Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology Final 2016
front 1 A thermosensory neuron in the skin converts heat energy to nerve impulses via a conversion called _____. | back 1 sensory transduction |
front 2 Sensory adaptation is apparent when _____. | back 2 a person is no longer aware of a heavy necklace that was put on earlier in the day |
front 3 Sensory transduction in the auditory system is much like transduction of _____. | back 3 mechanosensory stimuli |
front 4 The energy for sensory transduction by the lateral line system in fish comes from _____. | back 4 water movements |
front 5 The visual information used by honeybees includes these elements that are not apparent to humans. | back 5 the ability to distinguish ultraviolet radiation and 300 flashes of light per second |
front 6 When light first enters the human eye, the first structure that it must pass through is the _____. | back 6 cornea |
front 7 Rods and cones are similar in that they both _____. | back 7 release glutamate as the primary neurotransmitter |
front 8 The sense described as umami is one of _____. | back 8 savory and delicious sensation on the tongue |
front 9 Myosin heads have binding sites for _____. | back 9 ATP and actin |
front 10 Among these choices, the most energy-efficient form of animal movement, per kg of body mass, is _____. | back 10 swimming by large fish |
front 11 The perceived pitch of a sound depends on | back 11 which region of the basilar membrane was set in motion. |
front 12 The cochlea is an organ of auditory transduction that contains | back 12 fluid and cells that can undergo mechanosensory transduction. |
front 13 The lateral line system in fish transduces sensory information in a manner that, among these choices, is most similar to | back 13 human vestibular sense. |
front 14 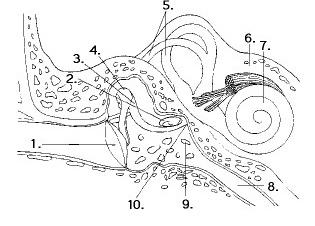 Hair cells are found in structures represented by numbers | back 14 5 and 7 |
front 15 Rods exposed to light will | back 15 hyperpolarize due to the closing of sodium channels. |
front 16 An injury to the occipital lobe will likely impair function of the | back 16 primary visual cortex. |
front 17 The olfactory bulb is located | back 17 in the brain. |
front 18 The calcium ions released into the cytosol during excitation of skeletal muscle bind to | back 18 troponin. |
front 19 A skeletal muscle with abnormally low levels of calcium ions would be impaired in | back 19 initiating contraction. |
front 20 The fundamental excitable cell in the nervous system is the _____. | back 20 neuron |
front 21 The central canal of the spinal cord and the ventricles of the human brain contain a filtrate of the blood, called _____. | back 21 cerebrospinal fluid |
front 22 The knee-jerk reflex has sensory neurons arising in the _____, interneurons in the _____, and efferent neurons that stimulate contraction in the _____. | back 22 quadriceps muscle ... spinal cord ... quadriceps muscle |
front 23 As vertebrates evolved, the increasingly complex structure of the brain conferred increasingly complex function, especially apparent in the _____. | back 23 cerebral cortex, which is greatly expanded in humans, other primates, and cetaceans |
front 24 Dolphins can be awake and asleep at the same time because _____. | back 24 one side of the brain can sleep while the other side maintains swimming and breathing behaviors |
front 25 Emotion, motivation, olfaction, behavior, and memory, in humans, are mediated by the _____. | back 25 limbic system |
front 26 Motor cortex and somatosensory cortex are _____. | back 26 organized in similar manner adjacent to each other, and are anatomically similar from one person to the next |
front 27 In adult humans, short-term memory relies on connections in the _____ whereas long-term memories appear to be based in the _____. | back 27 hippocampus ... cerebral cortex |
front 28 Addiction onset by cocaine and amphetamines is characterized by increased _____. | back 28 persistence of dopamine in the brain's synapses |
front 29 Parkinsonism is characterized by the loss of _____. | back 29 dopaminergic neurons |
front 30 Myelinated neurons are especially abundant in the | back 30 white matter in the brain and the white matter in the spinal cord. |
front 31 Although an exact count is not available, it is likely that the human brain has as many as | back 31 100 billion neurons. |
front 32 Calculation, contemplation, and cognition are human activities associated with increased activity in the | back 32 cerebrum. |
front 33 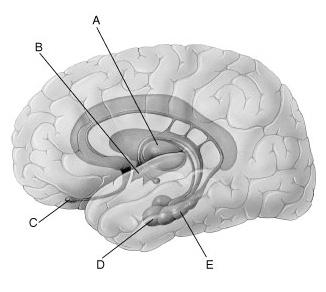 In the figure, which letter points to the amygdala? | back 33 D |
front 34 Of these choices, neuronal communication between the brain and the muscles of the leg is best conceptualized as _____. | back 34 electrical and chemical signaling |
front 35 The "information receiving" section of a neuron is its _____. | back 35 dendrites |
front 36 Choose the set that includes the most charged compounds that are more abundant inside neurons, in the cytosol, than outside the neurons, in the extracellular fluid. | back 36 potassium ions and proteins |
front 37 Ions move in the direction opposite to that favored by the chemical concentration gradient when _____. | back 37 they are pumped by proteins that require ATP hydrolysis and when the electrical charge gradient repulses or attracts them |
front 38 In a neuron, during the depolarization phase that may trigger an action potential _____. | back 38 some voltage-gated sodium channels are open |
front 39 The simultaneous arrival of graded depolarization and a graded hyperpolarization of equal but opposite magnitude at a particular location on the dendritic membrane is likely to _____. | back 39 cancel each other out, making it appear as if there was no change in membrane potential |
front 40 Select the choice that describes neurons with the fastest conduction velocity for action potentials. | back 40 thick, myelinated neurons |
front 41 A nerve poison that blocks acetylcholine receptors on dendrites would _____. | back 41 reduce the binding of acetylcholine to its receptors on the postsynpatic membrane |
front 42 At the neuromuscular junction, the arrival of acetylcholine on the muscle most immediately causes _____. | back 42 a graded depolarization |
front 43 Acetylcholine receptors on skeletal muscles are described as being "ionotropic" receptors because _____. | back 43 binding of acetylcholine to the receptor protein converts the protein to an open ion channel |
front 44 Most of the neurons in the human brain are | back 44 interneurons. |
front 45 An amino acid that operates at inhibitory synapses in the brain is | back 45 GABA. |
front 46 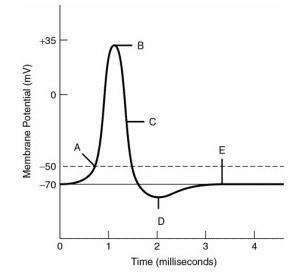 The minimum graded depolarization needed to operate the voltage-gated sodium channels is indicated by the label | back 46 A |
front 47 When several EPSPs arrive at the axon hillock from different dendritic locations, depolarizing the postsynaptic cell to threshold for an action potential, this is an example of | back 47 spatial summation. |
front 48 Hormones are _____. | back 48 chemical signals between cells, transported in blood or hemolymph |
front 49 The hormone epinephrine causes opposite effects in two populations of target cells because _____. | back 49 each set of target cells has different receptor-transduction mechanisms |
front 50 Oxytocin secretion and milk release from the mammary glands of lactating female mammals are initiated by _____. | back 50 the physical sensation of the baby sucking at the nipple |
front 51 In their mechanism of action, a difference between lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones is that _____. | back 51 lipid-soluble hormones bind to an intracellular receptor and this hormone-receptor complex binds to DNA |
front 52 The counter-regulatory functions of the pancreas refer to the fact that it _____. | back 52 releases one hormone that reduces glucose levels in the blood and another that increases them |
front 53 This disorder typically arises prior to puberty and is generally treated by injections of the hormone missing from the affected individual's bloodstream. | back 53 Type I diabetes mellitus |
front 54 The anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary differ in that _____. | back 54 many anterior pituitary hormones regulate other endocrine glands whereas posterior pituitary hormones regulate nonendocrine tissues |
front 55 How does the adrenal gland respond to stress? | back 55 The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine in response to short-term stress. |
front 56 Jet lag occurs when a person moves rapidly from one time zone to another, causing conflict between the body's biological rhythm and the new cycle of light and dark. Some scientists suspect that jet lag may result from disruption of the daily cycle of secretion of the hormone known as _____. | back 56 melatonin |
front 57 Which category of signal exerts its effects on target cells by binding to membrane-bound receptor proteins? | back 57 neurohormones |
front 58 Different body cells can respond differently to the same peptide hormones because | back 58 a target cell's response is determined by the components of its signal transduction pathways. |
front 59 The endocrine glands include the | back 59 parathyroid glands. |
front 60 Testosterone is an example of | back 60 an androgen. |
front 61 A cell with membrane-bound proteins that selectively bind a specific hormone is called that hormone's | back 61 target cell. |
front 62 Prostaglandins are local regulators whose chemical structure is derived | back 62 fatty acids. |