Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chem 115 reveiw
front 1  What is the product of the reaction below? | back 1 c |
front 2 If an aldehyde is oxidized, what type of compound would be produced? | back 2 a. a ketone b. a different aldehyde c. a carboxylic acid d. an alcohol |
front 3 An important reaction in chemistry is oxidation. Which is an oxidation reaction? | back 3 a. An alcohol is converted into a ketone. b. An oxygen is removed from an alcohol. c. A double bond between an oxygen and a carbon is broken. d. A carbonyl group is modified to produce an alcohol. |
front 4 What would be the product if we attempt to oxidize a 3º alcohol? | back 4 a. There would be no product, 3º alcohols cannot be oxidized. b. The product is a ketone. c. The product is a carboxylic acid. d. The product is a thiol. |
front 5 A reaction occurs in an acid solution during which two alcohol molecules react with a ketone. The product will be a(an) ___. | back 5 a. ketose b. acetal c. alcoholic ketone d. acidic ketone |
front 6 Which nucleophile, when reacted with 1-bromopropane (CH3CH2CH2Br), would produce a thiol? | back 6 a. OH- b. SH- c. I- d. -OCH3 |
front 7 Aldehydes and ketones both contain a carbonyl carbon atom. They differ in that ___. | back 7 a. the carbonyl carbon atom in ketones is attached to two other carbons and in aldehydes, the carbonyl carbon atom is also attached to at least one hydrogen atom. b. the carbonyl carbon atom in ketones is primary and in aldehydes, the carbonyl is secondary. c. the carbonyl carbon atom in ketones has a hydrogen attached to it. d. the carbonyl carbon atom in aldehydes has two carbon atoms attached to it |
front 8 Each of these is based on the propane molecule. Which is
NOT
| back 8 a. 1-propanol b. 1-propanethiol c. 2-propanol d. propanoic acid |
front 9 The common name for CH3-O-CH3 is ___. | back 9 a. methanal b. dimethanol c. ethyl ether d. dimethyl ether |
front 10 The reaction in which a primary alcohol becomes an aldehyde is an oxidation reaction. | back 10 TRUE |
front 11 Which nucleophile, when reacted with 1-bromopropane (CH3CH2CH2Br), would produce an alcohol? | back 11 a. OH- b. SH- c. I- d. -OCH3 |
front 12 A reducing agent found in some biological systems is ___. | back 12 a. H2O2 b. acetaldehyde c. Pt d. NADH |
front 13 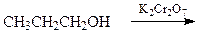 What is the major organic product of the following reaction? | back 13 a. CH3CH=CH2 b. CH3CH2CH2Cr c. CH3CH2CH3 d. CH3CH2CO2H |
front 14 When alcohols are dehydrated in the presence of H+
| back 14 True False |
front 15 What is the IUPAC name of this compound? | back 15 a. 4-methy-4-propylbutylaldehyde b. 4-methylhexanal c. 4-ethylpentanal d. 4-ethylpentylaldehyde |
front 16 Which compound is a hemiacetal? | back 16 b. |
front 17 The oxidation of methanethiol by I2
| back 17 a. |
front 18 If formaldehyde reacts with methanol in an acid solution, the product formed is ___. | back 18 a. a new aldehyde b. an alcohol that is very polar c. a hemiacetal d. an acid |
front 19 The compound that is expected to have the highest boiling point is ___. | back 19 the alcohol produced from methane. b. the thiol produced from methane. c. methane. d. They all boil at the same temperature since methane is the basis for the compounds. |
front 20 Benedict’s solution turns a blue color in the presence of glucose. | back 20 FALSE |
front 21 The method to determine the number of stereoisomers of a monosaccharide is to calculate 2n, where n is the total number of carbons in the molecule. | back 21 FALSE |
front 22 Cellulose is composed of glucose molecules connected by a-glycosidic linkages. | back 22 FALSE |
front 23 Both starch and cellulose are polysaccharides of glucose. | back 23 TRUE |
front 24 How many stereoisomers would a carbohydrate with 5 chiral carbons have? | back 24 a. 5 stereoisomers b. 20 stereoisomersc. c. 32 stereoisomers d. 60 stereoisomers |
front 25 Shown below is a cyclic form of D-galactose. This structure is classified as ___. | back 25 a. a-D-galactopyranoseb. b a-D-galactofuranosed. b |
front 26 Hyaluronic acid solutions serve as lubricants in the fluid of joints and are present in the vitreous humor of the eye. A portion of its structure is shown below. | back 26 a. Hyaluronic acid is a homopolysaccharide. b. Hyaluronic acid is a heteropolysaccharide. c. Hyaluronic acid is made of D-glucose residues. d. The monosaccharide residues in hyaluronic acid are of furanose form. |
front 27 The disaccharides are important in nature; a few examples of disaccharides are | back 27 a. D-abqueose, D-fructose, galactose, and glucose. b. raffinose, stachyose, and verbascose. c. cellobiose, lactose, maltose, and sucrose. d. amylopectin, amylose, and starch. |
front 28 Shown below is a cyclic form of D-Fructose. This structure is classified as ___. | back 28 a. a-D-fructopyranoseb. b-D-fructopyranose c. b-D-fructofuranose d. a-D-fructofuranose |
front 29 A pair of compounds are stereoisomers and they are nonsuperimposable mirror images. This pair of isomers is referred to as a pair of enantiomers. | back 29 TRUE |
front 30 Which of the following is a fruit sugar? | back 30 a. D-glucose b. Galactose c. Lactose d. D-Fructose |
front 31 D-glucose is often called by other names, such as corn sugar and grape sugar. It is also referred to as ___. | back 31 a. dextrose b. fruit sugar c. blood sugar d. dextrose and blood sugar |
front 32 What is the classification of this monosaccharide? | back 32 a. aldopentose b. aldohexose c. ketopentose d. ketohexose |
front 33 Shown below is a cyclic form of D-mannose. This structure is classified as ___. | back 33 a. a-D-mannopyranose b. b-D-mannofuranose c. a-D-mannofuranosed d. b-D-mannopyranose |
front 34 Blood type is determined by oligosaccharides attached to the surface of red blood cells. | back 34 TRUE |
front 35 How would this compound be classified? | back 35 a. carboxylic carbohydrate b. hydroxyaldehyde c. ketotriose d. aldotriose |
front 36 Relative sweetness is a measure of the sweetness of any chosen sweetener compared to that of | back 36 a. invert sugar. b. the sweetest carbohydrate, fructose. c. sucrose. d. saccharin. |
front 37 Glycogen and amylopectin are similar in that they are both polymers of glucose. Glycogen is the glucose storage form for ___ and starch is the glucose storage form for ___. | back 37 a. plants/plants b. animals/animals c. plants/animals d. animals/plants |
front 38 Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another are called | back 38 a. enantiomers b. anomers c. diastereomers d. Fischer projections |
front 39 The structural formula for erythrose is drawn here. The carbon atoms are numbered from the carbonyl group. | back 39 a. This is the only formula for erythrose; there are no stereoisomers.b. This is both a D and an b. This is both a D and an L structure, as determined by carbons #1 and #2. c. This is D-erythrose, as determined by carbon #3. d. This is L-erythrose, as determined by carbon #4. |
front 40 Glycogen is a polymer of glucose produced by plants for energy storage. | back 40 FALSE |
front 41 Fructose is different from glucose and galactose because | back 41 a. fructose is a pentose; the other sugars are hexoses. b. fructose is a ketose; the other sugars are aldoses. c. the cyclic form is a square; the other sugars display hexagons. d. fructose doesn’t have an open form; the other sugars do have an open form. |
front 42 An aldose is a carbohydrate that contains | back 42 a. hydroxy groups on the terminal carbons. b. water molecules on the alpha carbon. c. an aldehyde group. d. monosaccharides. |
front 43 Which of the following reactant is missing in the reaction below? | back 43 A |
front 44 The organic product expected from the following reaction is: | back 44 a |
front 45 Tertiary alcohols have three carbon atoms attached to carbon that has the OH directly attached. | back 45 TRUE |
front 46 Ethanol is miscible in water, while 1-pentanol has a solubility of just 2.2g/100 mL because solubility in water decreases with increasing alcohol size. | back 46 TRUE |
front 47 Hyaluronic acid solutions serve as lubricants in the fluid of joints and are present in the vitreous humor of the eye. A section of the structure for hyaluronic acid is: WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING STATEMENTS IS TRUE | back 47 a. The alternating pattern of glycosidic bond types are a-(1→3) and a-(1→4). b. The alternating pattern of glycosidic bond types are - (1→3) and - (1→4). c. The alternating pattern of glycosidic bond types are - (1→3) and a- (1→4). d. The alternating pattern of glycosidic bond types are - (1→3) and - (1→3). |
front 48 What is the classification of this monosaccharide? | back 48 a. aldotriose b. ketotriose c. aldotetrose d . ketotetrose |
front 49 Maltose is a monosaccharide | back 49 False |
front 50 The structure of the compound 2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal is shown below. How many stereoisomers are possible for this molecule? | back 50 a. 2 B. 4 c. 8 d. 16 |
front 51 Sucrose is a disaccharide of D-glucose connected to D-fructose by an a,b-(1 →2)- glycosidic bond. Sucrose is not a reducing sugar because | back 51 a. it is a disaccharide. b. it reacts with Benedict's solution. c. it contains both glucose and fructose. d. it cannot react to produce an aldehyde group. |
front 52 Which of the following statements is true about aldehydes? | back 52 a. Aldehydes have much lower boiling points than alcohols with a similar molecular weight.b. Aldehydes interact with like molecules through hydrogen bonding.c. The carbonyl carbon atom in an aldehyde can never be in position number 1.d. The parent chain of an aldehyde is named by dropping the final “e” from a corresponding alkane and adding “one.” |
front 53 Which compound type is most susceptible to a nucleophillic substitution reaction? | back 53 a. hydrocarbon b. alcohol c. alkyl halide d. acid |
front 54 The IUPAC name for the organic compound below is | back 54 a. 3-Butanol b. 2-Butanol c. Ethyl methyl ether d. 3-butanethiol |
front 55 What is mutarotation? | back 55 a. The conversion of a D-monosaccharide into an L-monosaccharide. b. The conversion of a-D-galacose into b-D-galactose. c. The conversion of a pyranose into a furanose. d. The conversion of an aldose into a ketose. |
front 56 Which are the most commonly found monosaccharides in nature? | back 56 a. those with 4 carbons b. those with 5-6 carbons c. those with 7-9 carbons d. those with 10 or more carbons |
front 57 The reduction of a ketone produces a 2° alcohol. | back 57 TRUE |
front 58 The structural similarity of acetals and ethers is the presence of ___. | back 58 a. C—O—C b. a carboxylic carbon c. C—O—H d. CHO |
front 59 Oxidation of a secondary alcohol results in the formation of a(n) ___. | back 59 a. tertiary alcohol b. acid c. aldehyde d. ketone |