Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 19 - Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves
front 1 Sensory Portion (PNS) | back 1 Consist of nerve fibers the conduct impulses TOWARD the CNS. |
front 2 Motor Arm (PNS) | back 2 Consists of nerve fibers that conduct impulses AWAY from the CNS. |
front 3 Somatic Divison | back 3 Sometimes called the voluntary system.
|
front 4 Autonmic Nervous System | back 4 Efferent division of the peripheral nervous system that innervates cardiac and smooth muscles and glands; also called the involuntary or visceral motor system. |
front 5 Sympathetic Nevous System | back 5 The division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for activity or to cope with some stressor (danger, excitement, etc.); the fight, fright, and flight subdivision. |
front 6 Parasympethetic Nervous System | back 6 The division of the autonomic nervous system that oversees digestion, elimination, and glandular function; the resting and digesting subdivision. |
front 7 Cerebral Hemisperes | back 7 The most superior portion of the brain.
|
front 8 Gyri | back 8 An outward fold of the surface of the cerebral cortex. |
front 9 Sulci | back 9 A furrow on the brain, less deep than a fissure. |
front 10 Fissures | back 10 The deepest depressions or inward folds on the brain. |
front 11 Longitudinal Fissure | back 11 Divide brain into left and right hemisperes. |
front 12 Transverse Fissure | back 12 Seperates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe. |
front 13 Central Sulcus | back 13 Divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. |
front 14 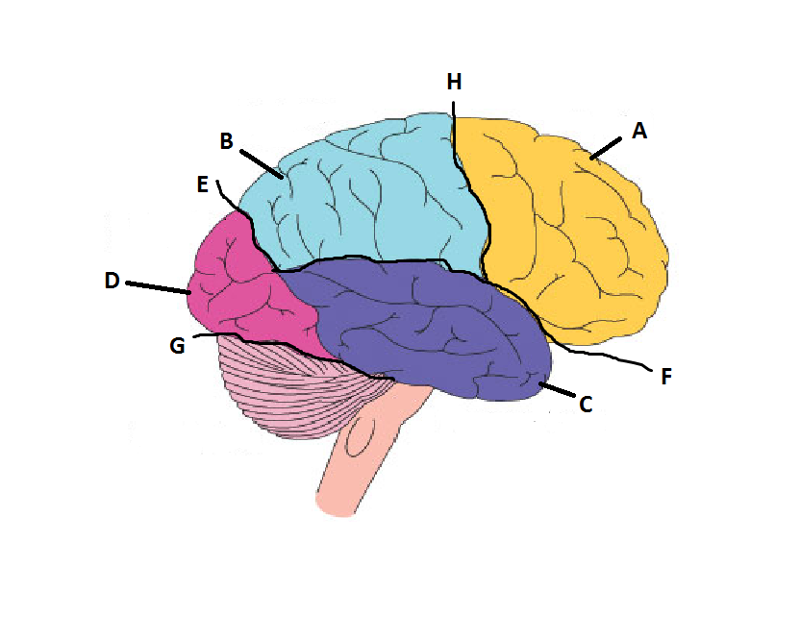 What is A? | back 14 Frontal Lobe |
front 15 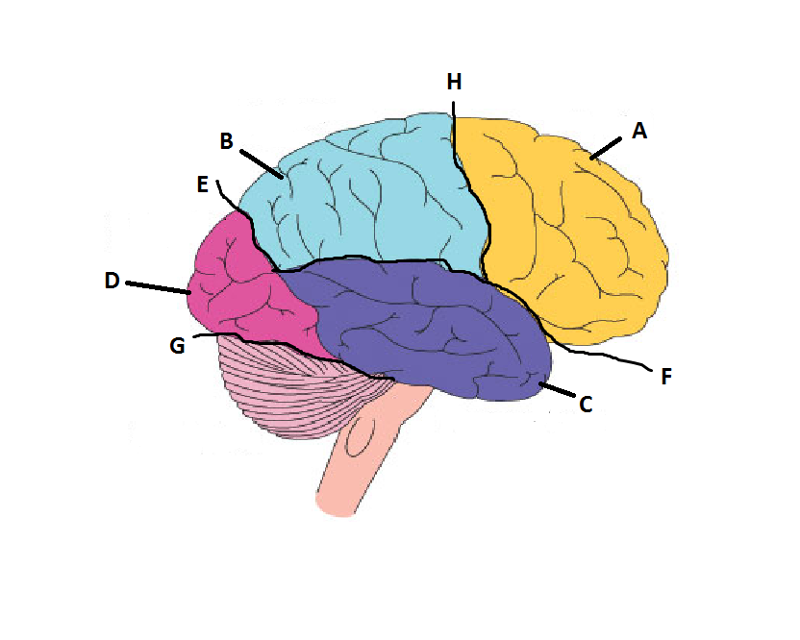 What is B? | back 15 Parietal Lobe |
front 16 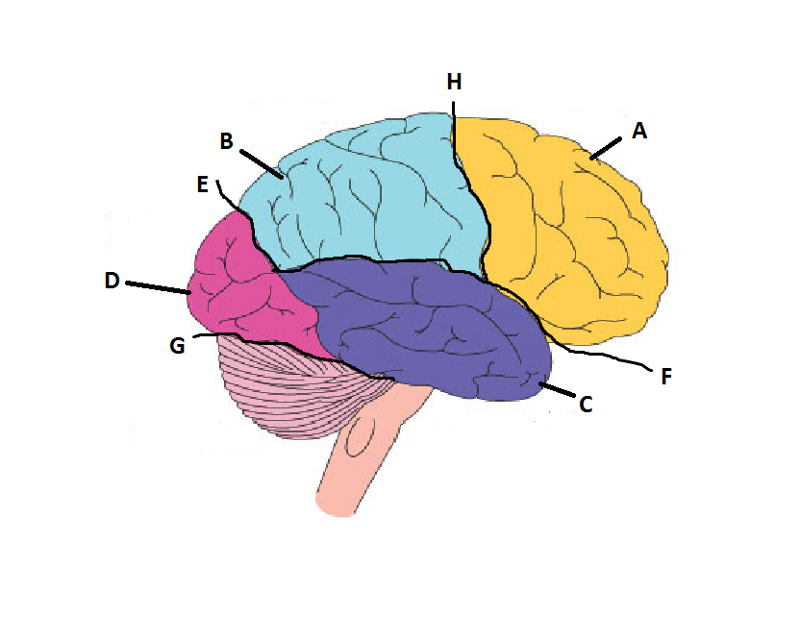 What is C? | back 16 Temporal Lobe |
front 17 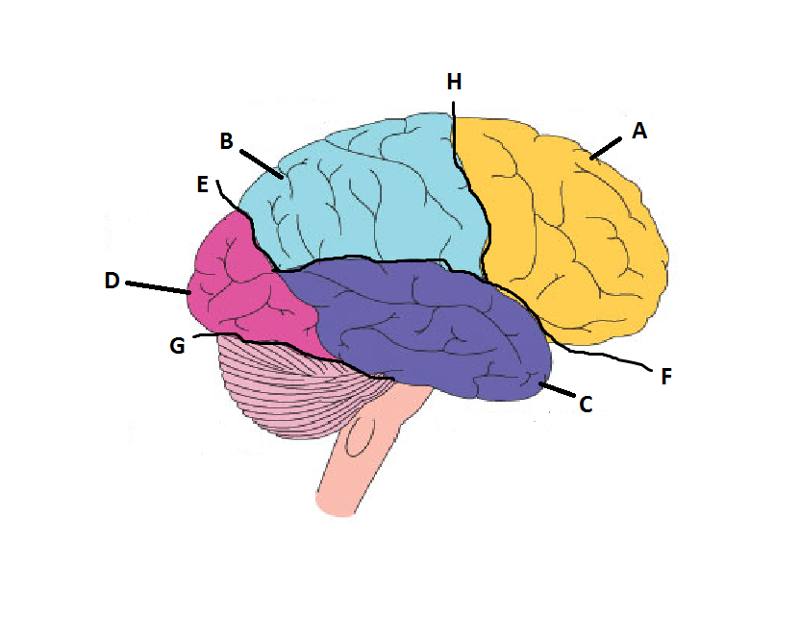 What is D? | back 17 Occipital Lobe |
front 18 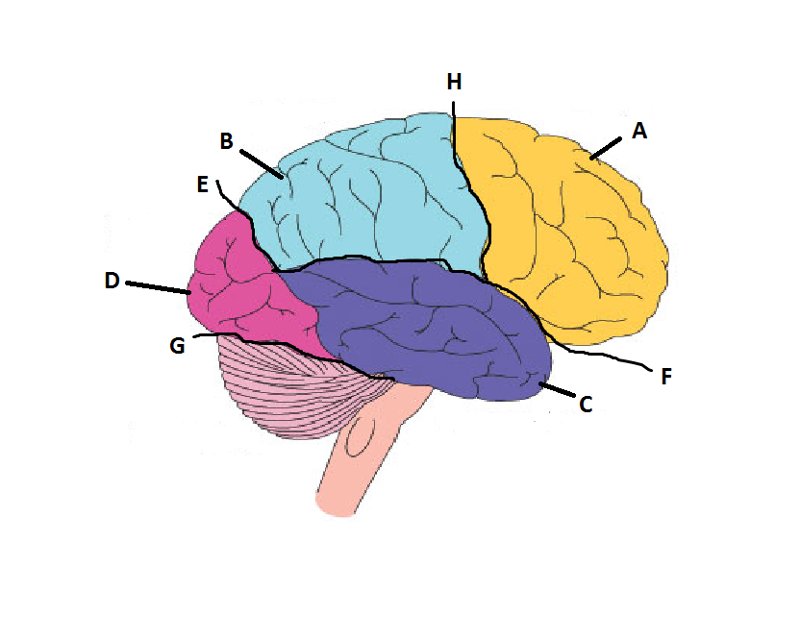 What is E? | back 18 Parieto-Occipital Sulcus |
front 19 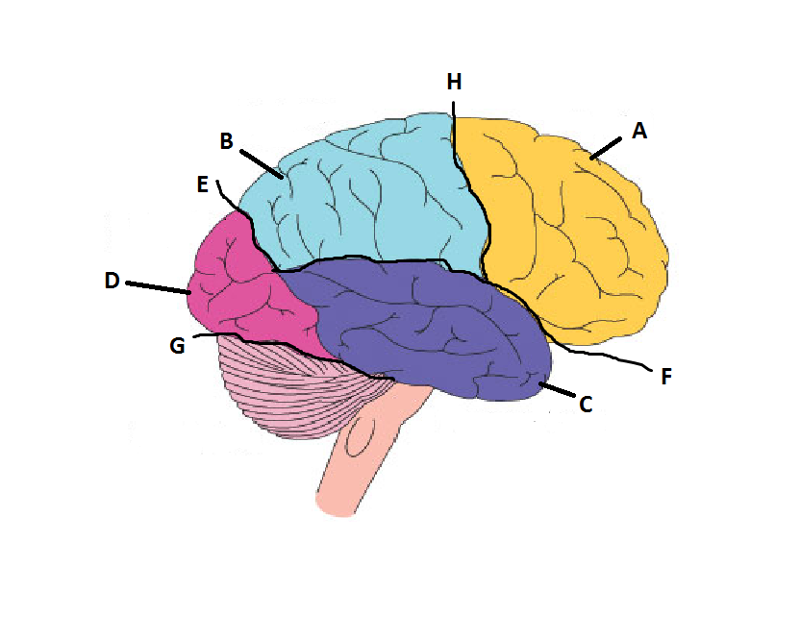 What is F? | back 19 Lateral Sulcus |
front 20 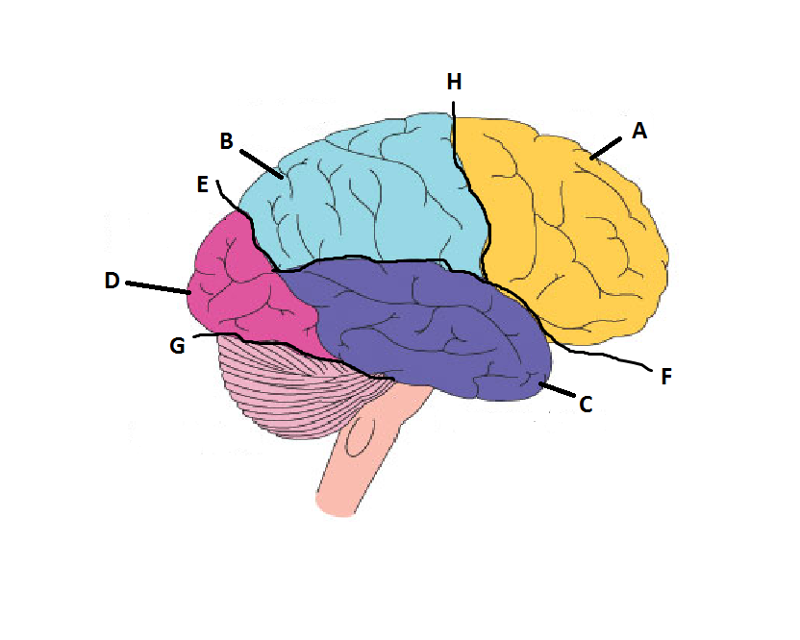 What is G? | back 20 Transverse Sulcus |
front 21 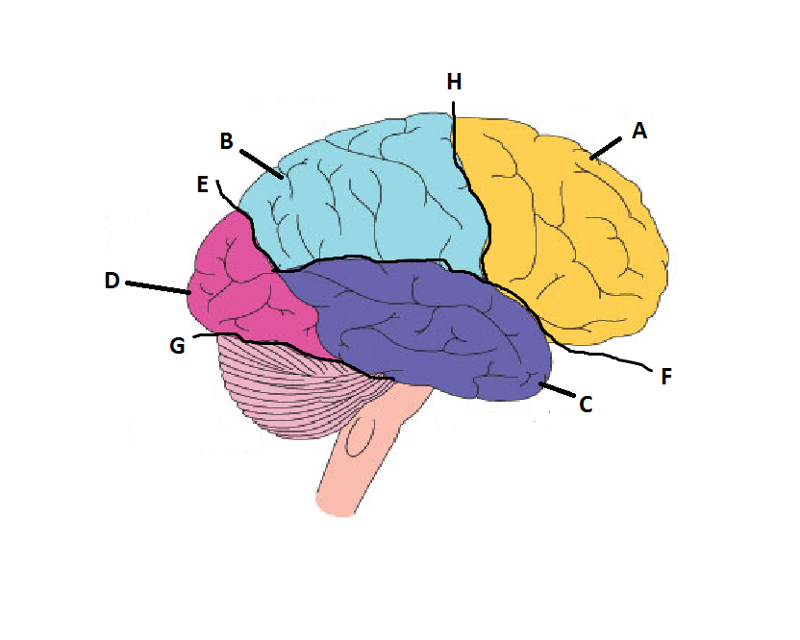 What is H? | back 21 Central Sulcuc |
front 22 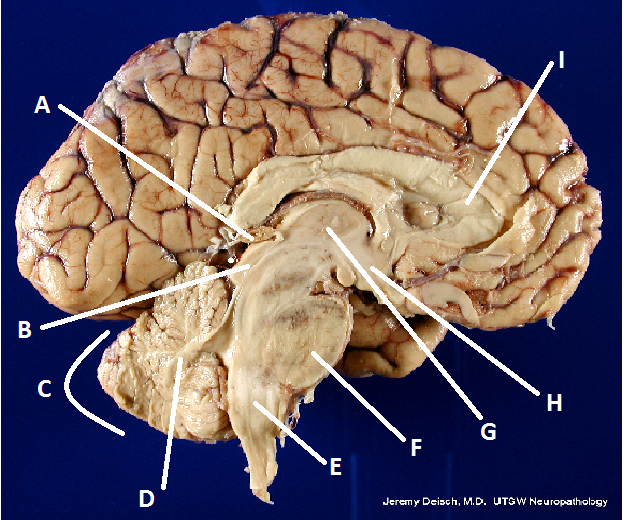 What is A? | back 22 Pineal body (gland) |
front 23 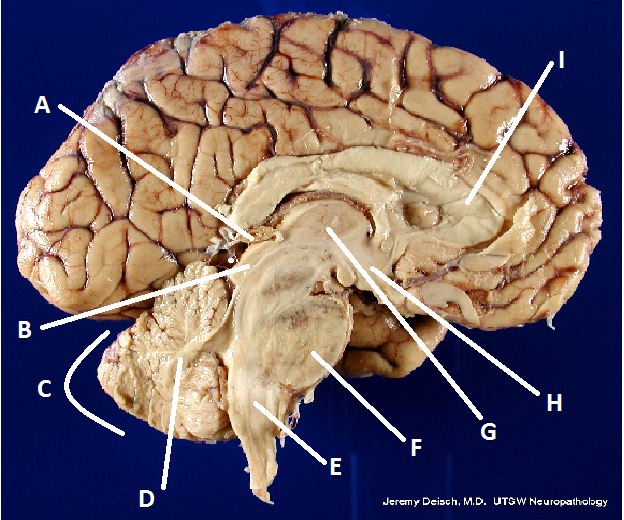 What is B? | back 23 Hypothalamus |
front 24 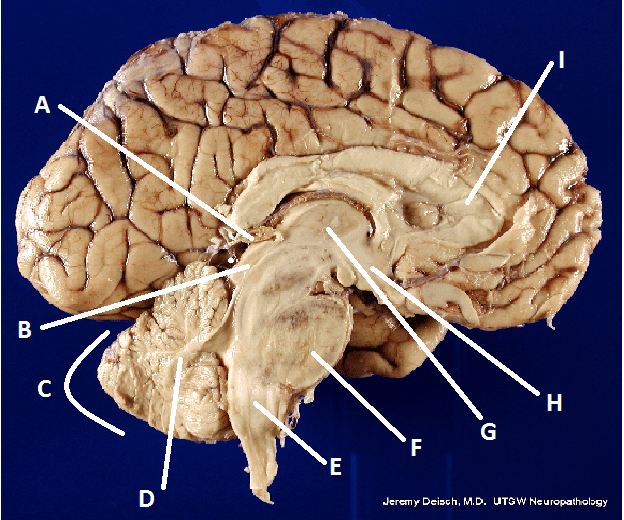 What is C? | back 24 Cerebellum |
front 25 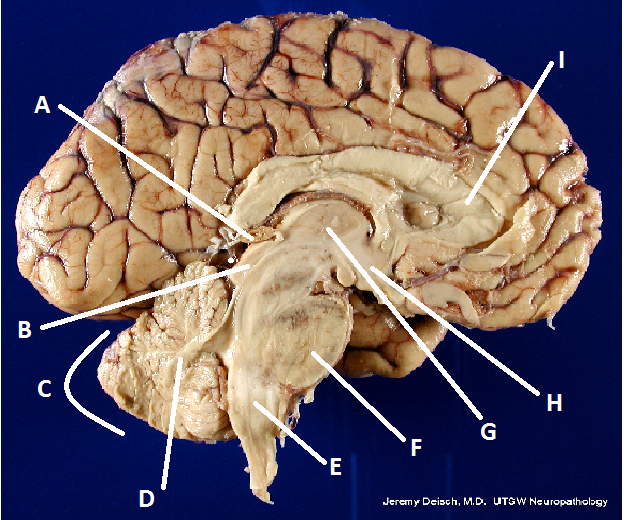 What is D? | back 25 Arbor Vita |
front 26 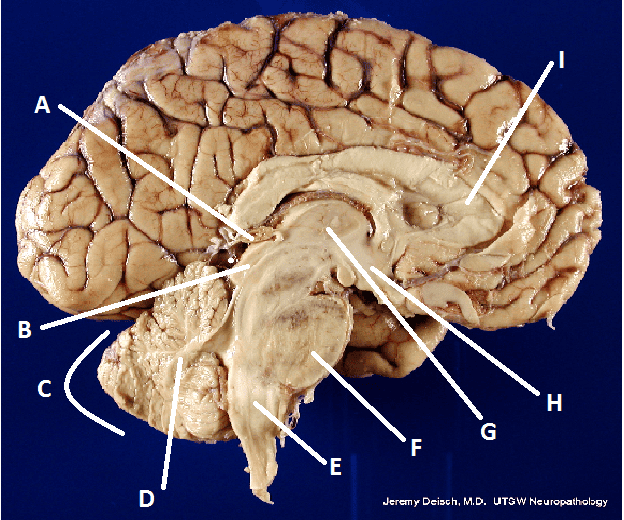 What is E? | back 26 Medulla Oblongata |
front 27 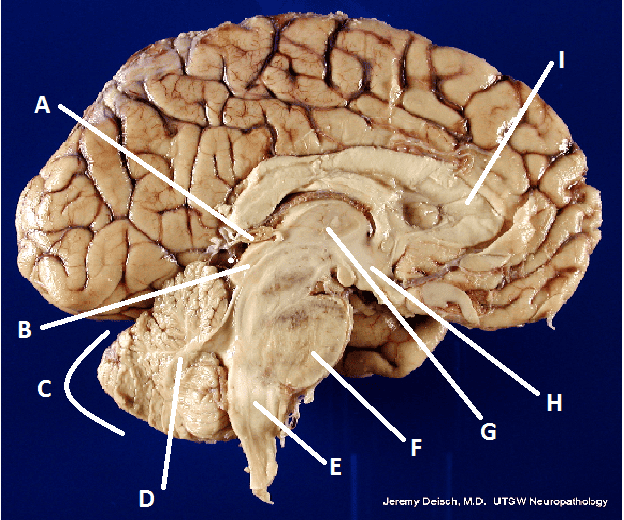 What is F? | back 27 Pons |
front 28 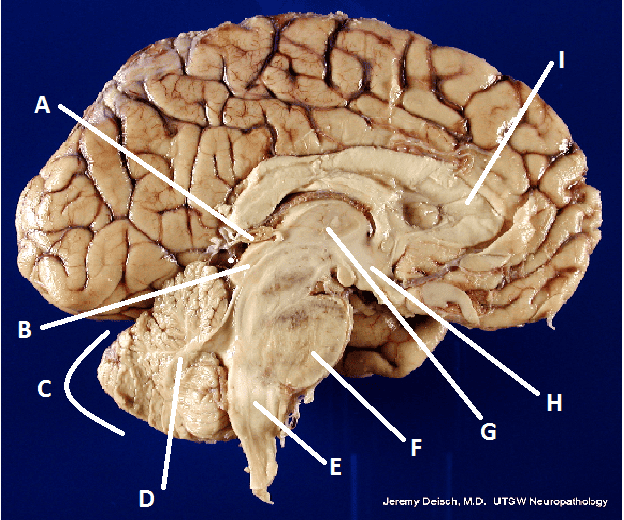 What is G? | back 28 Thalamus |
front 29 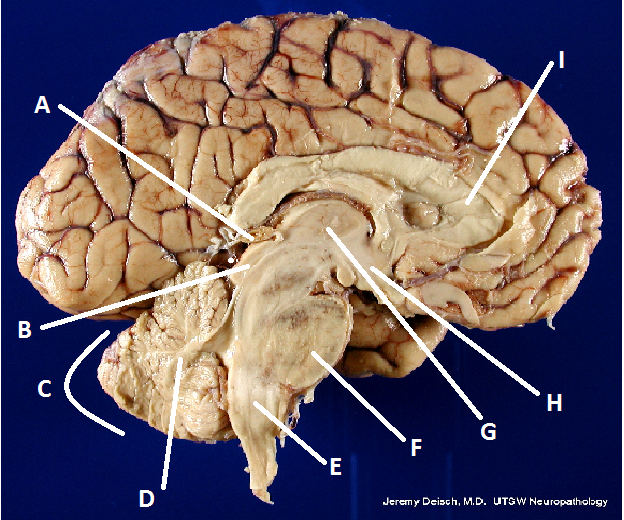 What is I? | back 29 Corpus Callosum |
front 30 Diencephalon | back 30 That part of the forebrain between the cerebral hemispheres and the midbrain including the thalamus, the epithalamus, and the hypothalamus. |
front 31 Olfactory Bulbs | back 31 Enlargements at the terminus of the olfactory nerve at the base of the brain just above the nasal cavities. |
front 32 Octip Chiasma | back 32 The partial crossover of fibers of the optic nerves. |
front 33 Thalamus | back 33 A mass of gray matter in the diencephalon of the brain. |
front 34 Hypothalamas | back 34 Region of the diencephalon forming the floor of the third ventricle of the brain. |
front 35 Pituitary Gland | back 35 Neuroendocrine gland located beneath the brain that serves a variety of functions including regulation of gonads, thyroid, adrenal cortex, lactation, and water balance. |
front 36 Mammillary Gland | back 36 Along with the anterior and dorsomedial nuclei in the thalamus, are involved with the processing of recognition memory. |
front 37 Epithalamus | back 37 Most dorsal portion of the diencephalon; forms the roof of the third ventricle with the pineal gland extending from its posterior border. |
front 38 Pineal Body | back 38 A hormone-secreting part of the diencephalon of the brain thought to be involved in setting the biological clock and influencing reproductive function. |
front 39 Choroid Plexus | back 39 A capillary knot that protrudes into a brain ventricle; involved in forming cerebrospinal fluid. |
front 40 Corpus Callosum | back 40 A broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain. |
front 41 Brain Stem | back 41 Collectively the midbrain, pons, and medulla of the brain. |
front 42 Cerebral Peduncles | back 42 A bundle of myelinated neurons joining different parts of the brain. |
front 43 Pons | back 43 the part of the brain stem connecting the medulla with the midbrain, providing linkage between upper and lower levels of the central nervous system. |
front 44 Medulla Oblongota | back 44 Inferiormost part of the brain stem. |
front 45 Superior Colliculi | back 45 Part of the copora quadrigemina |
front 46 Inferior Colliculi | back 46 Part of the copora quadrigemina |
front 47 Arbor Vitae | back 47 The arborescent appearance of the white matter in a vertical section of the cerebellum. |
front 48 Meninges | back 48 Protective coverings of the central nervous system; from the most external to the most internal, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. |
front 49 Dura Mater | back 49 Outermost and toughest of the three membranes (meninges) covering the brain and spinal cord. |
front 50 Arachnoid Mater | back 50 The middle layer of the three meninges. |
front 51 Pia Mater | back 51 Innermost layer of the meninges. |
front 52 Cranial Nerves | back 52 The 12 nerve pairs that arise from the brain. |
front 53 Olfactory (I) | back 53 Function: Smell (purely sensory) |
front 54 Optic (II) | back 54 Function: Sight (purely sensory) |
front 55 Oculomotor (III) | back 55 Function: Visual Motor |
front 56 Trochelear (IV) | back 56 Function: Visual Motor |
front 57 Trigeminal (V) | back 57 Function: Major sensor of face |
front 58 Adbucens (VI) | back 58 Function: Visual Motor |
front 59 Facial (VII) | back 59 Function: Visual, lacrimal, salivary. |
front 60 Vestibulochlear (VIII) | back 60 Function:Hearing (purely sensory) |
front 61 Glassophyryngeal (IX) | back 61 Function: Throat and mouth |
front 62 Vagus (X) | back 62 Function:Pharynx, larynx, and involuntary muslces |
front 63 Accessory (XI) | back 63 Function: Motor |
front 64 Hypoglossal (XII) | back 64 Function: Motor and tongue |