Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Activity 2: Studying the Histologic Structure of Selected Digestive System Organs
front 1 The Stomach | back 1 The Stomach |
front 2 How does the extra oblique layer of smooth muscle found in the stomach correlate with the stomach's churning movements? (Hint: 3 functions and what do they do? ) | back 2 1. Churn food 2. Mix food 3. Pummel food All above helps tot physically reduce the food to smaller fragments. |
front 3 The chief cells produce what? | back 3 Produces pepsinogen |
front 4 The parietal cells secret what? | back 4 HCl |
front 5 Enteroendocrine cells release what? | back 5 Hormones |
front 6 Gastroesophageal junction: 1. Describe the epithelium found in the esophagus and the beginning of the stomach (right after the gastroesophageal junction). 2. What is the functional importance of the epithelial differences seen in the esophagus and the stomach? | back 6 1. Stratified squamous epithelium is found in the esophagus, and simple columnar epithelium is found in the stomach (right after the gastroesophageal junction). 2. Stratified squamous epithelium=protection, Simple columnar epithelium=absorption |
front 7 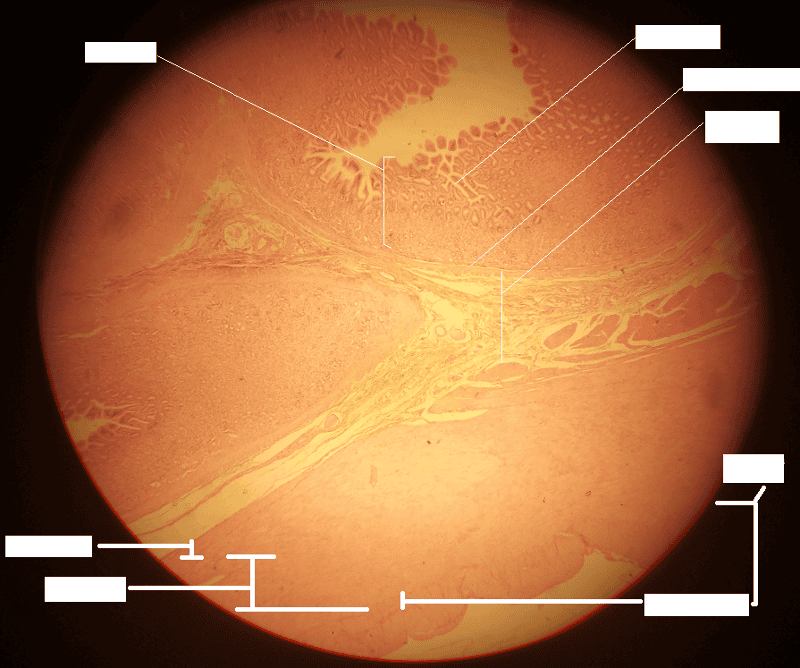 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: organ) | back 7 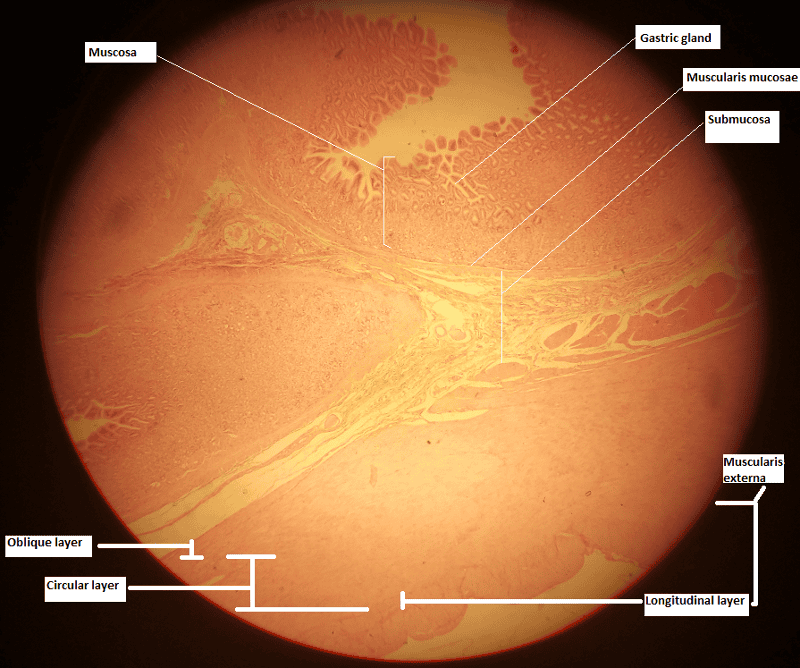 1. Look at the picture. 2. Stomach wall |
front 8 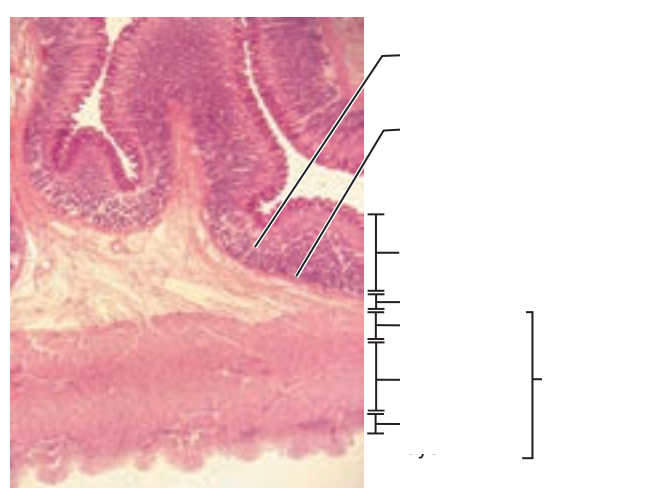 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: organ) | back 8 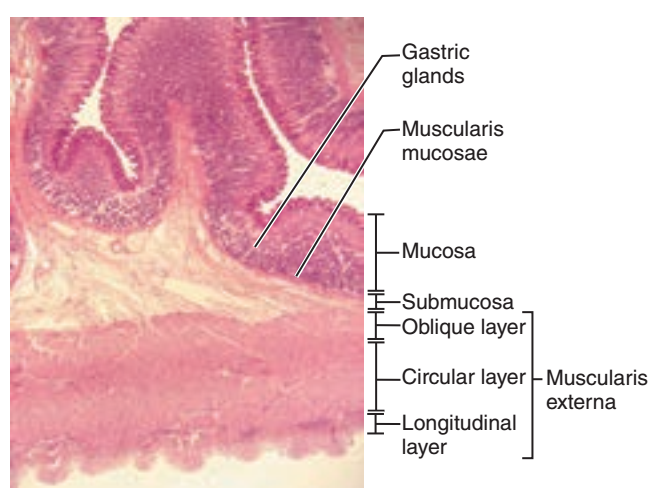 1. Look at the picture. 2. Stomach wall |
front 9 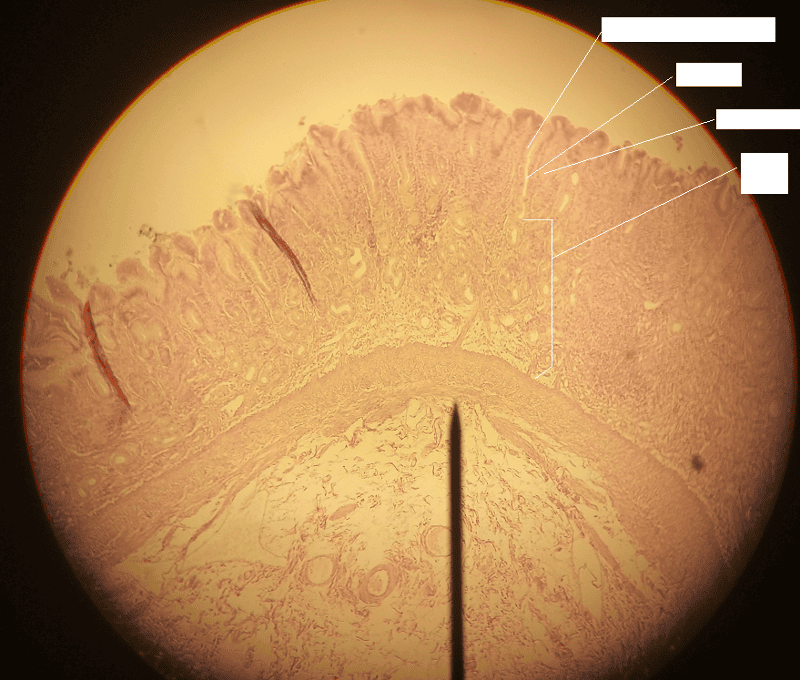 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: organ) | back 9 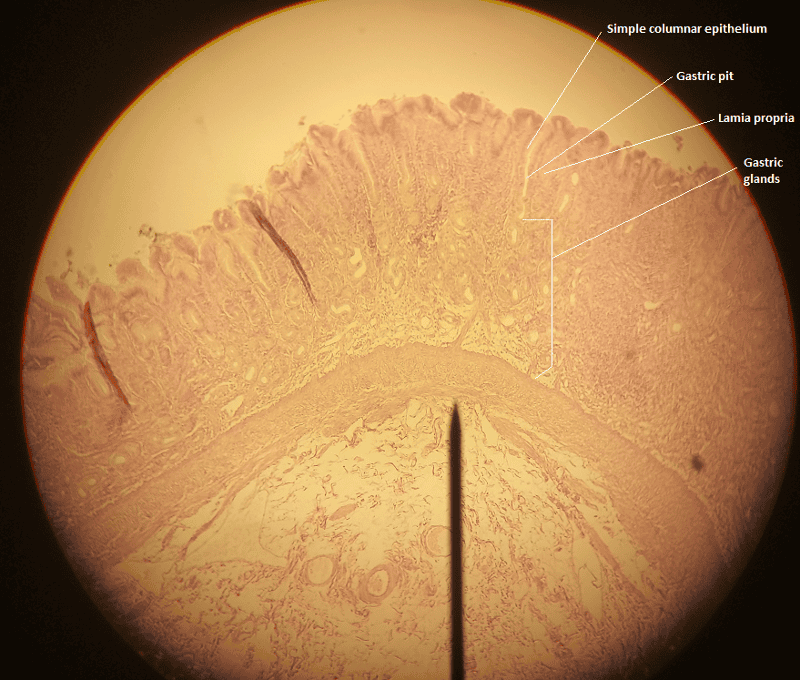 1. Look at the picture. 2. Stomach wall |
front 10 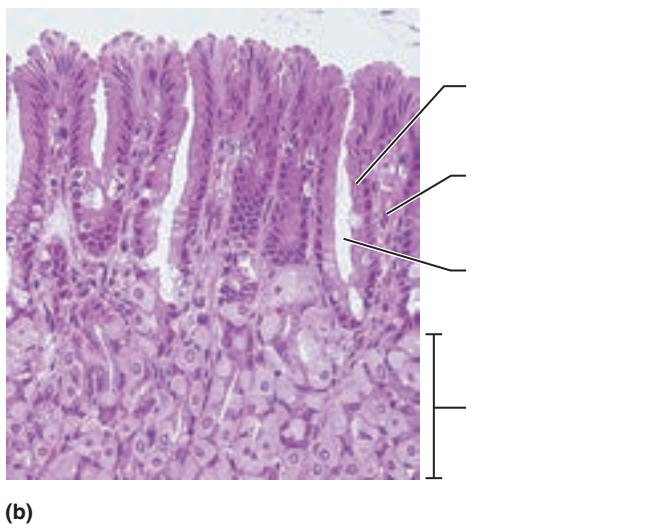 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: organ) | back 10 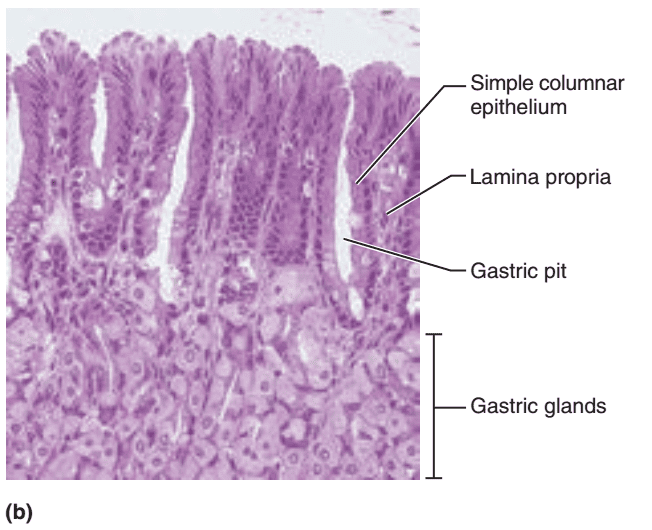 1. Look at the picture. 2. Stomach wall |
front 11 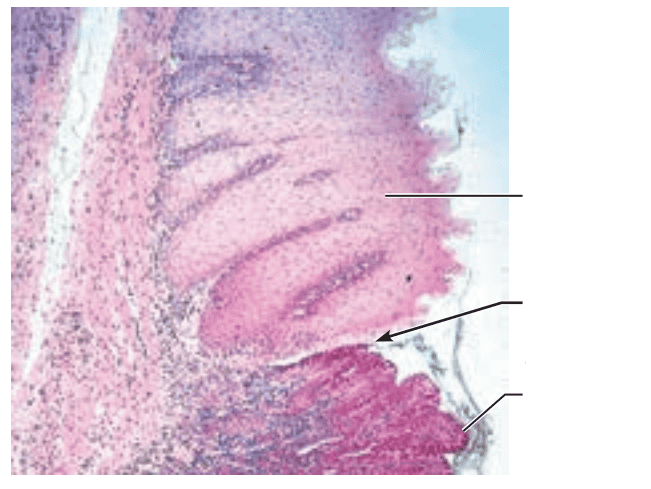 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: junction) | back 11 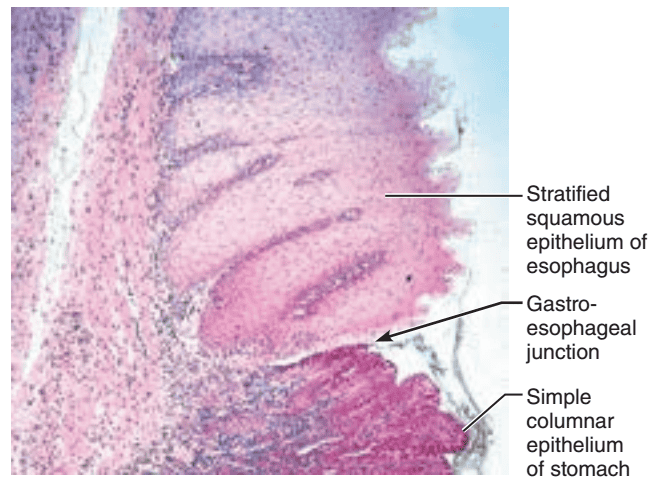 1. Look at the picture. 2. Gastroesophageal junction |
front 12 The Small Intestine | back 12 The Small Intestine |
front 13 The small intestine extends from what sphincter to what valve? | back 13 Extends from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve |
front 14 The small intestine is suspended by what double-layered peritoneum and from what abdominal wall? | back 14 Suspended by the mesentery from the posterior abdominal wall |
front 15 What are the 3 subdivisions of the small intestine? | back 15 1. Duodenum 2. Jejunum 3. ileum |
front 16 The duodenum extends from what sphincter and curves around the head of what organ? | back 16 Extends from the pyloric sphincter and curves around the head of the pancreas |
front 17 The jejunum is continuous with what subdivision of the small intestine? | back 17 Duodenum |
front 18 Most of the jejunum occupies what region of the abdominal cavity? | back 18 The umbilical region of the abdominal cavity |
front 19 The ileum makes up what portion of the small intestine? | back 19 Terminal portion of the small intestine |
front 20 The ileum joins the large intestine at what valve? | back 20 Joins the large intestine at the ileocecal valve |
front 21 The major portion of the ileum lies in what region of the abdominal cavity? | back 21 Hypogastric region of the abdominal cavity |
front 22 What 2 enzymes complete digestion in the small intestine? | back 22 1. Brush border enzymes 2. Pancreatic enzymes |
front 23 The brush border enzymes are what type of enzymes? | back 23 Hydrolytic enzymes |
front 24 The brush border enzymes are bound to what structures of what epithelium? | back 24 Bound to the microvilli of the simple columnar epithelium of the stomach |
front 25 How do pancreatic enzymes enter the stomach, and which specific subdivision of the small intestine do they enter through? | back 25 Enter by the main pancreatic duct and are ducted into the duodenum |
front 26 Bile is formed in what organ? | back 26 Liver |
front 27 How does bile enter the stomach, and which specific subdivision of the small intestine does it enter through? | back 27 Enter by the bile duct into the duodenum of the small intestine |
front 28 At the duodenum, the pancreatic duct and the bile duct join to form what structure? | back 28 The hepato-pancreatic ampulla |
front 29 The hepato-pancreatic ampulla empties into what lumen and through what structure? | back 29 Empties into the duodenal lumen through the major duodenal papilla |
front 30 The major duodenal papilla is controlled by what valve? | back 30 The hepato-pancreatic sphincter |
front 31 The hepato-pancreatic sphincter is what type of valve? | back 31 Muscle valve |
front 32 Nearly all of what occurs in the small intestine? | back 32 Nutrient absorption |
front 33 What 3 structural modifications increase the absorptive surface of the small intestine mucosa? | back 33 1. Microvilli 2. Villi 3. Circular folds |
front 34 Microvilli are microscopic projections of the surface ____ of the ____. | back 34 Microscopic projections of the surface plasma membrane of the columnar epithelial cells of the mucosa. |
front 35 Villi are ____ projections of what tunic? | back 35 Finger-like projections of the mucosa tunic |
front 36 The circular folds are deep folds of what 2 layers? | back 36 1. Mucosa layer 2. Submucosa layer |
front 37 What is the function of the circular folds of the small intestine? | back 37 Force chyme to spiral through the intestine, mixing it and slowing its progress |
front 38 The 3 structural modifications that help with absorption (i.e. microvilli, villi, circular folds) of the small intestine decrease in frequency and size towards where? | back 38 Towards the end of the small intestine |
front 39 What happens to any residue remaining undigested and unabsorbed food at the end of the small intestine? (Hint: enters what organ and through what valve?) | back 39 It enters the large intestine through the ileocecal valve |
front 40 In contrast, while the 3 structural modifications that help with absorption decrease in frequency and size toward the end of the small intestine, what happens to the lymphoid tissue in the submucosa? | back 40 The lymphoid tissue in the submucosa of the small intestine increases along the length of the small intestine |
front 41 The lymphoid tissue in the submucosa of the small intestine are also called what? (Hint: state common name as well) | back 41 Aggregated lymphoid nodules or Peyer's patches |
front 42 The aggregated lymphoid nodules or Peyer's patches are very apparent in what subdivision of the small intestine? | back 42 The ileum |
front 43 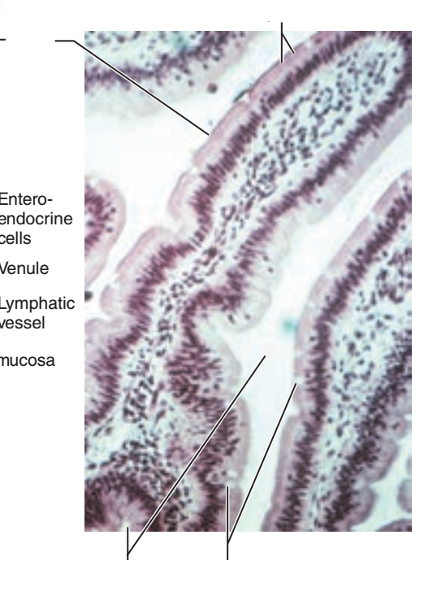 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? | back 43 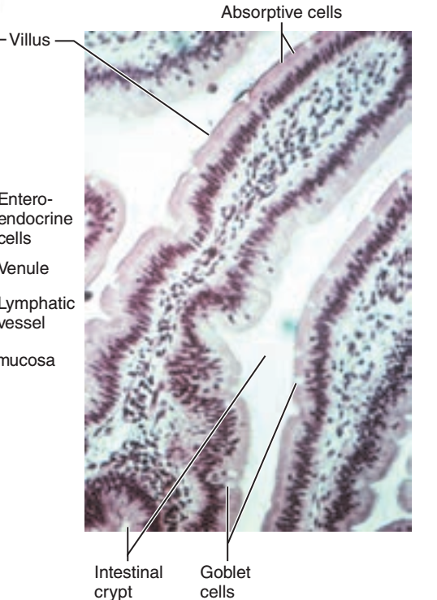 1. Look at the picture. 2. Small intestine |
front 44 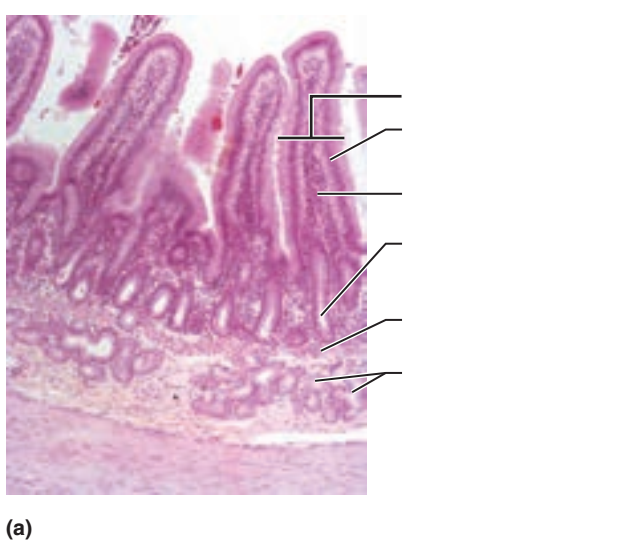 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: What specific region of the organ?) | back 44 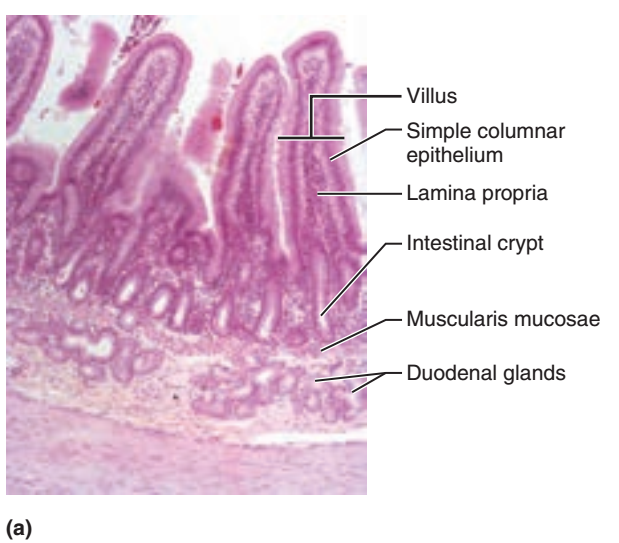 1. Look at the picture. 2. Dueodenum of small intestine |
front 45 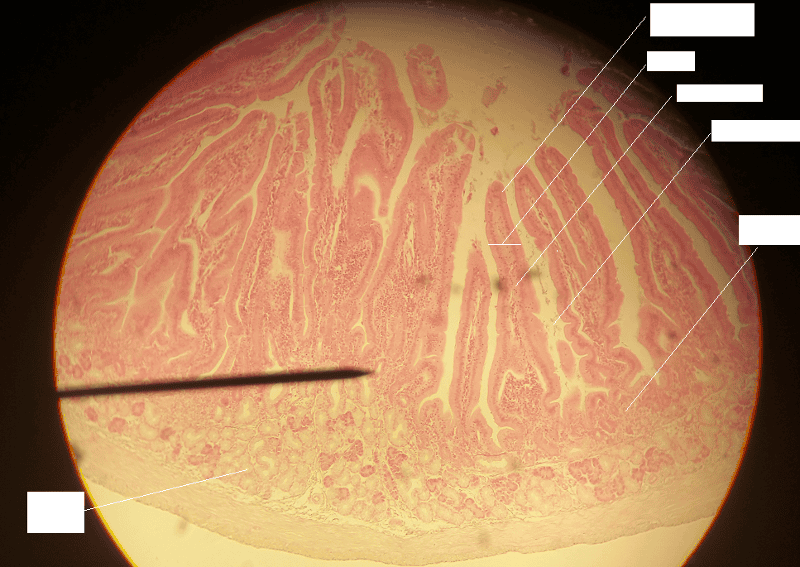 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: What specific region of the organ?) | back 45 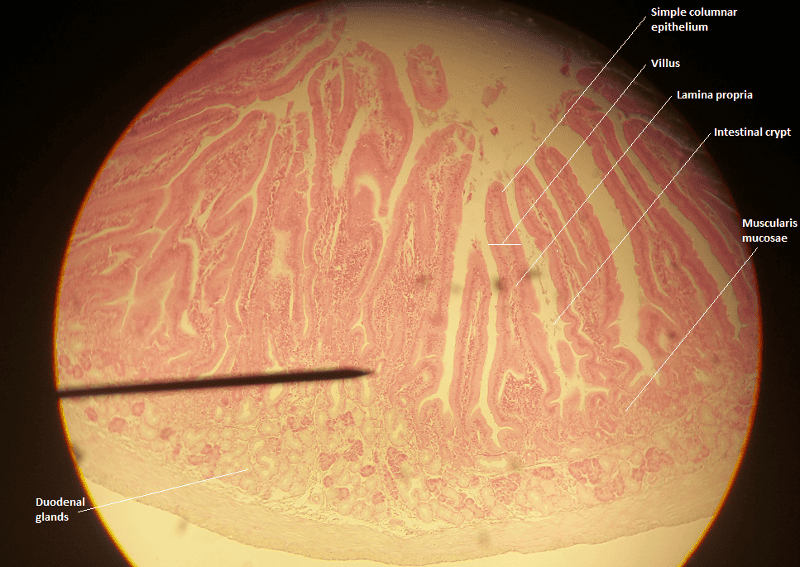 1. Look at the picture. 2. Duodenum of small intestine |
front 46 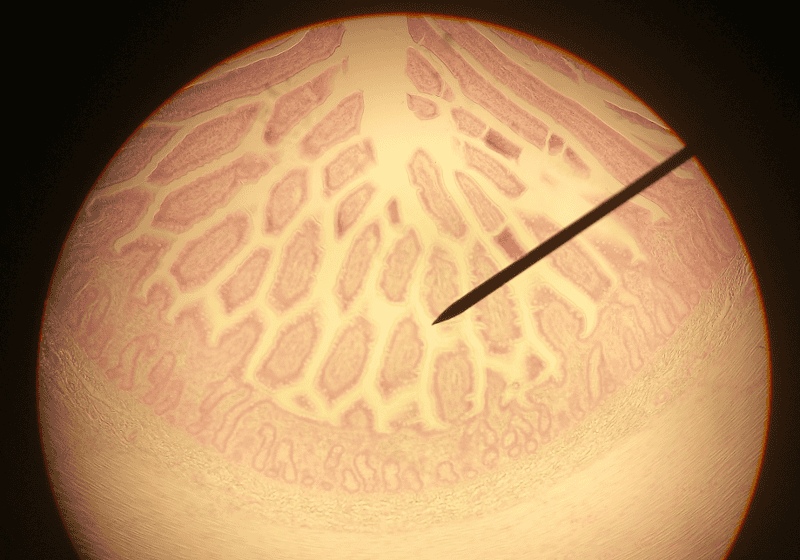 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: What specific region of the organ?) | back 46 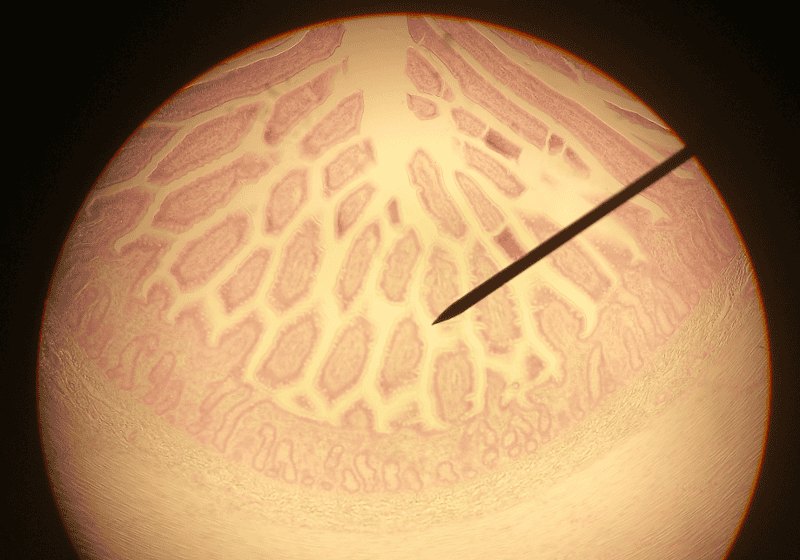 1. Look at the picture. 2. Jejunum of small intestine |
front 47 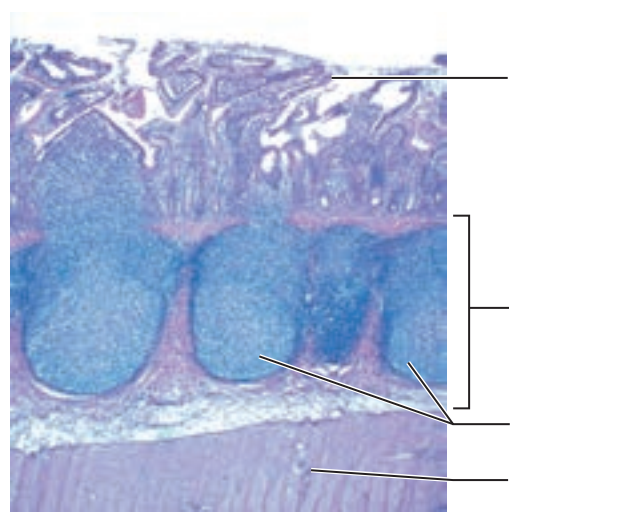 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: What specific region of the organ?) | back 47 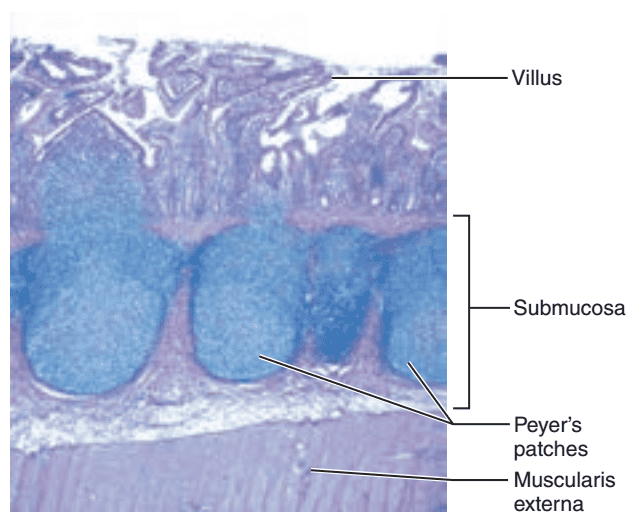 1. Look at the picture. 2. Ileum of small intestine |
front 48 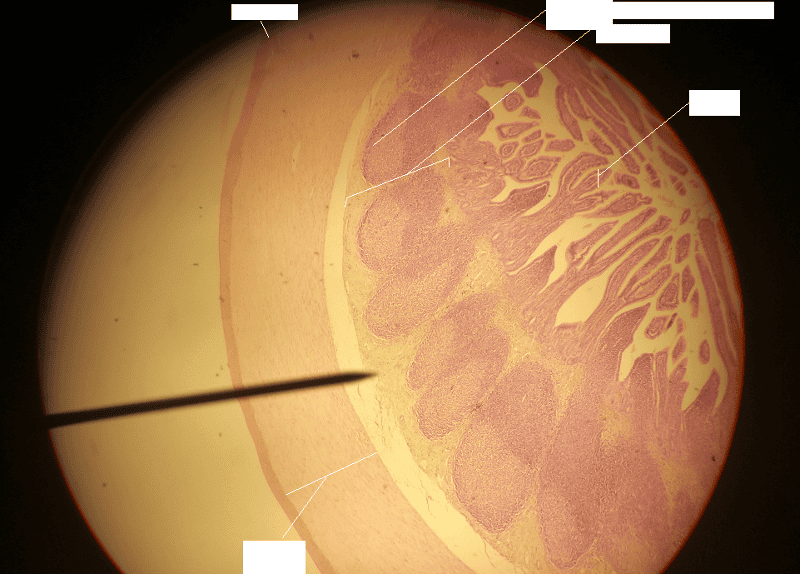 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? (Hint: What specific region of the organ?) | back 48 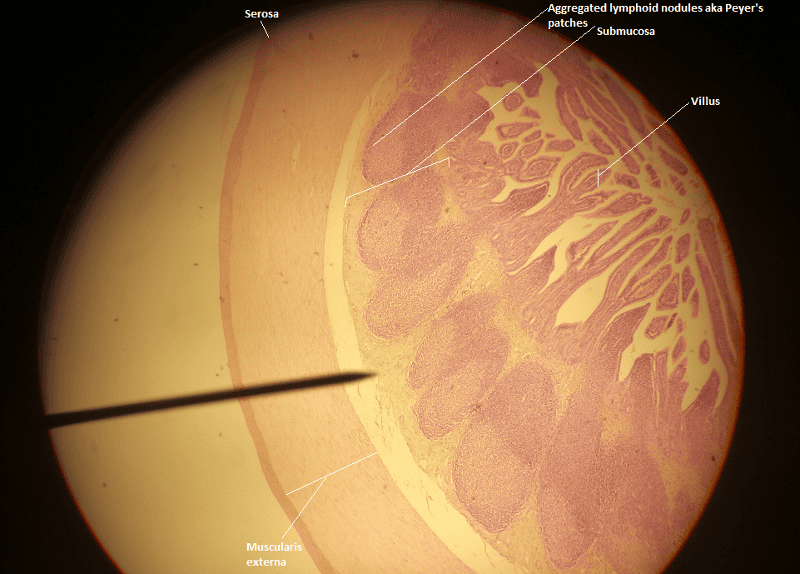 1. Look at the picture. 2. Ileum of the small intestine |
front 49 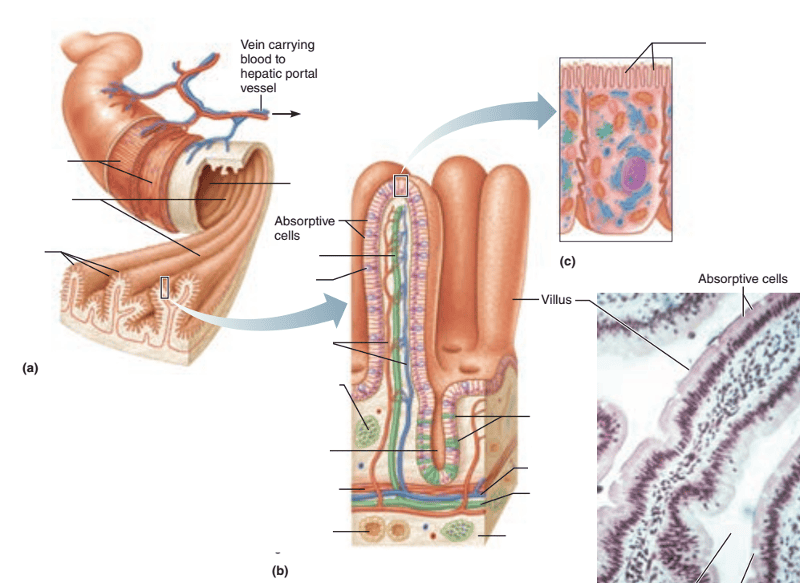 1. Identify the blanks. 2. What feature of the alimentary canal is shown in this histology slide? | back 49 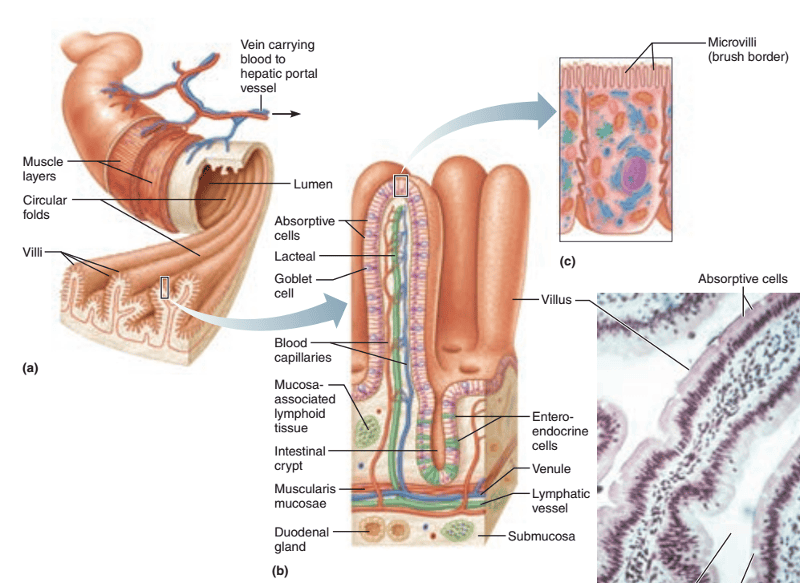 1. Look at the picture. 2. Small intestine cutout |