Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Festival 1 (Endocrine & Blood)
front 1 True or False: Positive chemotaxis is a feedback system that signals leukocyte migration into damaged areas. | back 1 True |
front 2 Which of the choices below is the parent cell for all formed elements of blood? polymorphonuclear cell megakaryocyte hemocytoblast normoblast | back 2 hemocytoblast |
front 3 Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus? neural hormonal enzyme humoral | back 3 enzyme |
front 4 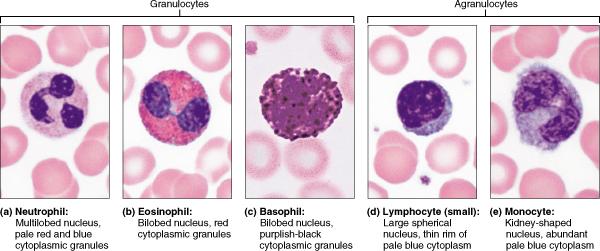 When we take anti-histamines, we are countering the effects of which type of leukocyte? neutrophils eosinophils lymphocytes basophils | back 4 basophils |
front 5 The main protein in blood plasma is ______ albumin hemoglobin plasmin erythropoietin | back 5 albumin |
front 6 Which of the following hormones helps the body avoid dehydration and water overload? thyroid-stimulating hormone antidiuretic hormone follicle-stimulating hormone oxytocin | back 6 antidiuretic hormone |
front 7 One of the least complicated of the endocrine control systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. Which of the following describes this mechanism? carbohydrate oxidation catabolic inhibition protein synthesis humoral stimulation | back 7 humoral stimulation |
front 8 Which of the following occurs in situations where more than one hormone produces the same effects at the target cell and their combined effects are amplified? summation synergism permissiveness antagonism | back 8 synergism |
front 9 True or False: Each hemoglobin molecule can transport two molecules of oxygen. | back 9 False |
front 10  What gland secretes growth hormone? thyroid gland adrenal cortex posterior pituitary (lobe) anterior pituitary (lobe) | back 10 anterior pituitary (lobe) |
front 11 True or False: Iodine is an essential element required for the synthesis of thyroxine. | back 11 True |
front 12  Hypersecretion of what hormone can produce the effects of gigantism (individual in the center of this image)? aldosterone growth hormone (GH) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) thyroid hormones (TH) | back 12 growth hormone (GH) |
front 13 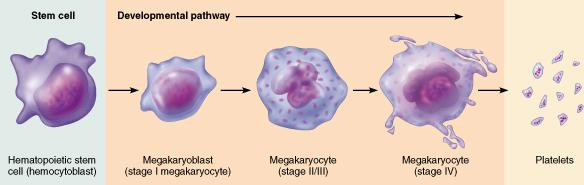 What part of the pathway to produce platelets is shared with other formed elements? megakaryoblast hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) lymphoid stem cell reticulocyte | back 13 hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast) |
front 14 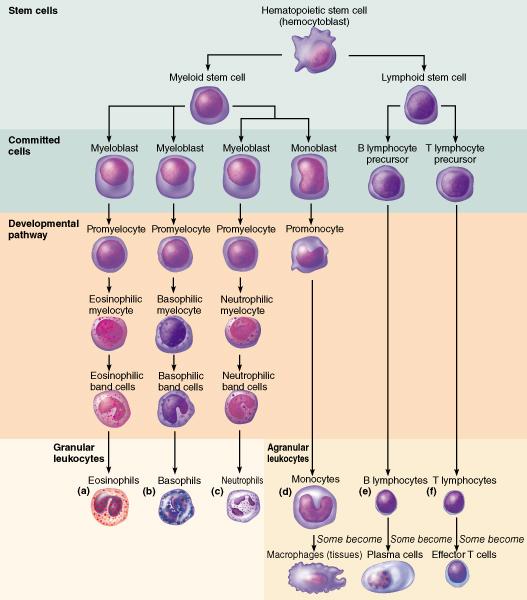 What do the lymphoid stem cells give rise to? lymphocytes granulocytes erythrocytes monocytes | back 14 lymphocytes |
front 15 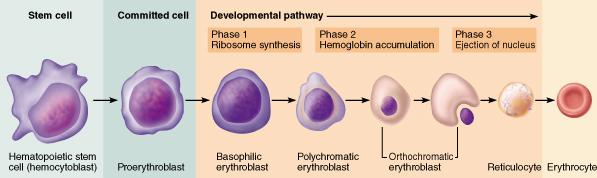 What part of the body does erythropoietin (EPO) target to increase erythropoiesis? kidneys bone marrow lungs liver | back 15 bone marrow |
front 16 Which hormone is the body's major metabolic hormone? adrenocorticotropic hormone thyroid hormone antidiuretic hormone parathyroid hormone | back 16 thyroid hormone |
front 17 True or False: The endocrine gland that is probably malfunctioning if a person has a high metabolic rate is the parathyroid. | back 17 False |
front 18 What is the primary function of hormones? cause allergic reactions influence metabolic activity of glands by electrochemical impulses alter cell activity activate extracellular enzymes | back 18 alter cell activity |
front 19 True or False: Diapedesis is the process by which red blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries. | back 19 False |
front 20 Hormones that regulate the secretory action of other endocrine glands are called ________ somatotropin tropins GHIH somatostatins | back 20 tropins |
front 21 True or False: Direct gene activation involves a second-messenger system. | back 21 False |
front 22 Which of the following hormones mainly serves to stimulate milk production by the breasts? prolactin follicle-stimulating hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone thyroid-stimulating hormone | back 22 prolactin |
front 23 Which of the following is characteristic of all leukocytes? They are nucleated. They have cytoplasmic granules. They are phagocytic. They are the most numerous of the formed elements in blood. | back 23 They are nucleated. |
front 24 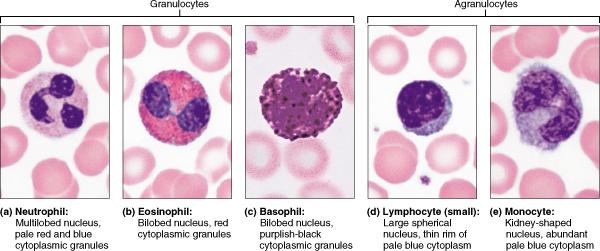 Which type of leukocyte is responsible for antibody production? basophils monocytes eosinophils lymphocytes | back 24 lymphocytes |
front 25 True or False: Oxytocin and ADH are produced in the posterior pituitary. | back 25 False |
front 26 Which of the following is a hormone produced by the posterior pituitary? oxytocin ADH HGH none of these | back 26 none of these |
front 27 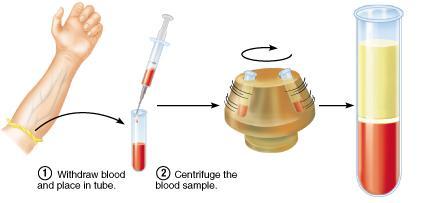 The majority of whole blood is ______ platelets plasma erythrocytes erythrocytes leukocytes | back 27 plasma |
front 28 Which of the formed elements contains hemoglobin and transports respiratory gases? erythrocytes agranular leukocytes platelets granular leukocytes | back 28 erythrocytes |
front 29 What is required for the production of anterior pituitary gland hormones? neural stimuli (from the sympathetic division of the ANS) hormonal stimuli humoral stimuli all of these | back 29 hormonal stimuli |
front 30 Which of the following is NOT a function of blood? distribution regulation hormone production protection | back 30 hormone production |
front 31 The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on ______. the membrane potential of the cells of the target organ the location of the tissue or organ with respect to the circulatory path nothing- all hormones of the human body are able to stimulate any and all cell types because hormones are powerful and nonspecific the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ | back 31 the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ |
front 32 What organ in the body regulates erythrocyte production? kidney brain liver pancreas | back 32 kidney |
front 33 Which of the following hormones stimulates the adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids that help the body resist stressors? thyroid-stimulating hormone follicle-stimulating hormone prolactin adrenocorticotropic hormone | back 33 adrenocorticotropic hormone |
front 34 On a blood smear slide prepared using Wright's stain, you observe a large cell with a U-shaped nucleus and pale blue cytoplasm. This cell is most likely a(n) _______ eosinophil basophil monocyte lymphocyte | back 34 monocyte |
front 35 Which of the following is correctly matched? aplastic anemia: results from excessive blood loss hemolytic anemia: results from inadequate iron intake hemorrhagic anemia: red blood cells rupture pernicious anemia: results from a vitamin B12 deficiency | back 35 pernicious anemia: results from B12 deficiency |
front 36 Which of the following is not a type of hormone interaction? permissiveness antagonism feedback synergism | back 36 feedback |
front 37 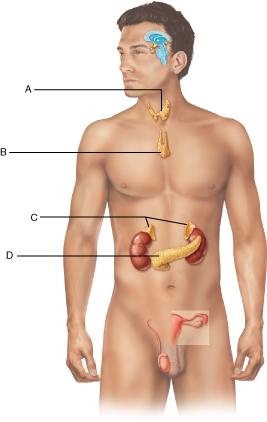 Which letter represents the adrenal glands? Select from letters A-D. A B C D | back 37 C |
front 38 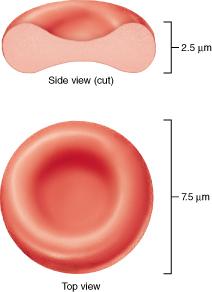 What is the name of the protein found in erythrocytes that allows for respiratory gas transport? albumin fibrinogen hemoglobin antibodies | back 38 hemoglobin |
front 39 True or False: Hemorrhagic anemias result from blood loss. | back 39 True |
front 40 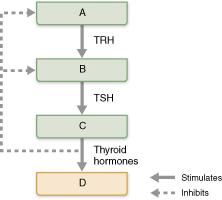 Where is thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) made? Select from letters A-D A B C D | back 40 A |
front 41 ______ is the situation when one hormone cannot exert its full effects without another hormone being present. Antagonism Synergism Activism Permissiveness | back 41 Permissiveness |
front 42 The most abundant leukocytes are __________. basophils monocytes neutrophils lymphocytes | back 42 neutrophils |
front 43 What is the average normal pH range of blood? 7.75-7.85 4.65-4.75 8.35-8.45 7.35-7.45 | back 43 7.35-7.45 |
front 44 Platelets __________. stick to the damaged area of a blood vessel and help seal the break have a life span of about 120 days have multiple nuclei are the precursors of leukocytes | back 44 stick to the damaged area of a blood vessel and help seal the break |
front 45 Which of the following glands is found atop the kidneys? pituitary adrenal parathyroid thyroid | back 45 adrenal |
front 46 In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the target organ. This is known as ________. sensitivity increase up-regulation a stressor reaction cellular affinity | back 46 up-regulation |
front 47 Which of the following is not a distribution function of blood? transport of hormones to their target organs transport of metabolic wastes from cells delivery of oxygen to body cells transport of salts to maintain blood volume | back 47 transport of salts to maintain blood volume |
front 48 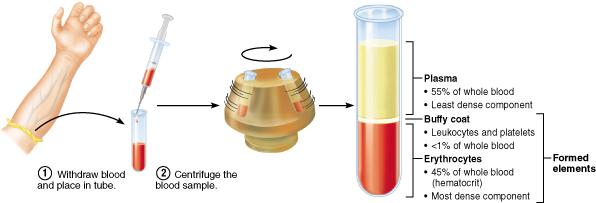 What is hematocrit a measure of? Hematocrit is the percentage of erythrocytes in a whole blood sample. Hematocrit is the percentage of leukocytes and platelets in a whole blood sample. Hematocrit is the percentage of plasma in a whole blood sample. Hematocrit is the percentage of formed elements in a whole blood sample. | back 48 Hematocrit is the percentage of erythrocytes in a whole blood sample. |
front 49 Bilirubin is cleared from the body by _________. the spleen the kidneys the liver the pancreas | back 49 the liver |
front 50 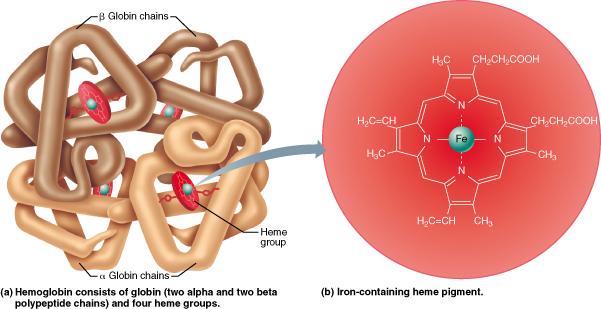 When oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, what bright red molecule is formed? hematocrit oxyhemoglobin carbaminohemoglobin deoxyhemoglobin | back 50 oxyhemoglobin |
front 51 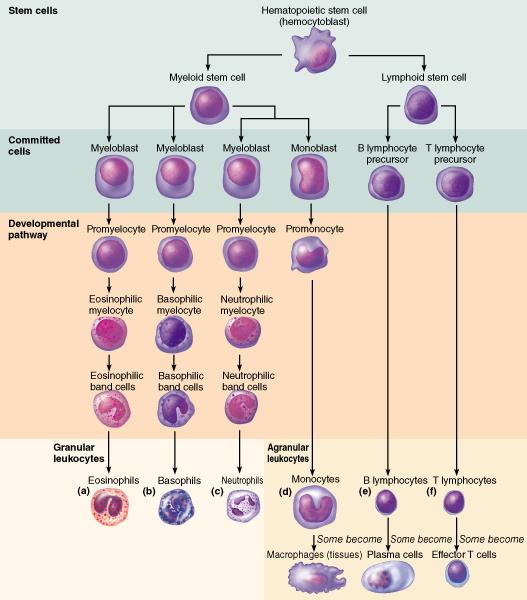 What do the lymphoid stem cells give rise to? monocytes lymphocytes erythrocytes granulocytes | back 51 lymphocytes |
front 52 True or False: Both "turn on" factors (hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli) and "turn off" factors (feedback inhibition and others) may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. | back 52 True |
front 53 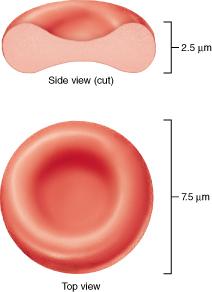 What triggers erythropoietin (EPO) production to make new red blood cells? reduced availability of oxygen excess of oxygen in the bloodstream too many erythrocytes too many platelets | back 53 reduced availability of oxygen |
front 54 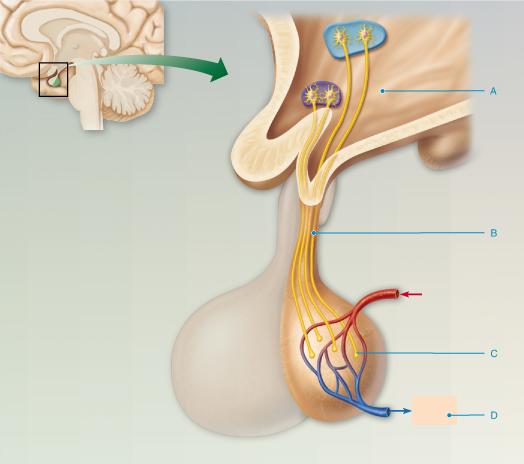 Where are the hormones oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) stored? Select from letters A-D. A B C D | back 54 C |
front 55 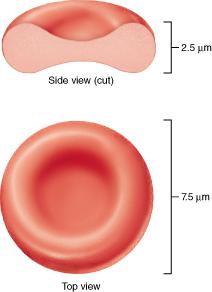 Which of the following is true of the structure of an erythrocyte? Erythrocytes are shaped like biconcave discs. Erythrocytes are nucleated cells. Erythrocytes are a fixed shape and cannot change shape. Erythrocytes are cell fragments. | back 55 Erythrocytes are shaped like biconcave discs. |
front 56 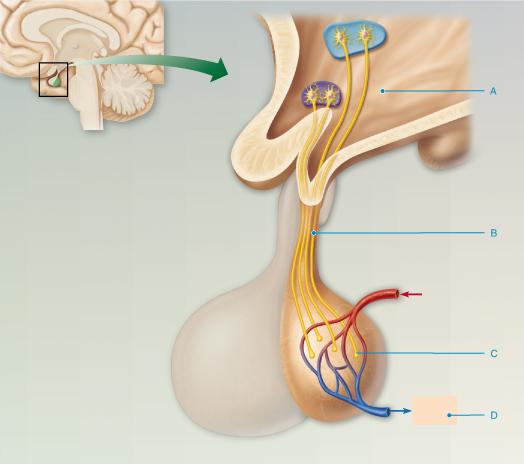 What hormone released into the blood (shown by letter D) by the posterior pituitary inhibits or prevents urine formation? thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) cortisol oxytocin antidiuretic hormone (ADH) | back 56 antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
front 57 Steroid hormones exert their action by _______. binding cell receptors and initiating cAMP activity entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene activating the hypothalamic release of regulating hormones entering the cell and activating mitochondrial DNA | back 57 entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene |
front 58 True or False: Up-regulation involves the loss of receptors and prevents the target cells from overreacting to persistently high hormone levels. | back 58 False |
front 59 Which of the following is a protective function of blood? prevention of blood loss maintenance of adequate fluid volume maintenance of normal pH in body tissue maintenance of body temperature | back 59 prevention of blood loss |
front 60 True or False: The primary source of RBCs in the adult human being is the bone marrow in the shafts of the long bones. | back 60 False |
front 61 True or False: Hemorrhagic anemias results from blood loss. | back 61 True |
front 62 Which of the following is NOT a major type of stimulus that triggers endocrine glands to manufacture and release hormones? neural humoral enzymatic hormonal | back 62 enzymatic |
front 63 Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis? moving to a lower altitude hypoxia of EPO-producing cells an increased number of RBCs decreased tissue demand for oxygen | back 63 hypoxia of EPO-producing cells |
front 64 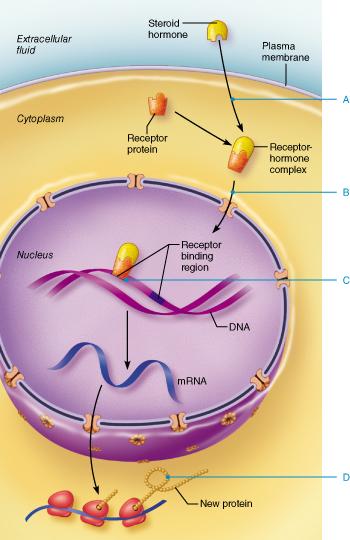 At what point does the receptor-hormone complex bind to DNA? Select from letters A-D. A B C D | back 64 C |
front 65 True or False: Hormones are long-distance chemical signals that travel in blood or lymph throughout the body. | back 65 True |
front 66 The ________ is the fluid portion of the blood. hemoglobin plasma buffy coat hematocrit | back 66 plasma |
front 67 True or False: Major hormones circulate to virtually all tissues. | back 67 True |
front 68 True or False: Growth hormone solely exerts its influence by targeting other endocrine glands to produce hormones. | back 68 False |
front 69 Which leukocyte functions in phagocytizing bacteria? lymphocyte neutrophil eosinophil basophil | back 69 neutrophil |
front 70 Which of the following is NOT an endocrine gland? adenoid adrenal pituitary thyroid | back 70 adenoid |
front 71 The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________. binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP synthesizing more than one hormone at a time altering gene expression in the nuclear DNA increasing the basal metabolic rate in the target organ | back 71 binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP |
front 72 Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular ________. calcium second messengers deactivating ions nucleotides | back 72 second messengers |
front 73 Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells in a manner similar to ________. steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells insulin, because insulin is a small peptide glucagon, because the structure of glucagon is similar to that of thyroid hormone growth hormone, because the thyroid works synergistically with thyroid hormone | back 73 steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells |
front 74  Which hypothalamic hormone stimulates the release of growth hormone from the anterior pituitary (lobe)? thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | back 74 growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) |
front 75 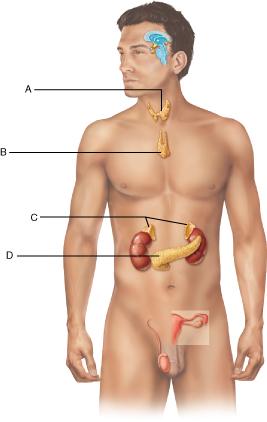 Identify the thyroid gland. Select from letters A-D. A B C D | back 75 A |
front 76 Which of the following is true about blood plasma? It contains about 20 dissolved components. It is about 90% water. It is the same as serum but without the clotting proteins. The main protein component is hemoglobin. | back 76 It is about 90% water. |
front 77 ADH ________. promotes dehydration increases urine production is produced in the adenohypophysis is inhibited by alcohol | back 77 is inhibited by alcohol |
front 78 The first step in hemostasis is __________. vascular spasm platelet plug formation fibrin production coagulation | back 78 vascular spasm |