Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Special Populations Chapter 4 - (Nicola)
front 1 The first 28 days outside the uterus | back 1 Neonate |
front 2 1-18 months | back 2 Infant |
front 3 18-30 months | back 3 Toddler |
front 4 30 months to 5 years | back 4 Pre-schooler |
front 5 6-12 years | back 5 School age |
front 6 13-18 years | back 6 Adolescence |
front 7 What is the pediatric surgical team more focused on for the patient
| back 7 Physiological |
front 8 A child less than 6 months cannot .... | back 8 Shiver |
front 9 A child less than 6 months is prone to which issues (in surgery) due
| back 9 Hypothermia, bradycardia (slow), and acidosis |
front 10 Which sinuses are present at birth | back 10 Ethmoid and maxillary |
front 11 What age does the frontal sinus develop | back 11 7 years |
front 12 When does the sphenoid sinus develop | back 12 After pubity |
front 13 Normal heart rate for infant to 2 years | back 13 80-30 with average heart rate of 110 |
front 14 Normal heart rate for 2-6 year old | back 14 70-120 with average heart rate of 100 |
front 15 Normal heart rate for 6-10 year old | back 15 70-110 with average heart rate of 90 |
front 16 Normal heart rate for 10-16 year old | back 16 60-100 with average heart rate of 85 |
front 17 Normal respiratory rate for 1 year old | back 17 10-40 rr per min |
front 18 Normal respiratory rate for 3 year old | back 18 20-30 rr per min |
front 19 Normal respiratory rate for 6 year old | back 19 16-22 rr per min |
front 20 Normal respiratory rate for 10 year old | back 20 16-20 rr per min |
front 21 Normal respiratory rate for 17 year old | back 21 12-20 rr per min |
front 22 Patients who are ...... are usually held by the anesthesia provider
| back 22 2 and under |
front 23 What is the appropriate out put of urine | back 23 1 to 2mL/kg/hr |
front 24 A method of ECG monitoring in which the intra-arterial catheter is
| back 24 Intra-arterial measurement |
front 25 A catheter passed through a peripheral vein and ending in the
| back 25 Central venous catheter |
front 26 The standard method of monitoring blood oxygenation levels for all
| back 26 Arterial blood gases |
front 27 The two common types of shock seen in all age groups are | back 27 Septic and hypovolemic |
front 28 A state of shock when the body is overwhelmed by the pathogenic
| back 28 Septic shock |
front 29 Result in decreased venous return that lowers cardiac output and
| back 29 Hypovolemic shock |
front 30 What is the most common cause of hypovolemic shock in pediatric
| back 30 Dehydration - quick fluid and blood replacement
|
front 31 Practically every antibiotic has been associated with the development | back 31 Pseudomembranous enterocolitis |
front 32 Inflammation of the small intestine and colon | back 32 enterocolitis |
front 33 What is the number one cause of death in children aged 1–15 | back 33 Accidents |
front 34 The most common bone fracture is of the ......., usually as a result
| back 34 clavicle |
front 35 What is the term used for difficult labor or delivery of a baby | back 35 Dystocia |
front 36 Abnormal accumulation of air in the pleural cavity | back 36 Pneumothorax |
front 37 What refers to patients whose body weight is 100 pounds greater than
| back 37 Morbid obesity |
front 38 Enlargement of the heart due to the increased demands placed on the
| back 38 Myocardial hypertrophy |
front 39 What is delayed due to the poor blood supply to the adipose tissue | back 39 Healing |
front 40 Obese patients are prone to an increased incidence of ...... | back 40 postoperative wound infections |
front 41 What is a surgical complication in which a wound ruptures along a
| back 41 Dehiscence |
front 42 What significantly improves pulmonary function in an obese patient in surgery | back 42 Reverse Trendelenburg position (Head up feet down) |
front 43 What must be used with obese patients to reduce the incidence of DVT | back 43 Intermittent venous compression boots |
front 44 What are the three most common complications after gastric bypass or
| back 44 Abdominal catastrophes, internal hernia, and acute gastric distention |
front 45 Often acute respiratory failure indicates peritonitis. If visceral
| back 45 Abdominal catastrophes |
front 46 What occur when there is protrusion of an internal organ into a
| back 46 internal hernia |
front 47 What occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate
| back 47 acute gastric distention |
front 48 What are often found during abdominal procedures on obese patients | back 48 gall stones |
front 49 The pancreas produces little or no insulin, and the individual must
| back 49 Type 1—insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) |
front 50 The pancreas produces different amounts of insulin. The individual is
| back 50 Type 2—non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) |
front 51 Complications associated with diabetes | back 51 Infection
|
front 52 Medical term, commonly known as a heart attack | back 52 Myocardial infarction |
front 53 The normal dosage of preoperative medication is decreased since
| back 53 Preoperative care of a diabetic patient |
front 54 Monitoring is necessary to determine the patient’s needs for insulin,
| back 54 Intraoperative care of a diabetic patient |
front 55 What is one of the most common postoperative complications of
| back 55 Increased rate of infection |
front 56 What substances are made when the body breaks down fat for energy. | back 56 Ketones |
front 57 Performing surgery in the third trimester can lead to a ....... | back 57 40% risk of premature labor |
front 58 What can be hard to locate in a late term uterus | back 58 Anatomical landmarks |
front 59 In pregnant patients, the three important items to remember are
| back 59 Increase in preterm labor, fetal death, and low birth weight |
front 60 The surgical technologist should aid the surgeon by
| back 60 palpating the uterus |
front 61 When positioning a pregnant patient in the .... position, a small
| back 61 supine |
front 62 For a pregnant patient the operating room table may be ...... to the
| back 62 tilted 30 degrees, Trendelenburg position |
front 63 Relief of pressure: (A) pressure on aorta and vena cava caused by
| back 63 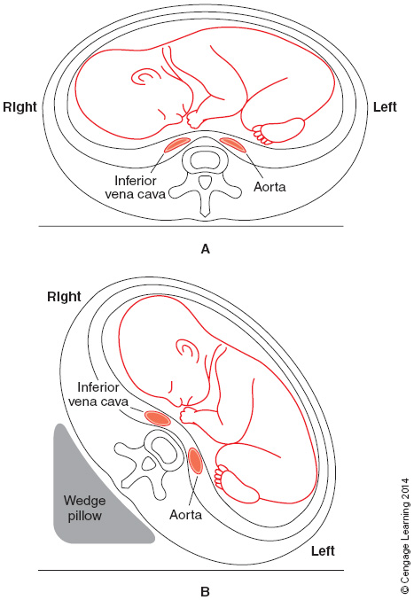 See opposite |
front 64 Degree of function of an immune system that is designed to keep a
| back 64 Immunocompetence |
front 65 Auto immune diseases include | back 65 Multiple sclerosis (debilitating - nervous system)
|
front 66 What drugs are also administered to recipients of organ transplants
| back 66 Immunosuppressant |
front 67 Patients who are receiving antineoplastic agents to combat cancer are ....... | back 67 Immunosuppressed. |
front 68 A cancer that produces painful external and internal lesions;
| back 68 Kaposi’s sarcoma (opportunistic in AIDS patients) |
front 69 Which surgical patient may present with multiple opportunistic
| back 69 AIDS |
front 70 For which patient should the parent(s) or legal guardian should be
| back 70 Patient with Down’s Syndrome |
front 71 What physical traits must be taken into consideration by the
| back 71 Microgenia, muscle hypotonia, a flat nasal bridge, macroglossia, a
|
front 72 Isolation precautions are based on .... guidelines | back 72 Center for Disease Control (CDC) |
front 73 The primary routes of transmission of microorganisms | back 73 Contact: direct or indirect
|
front 74 The wearing of protective attire is mandated by the | back 74 OSHA blood borne pathogens final rule |
front 75 Who requires the wearing of a NIOSH-certified respirator through its
| back 75 CDC |
front 76 What percentage of geriatric patients present with one or more
| back 76 80% |
front 77 What pertains to a disease or other pathological process that occurs
| back 77 Comorbid |
front 78 Studies suggest that 30% to 80% of substance abusers suffer from ....... | back 78 coexisting psychiatric illness |
front 79 The presence of a ......... would benefit the surgical team to
| back 79 counselor or social worker |
front 80 How do physicians often refer to the shorter the response time, the
| back 80 The “Golden Hour” and Trauma System |
front 81 Concept that medical treatment of a trauma victim within the first
| back 81 The "golden hour" |
front 82 What should be given the sooner the better for a heart attack victim,
| back 82 CPR |
front 83 Can meet all needs required for treating trauma patients, including
| back 83 Level I trauma center (Good Sam) |
front 84 Can treat seriously injured or ill patients, but does not have all of
| back 84 Level II trauma center (CDH & Edward) |
front 85 Most often a community or rural hospital in an area that does not
| back 85 Level III trauma center (Bolingbrook) |
front 86 Available in some states, the center can provide advanced trauma life
| back 86 Level IV trauma center |
front 87 An attempt to understand the mechanism of injury and the action and
| back 87 kinematics |
front 88 What results from forces such as deceleration, acceleration,
| back 88 Blunt trauma |
front 89 Examples in which blunt trauma is sustained include | back 89 motor vehicle accidents (MVAs)
|
front 90 What are classified as low velocity or high velocity | back 90 Bullet injuries
|
front 91 A scoring system used to assess the severity of a traumatic wound and
| back 91 Revised Trauma Score |
front 92 What involves the Glasgow Coma Scale, Neuro 3-15 scale, as well as
| back 92 RTS |
front 93 Hair, tissue, and gunpowder residue may be found on the hands of the .... | back 93 victim |
front 94 What should be placed in a bag, and taped, if they do not require
| back 94 Hands |
front 95 Vietnam veterans who have PTSD (1980) symptoms were at the time of
| back 95 post-Vietnam syndrome |
front 96 Epiphyses not closed until age 20 | back 96 Bone growth plate |
front 97 Male genitals | back 97 testes do not descend until 1 year old |
front 98 Bodily fluid | back 98 75% water first post natal week
|
front 99 Caloric requirements for pediatrics | back 99 Much higher than an adult |
front 100 Physical priorities in OR/ER | back 100 Open and maintain airway
|
front 101 Obesity issues/complications | back 101 varicose veins, edema in lower extremities, liver issues, pituitary issues |
front 102 Grounding pad placement on obese patient | back 102 Abdomen, thighs, buttocks |
front 103 Insulin = | back 103 breakdown of sugar |
front 104 Diabetic positioning priority | back 104 Pad all bony prominences |
front 105 Pregnancy and surgery | back 105 2nd trimester "golden window" |
front 106 Asymptomatic | back 106 No symptoms |
front 107 Hearing impaired patient will need | back 107 an interpreter |
front 108 Mycobacterium tuberculosis | back 108 TB |
front 109 Collection of bullets for evidence | back 109 Do not use serrated instruments or powdered gloves |
front 110 Hypothermia | back 110 Below 35 degrees |