Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 15: Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System
front 1 gluteus maximus | back 1 location of muscle relative to a bone or body region; relative size of muscle |
front 2 adductor magnus | back 2 action of the muscle; relative size of muscle |
front 3 biceps femoris | back 3 number of origins; location of muscle relative to a bone or body region |
front 4 transversus abdominis | back 4 location of muscle relative to a bone or body region; direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line |
front 5 extensor carpi ulnaris | back 5 action of muscle; location of the origin and or insertion of the muscle; location of muscle relative to bone or body region |
front 6 trapezius | back 6 shape of muscle |
front 7 rectus femoris | back 7 location of the muscle relative to a bone or body region; direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line |
front 8 external oblique | back 8 location of the muscle reltive to a bone or body region; direction in which the muscle fibers run relative to some imaginary line |
front 9 prime mover (agonist) | back 9 term for the biceps brachii during elbow flexion |
front 10 synergist | back 10 term that describes relation of brachialis to biceps brachii during elbow flexion |
front 11 antagonist | back 11 term for the triceps brachii during elbow flexion |
front 12 antagonist | back 12 term for iliopsoas during hip extension |
front 13 prime mover (agonist) | back 13 term for the gluteus maximus during hip extension when walking up the stairs |
front 14 fixator | back 14 terms for the rotator cuff muscles and deltoid when the elbow is flexed and the hand grabs a tabletop to lift the table |
front 15 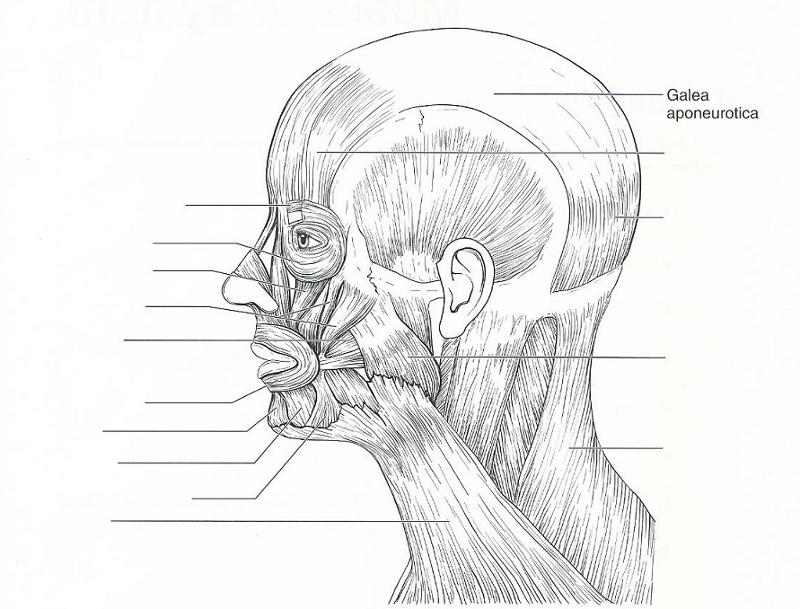 | back 15 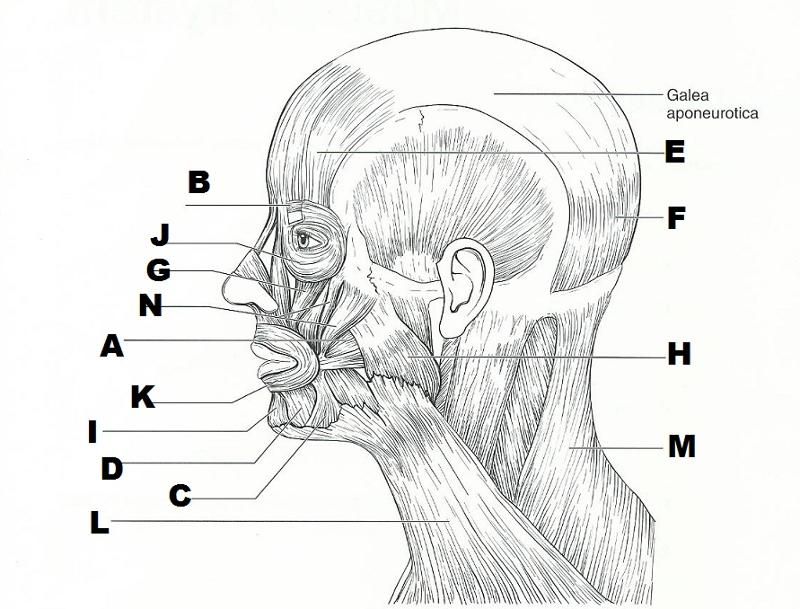 START FROM LEFT SIDE AND GO DOWN, THEN START ON THE UPPER RIGHT SIDE AND GO DOWN.
|
front 16 zygomaticus | back 16 used in smiling |
front 17 buccinator | back 17 used to suck in your cheeks |
front 18 Orbicularis Oculi | back 18 Used in blinking and squinting (closes eye) |
front 19 Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Mentalis Muscle | back 19 used to pout (pulls the corners of the mouth downward) |
front 20 epicranius (frontal belly) | back 20 raises your eyebrows for a questioning expression |
front 21 corrugator supercilii | back 21 used to form the vertical frown crease on your forehead |
front 22 orbicularis oris | back 22 your "kisser" |
front 23 masseter | back 23 prime mover to raise the mandible |
front 24 platysma | back 24 tenses skin of the neck during shaving |
front 25 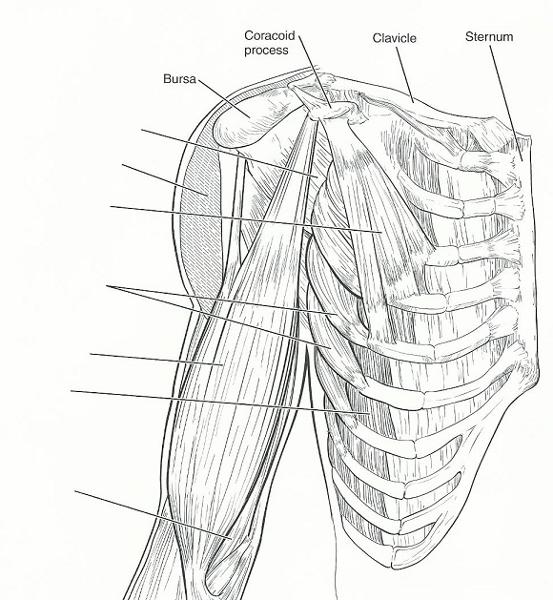 | back 25 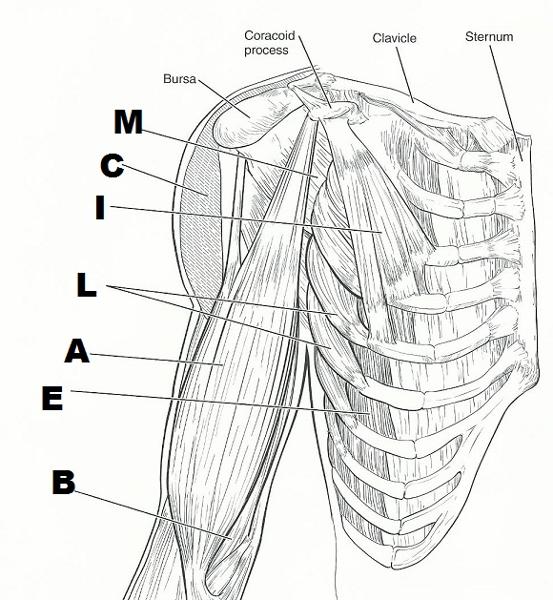 FROM TOP TO BOTTOM:
|
front 26 rectus abdominus | back 26 a major spine flexor |
front 27 latissimus dorsi | back 27 prime mover for arm extension |
front 28 pectoralis major | back 28 prime mover for arm flexion |
front 29 external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominus, rectus abdominus | back 29 assume major responsibility for forming the abdominal girdle |
front 30 deltoid | back 30 prime mover of shoulder abduction |
front 31 latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major | back 31 important in shoulder adduction; antagonists of the shoulder abductor |
front 32 serratus anterior | back 32 moves the scapula forward and rotates scapula upwards |
front 33 external intercostals | back 33 small, inspiratory muscles between the ribs; elevate the ribs |
front 34 trapezius | back 34 extends the head |
front 35 rhomboids | back 35 pull the scapula medially |
front 36 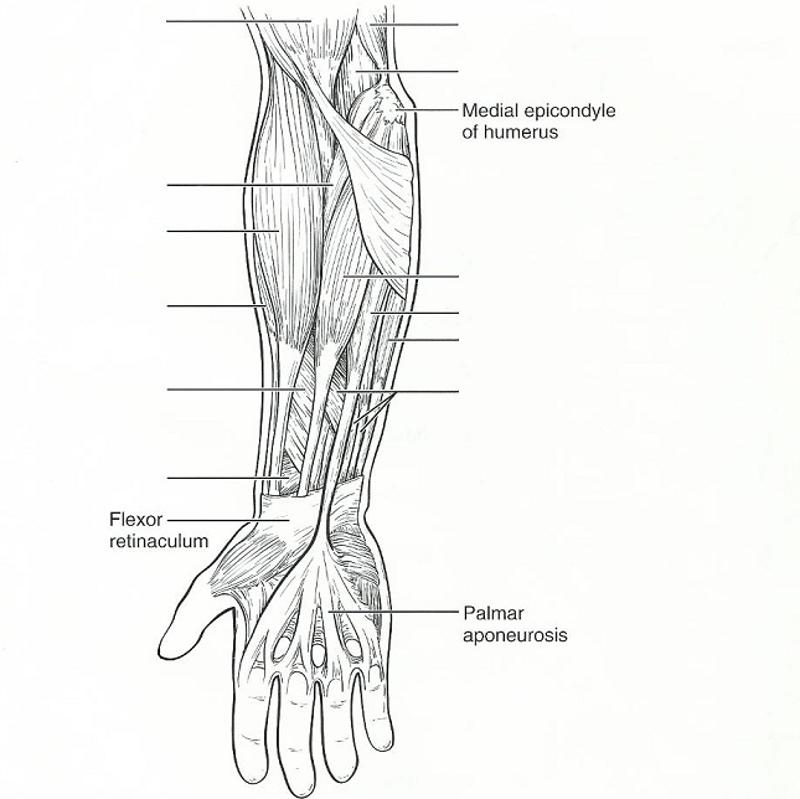 | back 36 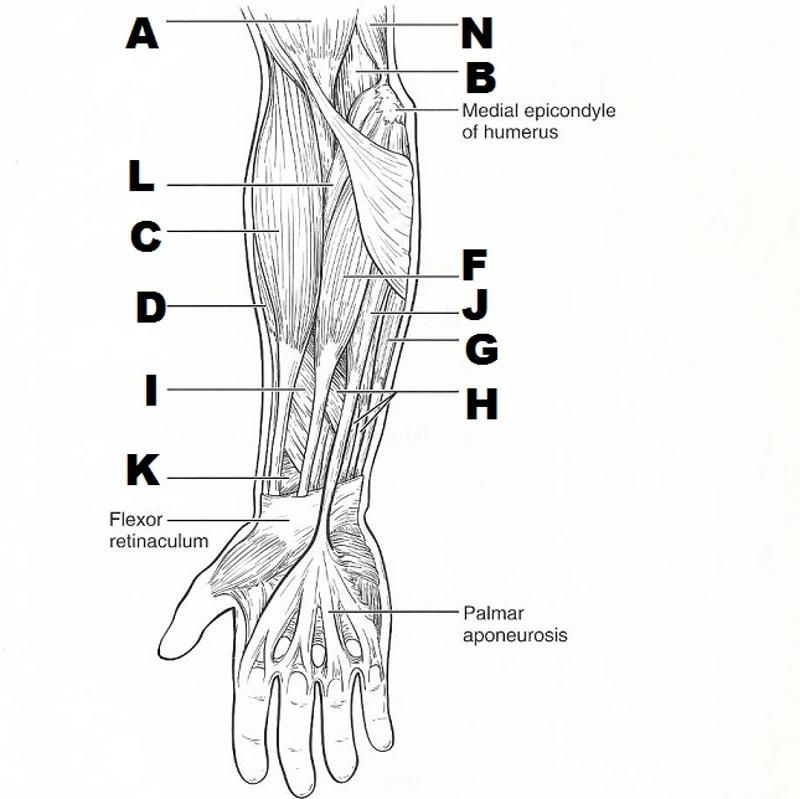 FROM LEFT TOP TO BOTTOM, THEN RIGHT TOP TO BOTTOM:
|
front 37 biceps brachii | back 37 flexes the forearm and supinates the hand |
front 38 supinator | back 38 synerhist for supination of hand |
front 39 brachialis; brachioradialis | back 39 forearm flexors; no role in supination |
front 40 triceps brachii | back 40 elbow extensor |
front 41 flexor carpi radialis | back 41 power wrist flexor and abductor |
front 42 flexor digitorum superficialis | back 42 flexes wrist and middle phalanges |
front 43 pronator quadratus, pronator teres | back 43 pronates the hand |
front 44 flexor pollicis longus | back 44 flexes the thumb |
front 45 extensor carpi radialis longus | back 45 extends and abducts the wrist |
front 46 extensor digitorum | back 46 extends the wrist and digits |
front 47 palmaris longus | back 47 flat muscle that is a weak wrist flexor; tenses skin of the palm |
front 48 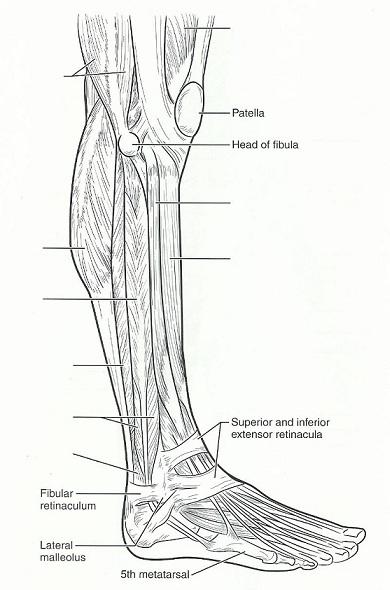 | back 48 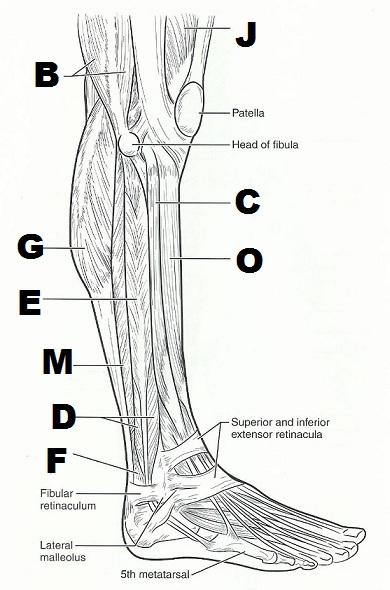 LEFT FROM TOP TO BOTTOM:
|
front 49 flexor hallucis longus | back 49 flexes the great toe and inverts the foot |
front 50 fibularis brevis, fibularis longus | back 50 lateral compartment muscles that plantar flex and evert the foot |
front 51 gluteus medius, tensor fasciae latae | back 51 abduct the thigh to take the "at ease" stance |
front 52 gluteus maximus | back 52 used to extend the hip when climbing stairs |
front 53 gastrocnemius, soleus | back 53 prime movers of plantar flexion of the foot |
front 54 tibialis posterior | back 54 prime mover of inversion of the foot |
front 55 tibialis anterior | back 55 prime mover of dorsiflexion of the foot |
front 56 adductor group | back 56 adduct the thigh, as when standing at attention |
front 57 extensor digitorum longus | back 57 extends the toes |
front 58 biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus | back 58 entend thigh and flex knee |
front 59 rectus femoris | back 59 extends knee and flexes thigh |
front 60 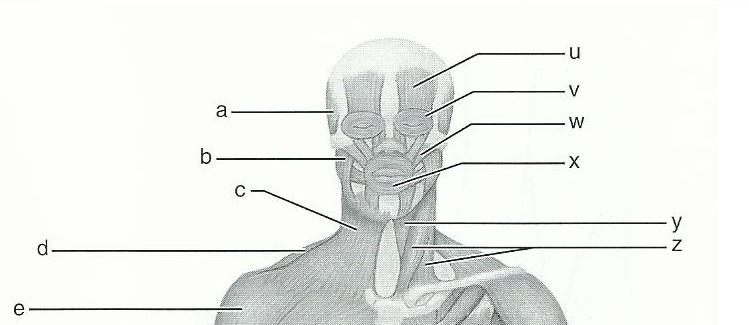 11 | back 60 A. TEMPORALIS
|
front 61 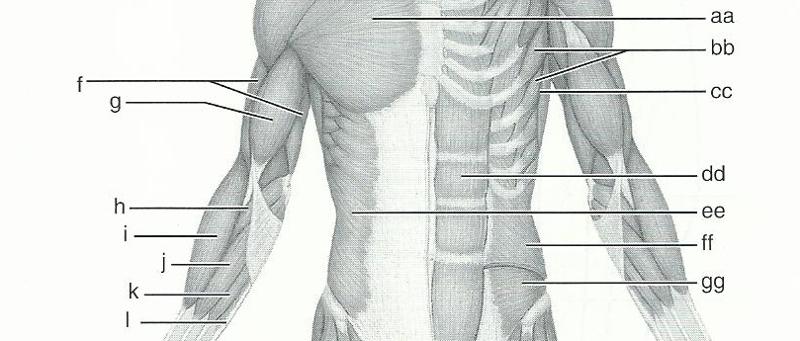 11 | back 61 AA - PECTORALIS MAJOR
|
front 62 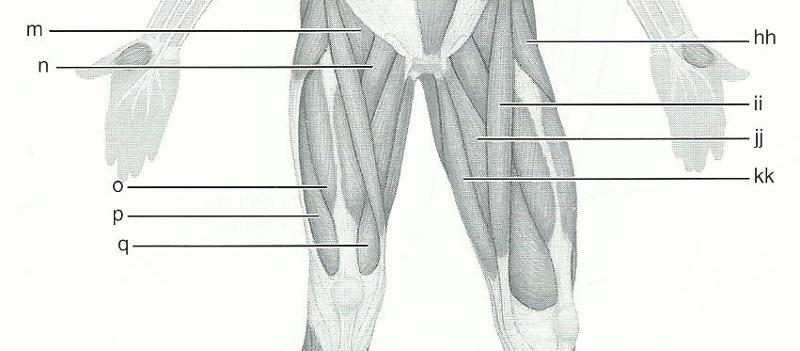 11 | back 62 M - ILIOPSAS
|
front 63 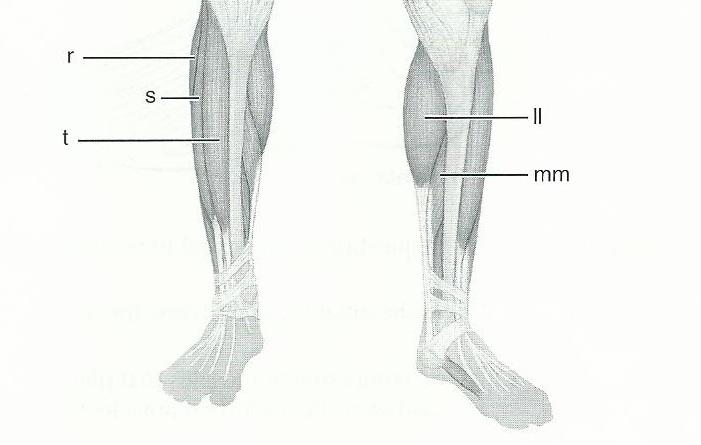 11 | back 63 R - PERONEUS LONGUS
|
front 64 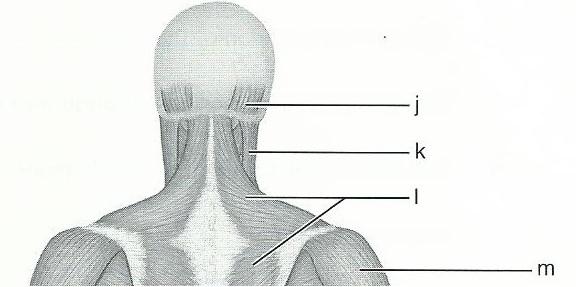 12 | back 64 J - OCCIPITALIS
|
front 65 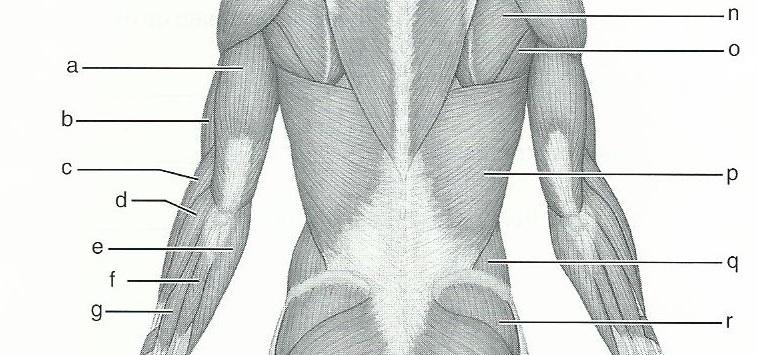 12 | back 65 A. TRICEPS BRACHII
|
front 66 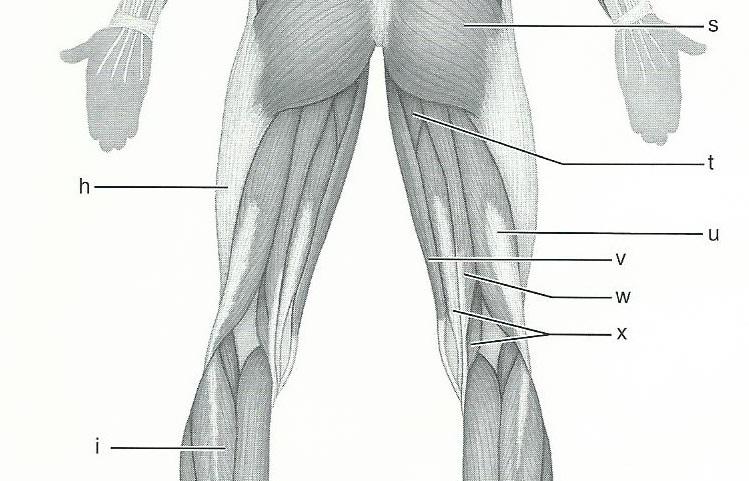 12 | back 66 H - ILIOTIBIAL TRACT
|
front 67 What are the 4 muscles commonly used for intramuscular injections? | back 67 Deltoid, Vastus Lateralis, Gluteus Medius, Gluteus Maximus |
front 68 Quadriceps | back 68 The insertion tendon of the ____ group contains a large sesamoid bone, the patella. |
front 69 calcanal | back 69 The triceps surae insert in common into the ____ tendon. |
front 70 mediala proximal | back 70 The bulk of the tissue of a muscle tends to lie ______ to the part of the body it causes to move. |
front 71 forearm | back 71 The extrinsic muscles of the hand originate on the ______ |
front 72 anterior | back 72 Most flexor muscles are located on the _____ aspect of the body; |
front 73 posteria | back 73 most extensors are located ______ |
front 74 knee | back 74 An exception to this generalization is the extensor-flexor musculature of the ____ |