Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Nutrition Final Exam Review
front 1 Health | back 1
|
front 2 Wellness | back 2
|
front 3 Lifestyle | back 3
|
front 4 Primary Prevention | back 4
|
front 5 Secondary Prevention | back 5
|
front 6 Essential Nutrients | back 6
|
front 7 Nonessential Nutrients | back 7
|
front 8 Dietary Standards | back 8
|
front 9 Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) | back 9
|
front 10 Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) | back 10
|
front 11 Adequate Intake (AI) | back 11
|
front 12 Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) | back 12
|
front 13 Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) | back 13
|
front 14 daily kcal intake for carbs | back 14
|
front 15 daily kcal intake for saturated fats | back 15
|
front 16 daily kcal intake for lipids/fats | back 16
|
front 17 daily kcal intake for proteins | back 17
|
front 18 Estimated Energy Requirement (EER) | back 18
|
front 19 Nutrient Density | back 19
|
front 20 Overnutrition | back 20
|
front 21 Malnutrition | back 21
|
front 22 Undernutrition | back 22
|
front 23 Four Themes of MyPlate | back 23
|
front 24 Variety (MyPlate Theme) | back 24
|
front 25 Proportionality (MyPlate Theme) | back 25
|
front 26 Moderation (MyPlate Theme) | back 26
|
front 27 Activity (MyPlate Theme) | back 27
|
front 28 Food Labels | back 28
|
front 29 Metabolism | back 29
|
front 30 Anabolism | back 30
|
front 31 Catabolism | back 31
|
front 32 GER (gastroesophagel reflux) | back 32
|
front 33 Strategies to prevent GER | back 33
|
front 34 3 Elements found in Carbohydrates | back 34
|
front 35 Ratio of elements in Carbs | back 35
|
front 36 Monosaccharides (simple carbohydrates) | back 36 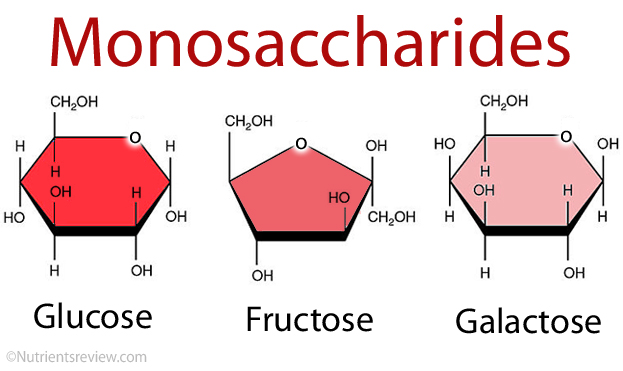
|
front 37 Disaccharides (simple carbohydrates) | back 37
|
front 38 Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates) | back 38
|
front 39 Glycogen | back 39
|
front 40 Glycogenesis | back 40
|
front 41 Carbohydrates | back 41
|
front 42 Blood glucose homeostasis | back 42
|
front 43 Glycogenolysis | back 43
|
front 44 Glycolysis | back 44
|
front 45 Gluconeogenesis | back 45
|
front 46 Ketone Bodies | back 46
|
front 47 Glucose | back 47
|
front 48 Fructose | back 48
|
front 49 Galactose | back 49
|
front 50 Sucrose | back 50
|
front 51 Lactose | back 51
|
front 52 Maltose | back 52
|
front 53 Starches | back 53
|
front 54 Fiber | back 54
|
front 55 Blood Glucose | back 55
|
front 56 Ketoacidosis/Ketosis | back 56
|
front 57 Insulin | back 57
|
front 58 Glucagon | back 58
|
front 59 Somatostatin effect on blood glucose | back 59
|
front 60 Epinephrine effect on the liver | back 60
|
front 61 Steroid Hormones (Insulin Inhibitor) effect on blood glucose | back 61
|
front 62 Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH) effect on blood glucose | back 62
|
front 63 Thyroid Hormones effect on blood absorption | back 63
|
front 64 Growth Hormones effect on blood glucose | back 64
|
front 65 Glycemic Index | back 65
|
front 66 Glycemic Load | back 66
|
front 67 What happens to fructose in the liver? | back 67
|
front 68 What happens to starch in the digestive tract? | back 68
|
front 69 Insoluble FIber | back 69
|
front 70 Soluble Fiber | back 70
|
front 71 Health Effects of Dietary Fiber | back 71
|
front 72 Since the 1940s ______ grains are generally enriched with niacin, folate, thiamine, riboflavin, and iron. | back 72 refined |
front 73 ______/______ grains are sources of magnesium, riboflavin, niacin, thiamin, vitamin B6, zinc, and some protein that are k=lost when refined. | back 73 whole/unrefined |
front 74 Palatibility (Lipids) | back 74
|
front 75 Satiety (Lipids) | back 75
|
front 76 Satiation (Lipids) | back 76
|
front 77 Emulsifier | back 77
|
front 78 Lipoproteins | back 78
|
front 79 Lecithin | back 79
|
front 80 Triglycerides (structure) | back 80
|
front 81 How can you tell the difference between carbohydrates and triglycerides by looking at the chemical formula? | back 81 no data |
front 82 What elements are found in triglycerides? | back 82
|
front 83 Physiologic Function of Triglycerides | back 83
|
front 84 Function(s) of Phospholipids | back 84
|
front 85 Function(s) of Sterols | back 85
|
front 86 What elements are found in fatty acids? | back 86
|
front 87 Cholesterol | back 87
|
front 88 How many carbons are found in glycerol? | back 88
|
front 89 Saturated Fatty Acid | back 89 
|
front 90 Monounsaturated Fatty Acid (MUFA) | back 90 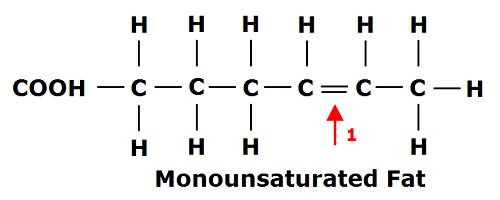
|
front 91 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA) | back 91 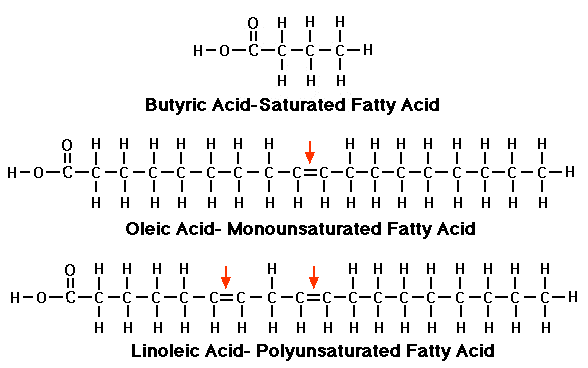
|
front 92 What two categories of polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential? | back 92
|
front 93 Americans consume a large amount of Omega-____. | back 93 omega-6 (linoleic) |
front 94 Americans consumption of Omega-___ is low. | back 94 omega-3 (linolenic) |
front 95 Types of Omega-_ help prevents heart disease. | back 95 omega-3 (linolenic) |
front 96 Rich sources of Omega-__ are deep water fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines, and herring. Omega-__ can also be obtained from plant sources such as canola oil, some nuts such as walnuts, soybean and soybean oils, and extra virgin or virgin oils. | back 96 omega-3; omega-3 |
front 97 Hydrogenation | back 97
|
front 98 Dietary Sources of Saturated Fatty Acids | back 98
|
front 99 Catabolism of Lipids | back 99
|
front 100 Acetyl CoA (Lipids) | back 100
|
front 101 Lipogenesis | back 101
|
front 102 When found in excess, glucose and amino acids are converted to what form of lipid? | back 102
|
front 103 Lipid metabolism is primarily regulated by _______, ____ _____, and ______ ______ ______. | back 103 insulin; growth hormones; adrenal cortex hormones |
front 104 Role of Bile Emulsification (Lipids) | back 104
|
front 105 Chylomicrons | back 105
|
front 106 Most Americans consume between _______ and _______ % of total energy as fat. How does this compare to the suggested ADMR? | back 106
|
front 107 Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL) | back 107
|
front 108 Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) | back 108
|
front 109 Protease | back 109
|
front 110 Amino Acids (20) | back 110
|
front 111 Essential Amino Acids (9) | back 111
|
front 112 Nonessential Amino Acids (11) | back 112
|
front 113 Amino Acid Pool | back 113
|
front 114 Functions of Proteins | back 114
|
front 115 Complete Protein | back 115
|
front 116 Incomplete Protein | back 116
|
front 117 Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM) | back 117 no data |