Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Digestive System
front 1 The breaking down of food molecules for use by body cells is known as | back 1 Digestion |
front 2 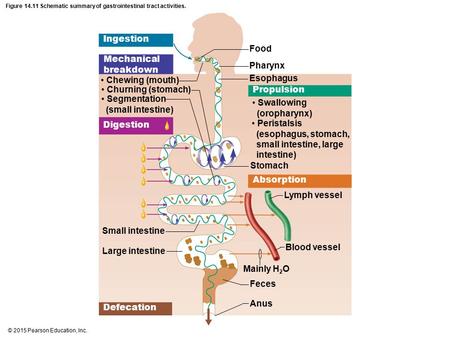 The Digestive Process includes: | back 2
|
front 3 There are two types of digestions: | back 3
|
front 4 The physical break down of food material with instruments, in this case teeth, tongue, etc. is known as | back 4 Mechanical Digestion |
front 5 The break down of food via enzymes, acids, carbohydrates (to simple sugars), lipids (to glycerol and fatty acids), proteins (into shorter AA sequences), etc... is known as | back 5 Chemical Digestion |
front 6 G.I. Tract stands for | back 6 Gastro Intestinal Tract (Digestive Tract) |
front 7 _____________ is a continuous tube, about 30 ft. long, which includes:
| back 7 G.I. Tract |
front 8 G.I. tract uses ______________________ as the supportive structure peripheral to the digestive tract. | back 8 Accessory Organs |
front 9 As accessory organs for the G.I. Tract we find: | back 9
|
front 10 Histiology of the GI Tract includes | back 10
|
front 11 The innermost lining of the GI tract, a continuous mucous membrane from the mouth to the anus. | back 11 Mucosa or Mucous membrane |
front 12 1) Mucosa's main function is to: | back 12
Which GI may perform one or the three of them depending the particular region. |
front 13 Mucosa consists of three sublayers: | back 13
|
front 14 a- Lining Epithelial in the GI Tract is found in TWO types: | back 14
|
front 15 Stratified Squamous Epithelium works for mouth and esophagus to (function)
| back 15
|
front 16 Simple Columnar Epithelium works from the esophagus to the anus for...
| back 16
|
front 17  b- Lamina Propia is
| back 17
|
front 18 c- Muscularis Mucosa is made of:
| back 18
|
front 19 2) Submucosa is the layer below the ______________ It is made of ________________ which binds _________ and ____________ together. It is highly _____________. | back 19
|
front 20 3) Muscularis Externa is the layer below the __________.
| back 20 Submucosa
|
front 21 4) Serosa is the ____________ layer, also called _______ _________________. | back 21 outer-most Viscerous Peritoneum |
front 22
| back 22
|
front 23 GI Tract structures and accesory organs: 1) ________________ is formed by cheeks, hard and soft palates and tongue, stratified squamous epithelium | back 23
|
front 24 2) _________________ moves food over the teeth, comprised of skeletal muscle. Also involved in speech, and contains taste buds. | back 24 Tongue |
front 25 3) ______________ are made of fleshy folds of skin surrounding the opening of the mouth | back 25 LIPS |
front 26 4) _____________________ The non-keratinized pigmented border between the skin and the mouth, this pigmented area occupies the transition zone. | back 26 Vermilion |
front 27 What zone does Vermilion transition? | back 27 It is the transition zone between Dry and Wet Skin |
front 28 5) _________ __________ is the mucous membrane connecting the gingiva to the lip. | back 28 Labial Frenulum |
front 29 6) ________________ is the space between the cheeks, and the teeth and gingiva | back 29 Vestibule |
front 30 7) _________________ is a membranous fold of tissue on the underside of the tongue which attaches the tongue to the floor of the mouth. | back 30 Lingual Frenulum |
front 31 8) ___________________ are projections (on the surface of the tongue in the GI Tract), and we find different types:
| back 31 Papillae
|
front 32 Papillae "mushroom-like", which covers the tip of the tongue | back 32 Funjiform Papillae |
front 33 Papillae Doughnut-like, form an inverted "V" on the posterior surface of the tongue. | back 33 Circumvallate Papillae |
front 34 Papillae conical, covers anterior 2/3's of the tongue | back 34 Filiform Papillae |
front 35 9) _________ _________ secrete saliva to keep membranes moist and to soften and dissolve food materials. Saliva also contains salivary enzyme called _________. | back 35
|
front 36 The major Salivary Glands are:
| back 36
|
front 37 This gland is located under and in front of the ears | back 37 Parotid Gland |
front 38 This gland is located under the base of the tongue | back 38 Submandibular Gland |
front 39 This gland is located under the tongue | back 39 Sublingual Gland |
front 40 The secretions of the salivary glands are called ________.
| back 40 Saliva
|
front 41 Salivary Amylase _______ _______ starches into simpler __________ | back 41
|
front 42 10) This accessory structure of GI tract is involved in mechanical digestion to destroy food in mouth. | back 42 Teeth |
front 43
| back 43
|
front 44 Permanent and Deciduous Teeth are divided in 4 types:
| back 44
|
front 45 Their main function is:
| back 45
|
front 46 Dental formula | back 46 I2/2 : C1/1 : B2/2 : M3/3 = 16 teeth total of One Half of the Mouth |
front 47 Oral Cavity involves different accessory organs like this one known as the "gums," this tissue surrounds the teeth, and its official name is ____________ | back 47 Gingiva |
front 48 The inflamation of gingivae is known as | back 48 Gingivitis |
front 49 The exposed portion of the teeth is known as _________ ____________, and the ___________ __________ is the top portion covered with a hard white material called ____________. | back 49
|
front 50 The constricted portion of the tooth where the crown and root meet is known as ___________ | back 50 Neck |
front 51 The portion of the tooth which is embedded in the alveolar portion of the maxillae or mandible is known as ________. It is covered with a bone-like substance called _________. | back 51
|
front 52 _________ __________ anchor the root in the bony socket (alveolus) of the jaw. This junction forms a fibrous joint called a _________ | back 52
|
front 53 ___________ is a protein-rich bonelike material, underlies the enamel cap and forms the bulk of the tooth. | back 53
|
front 54 _________ _________ is the unhardened central cavity of the tooth, contains arterial and venous capillaries and nerves. | back 54 Pulp Cavity |
front 55
| back 55
|
front 56 Remember that The grinding up of the food stuff by the teeth is called | back 56 Mechanical Digestion |
front 57
| back 57
|
front 58 _______ is a rounded mass of a substance, especially of chewed food at the moment of swallowing. | back 58 Bolus |
front 59 11) _______________ is a muscular tube (A10 inches long) from the pharynx to the stomach.
| back 59
|
front 60 12) ____________ is an enlarged section of the digestive tract which is formed of :
| back 60
|
front 61 ____________ The outside curvature of the stomach | back 61 Greater Curvature |
front 62 ___________ the inside curvature of the stomach | back 62 Lesser Curvature |
front 63 ____________ the large folds in the stomach that contain gastric pits with gastric glands | back 63 Rugea |
front 64 The smooth lining is dotted with millions of Gastric ________, which are holes that lead into tubular gastric glands that produce the stomach secretion called ____________ | back 64
|
front 65 Cells that line in the Gastric Pit are secretary gland cells, and are - Please tell what they do produce:
| back 65
|
front 66
| back 66 Secrete Mucus |
front 67
| back 67 secrete HCL (which activates Pepsin from Pepsinogens) |
front 68
| back 68 Secrete Gastrin (Hormone) |
front 69 Chief Cells - | back 69 Produce Pepsinogen and Secrete Lipase. |
front 70 The food that has been mixed with water and gastric juices, and has been in the GI Tract for more than 2-3 hours is calles | back 70 Chime |
front 71 __________ is an:
| back 71 Pepsin |
front 72 ____________ is an active enzyme that:
| back 72 Gastric Lipase |
front 73 ________ curds milk so it will stay in an infants stomach longer | back 73 Rennin |
front 74 _____________ promotes secretion of gastric juices and increases motility of the stomach until the pH reaches 2.0. This is made by _____________ | back 74
|
front 75 _____________ decreases gastric secretions | back 75
|
front 76 _________________ inhibit stomach emtying | back 76 Cholecystokinin |
front 77 13) ____________ is found in the duodenal loop formed as the duodenum leaves the stomach.
| back 77 Pancreas |
front 78 Pancreas contains exocrine and endocrine parts:
| back 78
|
front 79
| back 79
|
front 80
| back 80
|
front 81 14) The second largest gland of the body.
| back 81 Liver |
front 82 Liver functional cells are called __________ cells, they form ___________ | back 82
|
front 83 Liver is composed of seasame seed-sized structural and functional units called_____________. Consists of radial cords of ________ cells arranged around a _________ ______, capillaries enlarge to form vessels called ____________ which are lined with __________ reticuloendothelial cells (phagocytes). This remove ________ as ____________ and worn-out _______ cells from the blood as it flows past. | back 83
|
front 84 BILE Pathway
| back 84
|
front 85 2- These bile ducts join to form the _______________________________ | back 85
|
front 86 3- The common hepatic duct and the ___________ duct (from __________) join to form the ________ _____________ Duct. | back 86
|
front 87 4- The common bile duct and the pancreatic duct join to form the _________________ __________ which empties into the duodenum via called __________ _________ | back 87
|
front 88 Hepatic Blood supply 1- The ___________ artery delivers oxygenated blood from the aorta to the liver. | back 88
|
front 89 2- The ___________ ________ vein carries deoxygenated blood containing nutrients from the digestive tract. | back 89
|
front 90 3- The hepatic vein empties blood from the __________ to the IVC | back 90 Liver |
front 91 4- Blood from the ___________________ vein and the _____________ artery enters into the sinusoids of the ______________ of the liver. This blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the ________ cells and ____________ _______________ cells also known as ___________ cells | back 91
|
front 92 In liver, nutrients are stored or used to make new materials, poisons are stored or detoxified, and the blood is returned to the system. Each lobule drains into its ______________ vein . Many central veins join to form the _________ vein which drains into the IVC | back 92
|
front 93 _______ is a salt produced b the hepatic cells, used to ____________ fats into smaller droplets to increase the surface area for __________ to act on fats by braking them down. | back 93
|
front 94
| back 94
|
front 95 ____________ and _________ sumarize the hormonal and neural mechanism that control Bile secretion. HOWEVER, the major stimulus for enhance Bile secretion, is ___________ | back 95
|
front 96
| back 96
|
front 97 Functions of the Liver are
| back 97
|
front 98 15) _________________ is a pear-shaped sac which is used to store and concentrate bile salts. | back 98 Gallbladder |
front 99 Gallbladder main function is to secrete __________ into the _____________ for fat _______________. | back 99
|
front 100 16) ___________ is 1" Diameter.
| back 100
|
front 101
| back 101
|
front 102
| back 102
|
front 103
| back 103
|