Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
blood vessels
front 1 three layers of blood vessels from outside to inside | back 1 tunica externa:outermost layer, contains collagen fibers tunica media: middletunic, smooth muscles tunica intima: endothelium, innermost layer |
front 2 a blood vessel supplying blood to the larger blood vessel is called | back 2 vasa vasorum |
front 3 list the types of blood capillaries | back 3 continuous:gas exchange, found in brain, testes, lungs etc. least permeable and most common fenestrated: active filtration and absorption, found in kidneys and small intestines sinusoid: most permeable, found in liver, spleen, and especially bone marrow, lymphnodes |
front 4 anatomy of capillary bed | back 4 arteriole > precapillary sphincter > true capillary and metaarteriole > venule |
front 5 ____ are the capacitance blood vessels that holds up to ___ of blood | back 5 veins; 65% |
front 6 Normal range of systolic blood pressure is | back 6 100 - 140 mmHg |
front 7 when recording pulse, one should note: | back 7 rate, rhythm, volume, characteristics of an artery |
front 8 force per unit area exerted on an interior of a vessel wall by the contained blood is called | back 8 blood pressure |
front 9 the types of blood vessels circuits | back 9 pulmonary and systemic |
front 10 high blood pressure in pulmonary vasculature is called | back 10 pulmonary hypertension |
front 11 high blood pressure in systemic vasculature is called | back 11 systemic hypertension |
front 12 opposition to the blood flow is called | back 12 vascular resistance |
front 13 higher the friction, the higher the: | back 13 resistance |
front 14 increase in blood viscosity will increase the ___ and __ the resistance | back 14 friction; higher |
front 15 polycythemia will____ the friction and thereby___ resistance | back 15 increase; increase |
front 16 anemia will___ the friction and thereby___ resistance | back 16 decrease; decrease |
front 17 increase in the length of blood vessel will___ the resistance to blood flow | back 17 increase |
front 18 increasing the diameter of blood vessel will___ the resistance to blood flow | back 18 decrease |
front 19 Resistance is____ proportional to length of blood vessels | back 19 directly |
front 20 Resistance is____ proportional to diameter of blood vessel | back 20 inversely |
front 21 Higher the turbulent flow___ the resistance in blood vessels | back 21 higher |
front 22 Difference in blood pressure between any two points in a blood vessel is the | back 22 blood pressure |
front 23 Rate of flow of blood is___ proportional to the difference of blood pressure at any two points in circulation | back 23 directly |
front 24 rate of flow of blood is___ proportional to resistance in a blood vessel | back 24 inversely |
front 25 Define pulse pressure | back 25 difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure |
front 26 increasing the diameter of blood vessel will___ the resistance to blood flow | back 26 decrease |
front 27 blood flow = resistance/blood pressure | back 27 false |
front 28 Net filtration rate from a capillary is equal to | back 28 NFP = (HPc - HPif) - (OPc - OPif) |
front 29 force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by its contained blood is called | back 29 blood pressure |
front 30 the blood pressure in the capillaries ranges from to 20 to 40 mmHg | back 30 true |
front 31 the coronary arteries arises from the | back 31 aorta |
front 32 the inferior vena cava brings blood from the lower regions of the body and empties into the | back 32 right atrium |
front 33 the major long term mechanism of blood pressure control is provided by the | back 33 kidneys |
front 34 reduction in lumen diameter of a blood vessel as the smooth muscle contracts is known as | back 34 vasoconstriction |
front 35 the increase in lumen diameter of a blood vessel as the smooth muscle relaxes is known as | back 35 vasodilation |
front 36 exchange of gases and nutrients occurs by diffusion between the | back 36 capillaries and tissue cells |
front 37 any condition in which blood vessels are inadequately filled and blood cannot circulate normally is called | back 37 circulatory shock |
front 38 which of the following regulates blood flow at the entrance of each true capllary | back 38 precapilllary sphincter |
front 39 the common hepatic, left gastric, and splenic arteries are the branch of which of the following atery | back 39 celiac trunk |
front 40 which of the following types of blood vessels have the thickest tunica media of all vessels | back 40 elastic arteries |
front 41 which of the following conditions may not develop the varicose veins | back 41 walking on heels with pressure on the calf muscles |
front 42 at any given time, up to 65% of the body's blood supply is found in | back 42 veins |
front 43 most neural controls of blood pressure involve the input from baroreceptors that are sensitive to | back 43 changes in blood pressure |
front 44 which of the following blood vessels is the most susceptible to atherosclerosis | back 44 the aorta |
front 45 the heart produces a hormone called atrial natriuretic peptide that causes blood volume and blood pressure to decline | back 45 true |
front 46 the device used to measure blood pressure is called | back 46 sphygmomanometer |
front 47 the device used for listening to the breath sound is called___ and the sound produced by the blood flow through the narrow blood vessel during blood pressure measurement is called___ sound | back 47 stethoscope; sounds of korotkoff |
front 48 which of the following is a component of short term mechanism of blood pressure control? | back 48 baroreceptor control, chemoreceptor control, carotid sinus reflex, aortic body reflex |
front 49 superior vena cava is formed by the union of which of the veins | back 49 right and left brachiocephalic vein |
front 50 which of the following arteries gives rise to common hepatic, left gastric, and splenic arteries? | back 50 celiac trunk |
front 51 which of the following veins is the longest in the body | back 51 great saphenous vein |
front 52 posterior intercostal arteries are branches of | back 52 aorta |
front 53 basilic vein (superficial vein) is located | back 53 medially in the upper limb |
front 54 which of the following is true of femoral blood vessels | back 54 femoral vein is located medial to femoral artery |
front 55 superior and inferior vena cava, coronary sinus, anterior cardiac veins are the major blood vessels entering the | back 55 right atrium |
front 56 a thrombus in the first branch of the arch of the aorta would affect the flow of blood to the | back 56 right side of the head and neck and right upper arm |
front 57 the aorta ascending aorta aortic arch brachiocephalic trunk (right/left) subclavian artery (left/right) subclavian carotid artery (right/left) common carotid artery (right/left) internal/external carotid artery | back 57 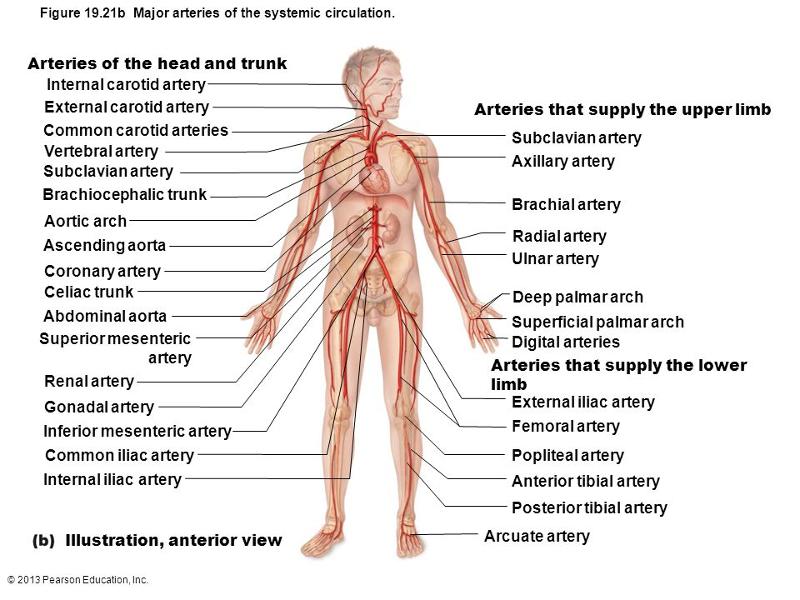 external common carotid artery supplies blood to the head and neck internal common carotid artery supplies the brain subclavian goes to the upper limb |
front 58 internal/external carotid artery subclavian artery axillary artery brachicephalic trunk | back 58 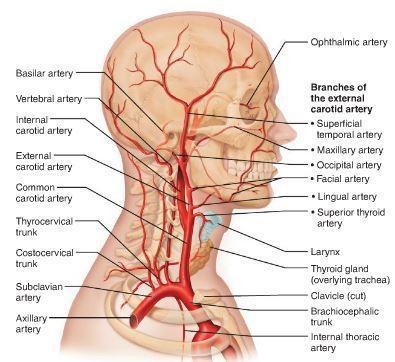 |
front 59 middle cerebral artery internal carotid artery circle of willis (vertebra artery, pontine artery, basilar artery, post cerebral artery,middle cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, anterior cerebral artery, internal carotid artery, posterior communicating artery) | back 59 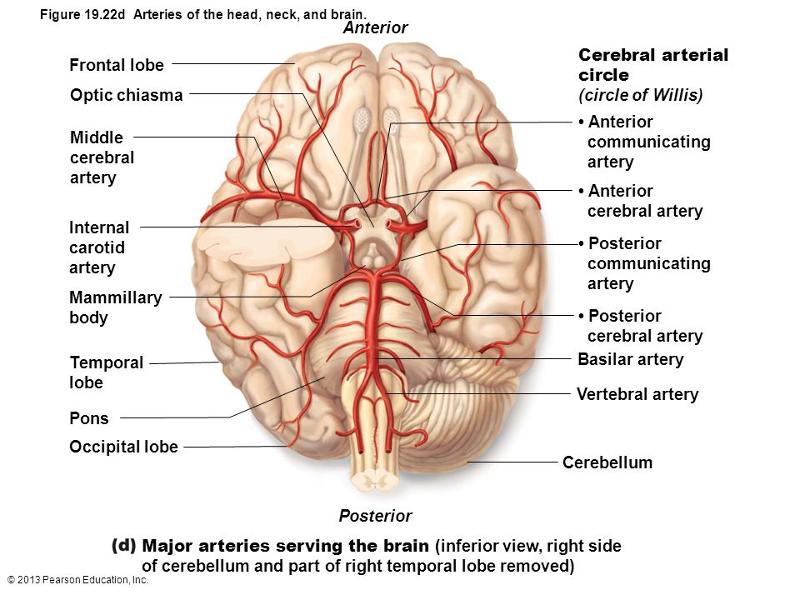 |
front 60 right subclavian artery left subclavian artery brachiocephalic trunk posteruir intercostal artery internal thoracic artery brachial artery axillary artery radial artery ulnar artery | back 60 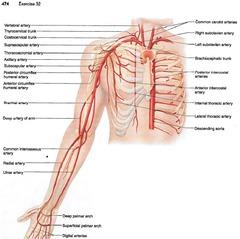 |
front 61 celiac trunk common hepatic artery gastroduodenal artery right/left gastric artery splenic artery left/right gastroepoploic artery | back 61 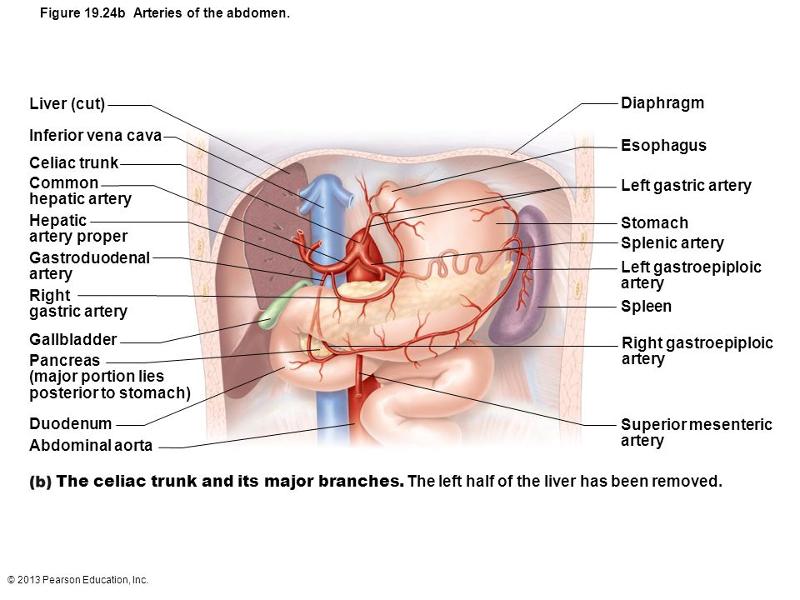 |
front 62 adrenal (suprarenal) gland middle suprarenal artery renal artery superior mesentric artery gonadal artery inferior mesenteric artery common artery | back 62 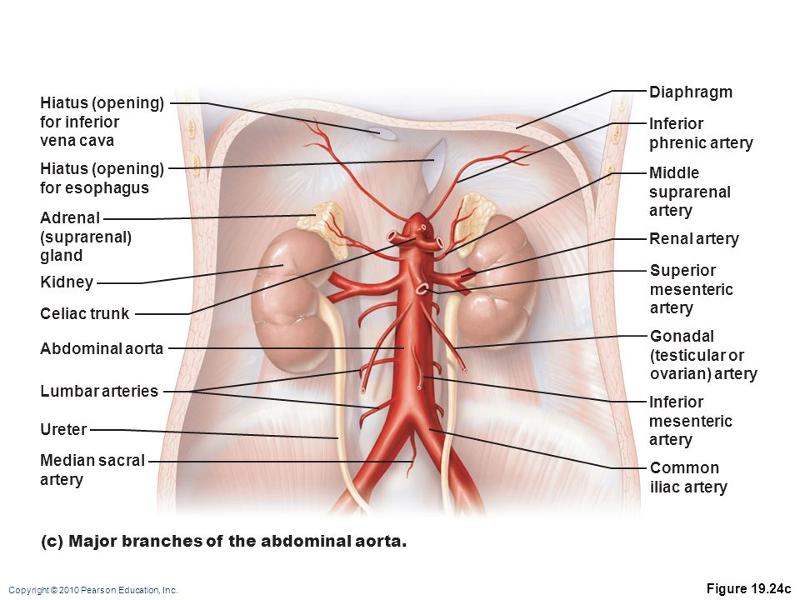 |
front 63 common iliac artery internal iliac artery external iliac artery femoral artery popliteal artery anterior tibial artery posterior tibial artery fibular artery dorasalis pedis artery | back 63 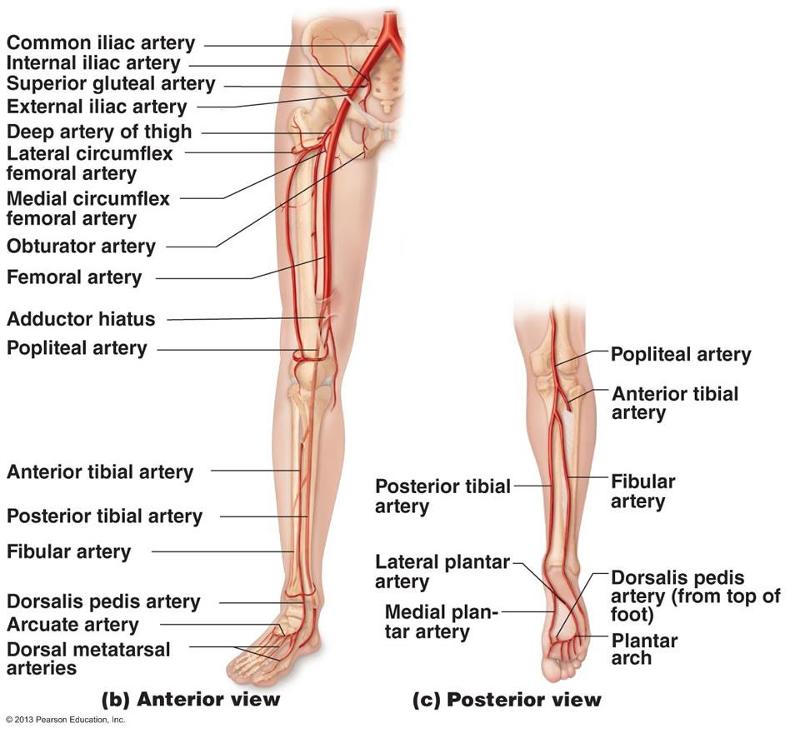 |
front 64 external jugular vein internal jugular vein subclavian vein superior sagittal sinus inferior sagittal sinus straight sinus transverse sinuses sigmoid sinus jugular foramen right internal jugular vein | back 64 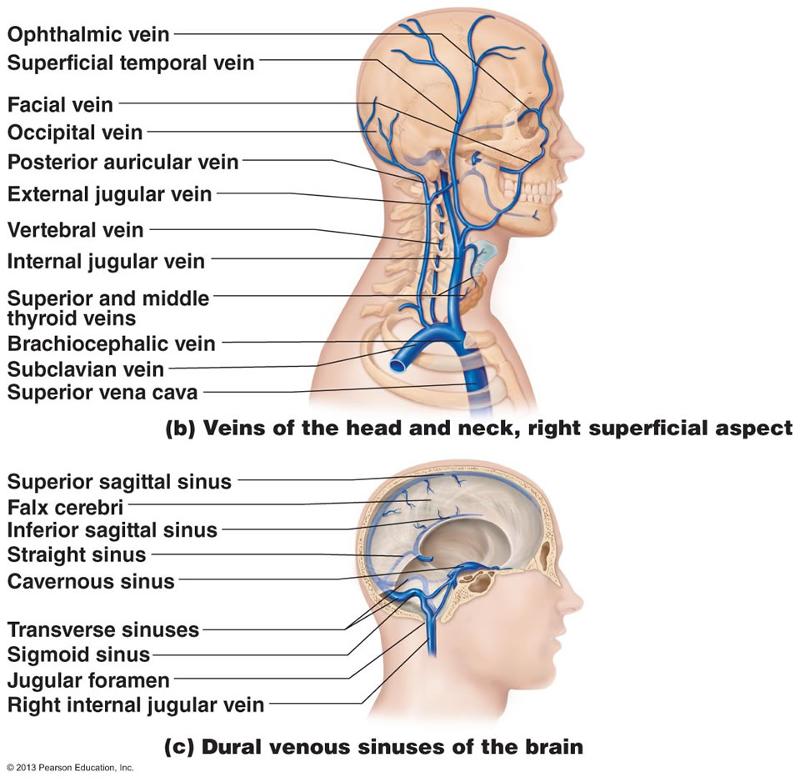 external/internal jugular veins combine to give rise to common iliac vein, common iliac vein combines to give rise to inferior vena cava |
front 65 brachiocephalic veins axillary vein brachial vein basilic vein internal jugular vein external jugular vein superior vena cava median cubital vein cephalic vein radial vein basilic vein ulnar vein | back 65 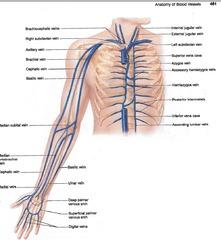 |
front 66 inferior vena cava right suprarenal vein left suprarenal vein renal veins left gonadal vein common iliac vein internal iliac vein inferior mesenteric vein superior mesenteric vein | back 66 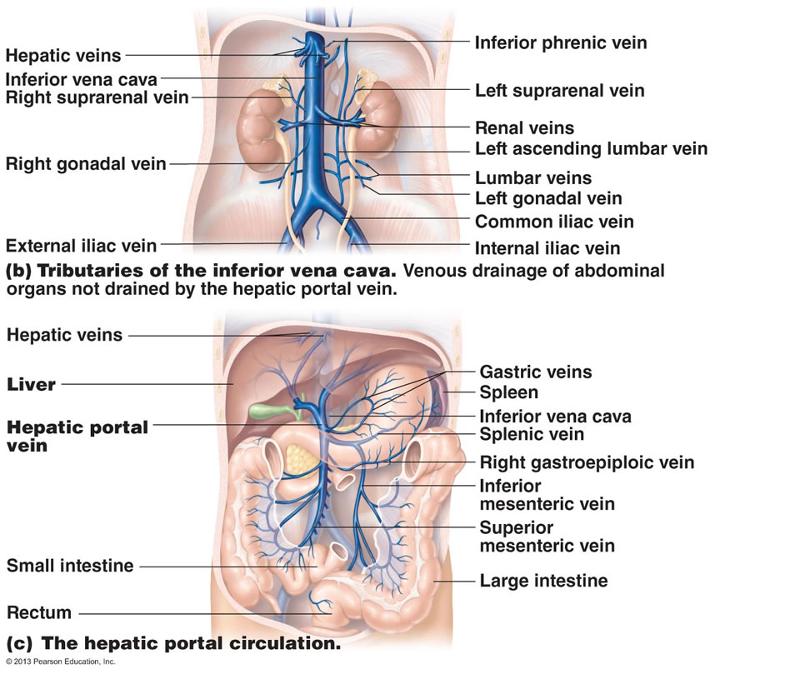 left renal vein is longer, right renal vein is shorter |
front 67 popliteal vein fibular vein anterior tibial vein internal iliac vein external iliac vein femoral vein great saphenous vein | back 67 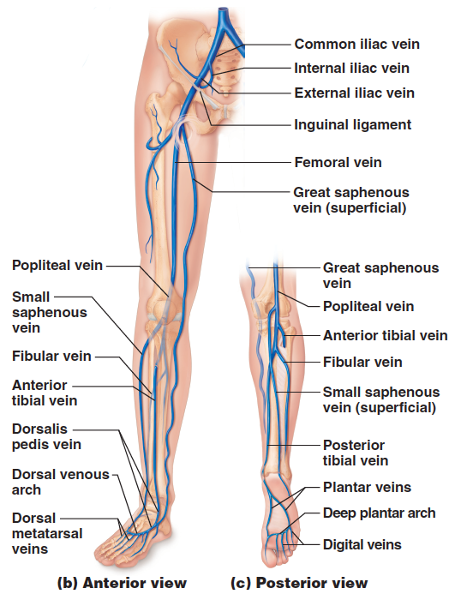 |
front 68 portal system | back 68 a set of capillaries arising from an organ,, that enters into another organ and breaks down into another set of capillaries |