Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy & Physiology: Circulatory System
front 1 Whole blood consists of | back 1 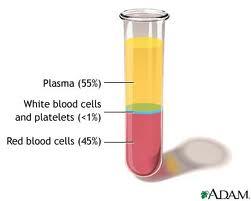 approx. 55% plasma & 45% formed elements: erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells) & platelets. |
front 2 What percent of blood is plasma? | back 2 55% |
front 3 What percent of blood is formed elements? | back 3 45% |
front 4 What does formed elements consist of? | back 4 erythrocytes, leukocytes & platelets |
front 5 What are erythrocytes? | back 5 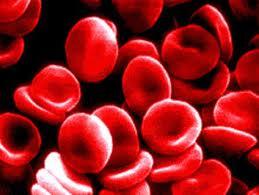 Red blood cells (RBC's) |
front 6 What are leukocytes? | back 6 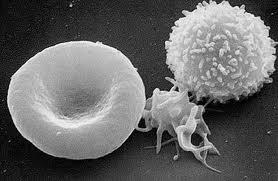 White blood cells (WBC's) |
front 7 What are platelets? | back 7 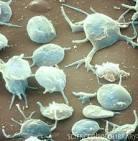 A small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting. |
front 8 Visual of Platelet functions --> | back 8 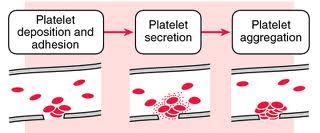 |
front 9 Formed elements are produced from | back 9 stem cells in red bone marrow. |
front 10 True/ False
| back 10 ~TRUE~ |
front 11 True/False
| back 11 ~TRUE~ |
front 12 There are ___ types of leukocytes. | back 12 5 |
front 13 The 5 different types of leukocytes can be distinguished on the basis of | back 13  size, appearance of the nucleus, staining properties, presence & absence of visible cytoplasmic granuels. |
front 14 White blood cells are active in | back 14 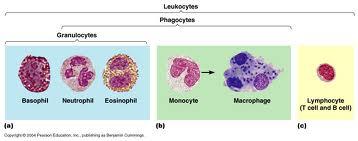 phagocytosis (neutrophils & monocytes) and antibody formation (lymphocytes). |
front 15 Blood serves to | back 15 transport oxygen & nutrients to body cells & to carry away carbon dioxide & metabolic wastes. |
front 16 True/False
| back 16 ~TRUE~ |
front 17 Does blood transport oxygen & nutrients to body cells? | back 17 ~YES~ |
front 18 Plasma contains approx. _a__% proteins, __b__, ___c__, _d___ & __e____, which are dissolved or suspended in water. | back 18 a. 10%
|
front 19 What happens to the proteins, ions, nutrients, waste products & hormones contained w/in plasma? | back 19 They are dissolved or suspended in water. |
front 20 The heart is a __a__ _a__ that sends blood to the __b_ for oxygenation through the __c__ __c__ & to the remainder of the body through the __d_ _d__. | back 20 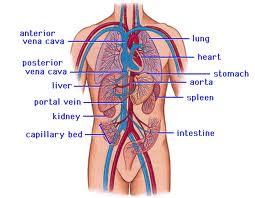 a. double pump
|
front 21 Blood is received by the _a__ & is pumped in circulation by the __b__. | back 21 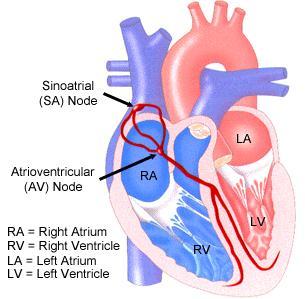 a. atria
|
front 22 True/False
| back 22 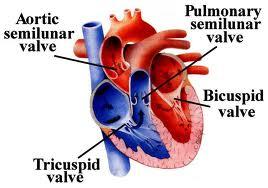 ~TRUE~ |
front 23 The valve on the LEFT SIDE of the heart is the___ valve? | back 23 BICUSPID |
front 24 The valve on the RIGHT SIDE of the heart is the ___ valve? | back 24 TRICSUPID |
front 25 What valves are found at the entrances of the pulmonary trunk & the aorta? | back 25 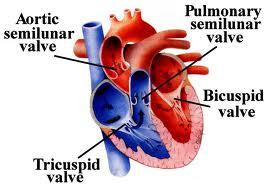 SEMILUNAR VALVES |
front 26 Blood is supplied to the heart muscle (myocardium) by what arteries? | back 26 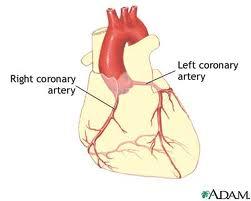 Coronary arteries |
front 27 What is the myocardium? | back 27 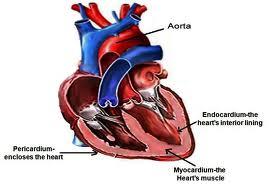 The heart muscle |
front 28 Circulation of blood through the heart- visualization- | back 28 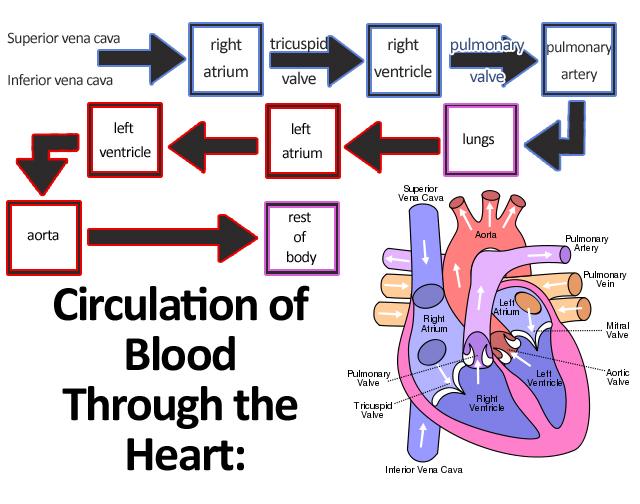 Follow the blood flow path, while looking at the picture to get a better understanding of the pathway our blood travels through our heart.
|
front 29 Blood drains from the ____a_____ directly into the ___b__ __b__ through the ___c__ __c__. | back 29 a. myocardium
|
front 30 The hearts intrinsic beat is initiated by the __a__ _a__ and transmitted along the conduction system through the __b____. | back 30 a. Sinoatrial node
|
front 31 The intrinsic beat intiated by the sinoatrial node along the conduction system through the mycardium -is a wave of electrical activity & is what is measured on a | back 31 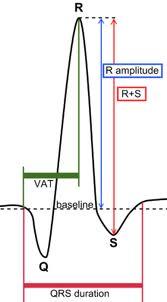 ECG- Electrocardiogram |
front 32 The cardiac cycle is the period from the | back 32 end of one ventricular contraction to the end of the next ventricular contraction. |
front 33 True/False
| back 33 a. systole
|
front 34 The contraction phase of the cardiac cycle is called | back 34 systole |
front 35 The relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle is called | back 35 diastole |
front 36 The vascular system contains | back 36 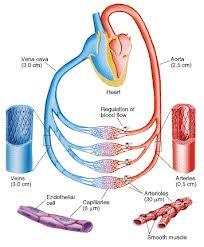 arteries, veins & capillaries. |
front 37 Arteries carry blood | back 37 AWAY from the heart |
front 38 Veins carry blood | back 38 TOWARD the heart |
front 39 Capillaries is where | back 39 exchange takes place between blood & cells of the body. |
front 40 True/False
| back 40 ~TRUE~ |
front 41 As arteries get farther away from the heart they | back 41 become thinner & thinner |
front 42 The smallest arteries are called | back 42 arterioles |
front 43 True/ False
| back 43 ~TRUE~ |
front 44 The ___a_________________ are the _b__ _b__ that empty into the __c__ __c__ of the heart. | back 44 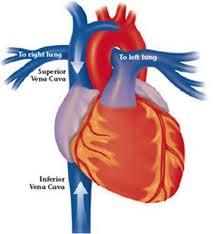 a. Superior & Inferior venae cavae
|
front 45 True/ False
| back 45 ~TRUE~ |
front 46 Vasoconstriction & Vasodilation result from | back 46 Contraction & relaxation of smooth muscle in the arterial walls. |
front 47 Vasocontriction is ______ of the smooth muscle in the artery wall. | back 47 contraction |
front 48 Vasodilation is ____ of smooth muscle in the artery wall. | back 48 relaxation |
front 49 True/False
| back 49 ~TRUE~ |
front 50 Vein walls are ___a___ & less ___b___ than those of the arteries, because they carry blood under lower pressure. | back 50 a. thinner
|
front 51 True/False
| back 51 ~True~
|
front 52 Mechanisms that help draw venous blood back to the heart include: | back 52 a. pressure of the skeletal muscles on the veins
|
front 53 Labled diagram of the heart | back 53 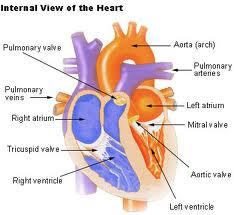 Thank you for using my notecards, I hope they were helpful. Please leave comments and post notecards of your own for others to use. ~ :-) ~ |
front 54 Major arteries & veins of the body.
| back 54 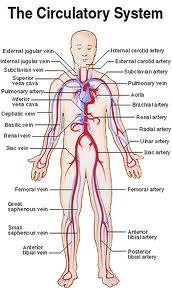 Notice the arteries are paralleled w/veins w/the same name (most of them). Example: Femoral artery & Femoral vein.
|