Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Tissues
front 1 Simple Squamous Epithelium | back 1 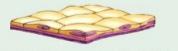 Description: single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm; the siples of the epithelia Function: allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in the sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae. Location: Kidney glomeruli; air sacs of lungs; lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels; lining of ventral body cavity (serosae) |
front 2 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium | back 2 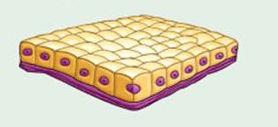 Description: single layer of cube-like cells with large, spherical central nuclei Function: secretion and absorption Location: kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface |
front 3 Simple Columnar Epithelium | back 3  Description: single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells bear cilia; layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells) Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cell) by ciliary action. Location: non ciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus. |
front 4 Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium | back 4 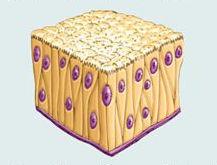 Description: single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels; may contain mucus-secreting goblet cells and bear cilia. Function: secretes substances, particularly mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action Location: non ciliated type in male's sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract. |
front 5 Stratified Squamous Epithelium | back 5 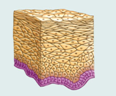 Description: thick membrane composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are flattened (squamous); in the keratinized type, the surface cels are full of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the more superficial layers. Function: protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion Location: non keratinized type forms the moist lining of the esophagus mouth, and vagina; keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane. |
front 6 Transitional Epithelium | back 6 Description: resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome shaped or squamous-like, depending on degree of organ stretch Function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine Location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra. |
front 7 Skeletal Muscle | back 7 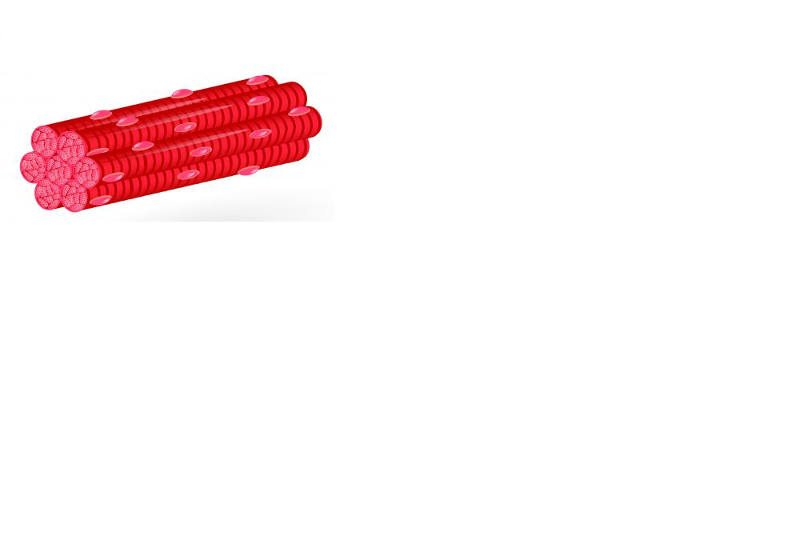 Description: long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells; obvious striations Function: voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation of the environment; facial expression; voluntary control Location: in skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally skin |
front 8 Cardiac Muscle | back 8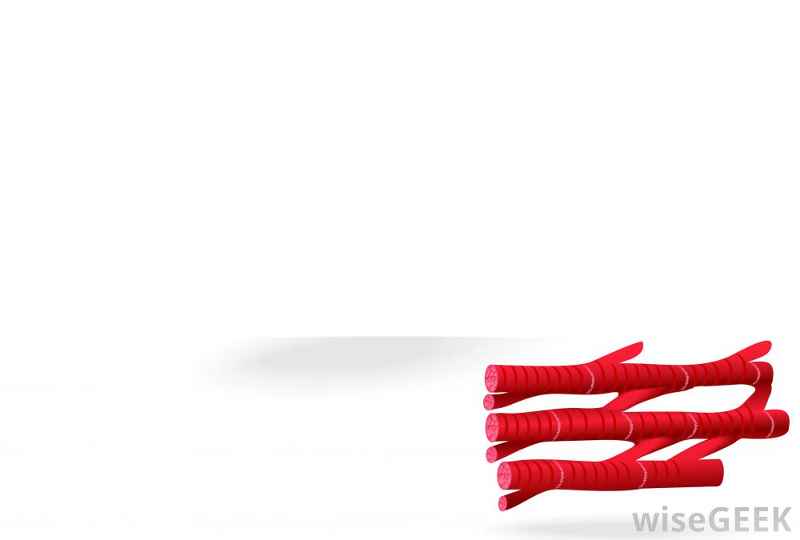  Description: branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigitate at specialized junctions called intercalated discs Function: as it contracts, cardiac muscle propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control Location: the walls of the heart |
front 9 Smooth Muscle | back 9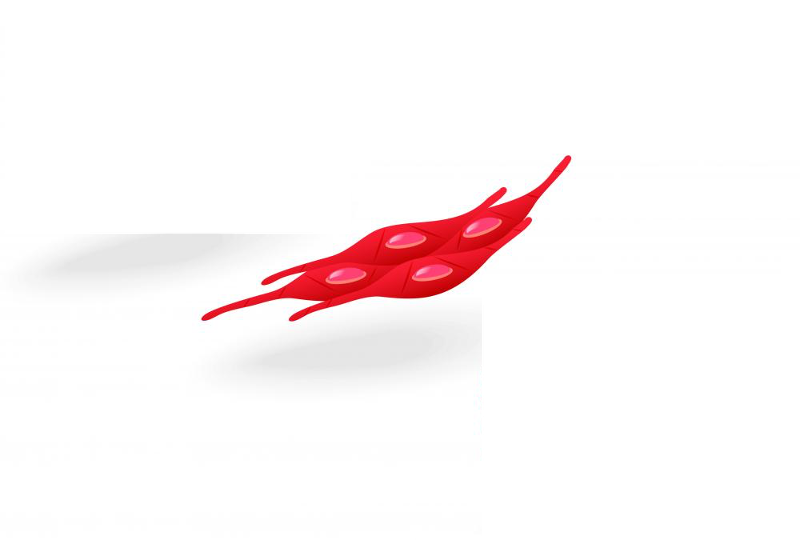  Description: spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets Function: propels substances (foodstuffs, urine) or a baby along internal passageways; involuntary control Location: mostly in the walls of hollow organs |
front 10 Nervous Tissue | back 10 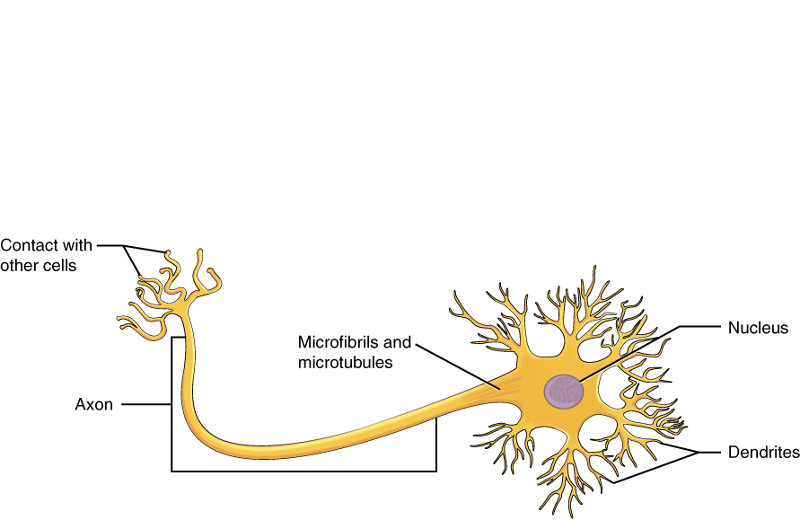 Description: neurons are branching cels; cell processes that may be quite long extend from the nucleus-containing cell body; also contributing to nervous tissue are non excitable supporting cells Function: neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands); supporting cells support and protect neuron Location: brain, spinal cord, and nerves |
front 11 Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue Areolar | back 11 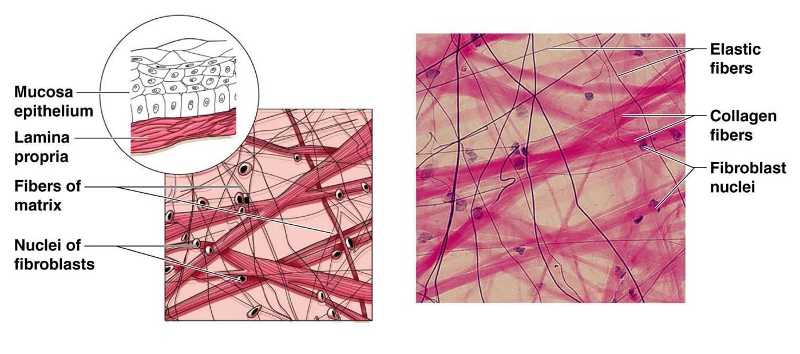 Description: Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells Function: Wraps and cushions organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid Location: Widely distributed under epithelia of body, e.g. forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs; surrounds capillaries. |
front 12 Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue Adipose | back 12 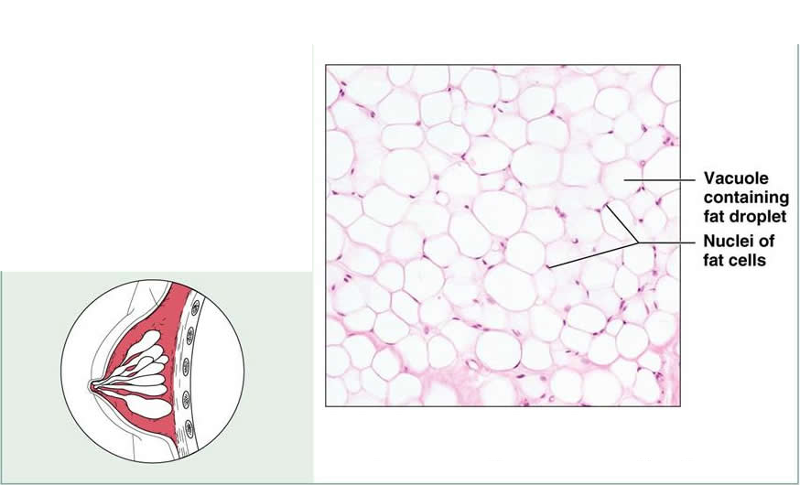 Description: Matrix as in areolar, but very sparse; closely packed adipocytes, or fat cells, have nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet Function: Provides reserve fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs Location: under skin; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts |
front 13 Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue Reticular | back 13 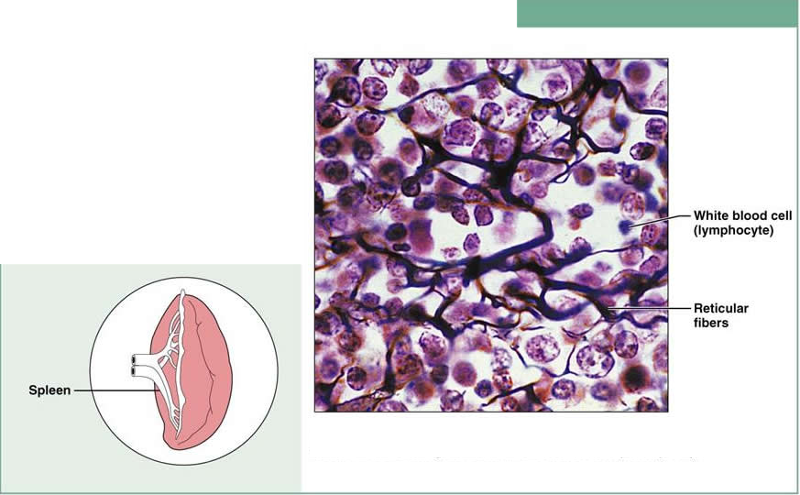 Description : Network of reticular fibers in a typical loose ground substance; reticular cells lie on the network Function: Fibers form a soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types, including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages Location: lymphoid organs (lymph node, bone marrow, and spleen) |
front 14 Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Regular | back 14 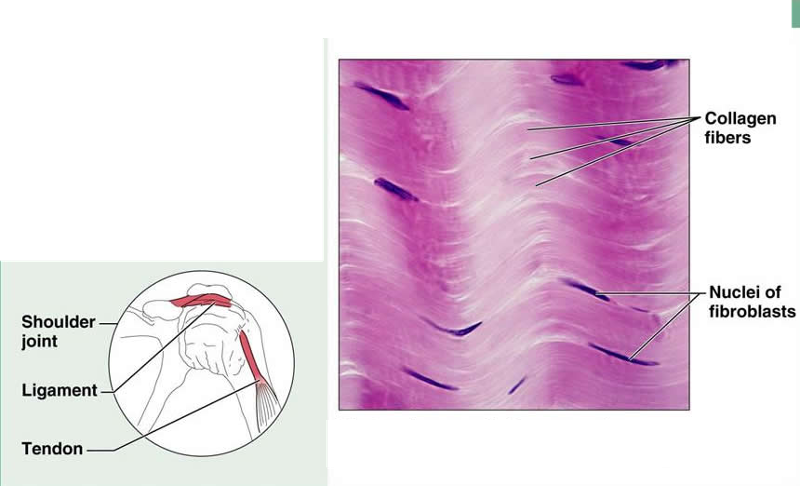 Description: Primarily parallel collagen fibers; a few elastic fibers; major cell type is the fibroblast Function: Attaches muscles to bones or to other muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction Location: Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |
front 15 Connective Tissue Proper: Elastic | back 15 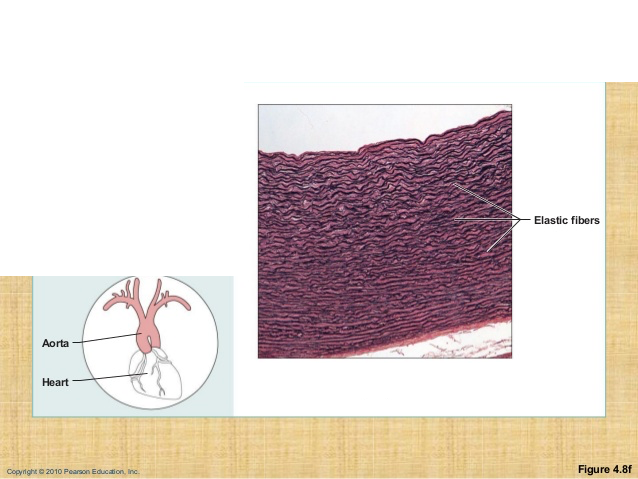 Description: Dense regular connective tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers Function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsating flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration Location: walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with the vertebral column; within the walls of the bronchial tubes. |
front 16 Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Irregular | back 16 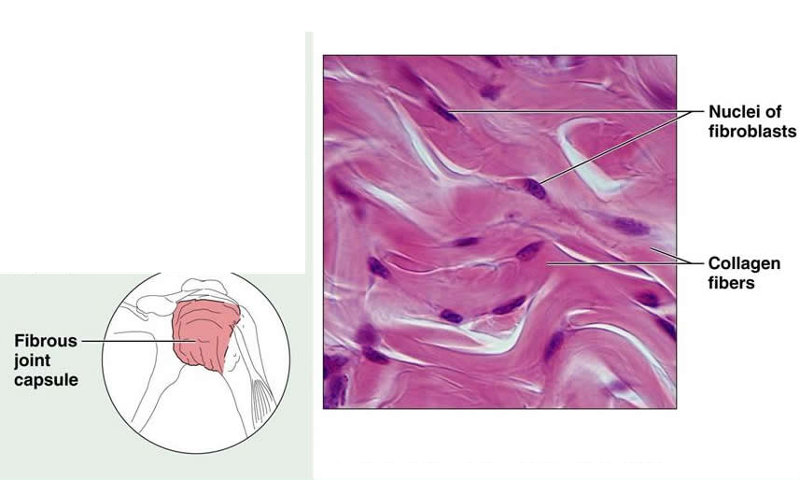 Description: primarily irregularly arranged collagen fibers; some elastic fibers; major cell type is the fibroblast Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength Location: fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract |
front 17 Cartilage: Hyaline | back 17 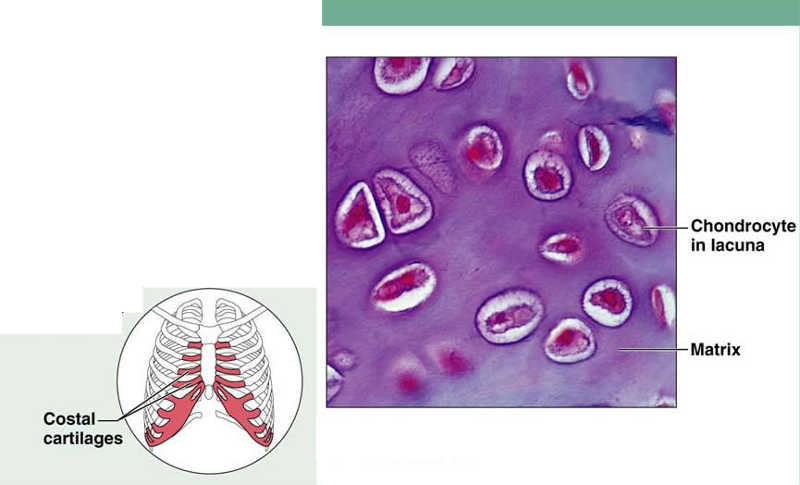 Description: amorphous but firm matrix; collagen fibers forms an imperceptible network; chondroblasts produce the matrix and, when mature (chondrocytes), lie in lacunae Function: supports and reinforces; serves as resilient cushion; resists compressive stress Location: forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms costal cartilages of the ribs; cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx |
front 18 Cartilage: Elastic | back 18 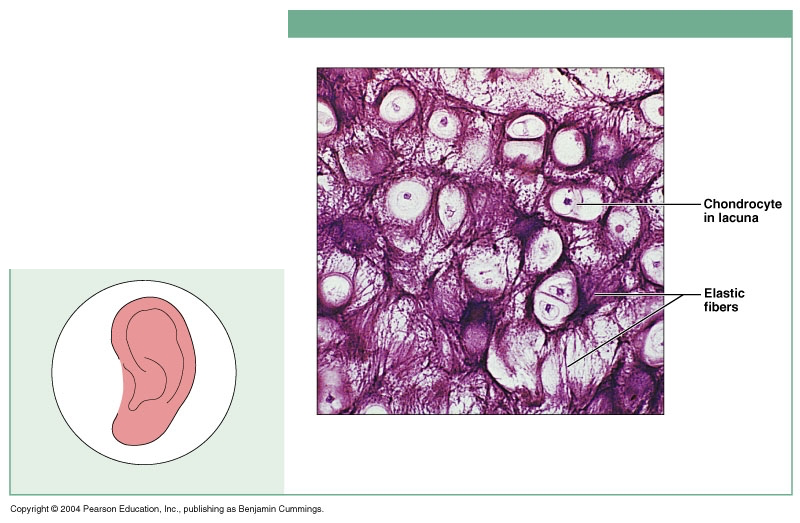 Description: similar to hyaline cartilage, but more elastic fibers in matrix Function: maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility Location: supports the external ear (auricle); epiglottis |
front 19 Cartilage: Fibrocartilage (Fibrous) | back 19 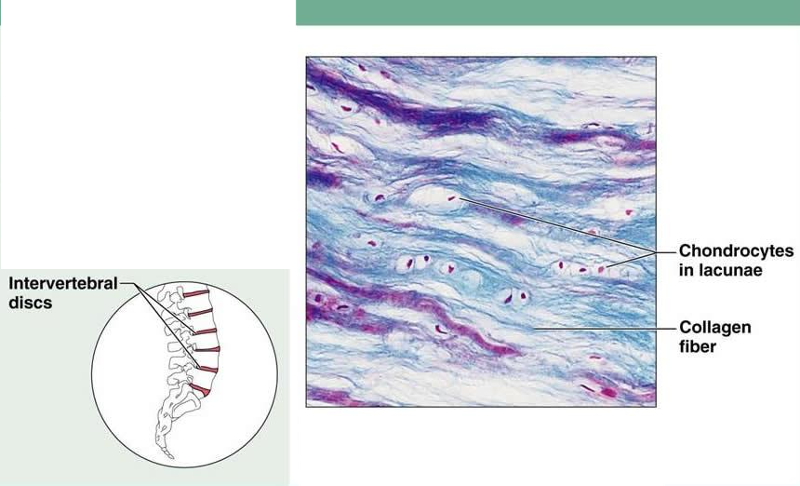 Description: Matrix similar to but less firm than matrix in hyaline cartilage; thick collagen fibers predominate Function: tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock Location: intervertebral disc; pubic symphysis; disc of knee joint |
front 20 Bones (Osseous Tissue) | back 20 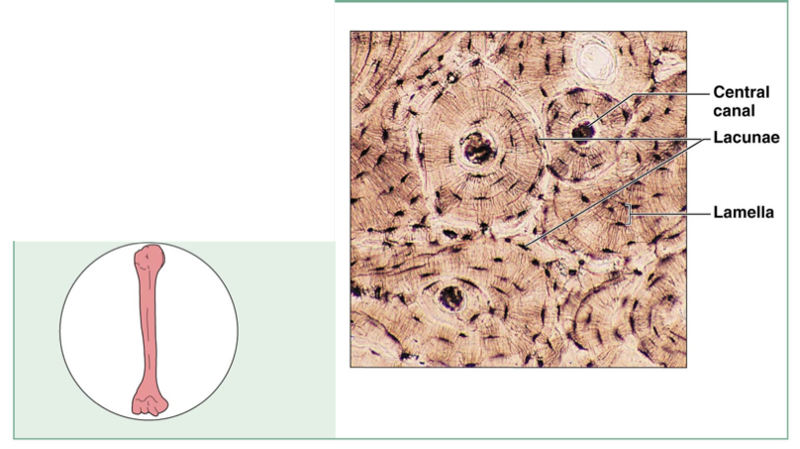 Description: hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in lacunae. Very well vascularized Function: bones support and protects (by enclosing); provides lavers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) Location: bones |
front 21 Blood | back 21 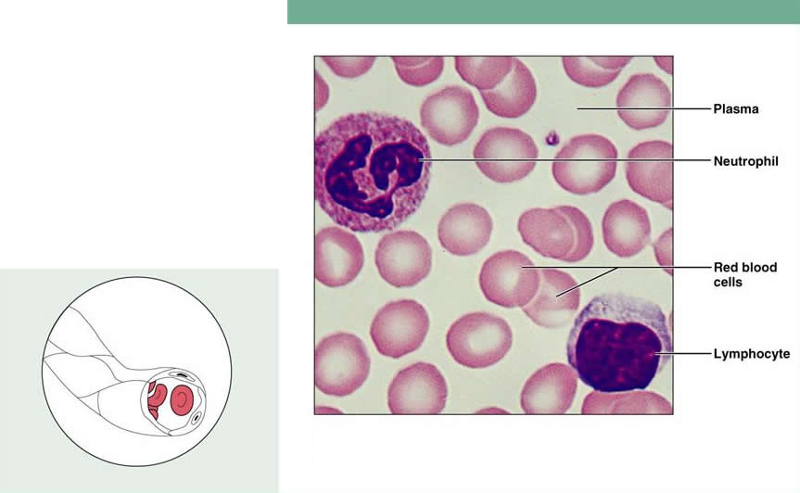 Description: red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma) Function: transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances Location: contained within blood vessels |