Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Mastering Chemistry End of Unit One - Beginning of Unit Two
front 1 Differentiate: Element Compound Mixture | back 1 Element - Single type of atom Compound - Multiple elements on one Mixture - Combination |
front 2 Classify as element, compound, mixture: Soda, NO, Ar, Zn, NaCl | back 2 Element: Ar, Zn Compound: NaCl, NO Mixture: Soda |
front 3 Classify as homogenous or heterogenous: Fruit salas, honey, bronze, smog, vodka | back 3 Homogenous: Vodka, honey, bronze Heterogenous: Fruit salad, smog |
front 4 A sample of seawater consists of water, sodium ions, chloride ions, and several other dissolved salts. These ions and salts are evenly distributed throughout the water. Which term or terms could be used to describe this sample of seawater? a. Mixture b. Heterogeneous mixture c. Homogeneous mixture d. Solution e. Pure chemical substance f. Compound g. Element | back 4 Mixture, homogeneous mixture, solution |
front 5 A copper foil is made from copper, absolutely free of impurities. Which term or terms could be used to describe this sample of copper? a. Mixture b. Heterogeneous mixture c. Homogeneous mixture d. Solution e. Pure chemical substance f. Compound g. Element | back 5 Pure chemical substance, element |
front 6 A sample of concrete contains cement, gravel, crushed rocks, sand, and water. Each of these contains different metals and minerals and hence has different colors and different properties. Which term or terms could be used to describe this sample of concrete? a. Mixture b. Heterogeneous mixture c. Homogeneous mixture d. Solution e. Pure chemical substance f. Compound g. Element | back 6 Mixture, heterogenous mixture |
front 7 A glass jar contains pure sodium chloride. Which term or terms could be used to describe the contents of this glass jar? a. Mixture b. Heterogeneous mixture c. Homogeneous mixture d. Solution e. Pure chemical substance f. Compound g. Element | back 7 Pure chemical substance, compound |
front 8 Intensive vs Extensive for Zinc: Density of 7.13g/cm3 Melting point 419.58C Mass of 63.74g Volume of 8.94mL Bluish gray in color | back 8 Intensive: Density of 7.13g/cm3, Melting point 419.58C, Bluish gray in color Extensive: Mass of 63.74g, Volume of 8.94mL |
front 9 You are given a sample resembling zinc. Which of the following properties could be used to help determine whether the sample is really zinc? The density of the sample The volume of the sample The melting point of the sample | back 9 The density of the sample The melting point of the sample |
front 10 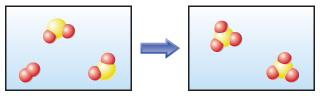 Chemical or physical change? | back 10 Chemical change The molecules after the change are different than the molecules before the change. |
front 11 A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid A is element or compound? a. Element b. Compound c. Can not determine | back 11 b. Compound |
front 12 A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solid B is element or compound? a. Element b. Compound c. Can not determine | back 12 c. Can not determine |
front 13 A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether gas C is element or compound? a. Element b. Compound c. Can not determine | back 13 b. Compound |
front 14 A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Explain your conclusions for each substance. | back 14 When solid carbon is burned in excess oxygen gas, the two elements combine to form a gaseous compound, carbon dioxide. Clearly substance C is this compound. Since C is produced when A is heated in the absence of oxygen (from air), both the carbon and oxygen in C must have been present in A originally. A is, therefore, a compound composed of two or more elements chemically combined. Without more information on the chemical or physical properties of B, we cannot determine absolutely whether it is an element or a compound. However, few if any elements exist as white solids, so B is probably also a compound. |
front 15 7-9 | back 15 no data |