Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Lecture Exam
front 1 Which property of muscle gives it the ability to stretch without damage? | back 1 extensibility |
front 2 This is the outermost layer of connective tissue surrounding a skeletal muscle. | back 2 epimysium |
front 3 The contractile organelles of a skeletal muscle fiber are thread-like structures called | back 3 Myofibrils |
front 4 Release of calcium from these structures triggers skeletal muscle contraction. | back 4 terminal cisterns of sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 5 Which of the following regions of a sarcomere contain thin filaments? | back 5 Both I band and A band |
front 6 Myofibrils contain | back 6 all of these answers are correct. |
front 7 What regulatory proteins can be found in the thin filaments of skeletal muscle fibers? | back 7 tropomyosin and troponin |
front 8 Which of the regions of a sarcomere contain titin? | back 8 from M line to Z disc |
front 9 What energizes the myosin head? | back 9 ATP hydrolysis reaction |
front 10 Skeletal muscle contraction will continue to occur as long as the following chemicals are available in the cytosol of the muscle fiber. | back 10 Calcium ions and ATP |
front 11 This is the least powerful type of skeletal muscle fiber. | back 11 slow oxidative fiber |
front 12 Which of the following microscopic structures is only found in the cardiac muscle tissue? | back 12 intercalated discs |
front 13 Which of the following types of muscle tissue contract when excited by their own autorhythmic muscle fibers? | back 13 cardiac muscle |
front 14 Smooth muscle tone is maintained by the prolonged presence of _____ in the muscle cell’s cytosol? | back 14 Calcium ions |
front 15 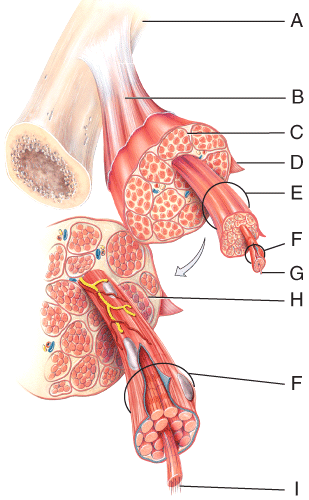 Which of the labeled structures on the diagram holds muscles with similar functions together, allows free movement of muscles, carries nerves, blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, and fills spaces between muscles? | back 15 B |
front 16 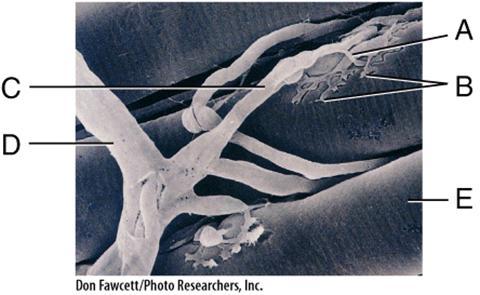 In the diagram, the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, is released from this area. | back 16 B |
front 17 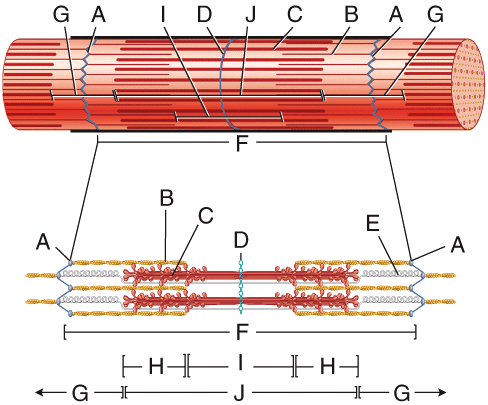 In the diagram, what is the basic functional unit of a myofibril? | back 17 F |
front 18 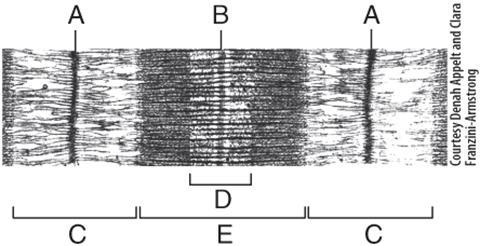 In the diagram, where are thick filaments found? | back 18 E |
front 19 Which of the following types of muscle tissue is capable of undergoing the stress-relaxation response when they are stretched? | back 19 single-unit smooth muscle fibers |
front 20 Cross bridges are formed during muscle contraction when _____ on the thick filaments binds to _____ on the thin filaments. | back 20 myosin; actin |
front 21 In a neuromuscular junction, the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) binding to receptors on the motor end plate lasts only briefly due to | back 21 rapid destruction of ACh in the synaptic cleft by acetylcholinesterase. |
front 22 Which of following is a common characteristic of fast glycolytic (FG) skeletal muscle fibers? | back 22 high amount of glycogen in the sarcoplasm. |
front 23 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic commonly used to name skeletal muscles? | back 23 Thickness of fibers |
front 24 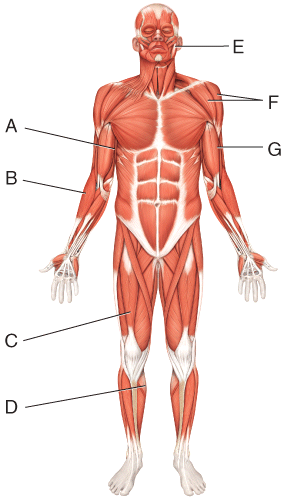 Where is the latissimus dorsi? | back 24 A |
front 25  Where is the rectus femoris? | back 25 C |
front 26 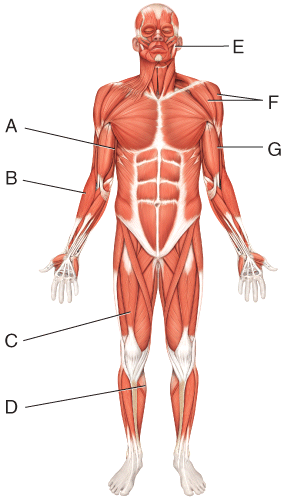 Where is the deltoid? | back 26 F |
front 27 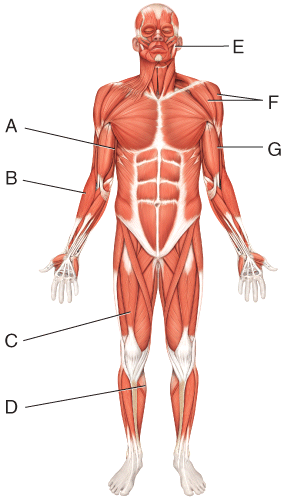 Where is the masseter? | back 27 E |
front 28 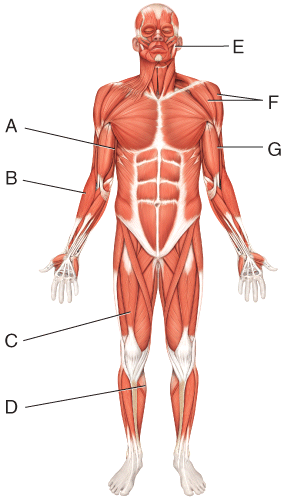 Where is the gastrocnemius? | back 28 D |
front 29 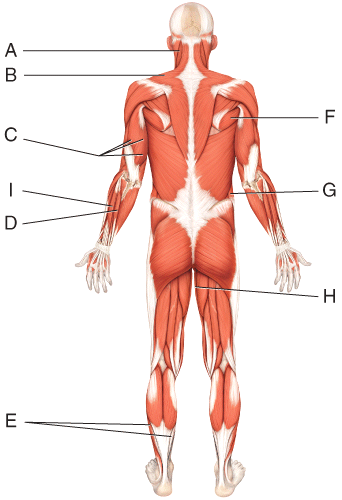 Where is the soleus? | back 29 E |
front 30 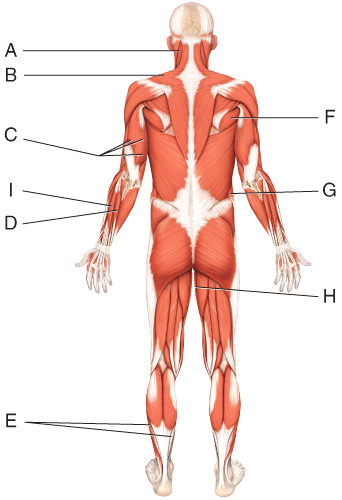 Where is the external oblique? | back 30 G |
front 31 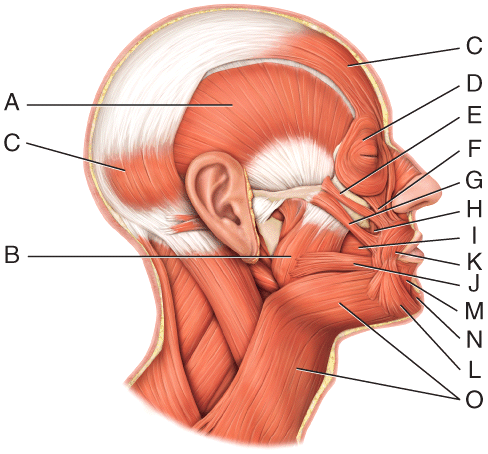 Where is the masseter? | back 31 B |
front 32 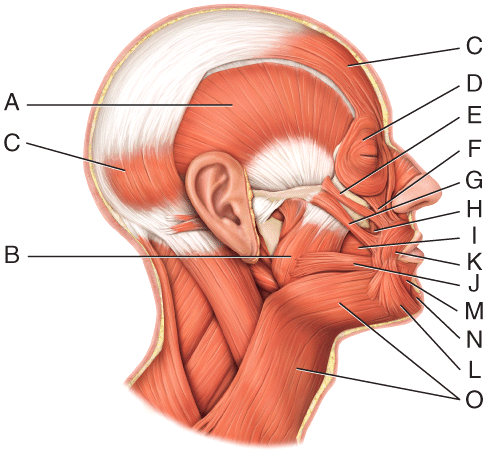 Where is the orbicularis oculi? | back 32 D |
front 33  Where is the lateral rectus? | back 33 E |
front 34  Where is the serratus anterior? | back 34 G |
front 35 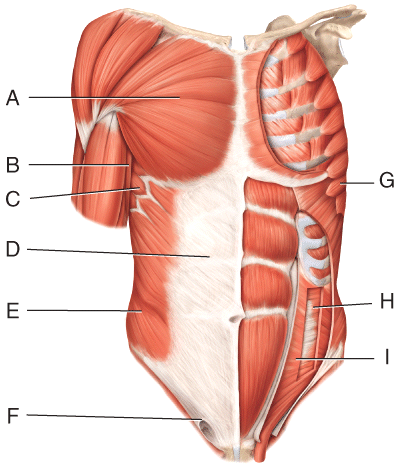 Where is the external oblique? | back 35 E |
front 36 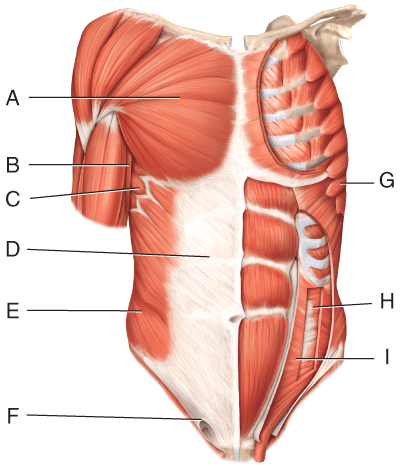 Where is the transverse abdominus? | back 36 H |
front 37 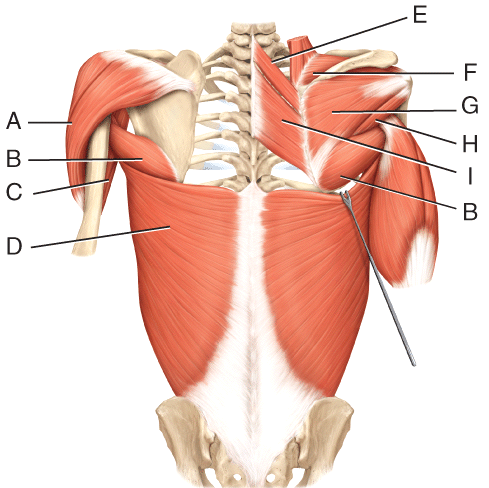 Where is the infraspinatus? | back 37 G |
front 38 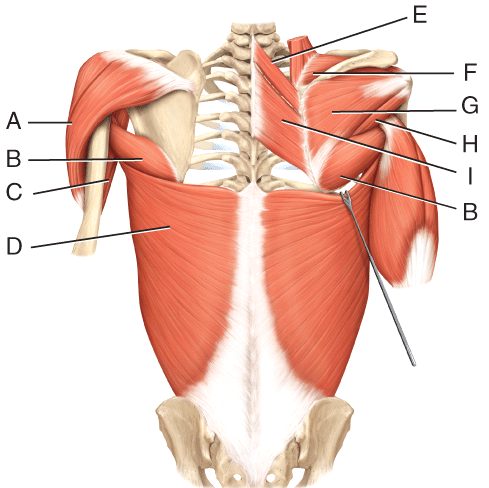 Where is the rhomboid major? | back 38 I |
front 39  Where is the brachioradialis? | back 39 C |
front 40 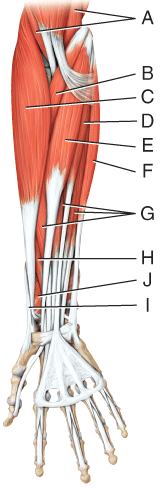 Where is the flexor carpi radialis? | back 40 E |
front 41 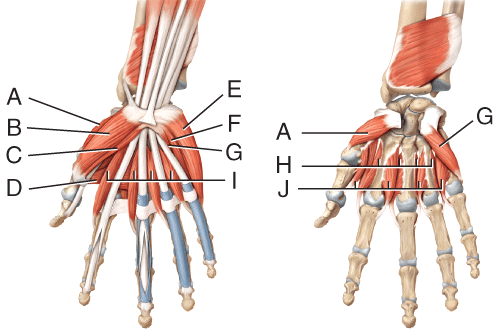 Where is the abductor digiti minimi? | back 41 E |
front 42  Where is the quadratus lumborum? | back 42 A |
front 43 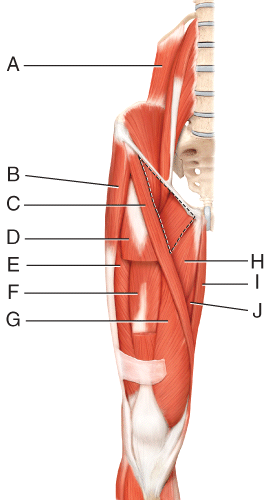 Where is the sartorius? | back 43 C |
front 44 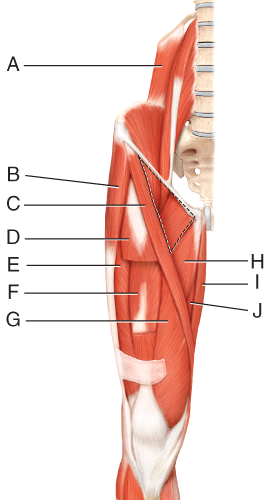 Where is the vastus intermedius? | back 44 F |
front 45 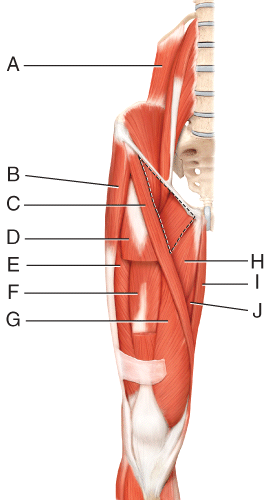 Where is the gracilis? | back 45 I |
front 46 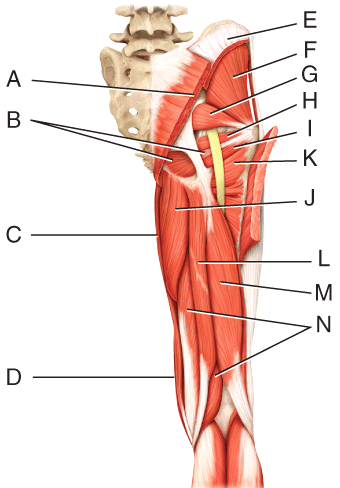 Which three muscles make up the hamstring? | back 46 L, M, N |
front 47 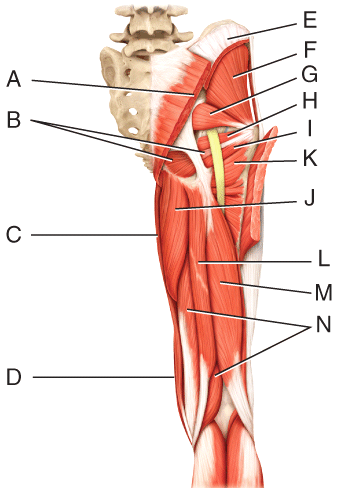 Where is the semitendinosus? | back 47 L |
front 48 A muscle that has three origins is called a | back 48 triceps |
front 49 A muscle that raises or elevates a body part is called a | back 49 levator |
front 50 A muscle that decreases the size of an opening is a | back 50 sphincter |
front 51 Which of the following is a muscle whose insertion is found on the clavicle and acromion process of the scapula within the pectoral girdle? | back 51 trapezius |
front 52 Which of the following types of joints lacks a joint cavity and is
held together by a fibrous connective tissue? | back 52 1 only |
front 53 Which of the following types of joints do NOT have a synovial cavity?
| back 53 1 and 2 |
front 54 Which of the following types of joints do NOT have a synovial cavity?
| back 54 3 only |
front 55 Moving the humerus laterally at the shoulder joint is an example of which type of movement? | back 55 Abduction |
front 56 Which type of movement involves a continuous sequence of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction resulting in a distal body part moving in a circle? | back 56 Circumduction |
front 57 What type of special movement occurs in your clavicles at your acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints when you cross your arms in front of your body? | back 57 Protraction |
front 58 Which special movement occurs when you bend your foot at the ankle in the direction of the foot’s superior surface as would occur when you stand on your heels? | back 58 Dorsiflexion |
front 59 Which special movement involves moving your thumb across the palm to touch the tips of the fingers on the same hand? | back 59 Opposition |
front 60 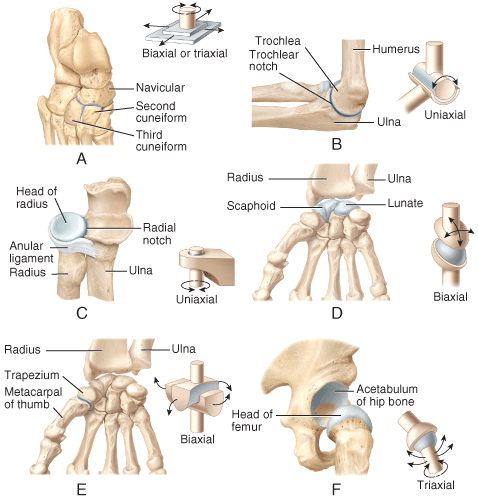 Which of the joints shown in the figure is classified as a multiaxial joint? | back 60 F |
front 61 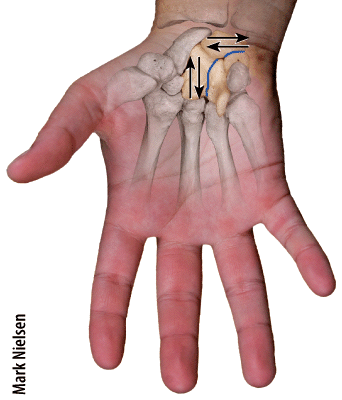 Which type of joint permits this type of movement? | back 61 1 only |
front 62 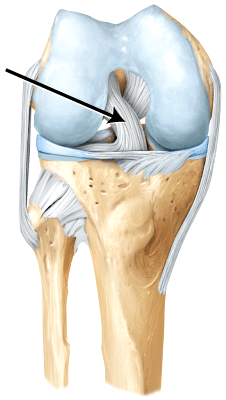 The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. | back 62 anterior cruciate |
front 63 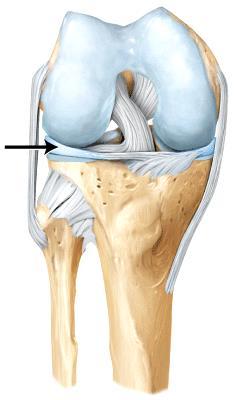 The line is pointing to the _____. | back 63 lateral meniscus |
front 64  The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. | back 64 coracohumeral |