Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Chapter 24 Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature Regulation
front 1 To quiz yourself select the cards option from the note card set and good luck with your class. | back 1 Here are other helpful study guides: http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/70700 http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/3288 http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/13802 http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/36677 http://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/13471 https://quizlet.com/57781682/metabolism-flash-cards/ |
front 2 The movement of H+ through the ATP synthase is best described as an example of ______. hydrolysis | back 2 facilitated diffusion |
front 3 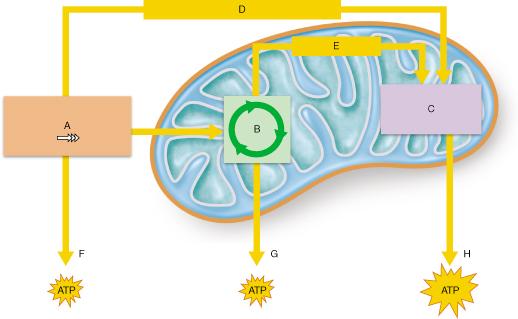 Oxygen is consumed during which of the lettered processes? A | back 3 C |
front 4 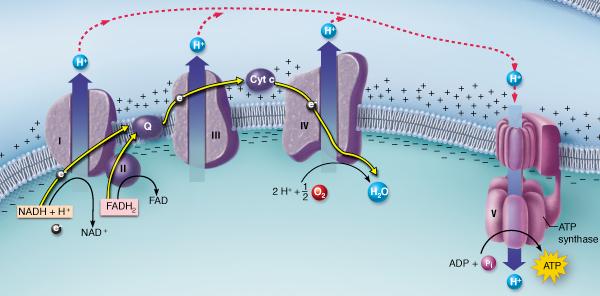 Which of the following events is NOT depicted in the figure? transfer of electrons and hydrogen atoms from a food molecule to
a coenzyme | back 4 transfer of electrons and hydrogen atoms from a food molecule to a coenzyme |
front 5 Proton pumps within the electron transport chain transport H+ ions ______. from matrix to intermembrane space | back 5 from matrix to intermembrane space |
front 6 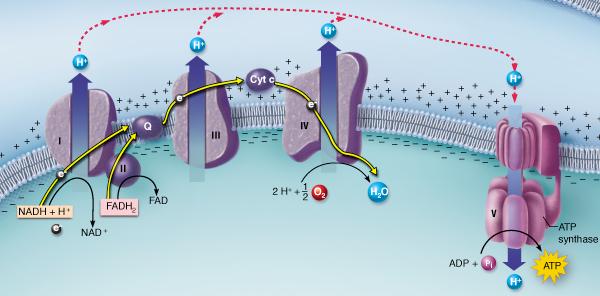 Which of the following describes the event depicted on the right side of the figure? active transport of H+ ions | back 6 oxidative phosphorylation |
front 7 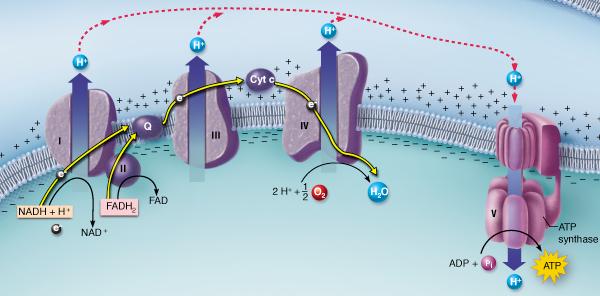 Which of the following pathways act as a source for the electrons carried by the NADH and FADH2 molecules shown in this figure? glycolysis | back 7 both A and B |
front 8 Which of the following is NOT an end product of the Krebs
cycle? | back 8 citric acid |
front 9 Most ATP in cellular respiration is generated in glycolysis. | back 9 False |
front 10 The body is able to form glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. | back 10 True |
front 11 The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available
fuel for neurons and blood cells is ________. | back 11 glucose |
front 12 It is important to ensure that your diet is adequately rich in
vitamins because ________. | back 12 most vitamins are coenzymes needed to help the body utilize essential nutrients |
front 13 Prostaglandins play a role in ________. | back 13 control of blood pressure |
front 14 Select the correct statement about proteins. | back 14 Proteins will be used by most cells for ATP synthesis if insufficient carbohydrates are ingested. |
front 15 The term essential nutrient refers to the chemicals that can be
interconverted in the liver so that the body can maintain life and
good health. | back 15 False |
front 16 The most abundant dietary lipids in the diets of most Americans are triglycerides. | back 16 True |
front 17 Ammonia, which is a byproduct of protein metabolism, is converted to
__________ primarily in the __________. | back 17 urea; liver |
front 18 The primary goal during the postabsorptive state is to
__________. | back 18 maintain blood glucose levels within an adequate range |
front 19 The process of breaking triglycerides down into glycerol and fatty
acids is known as ________. | back 19 lipolysis |
front 20 When ketone bodies are present in the blood and urine in large
amounts, it usually indicates increased metabolism of
________. | back 20 fatty acids |
front 21 A major means for conserving heat is __________. | back 21 vasoconstriction of cutaneous blood vessels |
front 22 During glycolysis, glucose must be activated by how many ATP
molecules? | back 22 two |
front 23 Most vitamins __________. | back 23 function as coenzymes in the body |
front 24 One function of vitamin A is to __________. | back 24 form visual pigments |
front 25 The hormone responsible for setting the basal metabolic rate is
__________. | back 25 thyroxine |
front 26 The site of electron transport is the __________. | back 26 mitochondrial inner membrane (cristae) |
front 27 The main integrating center for thermoregulation is located in the
__________. | back 27 hypothalamus |
front 28 Which coenzyme is reduced in both glycolysis and the Krebs
cycle? | back 28 NAD |
front 29 Which element below is considered a trace mineral? | back 29 chromium |
front 30 Which lipoprotein contains the most cholesterol? | back 30 LDL |
front 31 Nutritionally incomplete proteins are low in __________. | back 31 one or more of the essential amino acids |
front 32 Most of the ATP produced during cellular respiration is produced by
__________. | back 32 oxidative phosphorylation during the chemiosmotic process |
front 33 A function of the liver during the postabsorptive state is
__________. | back 33 to mobilize glucose reserves by glycogenolysis |
front 34 The hormone that controls essentially all events of the absorptive
state is __________. | back 34 insulin |
front 35 Which of the following factors makes it harder for an obese person to
lose weight? | back 35 an increase in alpha receptors (the kind that favors fat accumulation) in fat cells |
front 36 Which of the following is the amount of energy the body needs in
order to perform only the most essential activities and is often
referred to as the “energy cost of living”? | back 36 BMR |
front 37 Which of the following is NOT a physiological response to
hypothermia? | back 37 dehydration |
front 38 A kilocalorie is the amount of energy __________. | back 38 needed to heat 1 kilogram of water 1°C |
front 39 Essential nutrients refer to nutrients that are __________. | back 39 limited in synthesis and therefore must be consumed |
front 40 Prolonged high protein intake can lead to __________. | back 40 loss of bone mass |
front 41 Which of the following substances is considered a provitamin? | back 41 beta-carotene |
front 42 Which of the following fat-soluble vitamins is NOT stored in the
body? | back 42 vitamin K |
front 43 The final product of glycolysis is __________. | back 43 two molecules of pyruvic acid, two molecules of NAD+, and a net gain of two ATP |
front 44 Cyanide acts as a poison by __________. | back 44 interfering with the flow of electrons in the electron transport chain |
front 45 During fasts lasting several weeks, blood glucose is maintained by
__________. | back 45 gluconeogenesis |
front 46 A low-density lipoprotein contains __________. | back 46 a high lipid content |
front 47 The role of __________ is to transport excessive cholesterol from
peripheral tissue to the liver, where it is broken down and becomes
part of bile. | back 47 high-density lipoproteins |
front 48 The official medical measurement of obesity is the __________. | back 48 body mass index |
front 49 __________ acts to suppress appetite by inhibiting __________, which
is the most powerful known appetite stimulant. | back 49 Leptin; neuropeptide Y |
front 50 Which of the following statements about “redox” reactions in human
metabolism is correct? | back 50 Coenzymes accept hydrogen. |
front 51 Which of the following is a micronutrient? | back 51 mineral |
front 52 glucose | back 52 exclusive energy source for neurons |
front 53 cholesterol | back 53 serves as a precursor to hormones and maintains the fluidity of the plasma membrane |
front 54 protein | back 54 used to build enzymes |
front 55 vitamins | back 55 can function as coenzymes |
front 56 minerals | back 56 may be incorporated into structures to make them stronger |
front 57 A person who is starving is likely to exhibit __________. | back 57 negative nitrogen balance |
front 58 Fat-soluble vitamins can be toxic if consumed in large
quantities. | back 58 True |
front 59 Which of the following is an example of catabolism? | back 59 cellular respiration |
front 60 A substance that is reduced has lost an electron. | back 60 False |
front 61 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of glycolysis? | back 61 Glycolysis requires oxygen. |
front 62 Which of the following is a characteristic of the citric acid (Krebs)
cycle? | back 62 The citric acid cycle generates a rich supply of the reduced coenzymes, NADH and FADH2. |
front 63 The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is
__________. | back 63 oxygen |
front 64 glycogenesis | back 64 the formation of glycogen to store glucose |
front 65 glycogenolysis | back 65 the cleavage of glycogen to release glucose |
front 66 gluconeogenesis | back 66 the process of forming glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules |
front 67 beta oxidation | back 67 the initial phase of fatty acid breakdown |
front 68 lipogenesis | back 68 triglyceride synthesis |
front 69 As proteins are broken down for energy, __________ is generated; the
liver then converts this potentially toxic intermediate into
__________. | back 69 ammonia; urea |
front 70 In the absorptive state, __________. | back 70 insulin serves as the main regulatory hormone |
front 71 In the postabsorptive state, __________. | back 71 glycogen is broken down to release glucose |
front 72 __________ are considered "good" cholesterol; high blood
levels of this cholesterol are thought to be beneficial. | back 72 HDLs |
front 73 Which of the following is considered a long-term regulator of feeding
behavior? | back 73 leptin levels |
front 74 The body's overall rate of energy output is called the basal
metabolic rate. | back 74 False |
front 75 Which of the following would raise body temperature? | back 75 thyroxine |