Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Introductory terminology and orientation to anatomy
front 1 Visual inspection with the naked eye of the liver and gallbladder during surgrery is associated with which subdiscipline of anatomy? | back 1 gross anatomy |
front 2 Which of the following is most inferior? Mediastinum Pleural cavity Diaphragm Pelvic cavity Cranial cavity | back 2 Pelvic cavity |
front 3 The level of organization when different primary tissues are combined together and work together to perform a common function is called the _______ level. chemical cellular tissue organ organismal | back 3 organ |
front 4 What kind of cut would you make in a specimen to create anterior and posterior parts? | back 4 coronal |
front 5 Describe anatomical position | back 5 facing forward, head level, thumbs out, feet together and forward |
front 6 A patient or cadaver lying flat on his/her back is said to be in the __________ position. | back 6 supine |
front 7 what is histology? | back 7 subdiscipline of anatomy; the study of the microscopic structure of tissues |
front 8 What are the subdivisions of gross anatomy? | back 8 surface anatomy, regional anatomy, and systemic anatomy surface = anatomical structures visible on the surface of the body regional = bones muscles nerves vessels of an entire region systemic = all muscles of the entire body or all bones of entire body |
front 9 put in order levels of structural organization from smallest to biggest | back 9 chemical (atoms --> molecules --> organelles) cellular tissue organ organ system (we have 11) organismal |
front 10 what are the different tissue types of the human body? | back 10 epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous |
front 11 define anterior and posterior and name another word for each | back 11 anterior is toward the front of the body (ventral) and dorsal is toward the back of the body (posterior) |
front 12 define superior vs inferior and name another word for each | back 12 superior (cranial) is toward the head, inferior is toward the bottom of the body (caudal) |
front 13 define medial vs lateral | back 13 medial is toward the midline of the body and lateral is further from the midline |
front 14 define superficial vs deep | back 14 superficial is toward the surface of the body and deep is toward the center |
front 15 define proximal vs distal | back 15 proximal is closer to the attachment of the limb, distal is further away |
front 16 Be able to label unilateral, ipsilateral, bilateral, and contralateral | back 16 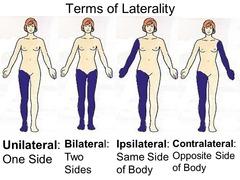 |
front 17 how do transverse, coronal (frontal) and midsagittal planes divide the human body? | back 17 transverse plane cuts through waist so body is divided in top and bottom coronal cuts so there is an anterior and posterior half midsagittal cuts body into two symmetric halves |
front 18 which body cavity contains brain and spinal cord? | back 18 dorsal |
front 19 in which body cavity is the heart housed? | back 19 inferior mediastinum |
front 20 in which body cavity are the trachea and esophagus housed? | back 20 superior mediastinum |
front 21 the ventral body cavity includes which two other body cavities? | back 21 the thoracic and abdominopelvic body cavities |
front 22 what does the pleural cavity house? | back 22 the lungs |
front 23 what are the eleven systems of the body? | back 23 skeletal muscular cardiovascular lymphatic nervous endocrine respiratory digestive urinary reproductive integumentary |
front 24 what are the major components and functions of the skeletal system? | back 24 bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and joints support, protection, leverage, hematopoiesis, mineral storage, and energy storage |
front 25 what are the major components and functions of the muscular system? | back 25 skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle heat production, movement |
front 26 what are the major components and functions of the cardiovascular system? | back 26 heart, blood vessels, blood transportation of oxygen and nutrients, removal of waste and carbon dioxide, and hormone transportation |
front 27 what are the major components and functions of the lymphatic system? | back 27 lymph vessels, lymph nodes, thymus gland, tonsils, and spleen fluid control, filtration, immunity |
front 28 what are the major components and functions of the nervous system? | back 28 brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs communication and homeostasis |
front 29 what are the major components and functions of the endocrine system? | back 29 hormone producing glands and cells communication and homeostasis |
front 30 what are the major components and functions of the respiratory system? | back 30 nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs gas exchange |
front 31 what are the major components and functions of the digestive system? | back 31 alimentary canal, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas mechanical and chemical breakdown of food, absorption, solid waste removal |
front 32 what are teh major components and functions of the urinary system? | back 32 kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra filtration and elimination |
front 33 what are the major components and functions of the reproductive system? | back 33 male: testes, duct system glands female: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, and external genitalia production of hormones, production of germ cells, housing developing fetus |
front 34 what are the major components and functions of the integumentary system? | back 34 skin, sebaceous (oil) glands, sudoriferous glands (sweat), hair, nails protection, temperature regulation, waste elimination, sensation |