethal to 50% of the population over 30 days; for humans, this dose is reached is between 300 and 400 rad |
front 69 At which energy range dose photodisentegration occur? | back 69 above 10 megaelectron volts (mEv) |
front 70 For which purpose is gonadal shielding recommended? | back 70 To reduce the probability of genetic mutations |
front 71 Which combination of technical factors is recommended to reduce patient dose? | back 71 high kVp low mAs |
front 72 What is the primary purpose of beam filtration? | back 72 To protect patient from low energy x-rays |
front 73 Patient dose during fluoroscopy can be minimized by which methods? (3) | back 73
|
front 74 When a pregnant patient must undergo a radiographic procedure, which practices will minimize radiation exposure? (3) | back 74
|
front 75 Which method should be the first choice to reduce exposure to the reproductive organs in every radiographic exam? | back 75 collimate to include only the anatomy of interest |
front 76 How should the radiology manager schedule a pregnant radiographer? | back 76 Maintain the employees same schedule before declaration of pregnancy |
front 77 how many millimeters of lead equivalency is recommended for lead aprons worn by pregnant radiographers? | back 77 0.5 |
front 78 How should a mobile C-arm fluoroscope be positioned to provide maximum radiation protection to the operator? | back 78 With the tube under the patient and as far away from the patient as possible |
front 79 If all other factors remain constant, how is radiation dose related to SOD? | back 79 by the inverse square law |
front 80 Over the entire gestational period, what is the fetal exposure limit? | back 80 0.5 rem (5 millisievert) |
front 81 Which term means the loss or change of a nitrogenous base in the DNA chain? | back 81 Mutation |
front 82 Which human cell is the most resistant to the effects of radiation? | back 82 neurons |
front 83 Which dose may cause temporary sterility of both males and females? | back 83 2 Gy |
front 84 Biologic damage resulting from the ionization of key atoms causing these molecules to become inactive or functionally altered is much more likely to occur after exposure to which type of radiation? | back 84 High LET radiation such as alpha particles |
front 85 Place the following actions in order of greatest to least impact for reducing occupational exposure during fluoroscopy. | back 85
|
front 86 Place the following actions in the order of greatest to least impact for reducing occupational exposure during fluoroscopy. | back 86
|
front 87 Which post processing action is always acceptable? | back 87 Annotating with an upright marker to show the patient was in an erect position |
front 88 How does a wide window width affect an image? | back 88 decreases contrast |
front 89 In CR systems, the photostimulable phosphor plate is made of which material? | back 89 Barium Fluorohalide |
front 90 Which radiopaque marker is image appropriate after micturition has taken place? | back 90 Post-void |
front 91 Which procedure is most effective for reducing localized image blurring caused by involuntary patient motion? | back 91 Decrease exposure time |
front 92 Assuming that AEC is to be used, what backup mAs are sufficient for a large adult AP lumbar spine done at 80 kVp? | back 92 100 mAs |
front 93 The radiographer is using AEC on a sinus examination. The quality control technologist directs the radiographer to repeat the Water's projection with increased contrast. Thus the radiographer changes the kVp from 85 to 72. What change to AEC settings or positioning is needed? | back 93 No change |
front 94 Which x-ray tube orientation represents the correct application of the anode heel effect? | back 94 The anode end is positioned toward the head for an AP thoracic spine projection |
front 95 A lateral lumbar spine image was obtained with a field size of 11X14 inches at 95 kVp and AEC with the center detector selected. The resulting image demonstrates excessive quantum noise. Which is the most likely cause for this appearance? | back 95 The patient was not accurately centered |
front 96 Which effect does switching to the small focal spot size have on a manifest image? | back 96 Image unsharpness decreases |
front 97 Which acronym describes a network of computers that manages digital images? | back 97 PACS |
front 98 How will raising the window level affect the digital image? | back 98 increases brightness |
front 99 A fixed kVp variable mA chart recommends exposure factors of 70 kVp and 32 mAs for an AP abdomen projection on an average-size patient. Based on this chart, which fixed kVp technique is most appropriate for an AP projection of a double contrast upper GI image? | back 99 90 kVp, 8 mAs 15% kVp rule |
front 100 Which mA station with result in a mAs value of 44 if the exposure time is 0.11 seconds? | back 100 400 mA |
front 101 Which image, when performed according to normal standards, will demonstrate the greatest magnification of the anatomy of interest? | back 101 Lateral cervical spine |
front 102 Which term refers to a graphical representation of pixel values? | back 102 Histogram |
front 103 The collimator light must be aligned to the radiation field within what percent of the SID? | back 103 2% |
front 104 With all other factors remaining the same, which SID results in the greatest exposure to the IR? | back 104 40 inches |
front 105 How are AEC devices for mammo different than those used with diagnostic radiography? | back 105 Greater accuracy required |
front 106 Which set of exposure factors is most likely to provide clear visualization of the upper cervical spine through the mandible when performing an AP wagging jaw projection? | back 106 75 kVp 25 mA and 2 seconds |
front 107 When using digital imaging, which has the greatest influence on contrast? | back 107 LUT |
front 108 The mobile chest image lacks which required element? | back 108 anatomical markers |
front 109 The center of the x-ray beam must be aligned to the center of the bucky tray to within what percent of the SID? | back 109 1% |
front 110 Which mAs setting is most likely to produce quantum mottle? | back 110 2.5 mAs |
front 111 Opening the collimators wider than necessary using digital radiography has which effect on image quality? | back 111 increased image noise |
front 112 Consider these different abdomen images of the same patient. What most likely caused the difference in these images? | back 112 Image A was produced at a shorter SID Image A was blacker, or more dense, so it makes sense that a shorter SI was used. |
front 113 How does aliasing appear radiographically when using CR? | back 113 Two superimposed images, slightly out of alignment |
front 114 Which is an advantage of digital imaging systems compared to traditional film screen systems? | back 114 Improved contrast resolution One advantage digital systems have over film-screen receptors is improved contrast resolution, or a greater ability to distinguish between structures of similar densities (this is also termed improved dynamic range). Digital systems are no less susceptible to image noise than traditional film-based systems. Spatial resolution is decreased relative to film-screen imaging due to the size of the pixel. Digital systems are more sensitive to scatter radiation than film-screen receptors. |
front 115 Which mAs value should be selected for a patient measuring 30 cm if 22 mAs is optimal for a patient measuring 25 cm? | back 115 44 mAs When using fixed kilovolts peak techniques, an increase in patient thickness of 4 to 5 cm requires that the mAs be increased by a factor of 2. In this example, an increase of 5 cm would require in increase from 22 mAs to 44 mAs. The other values represent increases of 25%, 40%, and 80%, respectively. |
front 116 Which scenario causes foreshortening of the anatomy on the image? | back 116 The humerus in contact with the IR, the forearm lifted off the image receptor, and the central ray directed perpendicular to the long axis of the humerus Foreshortening occurs when the part is angled in relationship to the central ray, or when the forearm is lifted off the IR, but the central ray is still directed perpendicular to the long axis of the humerus |
front 117 Which is the best way to avoid excessive quantum noise when using cassette based digital systems? | back 117 Increase the amount of exposure to the IR |
front 118 Which is a primary advantage of a rotating anode? | back 118 less heat is generated at the target |
front 119 Which factor will have the greatest impact on decreasing recorded detail or spatial resolution? | back 119 Motion |
front 120 At which location is the ionization chamber located in the AEC device? | back 120 between the grid and IR |
front 121 A portable chest x-ray is taken at 56 inches using 12 mAs at 72 kVp. Which technique should the radiographer use if the chest x-ray is repeated in the radiology dept at 72 inches to maintain density? | back 121 24 mAs at 72 kVp In order to maintain density when distance is changed, the radiographer should adjust mAs using the exposure/density maintenance formula (mAs1/mAs2 = D1 squared/D2 squared) |
front 122 Which technical factor increases the number of x-ray photons reaching the IR? | back 122 increase mA |
front 123 Which term refers to the positive electrode of the x-ray tube? | back 123 anode |
front 124 all other factors remaining the same, how will increasing the SID from 40 to 60 inches affect the appearance of a radiographic image? | back 124 decrease magnification |
front 125 Which device provides the required amount of voltage for x-ray production? | back 125 transformer |
front 126 Which factors affect spatial resolution in digital imaging? (2) | back 126
|
front 127 Which substance is added to the x-ray tube housing to increase heat dissipation? | back 127 oil |
front 128 Which combination results in an image with the greatest recorded detail? | back 128 2 inch object-to-image-receptor-distance (OID), 72 inch source-to-image-receptor-distance (SID), 0.6 mm focal spot size (FSS). Correct |
front 129 An image of the abdomen demonstrates appropriate density and scale of contrast, but motio blur is present due to peristalsis. If the original image was obtained with a 200 mA station and an exposure time of 0.35 seconds, which set of technical factors will produce a comparable exposure while minimizing motion artifact? | back 129 500 mA and 0.14 Seconds |
front 130 Which device is located in the primary section of the general x-ray circuit? | back 130 timer circuit |
front 131 which device in the x-ray circuit changes alternating current to direct current? | back 131 rectifier |
front 132 which effect does a step up transformer have on voltage and current? | back 132 voltage is increased and current is decreased |
front 133 Which effect will a low SNR have on the appearance of a digital radiographic image? | back 133 decreased contrast resolution SNR is largely dependent on the number of photons available for image formation. Fewer available photons results in a low SNR, which in turn results in higher image noise and decreased contrast resolution. |
front 134 A radiograph of optimal density is produced at 15 mAs and a SID of 40 inches. Which mAs value is required to produce the same radiographic density if this exam is repeated at an SID of 48 inches? | back 134 22 The density maintenance formula, mAs1/mAs2 = D1 squared/D2 squared, provides a method of compensating for changes in SID. In this instance, 15/x = (40)2/(48)2; 1600x = 34,560; x = 34,560/1600 = 22 mAs. The other answers result from math errors. |
front 135 Which post processing techniques may be used with digital imaging? (3) | back 135
|
front 136 Which advantage is gained by increasing the standard SID from 40 to 48 inches? | back 136 increased image resolution |
front 137 Beginning with the patients head in true lateral position, which positioning method is recommended for demonstrating the mandibular body without foreshortening on an axiolateral oblique method of the mandible? | back 137 Rotate the patients head 30 degrees toward the IR |
front 138  Consider this oblique hand image. Which statement correctly describes this image? | back 138 The hand is under-rotated |
front 139 Which lumbar spine structures are best demonstrated with the patient in a 45 degree LPO? | back 139 Left Z joints lumabar intervertebral foramina are shown on laterals |
front 140 Which type of pathology is defined as inflammation of an outpouching of the colon? | back 140 diverticulitis Diverticulitis is an inflammation of the outpouching of the colon. Diverticulosis is simply the condition of having outpouchings in the colon |
front 141 The Holmblad method is performed to demonstrate which radiographic appearance? | back 141 Open intercondylar fossa |
front 142 In which position should the patient be placed for insertion of the enema tip during a barium enema procedure? | back 142 Sims' |
front 143 Which body plane is positioned perpendicular to the IR on a lateral chest projection? | back 143 Midcoronal plane |
front 144 Which radiographic appearance results when the anterior surface of the patients elbow is rotated 45 degrees medially for an AP elbow projection? | back 144 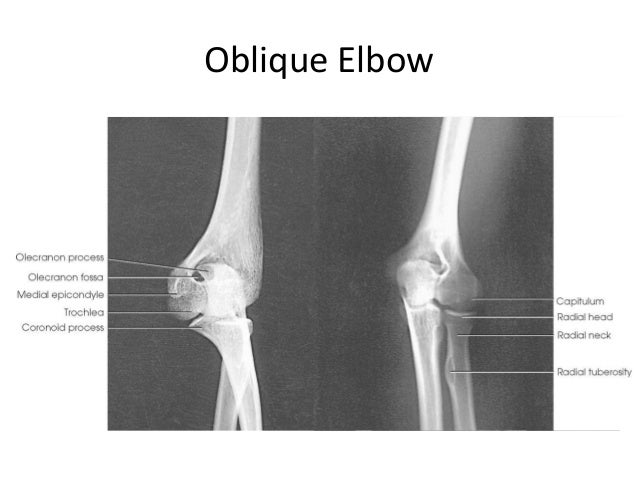 The coronoid process is seen in profile |
front 145 Which bones make up the ankle mortise? | back 145  tibia, fibula, and talus |
front 146 Where should the CR be directed for a lateral lumbosacral spine projection when using a 14X17in IR? | back 146 Iliac crest |
front 147 Which statement most accurately describes the position of the kidneys within the abdominal cavity of an average patient? | back 147 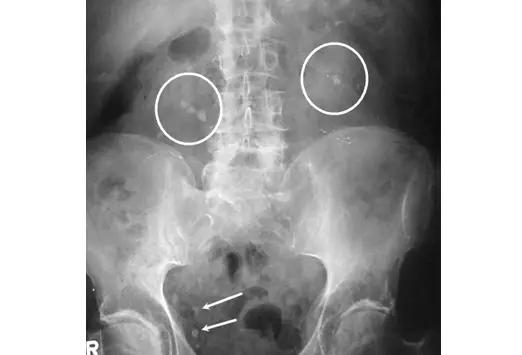 The left kidney is positioned slightly higher than the right kidney |
front 148 Which finding is demonstrated most clearly by a left lateral decubitus image of the abdomen? | back 148 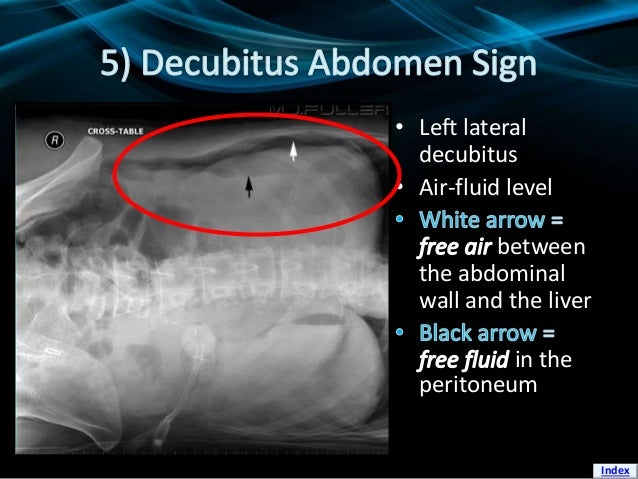 free air over the liver |
front 149 Which is the correct central ray location for an AP knee? | back 149 1/2 inch below the apex of the patella |
front 150 An AP shoulder image acquired with the epicondyles perpendicular to the image receptor with demonstrate which radiographic appearance? | back 150 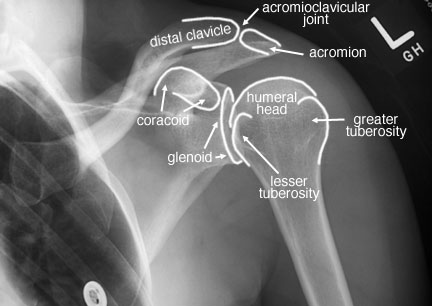 The lesser tubercle is seen in profile medially |
front 151 How far should the upper border of the IR extend above the shoulders for a PA chest? | back 151 1.5-2 inches |
front 152 How many posterior ribs should be visable above the diapragm on a PA chest? | back 152 10 |
front 153  Based on the appearance of the image, in which position was the patient placed for this postfluoroscopy image? | back 153 RAO The RAO position, shown here, demonstrates the stomach rotated clear of the vertebral column with air in the fundus and barium in the body and pylorus. The right lateral position shows the vertebral column lateral, the LPO position demonstrates barium is in the fundus and the air is in the pylorus and the supine position shows the vertebral column in its anterior perspective. |
front 154 Which structure is demonstrated without superimposition on a properly position medial oblique foot? | back 154  cuboid |
front 155 Place the parts of the respiratory tract in order from the most proximal to the most distal. | back 155
|
front 156 Which statement describes the presence of patient rotation on a lateral C spine image? | back 156  anterior to posterior displacement of Z joint |
front 157 Which describes the appearance of a PA axial projection of the skull using the Caldwell method? | back 157 petrous pyramids in lower 1/3 or orbit |
front 158 Which portion of the small intestine is most commonly affected by Crohns disease? | back 158 Ileum Cecum is part of large intestine |
front 159 Which positioning procedure is performed to demonstrate the right intervertebral foramina of the C spine? | back 159 LPO |
front 160 Which appearance is demonstrated by a lateral projection of the shoulder obtained using the Lawrence method? | back 160 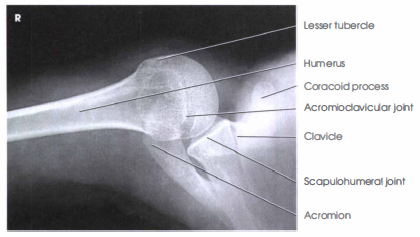 The proximal humerus is projected through the lung field |
front 161 Which radiographic finding is characteristic of C spine trauma resulting in a jefferson fracture? | back 161 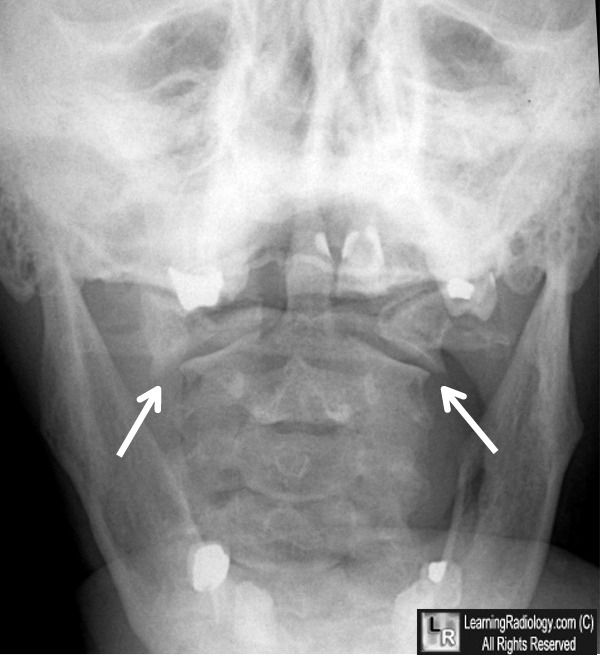 Open mouth view demonstrates a bilateral displacement of the lateral masses of C1 |
front 162 When is a cross table later preferred over a recumbent left lateral when obtaining images for a myelogram? | back 162 Contrast may move out of the area of interest when rolling into the lateral position |
front 163 For which purpose is orthoroentgenography performed? | back 163 long bone measurement |
front 164 Which method of respiration will demonstrate the maximum number of ribs above the diaphragm when performing an AP projection of the upper ribs? | back 164 suspended deep inspiration |
front 165 A PA axial projection of the coccyx is performed because the patient is unable to tolerate the supine position due to injuries sustained after falling backward. How should the CR be adjusted for this projection? | back 165 10 degrees cephalad |
front 166 Which anatomical structure is the most medial? | back 166 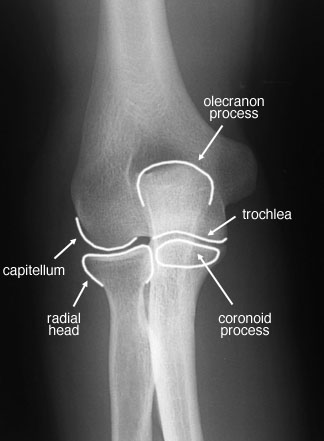 Coronoid tubercle |
front 167 If a radiographic image is requested to show the nephrogram phase of an intravenous urogram, how long after IV contrast administration should this image be obtained? | back 167 30 seconds to 1 minute The nephrogram phase of an IVU should be obtained within the first 30 seconds to one minute post injection in order to show the initial blush as contrast enters the nephrons, but has not yet reached the collecting tubules. |
front 168 An AP pelvis image shows evidence that the patient is rotated toward the right hip. Which statement below best describes the appearance of this image? | back 168 Right iliac wing appears larger than the left iliac wing |
front 169 In which exam is contrast introduced in to the area of interest in a retrograde fashion? | back 169 ERCP |
front 170 Which is the correct CR location for a PA hand projection? | back 170 3rd MCP |
front 171 The right RPO chest position may be used instead of the LAO position to demonstrate the heart and great vessels. How will using the RPO position affect the appearance of these structures? | back 171 The left lung appears shorter than the right |
front 172 Which alternative procedure is recommended when positioning a patient for a Swimmers lateral of the cervicothoracic region if the shoulder away from the image receptor cannot be fully depressed | back 172 angle the central ray 3-5 degrees caudad |
front 173 Which anatomical structure is the most distal? | back 173  Radial tuberosity |
front 174 Which tarsal bone is best seen when the plantar surface of the foot is positioned perpendicular to the image receptor, and a 40 degree cephalic CR is directed to the base of the third metatarsal? | back 174 Calcaneus |
front 175 Where should the CR enter the patient on an AP projection of the chest with the patient in the lateral decubitus position? | back 175 three inches below the jugular notch |
front 176 Which method of respiration is recommended for a soft tissue neck exam to evaluate the trachea? | back 176 shallow breathing |
front 177 What should be demonstrated on a properly exposed supine image of the abdomen? | back 177 perirenal fat |
front 178 Which statement describes a properly positioned lateral foot image? | back 178 superimposition of the first and fifth metatarsal heads |
front 179 Which wrist projection best demonstrates a Colles' fracture? | back 179 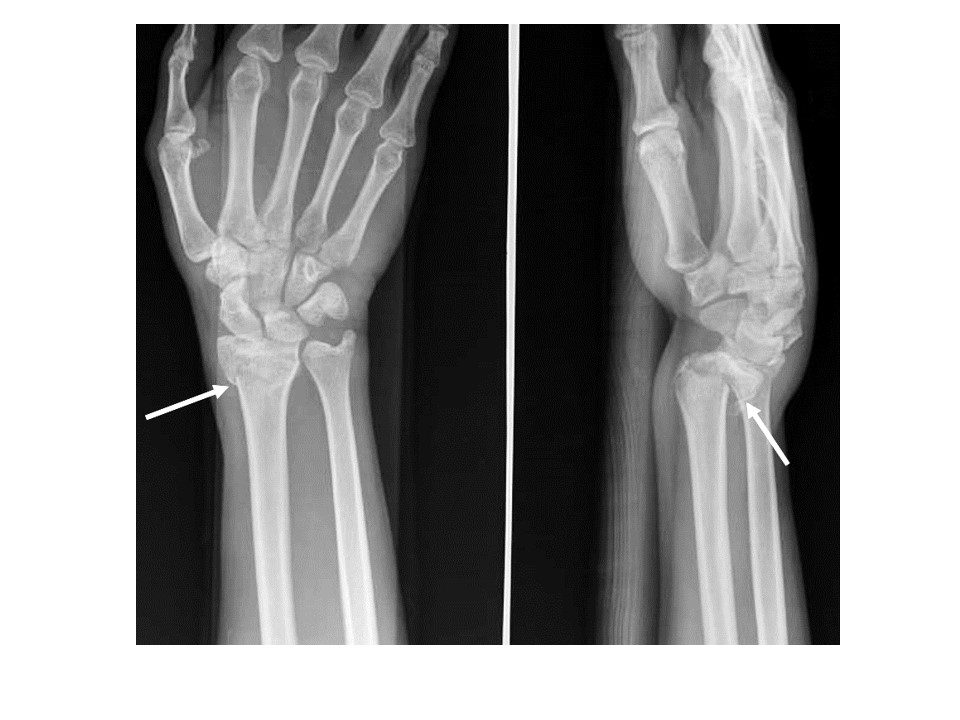 Lateral Wrist |
front 180  | back 180 no data |
front 181 In which position is the knee placed in order to demonstrate the head of the fibula without superimposition? | back 181 45 degrees medial rotation |
front 182 Which anatomical landmark coincides with the level of CR entrance point for a PA chest radiograph? | back 182 inferior border of scapula |
front 183 The alexander method is used to demonstrate dislocation of which joint? | back 183 acromioclavicular |
front 184 After contrast has been administered into the hip joint during arthrography, what should the patient do? | back 184 Exercise the joint to allow the contrast to completely fill the joint space |
front 185 Which is the CR location for an AP oblique projection of the urinary bladder during a cystogram? | back 185 2 inches superior to the pubic symphysis and 2 inches medial to the elevated ASIS |
front 186 Which CR orientation is recommended for a standard AP axial projection of the skull to demonstrate the dorsum sellae within the foramen magnum | back 186 30 degrees to the OML A standard AP axial projection (Towne method) of the skull is performed with the CR positioned at a 30-degree angle to the OML. |
front 187 How should the CR be angled to compensate for a patient who is unable to assume the erect lordotic position for an AP axial lordotic projection of the chest? | back 187 15-20 degrees cephalic |
front 188 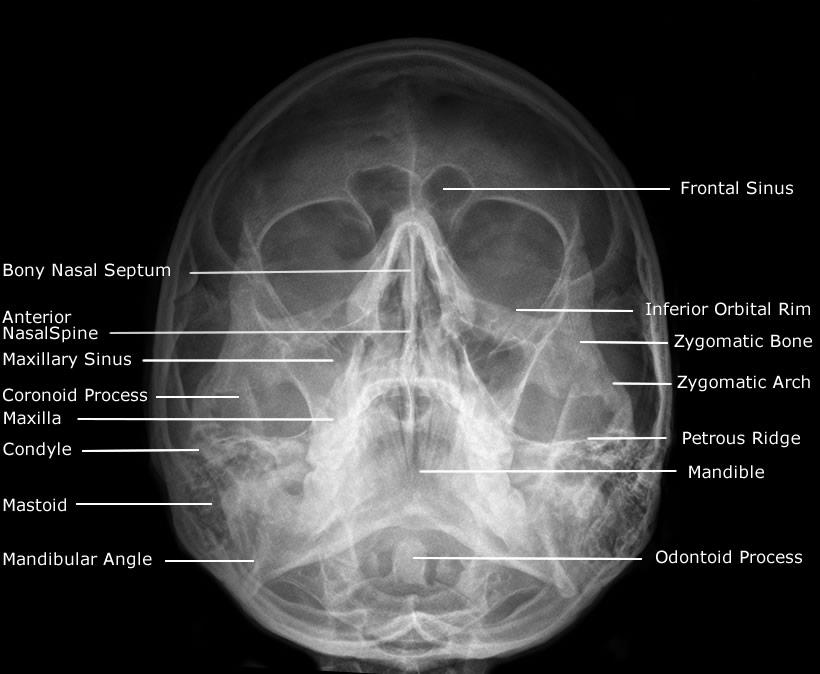 Which skull positioning line is situated perpedicular to the IR when performing a Water's method of the facial bones? | back 188  MML this projects the petrous pyramids below the maxillary sinuses. |
front 189 The appendix is connected anatomically to which structure? | back 189 cecum |
front 190 Which CR angle is recommended to demonstrate the coronoid process of the elbow using the Coyle Method? | back 190 45 degrees away from the shoulder |
front 191 How are the patients hand and fingers positioned for a PA wrist projection? | back 191 hand pronated with fingers flexed |
front 192 At which location is the CR directed for an AP projection of the thoracic spine? | back 192 midway between the sternal notch and the xiphoid process |
front 193 How should the radiographer rotate the patients lower leg and foot for an AP oblique projection of the second toe? | back 193 30-45 degrees medially |
front 194 Which position/projection of the elbow best demonstrates the trochlear notch of the ulna? | back 194  lateral |
front 195 Which x-ray tube orientation is used to create a 90 degree angle between the CR and the metatarsals for an AP axial projection of the foot | back 195 10 degrees posteriorly |
front 196 Where should the CR enter the patient for a lateral sacrum projection? | back 196 3-4 inches posterior to the ASIS |
front 197 Which projection demonstrates the Right kidney in profile? | back 197 30 degree LPO |
front 198 Which projection of the foot demonstrates the cuboid bone in profile with the least bony superimposition? | back 198 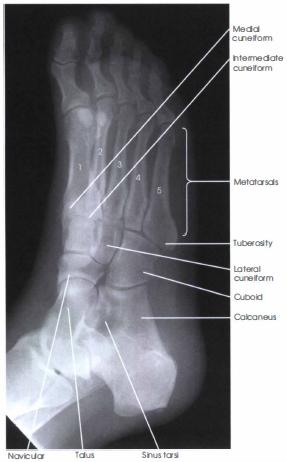 medial oblique |
front 199 If a patient is to undergo a small bowel series without a preceding upper upper GI series, how much barium sulfate suspension should be given? | back 199 two 250cc cups |
front 200 Which is the proper amount and direction of heel rotation recommended for a PA projection of the patella? | back 200 5-10 degrees laterally |
front 201 Study the four digital images of both shoulders. What best describes the quality of these images? | back 201 the degree of internal rotation was inadequate on both sides Neither image shows the lesser tubercle in profile medially |
front 202 On a radiograph of a shoulder, the greater tubercle is visualized in profile. Which projection was taken? | back 202  External rotation |
front 203 There are several methods to overcome sagging of the lumbar spine in the lateral position. Where should the radiographer begin? | back 203 Assessing the line connecting spinous processes relative to the table top |
front 204 Which CR angle is recommended for an AP axial projection of the toes? | back 204 15 degrees toward the heel |
front 205 When performing a RAO of the sternum, a radiographer will rotate the pt 15-20 degrees. Why is this done? | back 205 to prevent superimposition of the vertebra and the sternum A 15-20 degree rotation is used to prevent superimposition of the vertebrae and sternum. If this rotation is not used, then the spine will be blocking the sternum. Rotating the patient will not move the sternum from the shadow of the heart. The heart shadow will still be superimposed on the sternum. |
front 206 Which condition may increase bowel motility? | back 206 Malabsorption syndrome |
front 207 Which projection of the stomach demonstrates the duodenal bulb filled with barium and free of superimposition? | back 207 RAO Duodenum is on right side |
front 208 Place the parts of the GI tract in order from proximal to distal. | back 208
|
front 209 Which projection is freest of bony superimposition over the TMJ? | back 209 Schuller |
front 210 which projection will clearly show a clay shovelers frature? | back 210 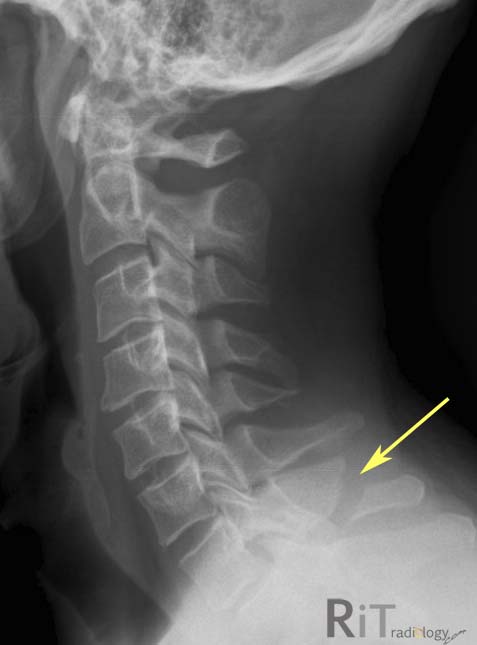 lateral cervical |
front 211 What is the angle between the intervertebral foramina and the midsaggital plane in the thoracic spine? | back 211 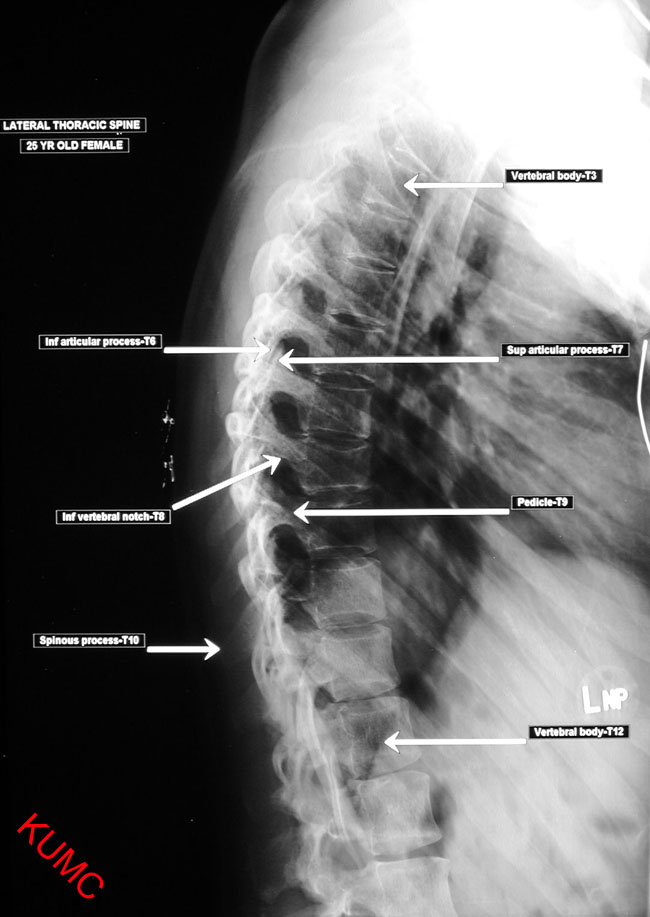 90 |
front 212 Which position of the elbow will clearly demonstrate the radial neck free of ulnar superimposition? | back 212  |
front 213 According to Merrills Atlas where should the central be centered to best demonstrate the rami for a posteroanterior mandible projection? | back 213 acanthion |
front 214 This 45 degree oblique ankle image demonstrates the calcaneus obscuring the distal aspect of the lateral mortise and distal fibula. How should the radiographer correct this image? | back 214 Dorsiflex foot |
front 215 On a lateral radiograph of a patients leg, where will the patients tibia be in relation to the fibula? | back 215  partially superimposed Only the proximal and distal ends of the two bones should be superimposed. |
front 216 Which describes correct positioning for a PA chest projection? (3) | back 216
|
front 217 Correct positioning for an AP pelvis requires the lower limbs to be internally rotated until which structures are parallel with the IR? | back 217 Femoral necks |
front 218 While reviewing an AP portable chest exam on the display a radiographer notices the medial ends of the clavicles are demonstrated just below the top of the apices of the lungs. Which positioning error has occurred? | back 218 The central ray angle was angled towards the head |
front 219 Can the positioning of this open mouth odontoid view be improved? | back 219 No, its the best that can be achieved with this patient |
front 220 On a fan lateral radiograph of a left hand, which group of bones is best visualized? | back 220 Phalanges |
front 221  A radiographers critiques an AP ankle. The medial mortise joint is open while the lateral mortise joint is closed. How can the radiographer adjust the ankle to correct this image? | back 221 No correction needed |
front 222 A radiographer critiques an AP image of the ribs. The left SC joint is demonstrated without vertebral column superimposition. What should the radiographer do? | back 222 Rotate patient to the right |
front 223 What is the correct position of the midsagittal plane with respect to the IR when performing a true lateral projection of a skull? | back 223 parallel to the IR |
front 224 Where should the radiographer direct the CR for a PA chest? | back 224 MSP 18-20 cm below the vertebral prominens |
front 225  How should the radiographer correct this image of a medial oblique foot? | back 225 Increase medial rotation |
front 226 Where is the anterior arch of C1? | back 226  |
front 227 Which exam may be used to assess cruciate ligament pathology? | back 227  knee arthrogram |
front 228 Why are dorsal decubitus projections of the abdomen obtained? | back 228  to see free gas or fluid levels in the abdomen |
front 229 Which bony landmark is commonly used for central ray location on an AP chest projection? | back 229 jugular notch |
front 230 Which procedure is most appropriate when performing a cervical spine exam for suspected trauma on a patient on a backboard with the head immobilized? | back 230 Obtain a cross table lateral for the physician prior to further imaging |
front 231  A lateral scapula image demonstrates the lateral border of the scapula next to the ribs and the vertebral border of the scapula demonstrated posterolaterally. How should the radiographer correct this image? | back 231 decrease patient obliquity |
front 232 A trauma patient arrives in the radiology department on a backboard with possible trauma to the anterior chest wall. Which is the best method for obtaining an oblique sternum radiograph in this setting? | back 232 place the patient in a 15-20 degree LPO |
front 233 Which position is used to demonstrate the left kidney in profile for an IVU? | back 233 30 degree RPO |
front 234 When imaging the toes, how much is the central ray angled for the AP axial image? | back 234 15 degrees |
front 235 What can be demonstrated with a left lateral decub position of the thorax? | back 235 Air in the Right pleural space and fluid in the left pleural space Air up fluid down |
front 236 An 82 year old female patient is transported to the x-ray dept for an exam of the right hip. The ordering physician informs the radiographer that the patient fell at home, and there is high suspicion for a femoral neck fracture. Which positioning guideline is best for the radiographer to follow? | back 236 Do not move the affected leg |
front 237 Which type of fracture results from a direct blow to the front of the orbit? | back 237 Blowout |
front 238 Body habitus can affect many things, including the position of the gallbladder. Place the body habitus in order from which habitus will cause the gallbladder to occupy the highest position in the abdominal cavity to the habitus that will cause the gallbladder to occupy the lowest position in the abdominal cavity. | back 238 
|
front 239 What is the proper amount of internal leg rotation for the ankle mortise joint to appear open? | back 239 15-20 degrees |
front 240 For a lateral femur, if a patient is rotated too far anteriorly, what will happen to the condyles on the distal femur? | back 240 medial condyle will be anterior to lateral condyle |
front 241 Which anatomy is well visualized when the foot is is properly positioned and exposed in an axial plantodorsal projection of the heel? | back 241 an open middle talocalcaneal joint |
front 242 An image demonstrates the patella superimposing the medial condyle of the knee and little superimposition between the head of the fibula and the proximal tibia. Which projection of the knee has been correctly performed? | back 242 AP with medial rotation |
front 243 Which is the best projection to evaluate the coronoid process in profile? | back 243  Medial oblique elbow |
front 244 To demonstrate scoliosis, which procedure is best? | back 244 Erect AP of the entire spine |
front 245 A lateral knee image reveals that the femoral condyles are not superimposed with the medial condyle situated posteriorly. How should the radiographer correct this image? | back 245  Position patella closer to the IR |
front 246 While performing an AP Projection of the scapula, what should be done to the patients are to move the patients scapula in a lateral direction? | back 246 abduction |
front 247 What should the radiographer do to correct this image? | back 247  No correction needed |
front 248 Which CR angulation is recommended to prevent foreshortening of the sacrum on an AP projection? | back 248 15 degrees cephalad |
front 249 What should be done to correct positioning on an AP elbow with lateral rotation when the radial head is slightly superimposed over the proximal ulna on the first effort? | back 249  The elbow joint should be rotated laterally The AP with lateral rotation should demonstrate the radial head, neck and tuberosity free from superimposition of the ulna
|
front 250 Which projection is a radiographer performing if the patients hand is turned in extreme internal rotation, with the central ray directed perpendicular to the first MCP joint? | back 250 AP thumb |
front 251 Which finding is considered a contraindication for myelography? | back 251 blood in CSF Blood in the cerebrospinal fluid indicates that there is an irritation within the subarachnoid space, which can be exacerbated by the injection of contrast medium. |
front 252 Which describes the correct positioning for demonstrating the right SI joint, with the joint space open? | back 252 25 degree LPO Upside joint is imaged |
front 253 When attempting to demonstrate air-fluid levels, what is the correct central ray orientation for an AP semierect chest projection? | back 253 parallel to the floor |
front 254  Which position was used to produce the image of the stomach? | back 254 LPO fundus This is undeniably the case, as the bulk of the barium is seen in the fundus of the stomach which is the lowest part of the stomach in that position. |
front 255 Where should the radiographer center to demonstrate the only point of articulation between the upper limb and the trunk? | back 255 Level of T2/T3 and 1 to 2 inches lateral from the MSP |
front 256 Identify the medical condition in a patients history which should be cleared by the radiologist before the injection of an ionic, water soluble, injectable contrast agent. | back 256 Diabetes |
front 257 A patient with advanced Alzheimer's disease needs to have a lung biopsy. Which condition is involved in legally obtaining informed consent to perform this procedure? | back 257 A guardian has been fully informed |
front 258 Which disease is contracted by exposure to infected blood and blood products? | back 258 Hepatitis B Contact with infected blood or blood products is necessary to transmit Hepatitis B. Tuberculosis, Smallpox, and Rubella are transmitted via airborne or airborne droplet methods. Hep B affects the liver and is transmitted by dirty needles, sex, tattoos, razors and toothbrushes |
front 259 A patient become unresponsive after receiving an injection of iodinated contrast media. The patients blood pressure is 80/50. what has likely occured? | back 259 anaphylactic shock |
front 260 Which type of contrast is recommended if the patient has a perforated bowel? | back 260 Gastrografin Gastrografin or other water soluble contrast media is used, because it is safer for Gastrografin to leak out of the bowel and into the peritoneal cavity. Isovue is expensive |
front 261 If a patient with a compound fracture has an immobilization device in place, what is the best action by the radiographer? | back 261 Leave the device in place unless directed by a physician to remove it |
front 262 Which condition could lead to neurogenic shock? | back 262 Head trauma neurogenix shock is the failure of arterial resistance and causes a pooling of blood in periphery vessels |
front 263 During a myelogram, a patient on the table stops breathing, and cardiac arrest is suspected. In an emergency like this where would needed equipment and supplies be found? | back 263 crash cart |
front 264 Which normal effect of aging is a common obstacle to communication with elder adults? | back 264 hearing impairment |
front 265 which example represents a violation of HIPAA? | back 265 Patients condition is discussed by staff in the break room |
front 266 Which is an example of a violation of patients privacy? | back 266 A named patient is called for his barium enema |
front 267 A patient with a history of stroke and hemiparalysis is transported to the x-ray dept by wheelchair. Which action should be taken first by the radiographer? | back 267 Place the patients strong side next to the table |
front 268 A patient with a wound infection cause by MRSA should be under which precation? | back 268 Contact Patients infected with multidrug-resistant infections such as MRSA are placed under contact precautions, which are designed to prevent the transmission of pathogens by direct skin-to-skin contact it protects the patient |
front 269 Which statement most accurately explains the typical reaction a patient can expect following the IV administration of low osmolar iodinated contrast? | back 269 You might feel a warm sensation |
front 270 How can a radiographer be less intimidating to a child? | back 270 Squat down to the childs level |
front 271 If a patient contracts an infectious microorganism from soiled linen, which term refers to this method of disease transmission? | back 271 Fomite |
front 272 What is the proper sequencing of exams if the patient needs a BE, IVU, and thyroid uptake on the same day? | back 272 Thyroid uptake, IVU and BE |
front 273 What contrast would be used for a patient who has asthma? | back 273 Iodinated nonionic |
front 274 What are the three common sites for measuring the pulse of an adult patient? | back 274 Brachial radial & carotid |
front 275 What is the term for the pressure in the arterial blood vessels when the left ventricle contracts? | back 275 Systolic |
front 276 A step up transformer with 300 turns in the primary coil is supplied with 220 volts to this primary. How many secondary turns are needed to produce 66,000 volt output? | back 276 90,000 turns |
front 277 What is the result if the total lead content of a grid is decreased? | back 277 decreased scatter absorption |
front 278 In tomography, the radiographer is able to control the thickness of the slice by altering which of the following? | back 278 exposure angle The exposure angle (A) is the arc formed by the movement of the x-ray tube |
front 279 What statement is correct regarding the relationship of patient dose to EI? | back 279 EI gives an approximation of the patients dose |
front 280 If all of the images from one radiographic room seem to appear excessively noisy, what might the radiographer suspect? | back 280 The AEC is set an inappropriate speed class |
front 281 Which component of a diagnostic x-ray tube restricts the primary beam to the area of interest? | back 281 collimator |
front 282 What is a method of electronic display resolution and quality control testing? | back 282 SMPTE |
front 283 A finished radiograph has marked quantum mottle. positioning, collimation and, identification markers are correct. Which action should the radiographer take? | back 283 increase exposure factors |