Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
GSU Muscles of the hip and thigh
front 1 A doctor tells a soccer player that he has "a pulled hamstring" muscle. This results from a tearing of the origination of a hamstring muscle from the ___________. | back 1 ischial tuberosity |
front 2 If the femoral nerve is cut, which muscle compartment would be most affected? | back 2 anterior thigh |
front 3 what is the deep tissue that invests the thigh? | back 3 fascia lata |
front 4 What is the iliotibial tract? which muscles attach here? | back 4 thickened portion of the fascia lata. attachment site for two muscles. --> gluteus maximus and tensor fascia latae |
front 5 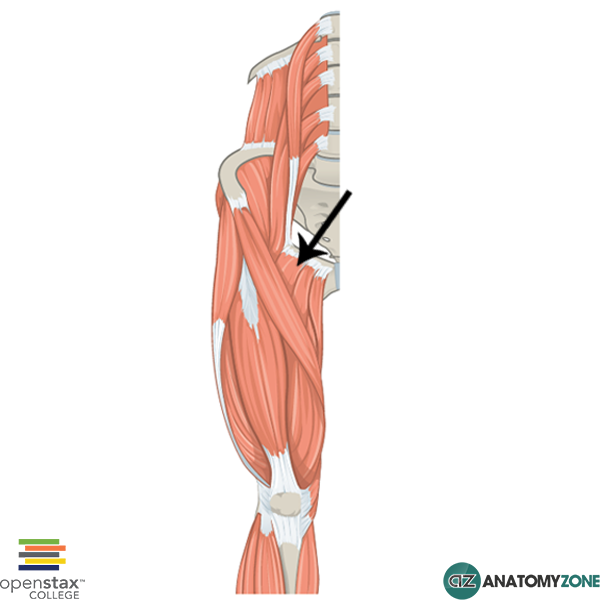 O I A INN of PECtinius | back 5 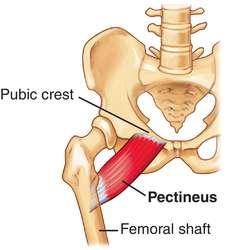 O superior ramus of pubis I pectineal line of femur, just inferior to lesser trochanter A adduct hip, flex hip. (assists with medial rotation of hip joint.) INN femoral (L2, L3) and may receive branch from obturator nerve |
front 6 Origin, insertion, action and innervation of gluteus maximus? | back 6  O posterior ilium, dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx and sacrotuberous ligament I gluteal tuberosity of the femur and iliotibial tract A extend hip/thigh and lateral rotation of hip/thigh; steadies thigh and helps rise from sitting position Inn inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2) |
front 7 O I A INN of gluteus medius? | back 7 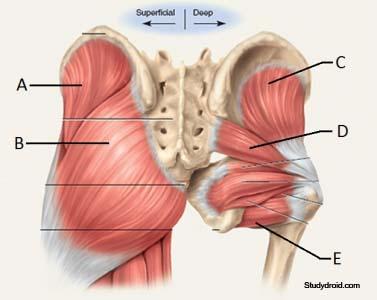 O outer surface and crest of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines I lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur A abduct hip/thigh. anterior portions medially rotate hip joint. keep pelvis level when opposite limb is elevated. INN superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1) |
front 8 O I A INN of gluteus minimus? | back 8 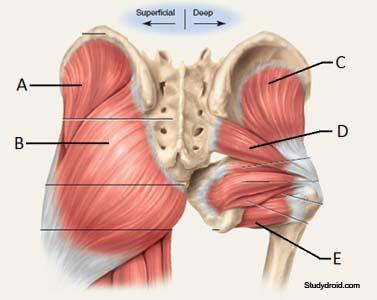 O outer surface and crest of ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines I anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur A abduct hip/thigh. anterior portions medially rotate hip joint. keep pelvis level when opposite limb is elevated. INN superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1) |
front 9 where does the iliotibial tract insert? name of structure and the bone that it is on | back 9 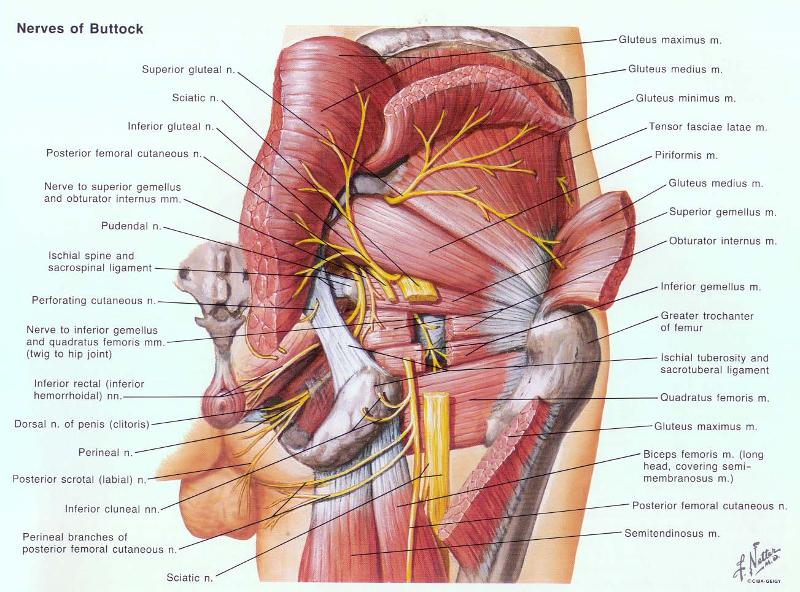 gerdy's tubercle on lateral surface of tibia |
front 10 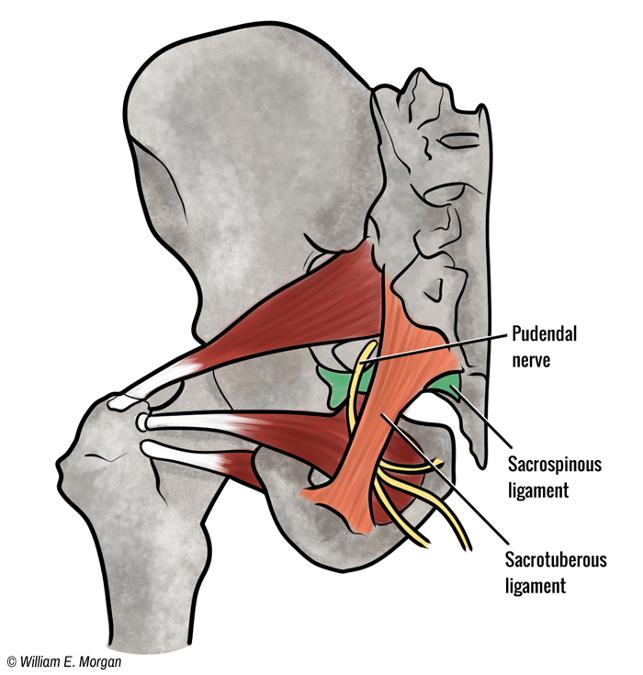 What is the O I A INN of piriformis | back 10 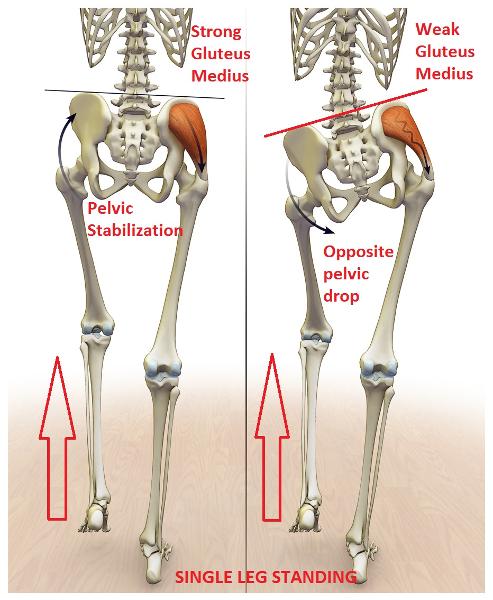 O anterior sacrum 2nd-4th sacral segments, superior margin of the greater sciatic notch, and sacrotuberous ligament I superior border of the greater trochanter of the femur A laterally rotate extended hip joint, abduct flexed hip joint, stabilize femoral head in acetabulum INN branches of anterior rami of S1,S2 |
front 11 Which nerve may be damaged if someone display excessive pelvic tilt while walking? | back 11 superior gluteal nerve |
front 12 If the right superior gluteal nerve is damaged, the pelvic drop will be toward which side of the body? | back 12 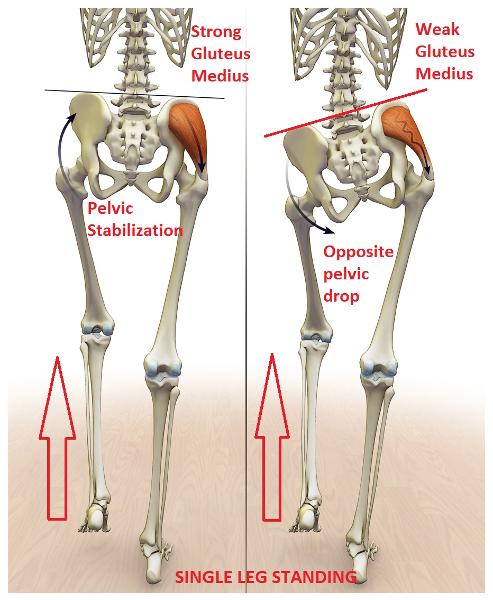 left side of the body |
front 13 O I A INN of tensor fasciae latae? | back 13 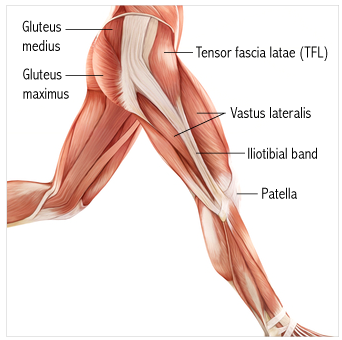 O anterior superior iliac spine; anterior part of iliac crest I iliotibial tract which attaches to lateral condyle of tibia (Gerdy tubercle) A flex hip, abduct hip. Stabilizes the extended knee joint Inn superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1) |
front 14 What action are the deep gluteal muscles responsible for? | back 14 lateral rotation also help stabilize the hip joint |
front 15 What is the O I A INN of piriformis | back 15 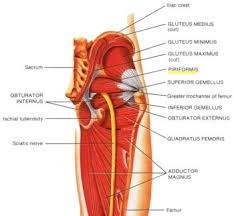 O anterior sacrum 2nd-4th sacral segments, superior margin of the greater sciatic notch, and sacrotuberous ligament I superior border of the greater trochanter of the femur A laterally rotate extended hip joint, abduct flexed hip joint, stabilize femoral head in acetabulum INN branches of anterior rami of S1,S2 |
front 16 What are the two major anterior hip muscles? | back 16 psoas major and iliacus |
front 17 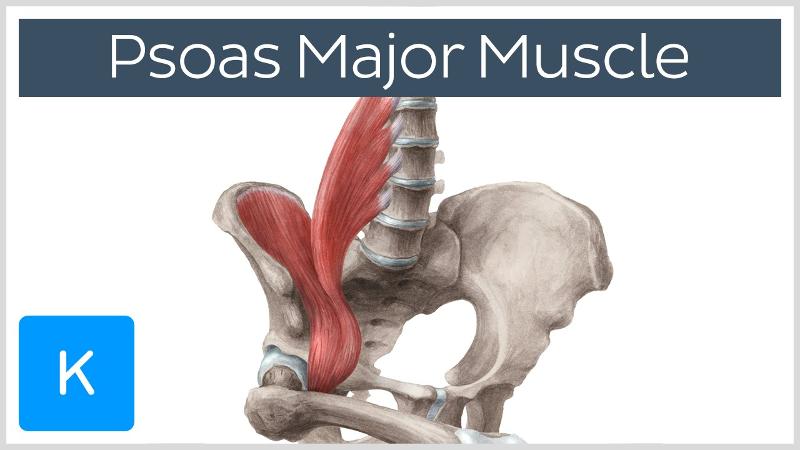 O I A INN of psoas major? | back 17  O sides of T12-L5 vertebrae and discs between them. transverse processes of all lumbar vertebrae I lesser trochanter of the femur A acting conjointly with iliacus in flexing and stabilizing hip joint, psoas major is also a postural muscle that helps control deviation of the trunk and is active during standing INN Anterior rami of lumbar nerves (L1, L2, L3) |
front 18 which ligament spans pubic tubercle and anterior superior iliac spine? | back 18  inguinal ligament |
front 19 which is the largest nerve of the body and exits inferior to pirifomis? | back 19 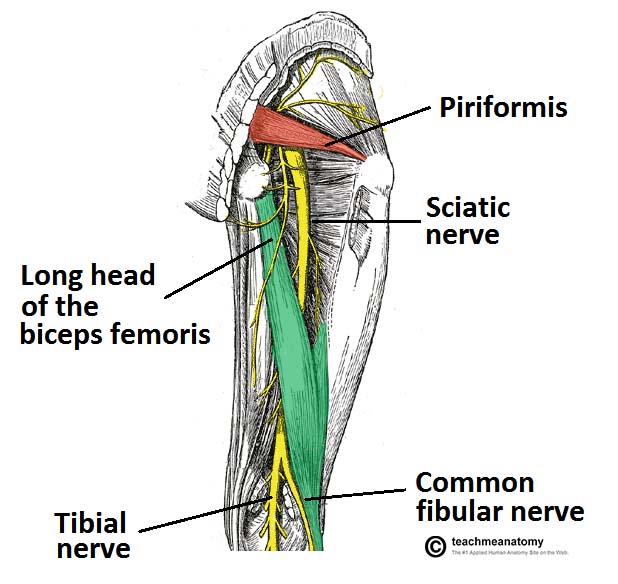 sciatic nerve |
front 20 O I A INN of iliacus? | back 20 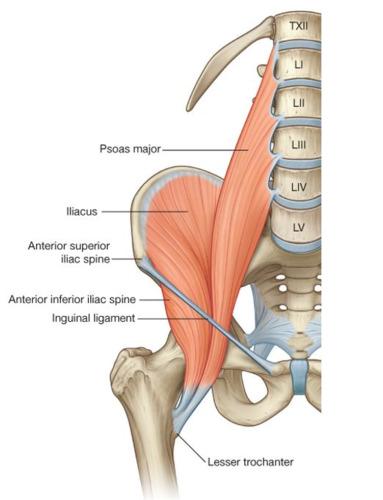 O iliac fossa, iliac crest, ala of sacrum, and anterior sacro-iliac ligaments I tendon of psoas major, lesser trochanter, and femur distal to lesser trochanter A acting conjointly with psoas major in flexing and stabilizing hip joint. INN femoral n (L2, L3) |
front 21 what are the anterior thigh muscles? | back 21 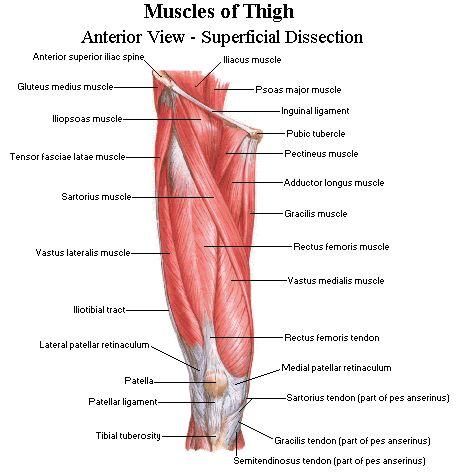 sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius |
front 22 vastus medialis O I A INN | back 22 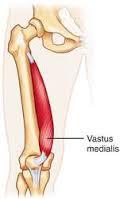 intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera Via common tendinous (quadriceps tendon) and independent attachments to the base of the patella; indirectly via patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity. attaches to tibia and patella via aponeurosis (medial and lateral patellar retinacula) extend leg femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) |
front 23 O I A INN of sartorius? | back 23 anterior superior iliac spine and superior part of notch inferior to it medial surface of proximal tibia flexes, abducts and laterally rotates hip joint. flexes knee joint. femoral n (L2, L3) |
front 24 all anterior thigh muscles are innervated by which nerve? | back 24 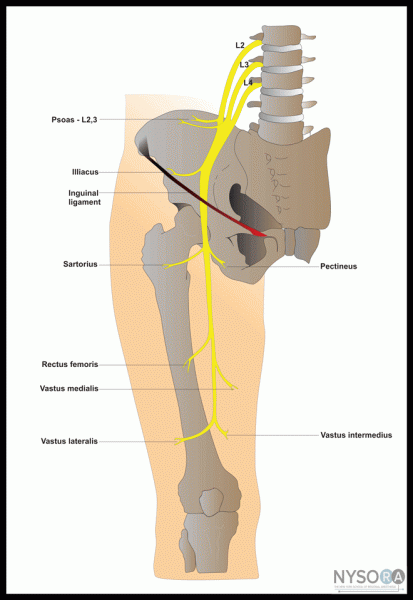 femoral nerve |
front 25 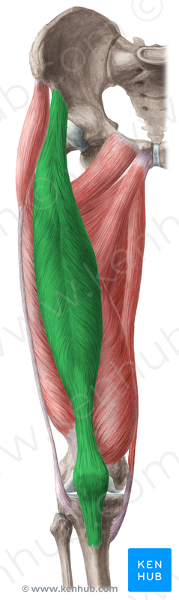 rectus femoris O I A IN | back 25  anterior inferior iliac spine and ilium superior to acetabulum Via common tendinous (quadriceps tendon) and independent attachments to the base of the patella; indirectly via patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity. extends knee joint; rectus femoris also stabilizes hip joint and helps iliopsoas flex hip joint femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) |
front 26 O I A INN of quadratus femoris | back 26 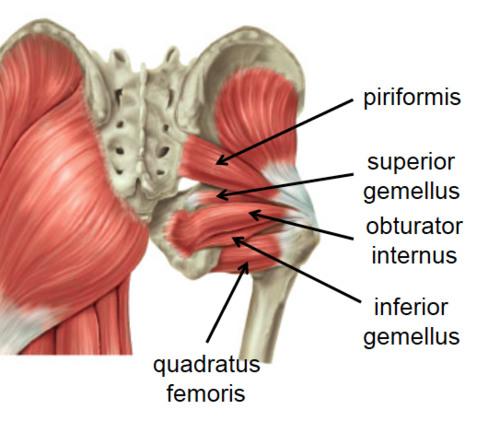 O lateral border of ischial tuberosity I quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of femur and area inferior to it A laterally rotates hip joint; also pulls femoral head into acetabulum to stabilize hip joint/pelvis Inn nerve to quadratus femoris L5 S1 |
front 27 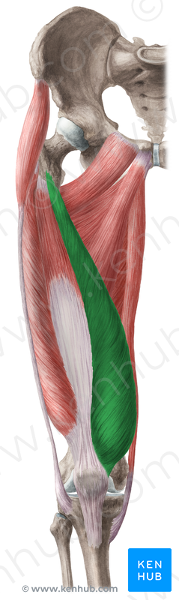 vastus medialis O I A INN | back 27 intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera Via common tendinous (quadriceps tendon) and independent attachments to the base of the patella; indirectly via patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity. attaches to tibia and patella via aponeurosis (medial and lateral patellar retinacula) extend leg femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) |
front 28 vastus intermedius O I A INN | back 28 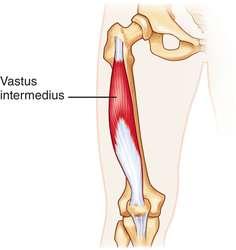 anterior and lateral surfaces of shaft of fermur Via common tendinous (quadriceps tendon) and independent attachments to the base of the patella; indirectly via patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity. extend leg femoral nerve (L2,L3,L4) |
front 29 what is the main action of the medial thigh muscles? | back 29 adductors |
front 30 the majority of medial thigh muscles are innervated by which nerve? What are the exceptions? | back 30 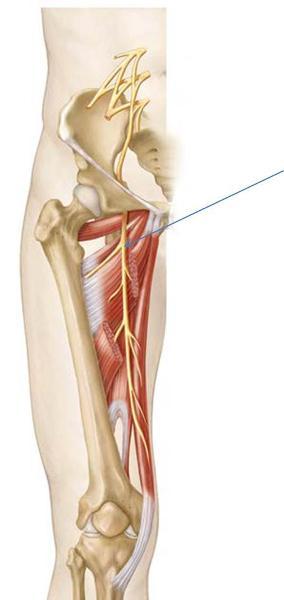 obturator; pectinius is innervated by both femoral and obturator the hamstring part of adductor magnus is innervated by tibial division of sciatic n (L4) |
front 31 what are the medial thigh muscles? | back 31 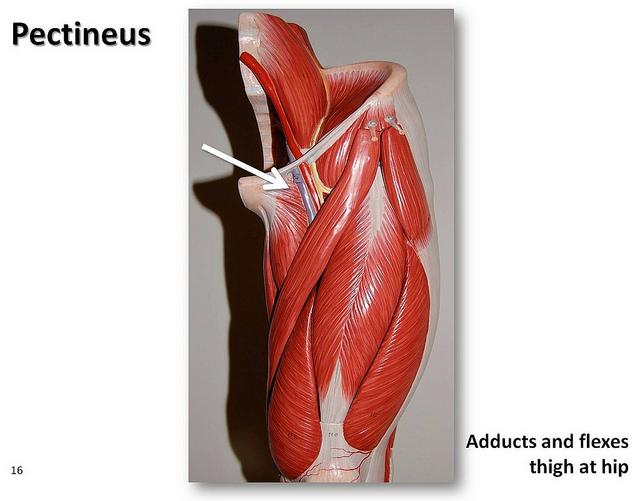 gracilis, pectinius, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus |
front 32 O I A INN of gracilis | back 32 body and inferior ramus of pubis medial surface of proximal tibia adduct hip, flex knee and helps rotate knee medially obturator n (L2, L3) |
front 33 O I A INN of pectinius | back 33  O superior ramus of pubis I pectineal line of femur, just inferior to lesser trochanter A adduct hip, flex hip. (assists with medial rotation of hip joint.) INN femoral (L2, L3) and may receive branch from obturator nerve |
front 34 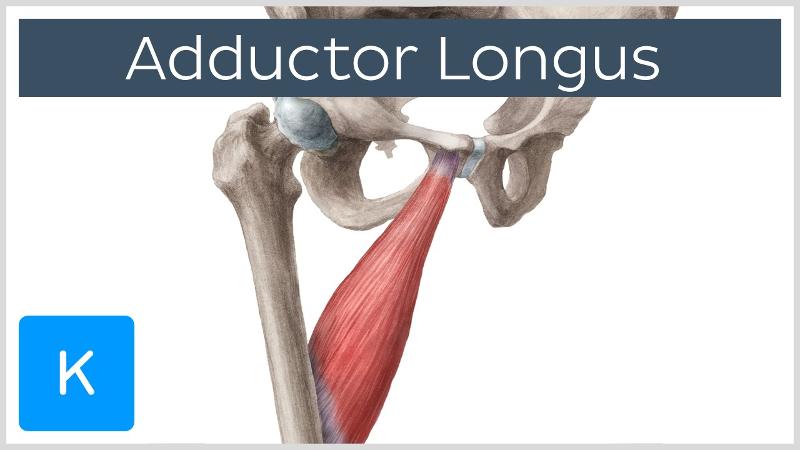 O I A INN of adductor longus | back 34  O body of pubis inferior to pubic crest I middle third of linea aspera of femur A adduct hip INN obturator n (L2, L3, L4) |
front 35 O I A INN of adductor brevis? | back 35 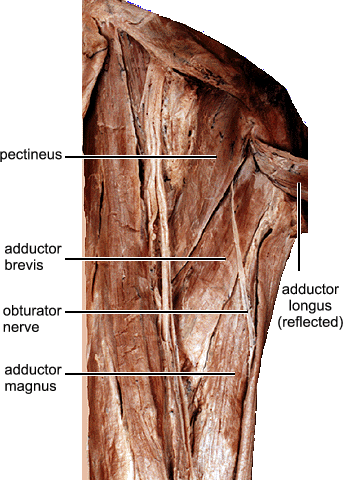 O body and inferior ramus of pubic bone I pectineal line and proximal part of linea aspera of femur A adduct hip and to some extent flexes hip INN obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4) |
front 36 O I A INN of adductor magnus? | back 36 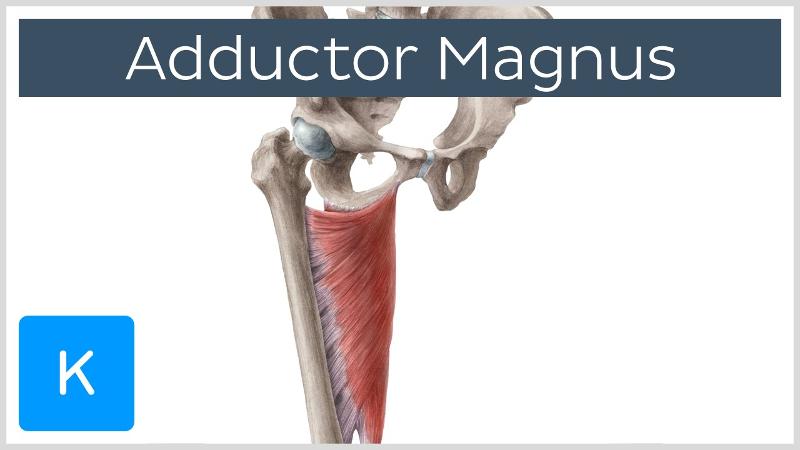 O adductor part: inferior ramus of pubis, and ramus of ischium hamstring part: ischial tuberosity I adductor part: gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera, and medial supracondylar line hamstring part: adductor tubercle of femur A adduct hip. Adductor part also flexes hip joint and hamstring part extends it. INN adductor part: obturator n (L2, L3, L4) hamstring part: tibial division of sciatic n (L4) |
front 37 What are the posterior thigh muscles? | back 37 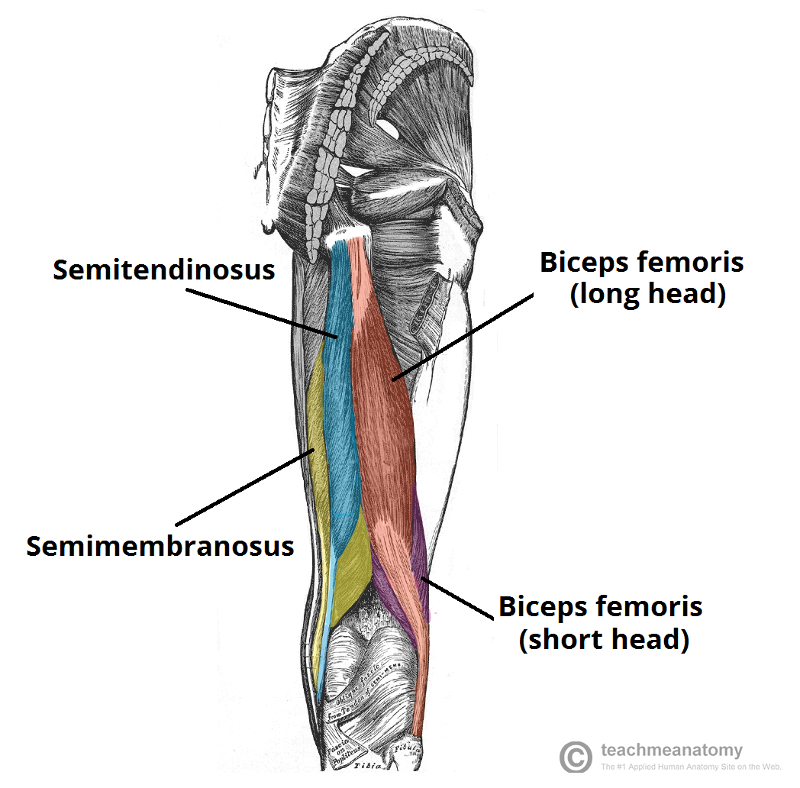 biceps femoris (long head and short head) semitendinosis semimembanosus |
front 38 What nerve innervates the majority of posterior thigh muscles? what is the exception? | back 38 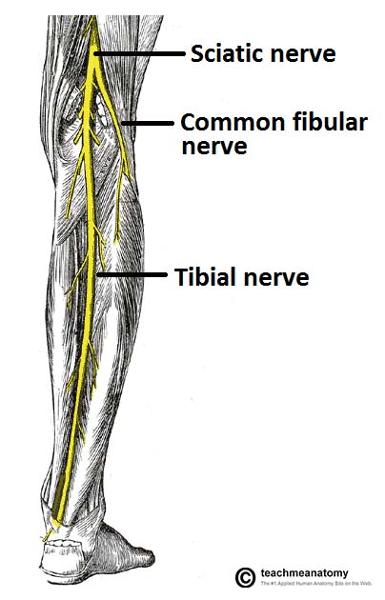 tibial division of sciatic nerve (L4-S3). the short head of biceps femoris is innervated by the common fibular nerve (L4-S2) |
front 39 what is the deepest and largest medial thigh muscle? | back 39 adductor magnus |
front 40 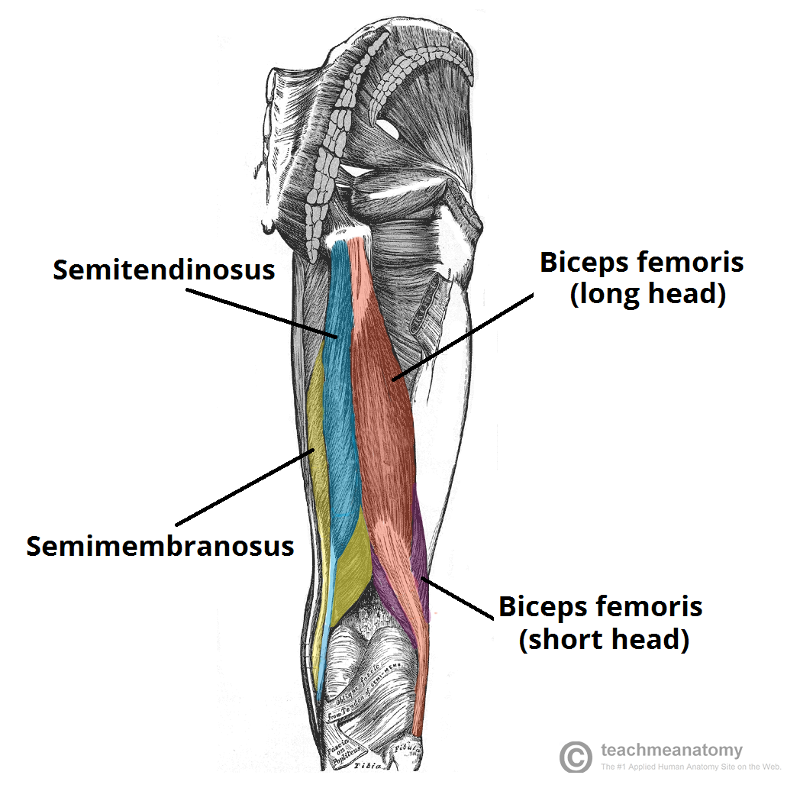 O I A INN of biceps femoris, long head | back 40  O ischial tuberosity I lateral side of head of fibula; tendon is split at this site by fibular collateral ligament of the knee A flexes knee joint and rotates it laterally when knee is flexed; extends hip joint (like when starting to walk) INN tibial division of the sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2) |
front 41 O I A INN of PECtinius | back 41  O superior ramus of pubis I pectineal line of femur, just inferior to lesser trochanter A adduct hip, flex hip. (assists with medial rotation of hip joint.) INN femoral (L2, L3) and may receive branch from obturator nerve |
front 42 O I A INN of semitendinosis | back 42 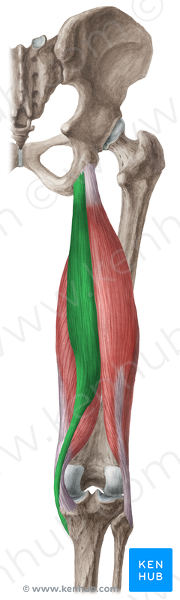 O ischial tuberosity I medial surface of proximal tibia A extend hip, flex knee, and rotate leg medially when knee is flexed. when hip and knee are flexed, can extended trunk. INN tibial division of sciatic n (L5, S1, S2) |
front 43 O I A INN of semimembranosis | back 43 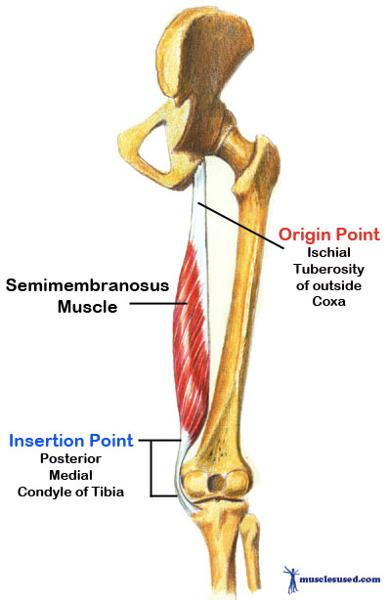 O iscial tuberosity I posterior surface of medial condyle of tibia A extend hip, flex knee, and rotate leg medially when knee is flexed. when hip and knee are flexed, can extended trunk. INN tibial division of sciatic n ( L5, S1, S2) |
front 44 Spinal cord levels of inferior gluteal nerve? | back 44 L5, S1, S2 |
front 45 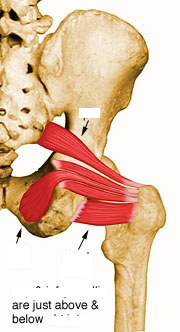 O I A INN of obturator internus | back 45 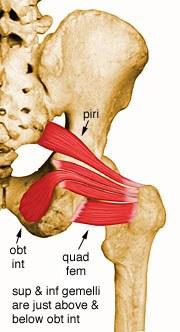 O pelvic surface of ilium and ischium; obturator membrane I medial surface of greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) of femur A laterally rotate extended hip joint, abduct flexed hip joint, steady femoral head in acetabulum Inn nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1) |
front 46 O I A INN of inferior and superior gemelli | back 46 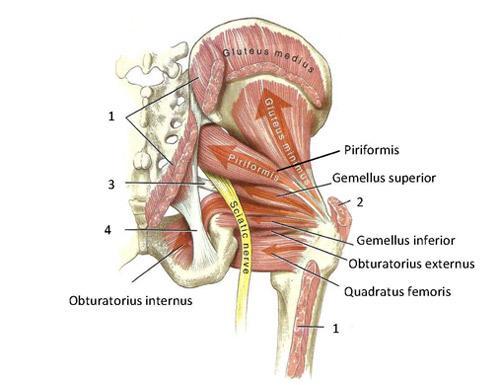 O superior: ischial spine inferior: ischial tuberosity I medial surface of greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) of femur A laterally rotate extended hip joint, abduct flexed hip joint, steady femoral head in acetabulum Inn superior: nerve to obturator internus L5, S1 inferior: nerve to quadratus femoris L5, S1 |
front 47 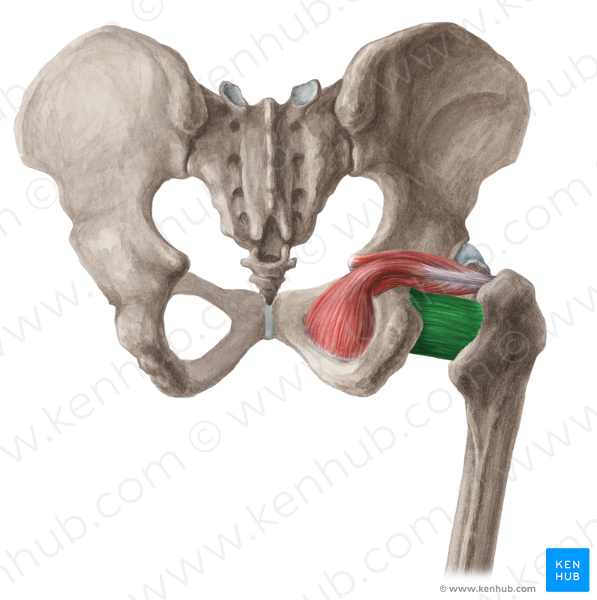 O I A INN of quadratus femoris | back 47 O lateral border of ischial tuberosity I quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of femur and area inferior to it A laterally rotates hip joint; also pulls femoral head into acetabulum to stabilize hip joint/pelvis Inn nerve to quadratus femoris L5 S1 |
front 48 what are the quadriceps femoris muscles? | back 48 rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius |
front 49 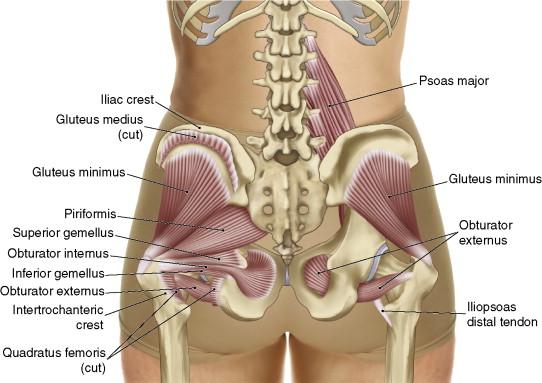 O I A INN of obturator externus | back 49 O margins of obturator foramen and obturator membrane I trochanteric fossa of femur A laterally rotates hip joint, pulls head of femur into acetabulum holding pelvis steady; adduction Inn obturator nerve (L3, L4) |
front 50 what structures pass through adductor hiatus | back 50 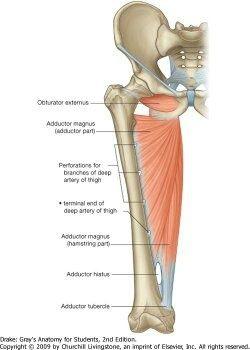 femoral artery and vein from the anterior compartment of the thigh to the popliteal fossa posterior to the knee |
front 51 what are the borders of the adductor hiatus? | back 51 distal aponeurotic attachment of the adductor part of the adductor magnus and tendon of hamstring part. |
front 52 where does the iliotibial tract insert? | back 52 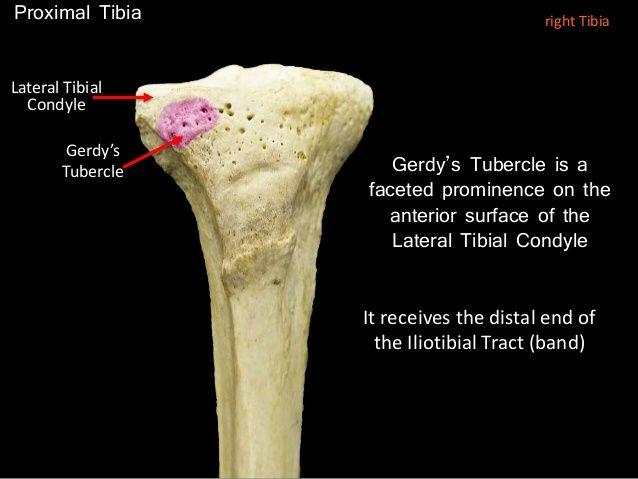 gerdy's tubercle on lateral surface of tibia |