Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ventricles, meninges, CSF and blood vessels of the brain
front 1 Which dural septum lies in the longitudinal fissure between the two cerebral hemispheres? | back 1 falx cerebri |
front 2 CSF flows from each lateral ventricle into the ___________ via an interventricular foramen. | back 2 third ventricle |
front 3 What meninx is directly adhered to the surface of the brain, giving the brain its shiny appearance? | back 3 pia mater |
front 4 Which arteries are NOT part of the Circle of Willis? Middle cerebral aa. Anterior cerebral aa. Posterior cerebral aa. Internal carotid aa. Posterior communicating aa. | back 4 middle cerebral |
front 5 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced by __________. | back 5 choroid plexuses |
front 6 Reabsorption of CSF occurs via the __________ into the superior sagittal sinus. | back 6 arachnoid villi |
front 7 What dural sinus enters the jugular foramen and continues as the internal jugular vein? | back 7 sigmoid sinus |
front 8 The __________ is derived from the diencephalon portion of the lumen of the neural tube. | back 8 third ventricle |
front 9 What artery or arteries pass through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae? | back 9 vertebral arteries |
front 10 Place these potential/actual spaces in order from SUPERFICIAL TO DEEP.
| back 10 Epidural space, subdural space, & subarachnoid space |
front 11 what are the three cranial meninges from superficial to deep? | back 11 dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater |
front 12 what are the two layers of dura mater in the skull, from superficial to deep? | back 12 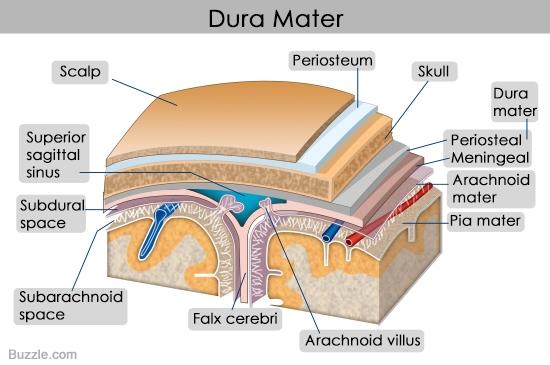 periosteal layer and meningeal layer |
front 13 which layer of dura mater is continuous in the vertebral sheath of spinal cord? which layer of dura mater is absent in the spinal cord? | back 13 meningeal layer; periosteal layer |
front 14 which layer of dura mater forms the dural septa? | back 14 meningeal layer |
front 15 what is dural septa? | back 15 double layered folds of dura mater that insert into fissures |
front 16 what are the three dural septa of the brain? | back 16 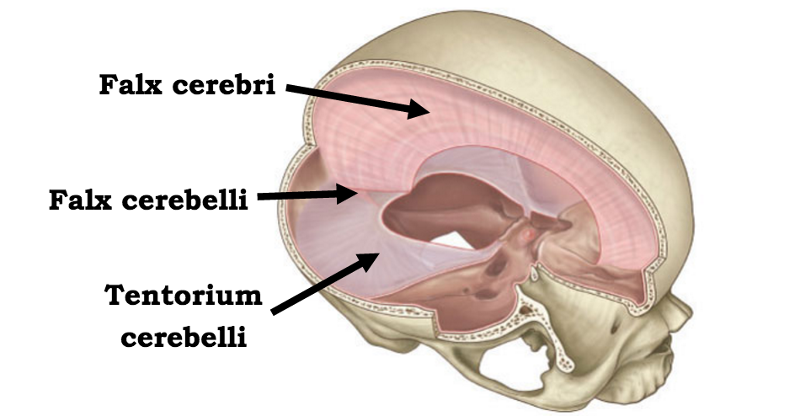 falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, and tentorium cerebelli |
front 17 crescent-shaped fold of meningeal layer of dura mater that descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain | back 17 falx cerebri |
front 18 meningeal layer that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum | back 18 tentorium cerebelli |
front 19 function of the dural septa? | back 19 prevent excess movement, like packaging material |
front 20 meningeal layer that separates the two cerebellar hemispheres | back 20 falx cerebelli |
front 21 the falx cerebri contains which two dural venous sinuses? where are they located? | back 21 superior sagittal sinus runs on superior edge and inferior sagittal sinus located on inferior edge |
front 22 the tentorium cerebelli houses which dural venous sinus? | back 22 transverse sinus |
front 23 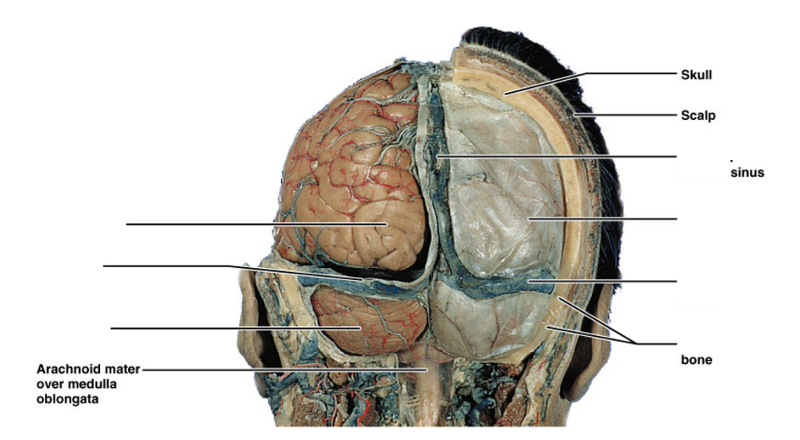 label | back 23 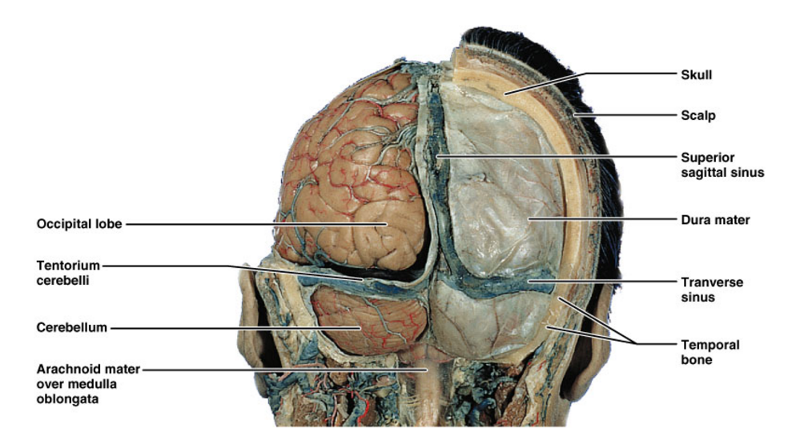 |
front 24 space where layers of dura mater separate are | back 24 dural venous sinuses |
front 25 what in contained in the dural venous sinuses? | back 25 venous blood from the veins of the brain and CSF returned from the subarachnoid space |
front 26 be able to make dural venous sinus chart | back 26 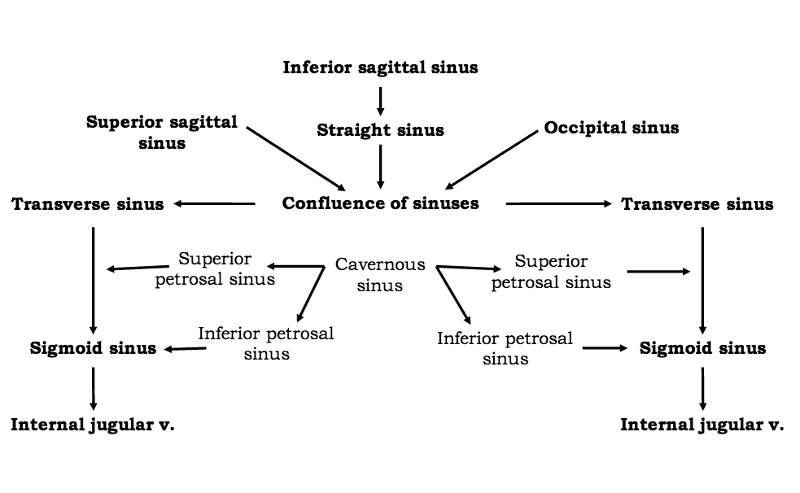 |
front 27 define arachnoid granulations/villi | back 27 projections of the arachnoid villi into the dural sinuses that allow CSF entrance from the subarachnoid space into the venous system. |
front 28 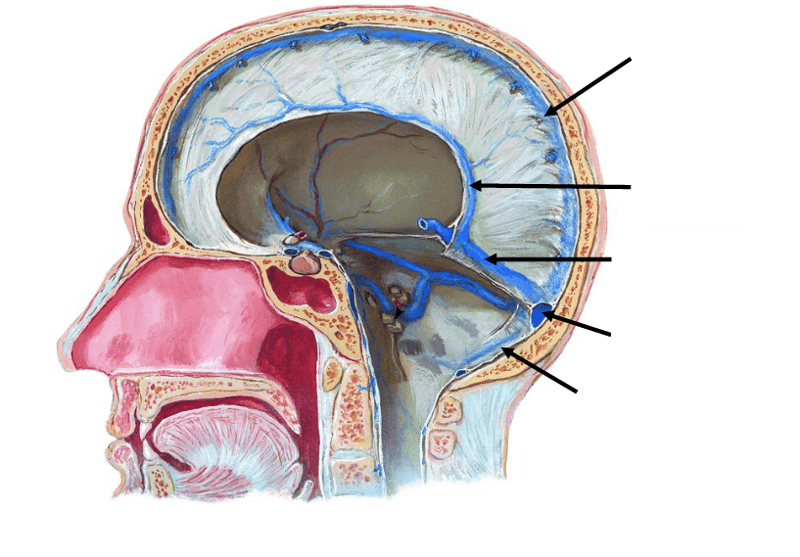 label | back 28 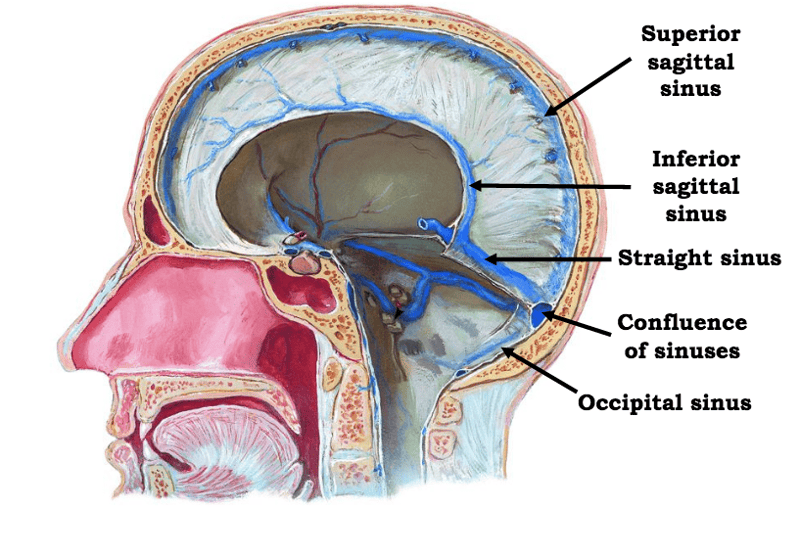 |
front 29 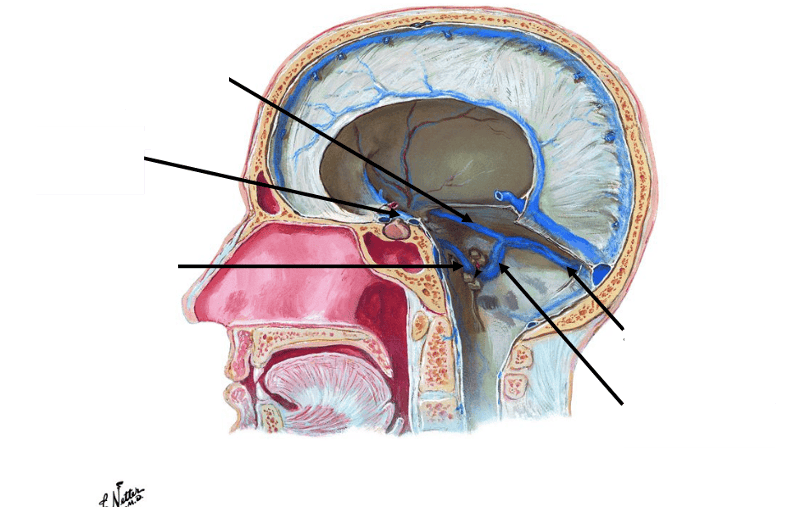 | back 29 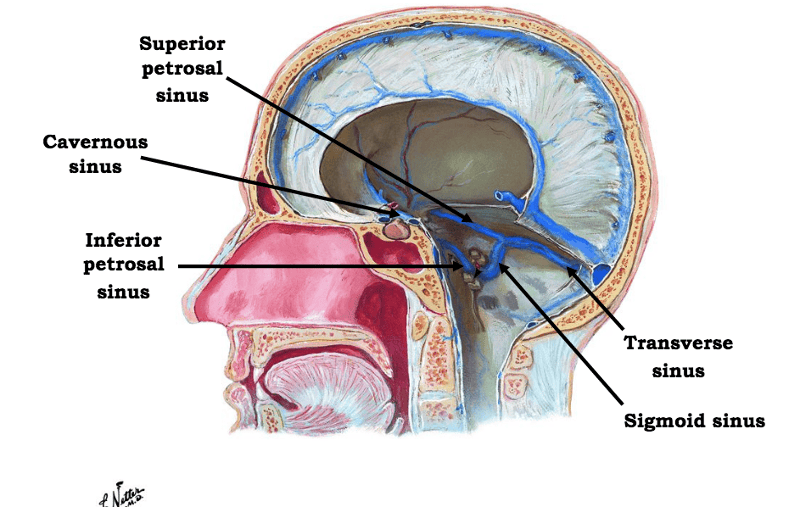 |
front 30 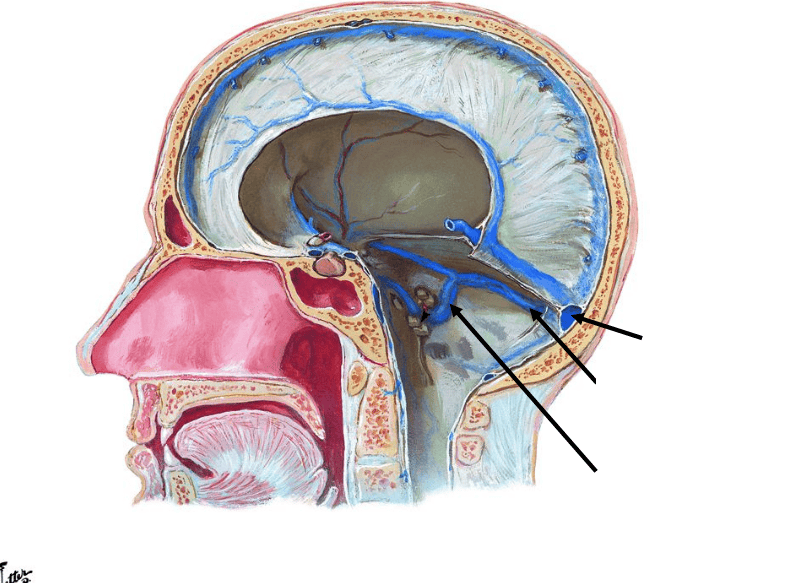 | back 30 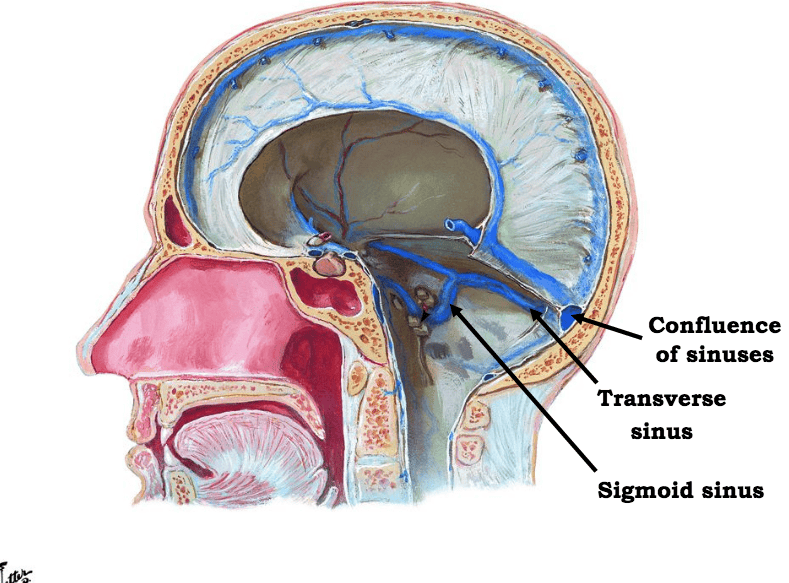 |
front 31 which sinus is situated on the inferior border of the petrous part of the temporal bone? | back 31 inferior petrous sinus |
front 32 name the two potential and on actual meningeal spaces of the brain | back 32 potential: epidural and subdural actual: subarachnoid |
front 33 space between the skull and dura mater of the brain | back 33 extradural/epidural |
front 34 space between dura mater and arachnoid mater of the brain | back 34 subdural space |
front 35 space between arachnoid and pia mater of the brain | back 35 subarachnoid space |
front 36 location of CSF and blood vessels around the brain | back 36 subarachnoid space |
front 37 what type of blood would be gathering in the case of an extradural hematoma? which blood vessel is damaged? | back 37 arterial blood; the middle meningeal artery is damaged in most situations |
front 38 what type of blood is building up in a subdural hemorrhage | back 38 venous blood |
front 39 what type of fluid is building up in a subarchnoid hemorrhage | back 39 CSF |
front 40 _____ arise from the lumen of the neural tube (ie neural canal) | back 40 ventricles |
front 41 which ventricle arises from the telencephalon? | back 41 the paired C shaped lateral ventricles |
front 42 which neural tube gives rise to the third ventricle | back 42 diencephalon |
front 43 which ventricle arises from the mesencephalon | back 43 cerebral aquaduct |
front 44 from which neural tubes does the fourth ventricle arise? | back 44 metencephalon and myelencephalon |
front 45 what forms the central canal? | back 45 lumen associated with the neural tube which will become the spinal cord |
front 46  label | back 46 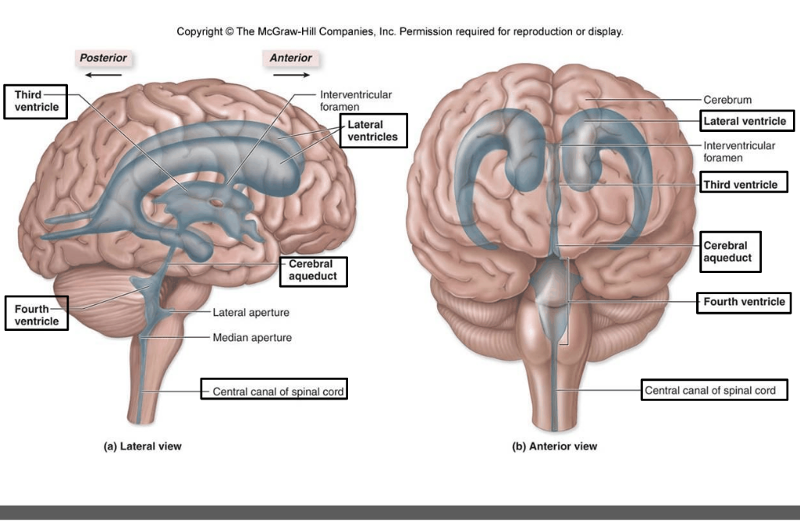 |
front 47 what forms CSF and where is it found? | back 47 a choroid plexus forms CSF and there is choroid plexus found in all ventricles |
front 48 what type of cells is choroid plexus made of? | back 48 modified ependymal cells |
front 49 what are the three functions of CSF | back 49 shock absorber for brain transports nutrients and removal of waste in deep brain helps maintain proper ion balance in neural tissue |
front 50 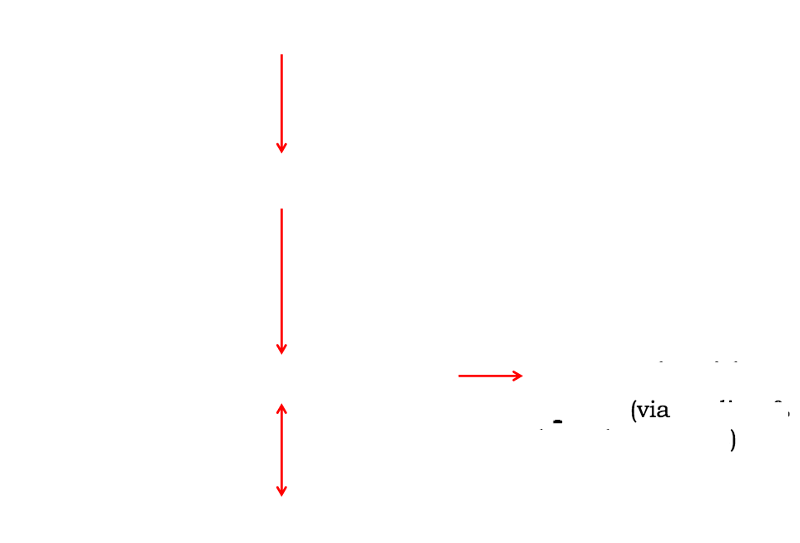 what is the order of the of CSF through the ventricles? | back 50 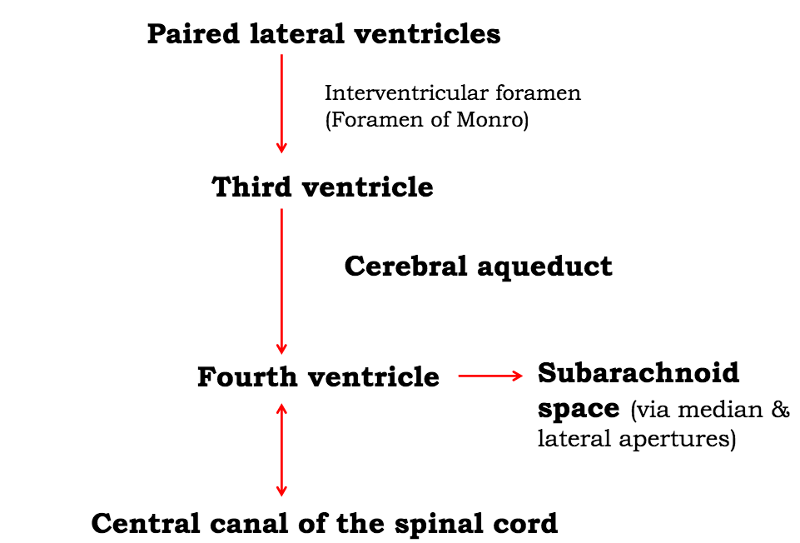 |
front 51 what is hydrocephalus | back 51 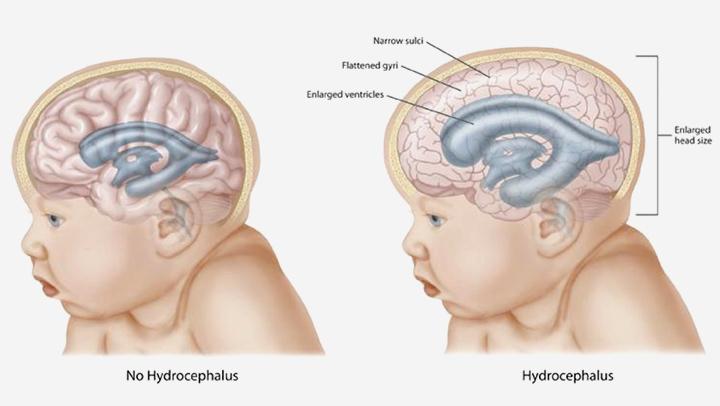 it is caused by obstruction of circulation of CSF leads to accumulation of fluid compresses the brain/pushes skull outward in babies |
front 52 what are the two major pairs of arteries that supply blood to the brain? | back 52 vertebral arteries and internal carotid arteries |
front 53 which arteries supply the posterior circulation of the brain? | back 53 the vertebral arteries |
front 54 which arteries do the vertebral arteries branch off of? | back 54 subclavian |
front 55 which major arteries enter the skull through the foramen magnum? | back 55 vertebral arteries |
front 56 which artery supplying blood to the brain branches off the common carotid arteries? | back 56 internal carotid arteries |
front 57 the internal carotid arteries supply the anterior or posterior circulation of the brain | back 57 anterior |
front 58 what is the pathway for the internal carotid arteries to enter the skull? | back 58 enter the skull through the carotid canal and then through the internal opening of the foramen lucerum |
front 59 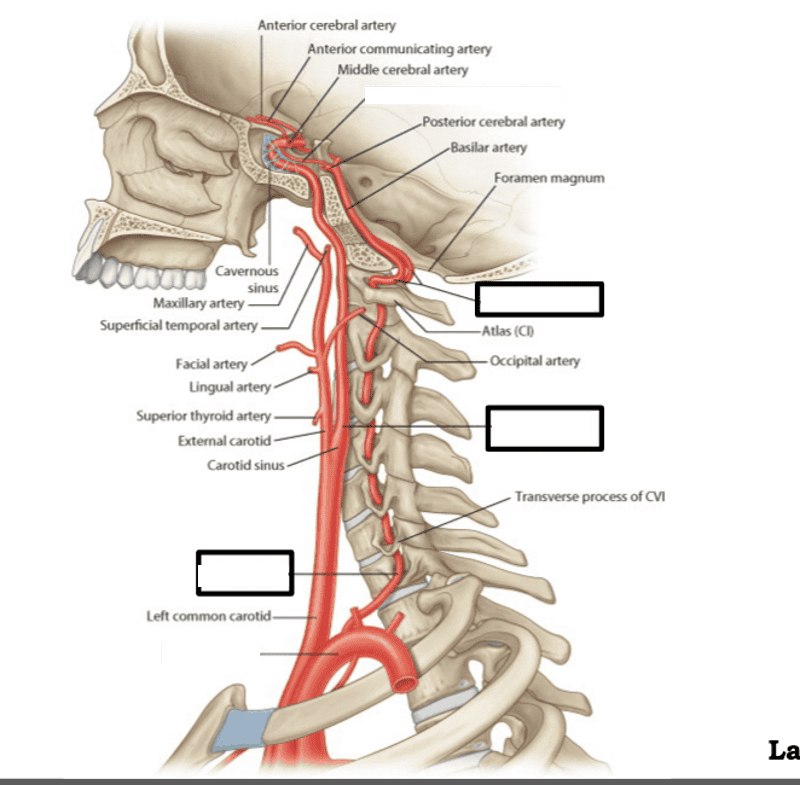 label | back 59 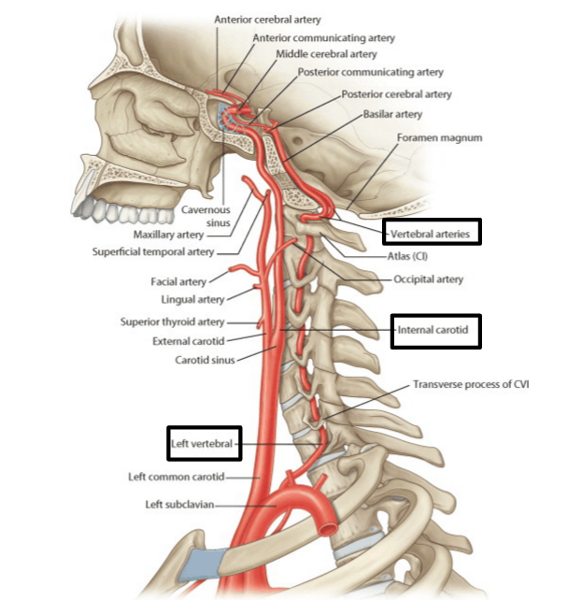 |
front 60 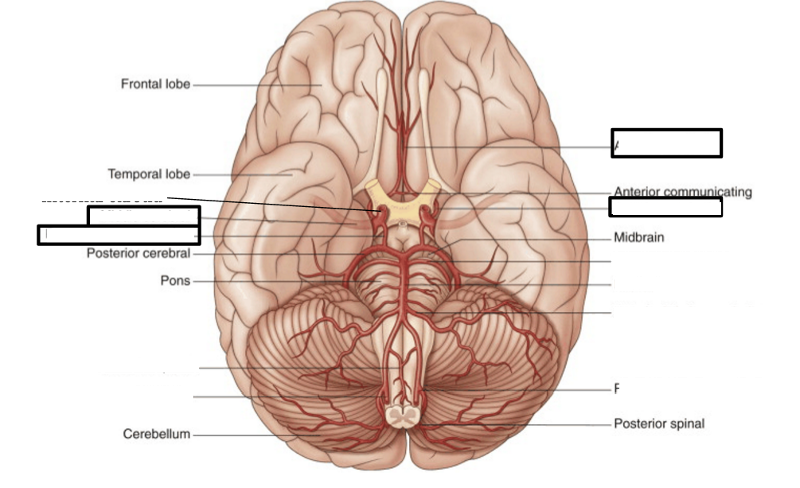 label | back 60 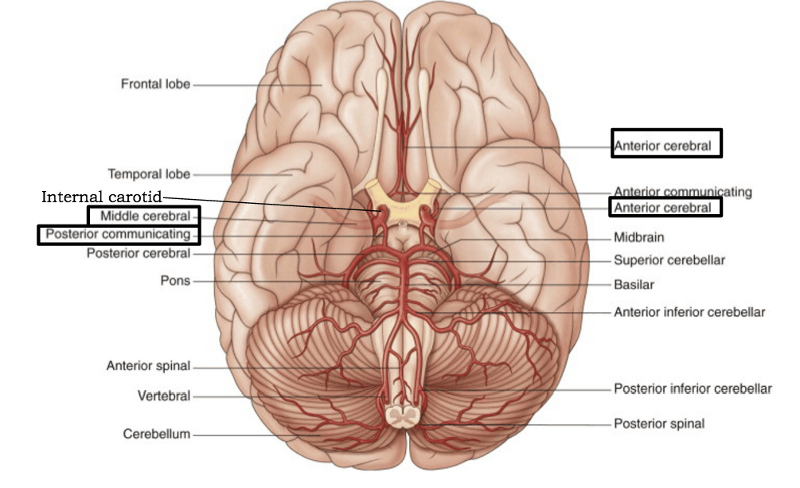 |
front 61 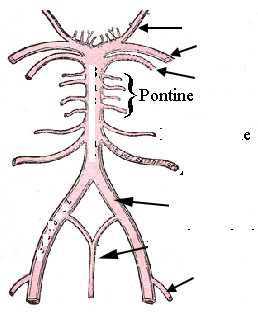 draw and label | back 61 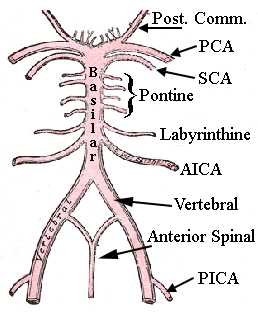 PCA = posterior cereberal SCA = superior cerebellar PICA = posterior inferior cerebellar artery AICA = anterior inferior cerebellar artery |
front 62 what are the major branches of the internal carotid artery | back 62 anterior cerebral middle cerebral posterior communicating |
front 63 which branch of the internal carotid artery is located in the longitudinal fissure and wraps around the corpus callosum? | back 63 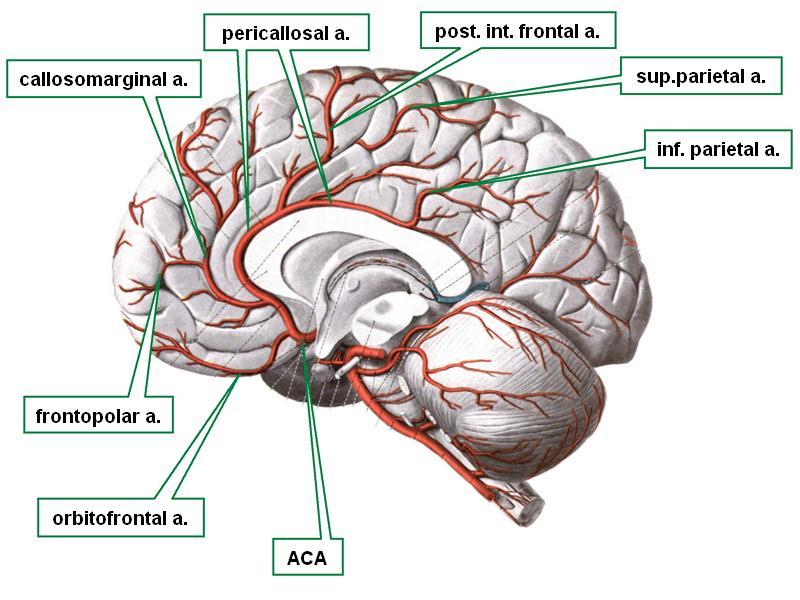 anterior cerebral artery |
front 64 which branch of the internal carotid artery passes through the lateral fissure to supply the lateral aspect of the brain? | back 64 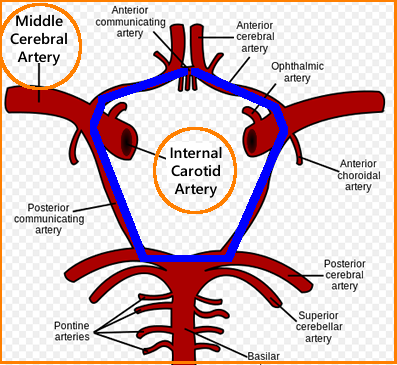 middle cerebral artery |
front 65 which artery branching off the internal carotid artery connects anterior and posterior circulation of the brain? | back 65 posterior communicating artery |
front 66 what are the major branches of the vertebral artery? | back 66 posterior inferior cerebellar anterior spinal basilar |
front 67 what are the branches of the basilar artery? | back 67 anterior inferior cerebellar pontine labyrinthine superior cerebellar posterior cerebral |
front 68 which artery feeds the anterior portion of the spinal cord? | back 68 anterior spinal artery |
front 69 which arteries make up the Circle of Willis? | back 69 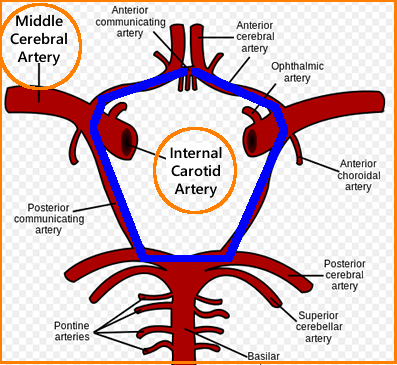 anterior communicating artery anterior cerebral artery internal carotid artery posterior communicating artery posterior cerebral artery |
front 70 which artery is a terminal branch of the internal carotid and supplies most of the medial and superior surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres (specifically on the frontal and parietal lobes) | back 70 anterior cerebral artery |
front 71 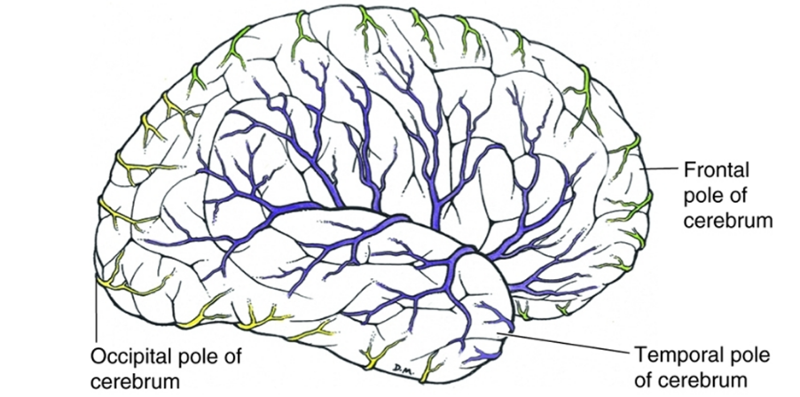 out of the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries, which feeds the more lateral aspects of the brain and which feed the more medial | back 71 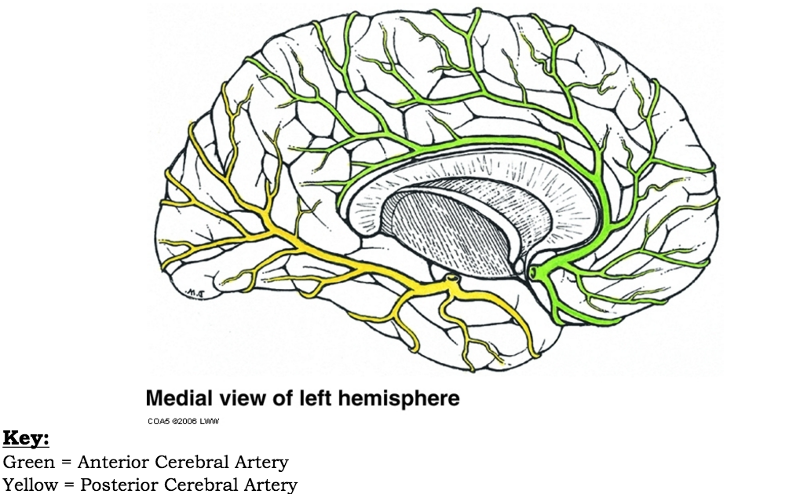 medial = anterior and posterior lateral = middle |
front 72 the terminal branch of the internal carotid artery which passes between the temporal and frontal lobes to reach the lateral part of the cerebral hemispheres | back 72 middle cerebral artery |
front 73 if you had upper limb, face, and tongue deficits due to a stroke, which artery would you think was damaged? | back 73 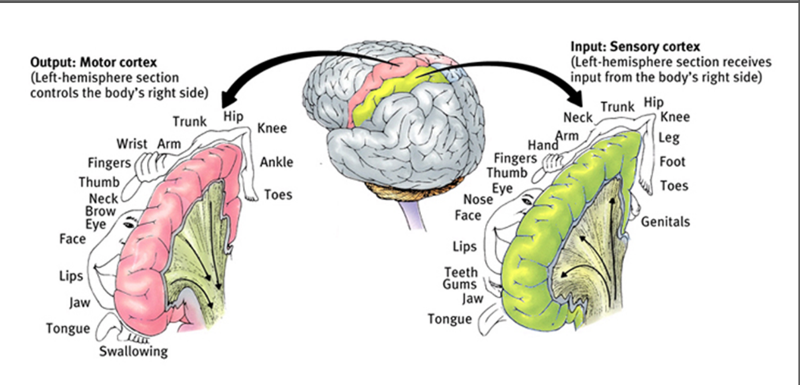 middle cerebral artery |
front 74 if you had lower limb deficits due to a stroke, which artery would you think was damaged? | back 74 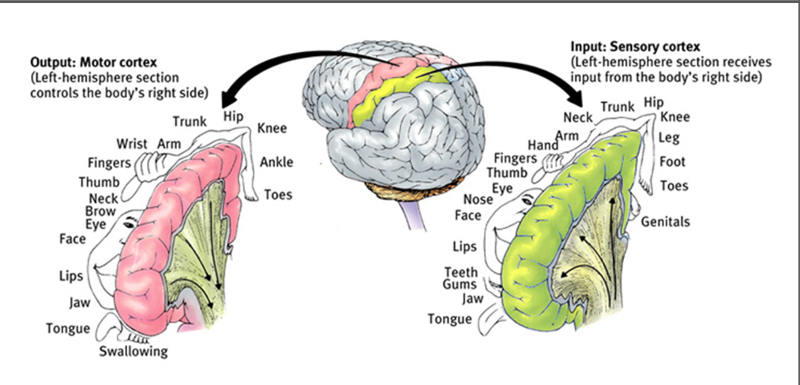 anterior cerebral artery |
front 75  which artery is being described here? | back 75 posterior cerebral |
front 76 if vision loss occurs after a stroke, damage to which blood vessel may have occurred? | back 76 posterior cerebral artery it supplies all of the occipital lobe, which is responsible for vision |
front 77 Be able to draw complete bloodflow pattern in brain | back 77 no data |