Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
final exam
front 1 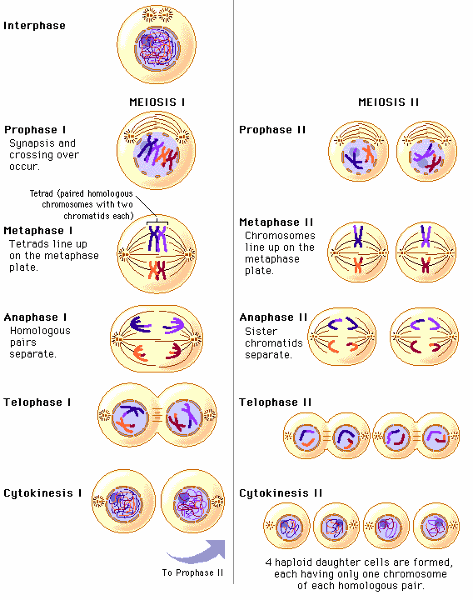 What’s the difference between mitosis and meiosis? | back 1 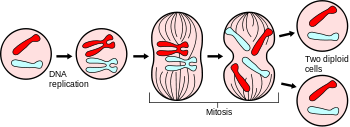 In mitosis two identical sets of daughter nuclei, -46 Meiosis number of chromosomes is divided into half- 23 |
front 2 What are the steps in oocyte production? | back 2 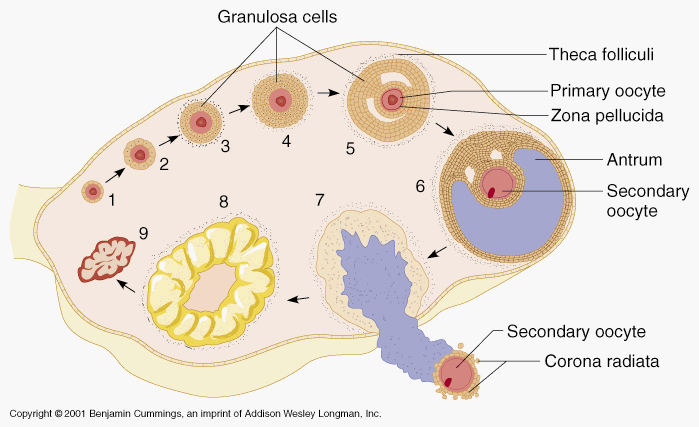 germ cells produce -->> primordial germ cell (PGC),-->>> mitosis, forming oogonia. oogenesis, the oogonia -->> primary oocytes.--->> SECONDARY |
front 3 What are the steps in spermatocyte production? | back 3 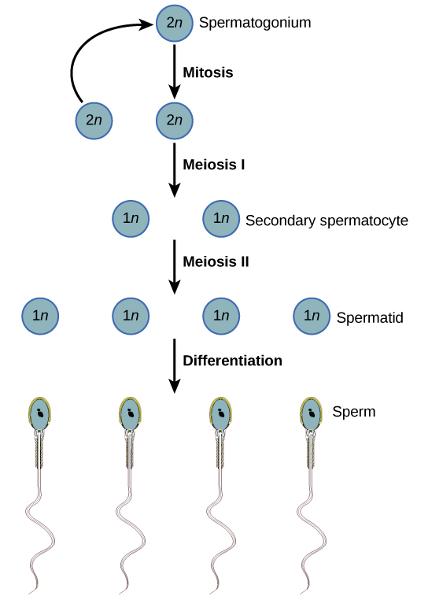 interphase before meiosis I, synapsis before the first meiotic division. meiosis II, the two daughter cells go through a second division to yield four cells containing a unique set of 23 single chromosomes into four sperm cells. |
front 4 What are the three steps of urine formation and what is excreted and reabsorbed? | back 4 
Filtration
Reabsorption
( peritubular
copillaries). reabsorbed are water,
glucose and other nutrients, and sodium (Na+) ions |
front 5 Trace the flow of blood and the flow of filtrate/urine through the kidney. | back 5 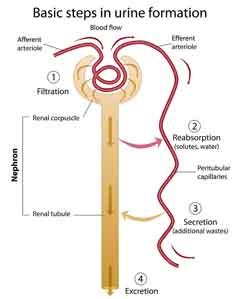
1-Glomerulus and
Bowman's capsule: |
front 6 What ions are predominant in extracellular fluid vs. intracellular fluid? | back 6 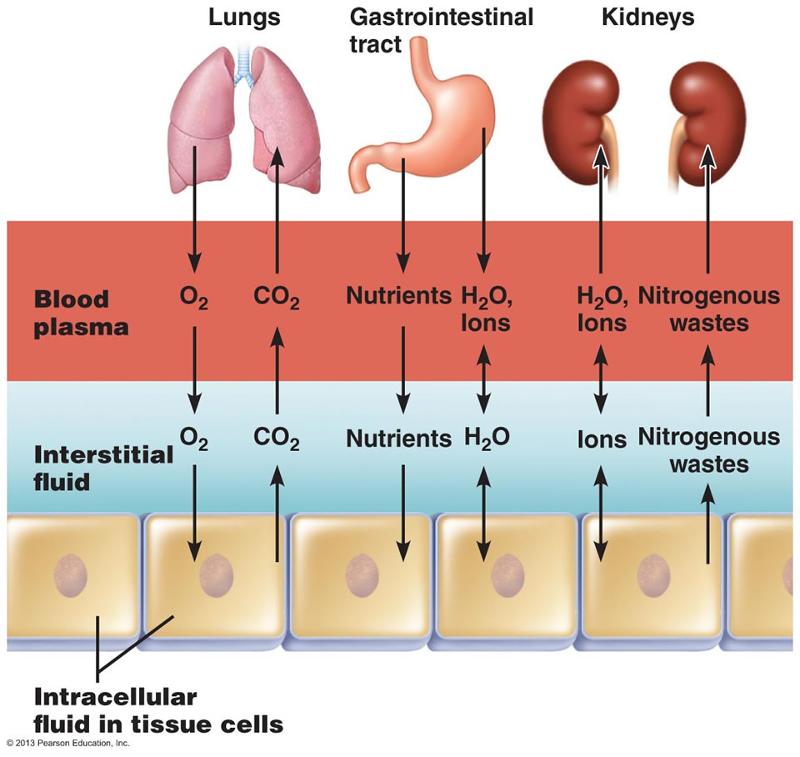 Extracellular fluids sodium, calcium, chloride and bicarbonate ions
Intracellular fluids potassium, magnesium,
phosphate, and sulfate ions |
front 7 What are the different causes of Respiratory acidosis and alkalosis? | back 7 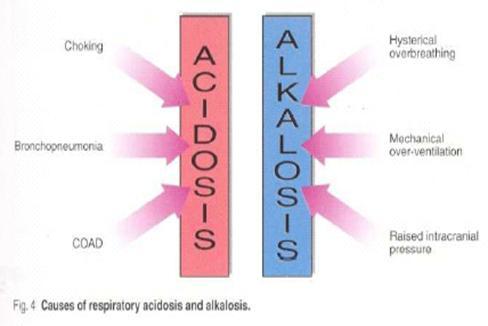 alkalosis pH above acidosis pH below Respiratory alkalosis isn’t enough carbon diox ide
Respiratory Acidosis too much CO2
|
front 8 What is normal body pH range? | back 8 7.35 to 7.45 |
front 9 What causes the flow of filtrate out of the glomeruli? | back 9 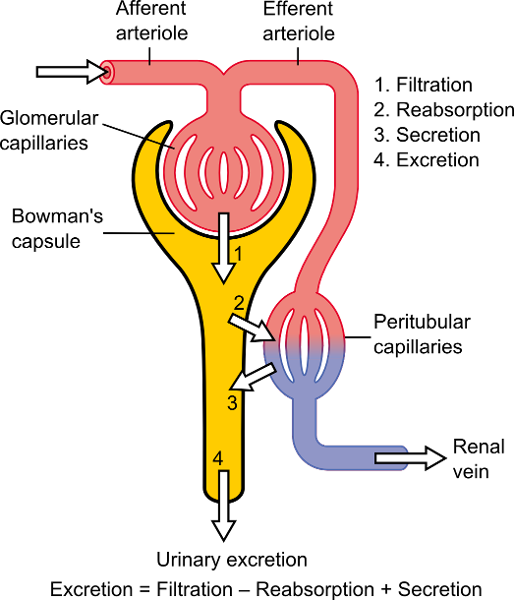 HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE |
front 10 What is Boyle’s law? | back 10 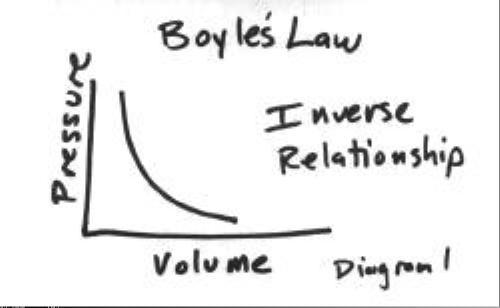 INVERSELY RELATED TO PRESSURE |
front 11 What is Frank-Starling law? | back 11 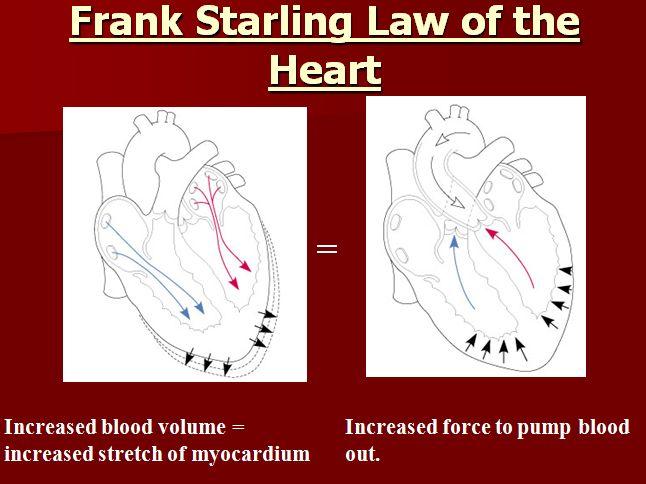 EQUAL IN / EQUAL OUT |
front 12 What is Dalton’s law and how does it apply to respiration? | back 12 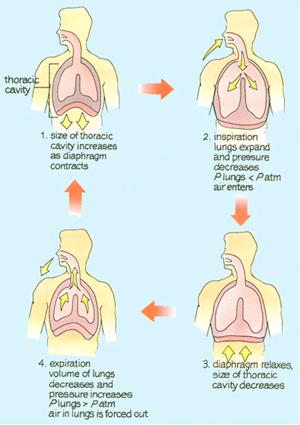 Total pressure=partial pressure gases |
front 13 Production, activation and function of digestive enzymes and hormones including gastrin, pepsinogen, pepsin, cholecystokinin, trypsin, trypsinogen, chymotrypsin, amylase. | back 13  AMYLASE - a carbohydrase - an enzyme that breaks down starch into glucose
gastrin
is secreted by the stomach cells to regulate the production of gastric
juices.
PEPSIN Pepsin is an enzyme used to partially hydrolyze protein. Pepsin is released in an inactive form Pepsinogen. pepsinogen reacts with HCl to form pepsin cholecystokinin -a polypeptide hormone secreted in the small intestine, stimulates gallbladder contraction and secretion of pancreatic enzymes. Trypsin and Chymotrypsin are enzymes that break bonds next to specific amino acids breaks proteins into amino acids in the DUODENUM |
front 14 Summarize the correct sequence from the formation of a drop of urine to the elimination from the body. | back 14 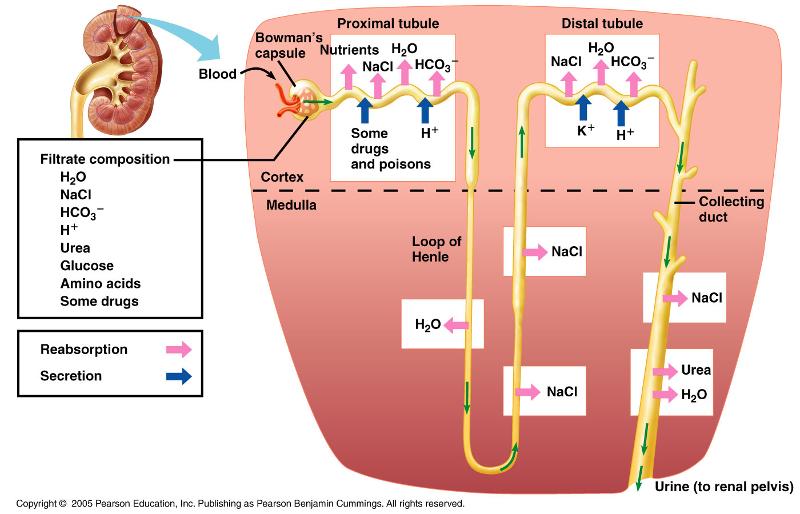 Formation of urine Blood leaves the heart via the aorta and enters the renal artery where it flows into the interlobar arteries. From there it branches off to the arcuate artery, which curves along the outer edge of the pyramids. From the arcuate artery, blood flows to the cortical radiate arteries then into the afferent arteriole. From the afferent arteriole, it goes into the : glomerulus for filtering. ADH- DCT DISTAL CONVELATED TUBE all waste goes to the proximal convoluted tubule, while blood that will stay in the body goes to the efferent arteriole. More blood filtering takes place in the peritubular capillaries. Blood that will stay in the body exits through the cortical radiate veins, then goes into the arcuate vein, then into the interlobar vein, then the renal vein, then back to the heart via the inferior vena cava. At the same time this is happening, the waste that was sent to the proximal convoluted tubule travels down the descending loop of henle, then up the ascending loop of henle to the distal convoluted tubule where it is dumped into the collecting duct. From the collecting duct, it goes into the ureters, travels to the bladder, and then leaves the body via the urethra. |
front 15 What is aldosterone? | back 15 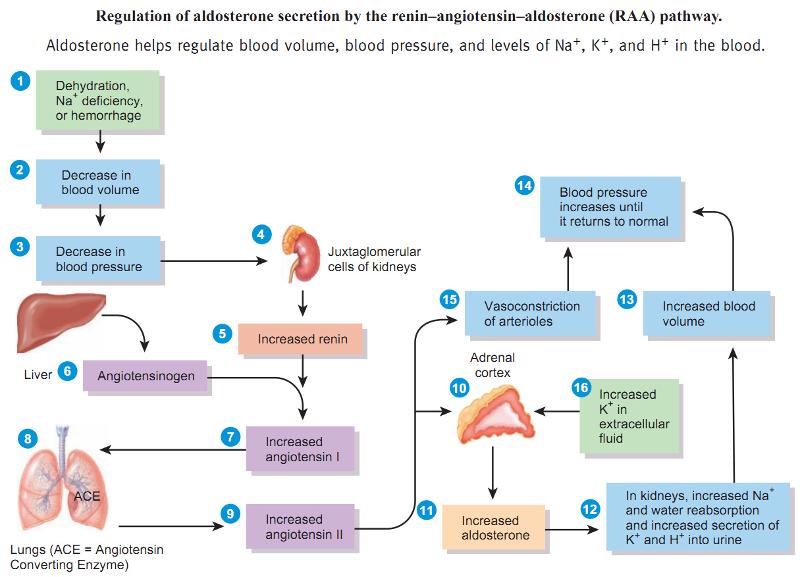 A corticosteroid hormone that stimulates absorption of sodium by the kidneys and so regulates water and salt balance (LH/ FSH) |
front 16 What is renin? | back 16 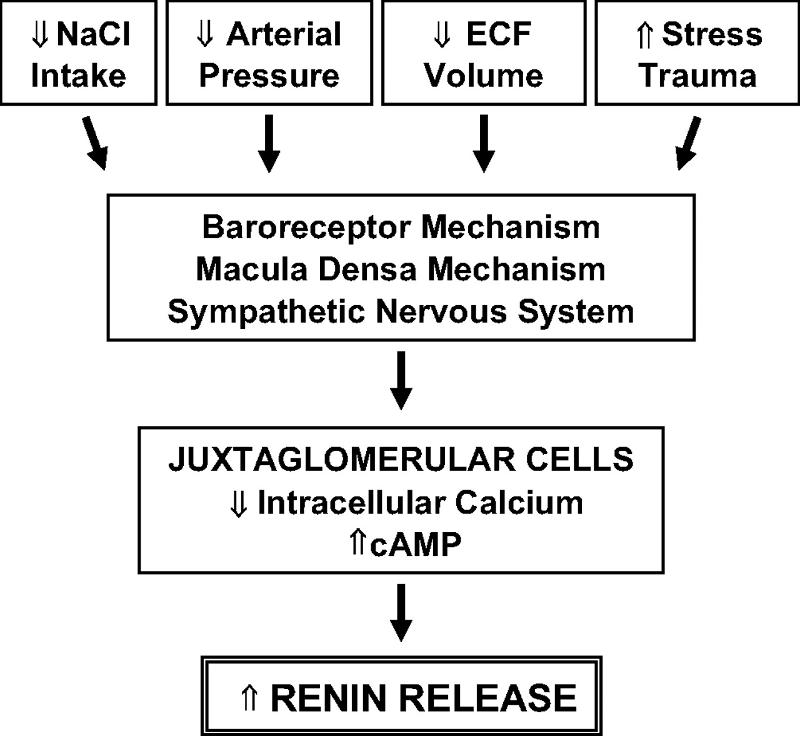 An enzyme secreted by and stored in the kidneys that promotes the production of the protein angiotensin (juxtaglomerular apparatus) |
front 17 WHAT IS ANP ? | back 17 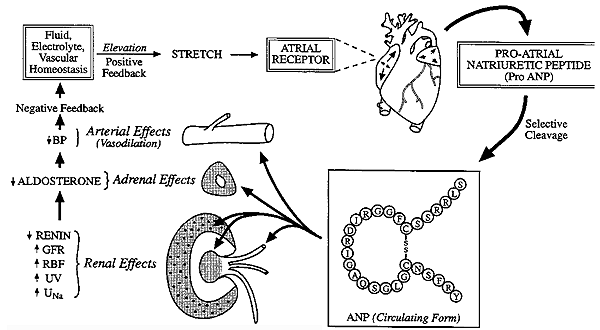 Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), (polypeptide) ANP acts to reduce the water, sodium and adipose loads on the circulatory system, thereby reducing blood pressure. |
front 18 What is ADH? | back 18 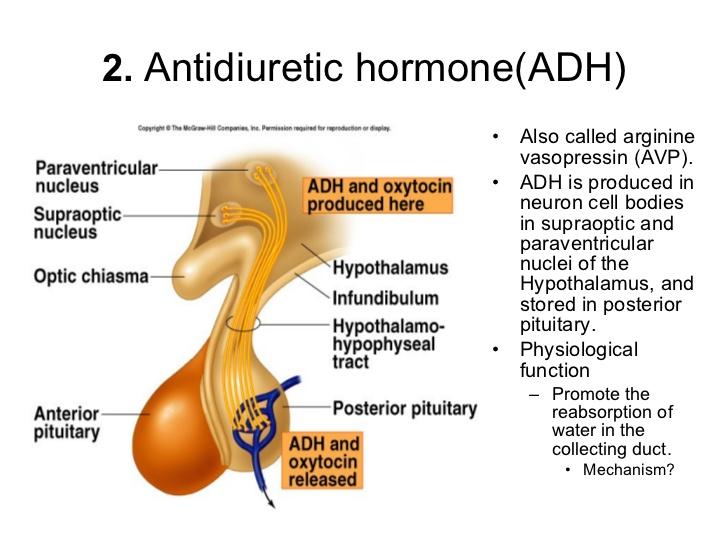 water regulator in the body. |
front 19 What are 2 ways you could check someone’s renal health? | back 19 Albuminuria-to-creatinine ratio (ACR). Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) |
front 20 If you wanted to create a more concentrated urine, what would your body do? | back 20 ADH causes the DCT and collecting ducts to be more permeable to water |
front 21 What are the effects of angiotensin II? | back 21 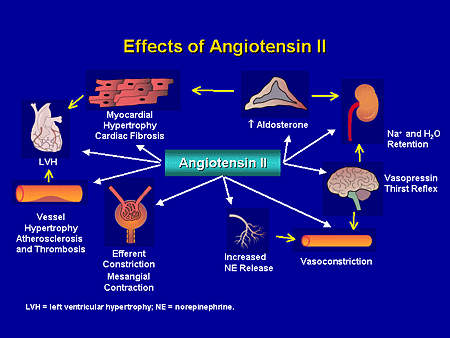 1. Constricts arteriolar smooth muscle, causing map to rise 2. stimulates reabsorption of Na+ Triggers adrenal cortex to release aldosterone Aldosterone increases na+ reabsorption 3. Stimulates hypothalamus to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and activates thirst center ADH - causes water to be retained 4. Constricts efferent arterioles, decreasing capillar hydrostatic pressure and increasing fluid reabsorption 5. Causes glomerular cells to contract, decreasing surface area available for filtration |
front 22 Explain the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism. What is its goal? | back 22 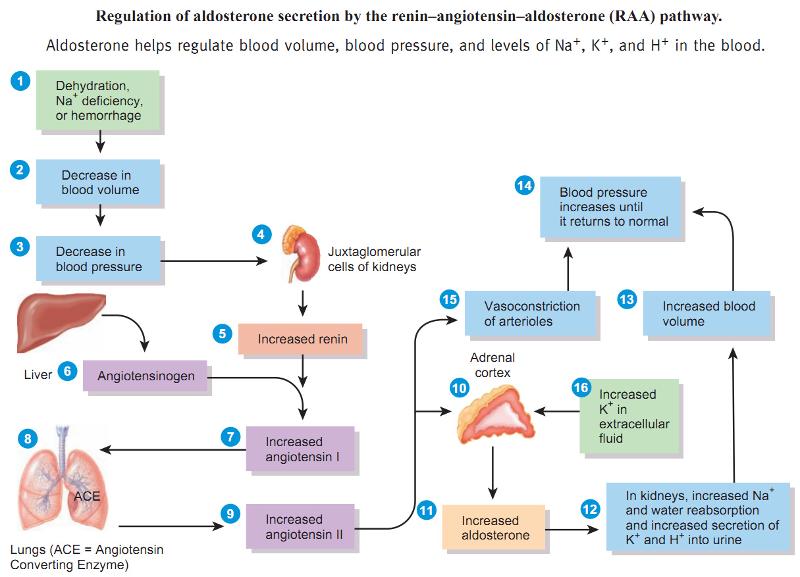 is a hormone system regulating blood pressure (BP) and fluid volume, a third major participant in this system called aldosterone. The level of activity of the renin-angiotensin system determines and is determined by the body’s BP |
front 23 In the loop of Henle, how does the descending & ascending loop differ in their permeability to water & sodium? | back 23 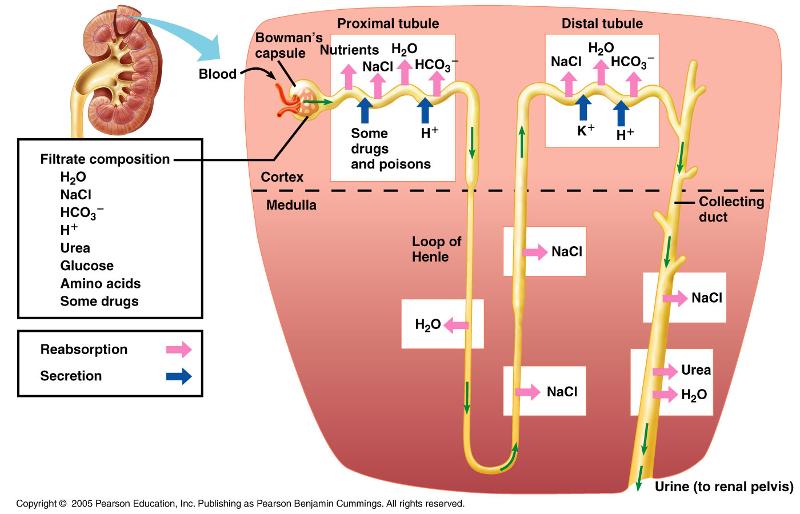 descending (NO SALT): impermeable to Na+, but permeable to water/ h2o reabsorbed ascending (NO H20) - permeable to na+ but impermeable to water : na+, k+, Cl- |
front 24 What substances move through passive reabsorption? | back 24 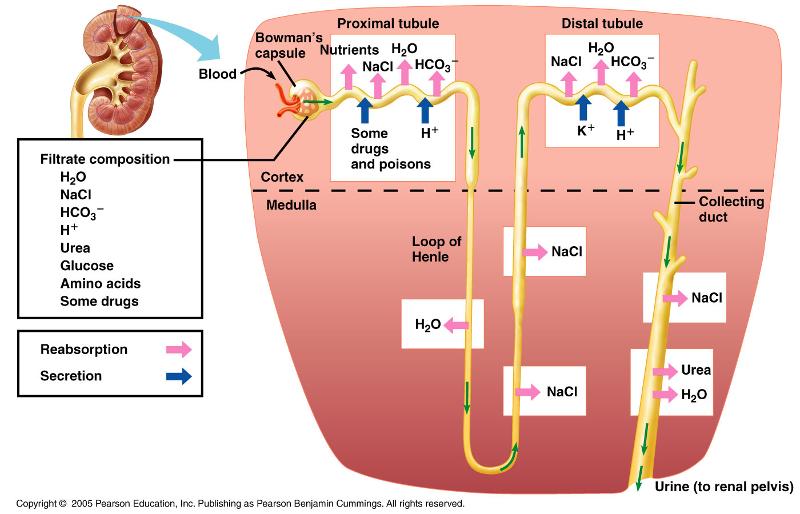
-H20 is highly permeable |
front 25 In tubular reabsorption, substances are returned to the __________ from the ____________. | back 25 Distal convoluted tube Proximal convoluted tubule (pct) |
front 26 Why is pressure important in glomerular filtration? | back 26 The pressure helps to force liquid out of the blood. |
front 27 What are the 3 steps in forming urine? Where does each occur? | back 27 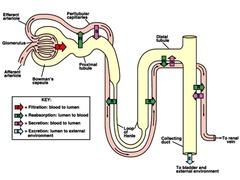 1. Glomerular filtration 2. tubular reabsorption : primarily in the proximal tubule 3. tubular secretion : distal tubules |
front 28 What are the collecting ducts? | back 28 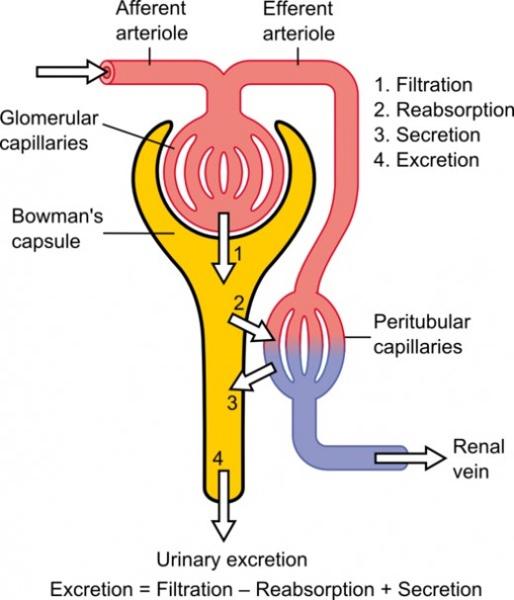 receive filtrate from many nephrons principle cells of collecting ducts - help maintain water and salt balance |
front 29 Name/describe the parts and processes of a nephron. | back 29 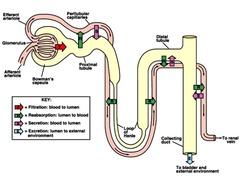 Glomerulus - tufts of capillaries; filtration Bowman's capsule - enlarged, cup-shaped capsule surrounding glomerulus - collects filtrate Proximal convoluted tubule (pct) - tubular reabsorption Loop of henle - Sodium (Na+) and water balance Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) - tubular secretion |
front 30 What are mesangial cells? | back 30 Immunoreactive transformed smooth muscle cells that can contract in response to circulating vasoactive substances impeding glomerular blood flow and filtration. |
front 31 What are the functions of the cells of JGA? | back 31 Granular cells (renin) macula densa (monitor flow rate of filtrate.) |
front 32 What are the layers of the glomerular filtration barrier? | back 32 Leaky endothelium (pores/fenestrae) basement membrane (porous matrix of negatively charged glycoproteins) podocytes (specialized epithelial cells with interdigitating pedicels separated by filtration slits). |
front 33 What substances filter easily? What substances don't filter? What substances filter moderately? | back 33 Water, urea, glucose and inulin. Albumin and hemoglobin. Myoglobin. |
front 34 The electrolytes of greatest importance to | back 34 sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, phosphate, bicarbonate, and hydrogen ions |
front 35 Posterior pituitary hormones and effect on the kidneys. | back 35 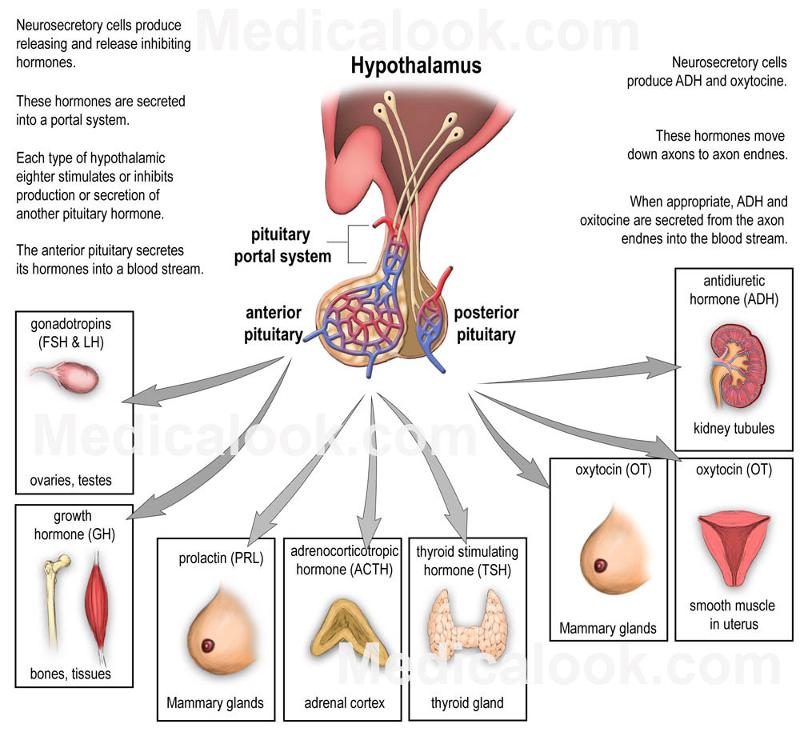 ADH antidiuretic hormone, which helps control body water balance through its effect on the kidneys and urine output oxytocin, which triggers the contractions of the uterus that occur during labor. |
front 36 Anterior pituitary hormones and effect on reproductive organs. | back 36 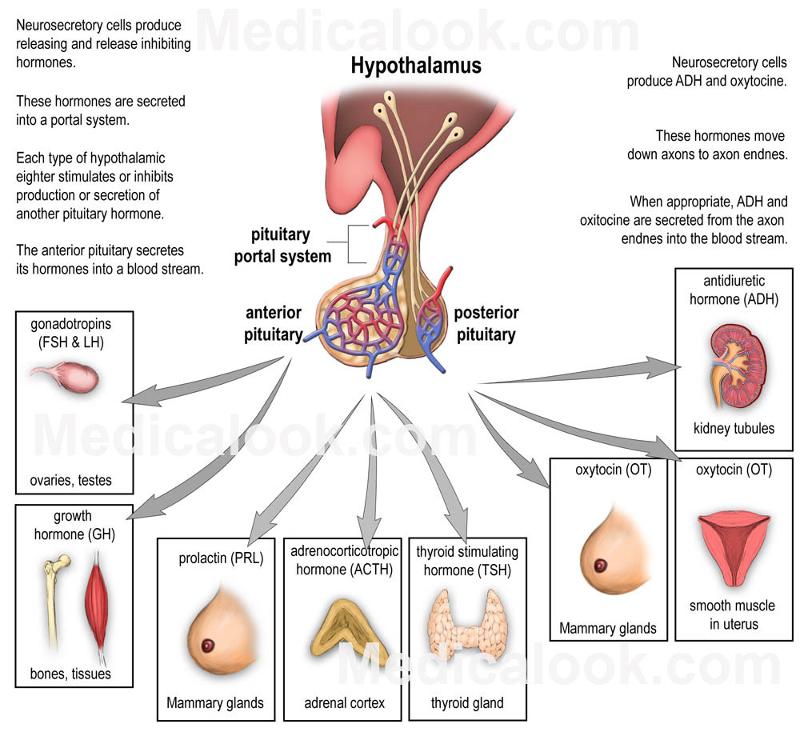 growth hormone, which stimulates the growth of bone and other body tissues and plays a role in the body's handling of nutrients and minerals prolactin, which activates milk production in women who are breastfeeding thyrotropin, which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones corticotropin, which stimulates the adrenal gland to produce certain hormones hormones that signal the ovaries and testes to make sex hormones. The pituitary gland also controls ovulation and the menstrual cycle in women. |
front 37 How do the kidneys control blood pressure and pH? | back 37 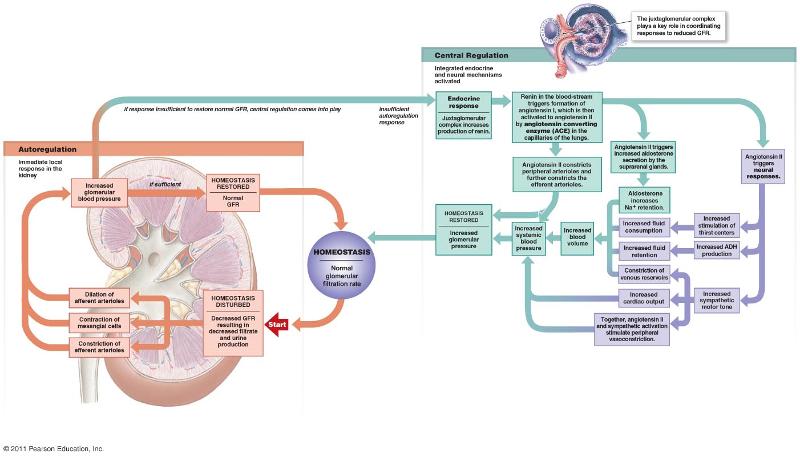 buffers dissolved in the blood. remove excess chemicals remove H+ ions |
front 38 How do the lungs control pH? | back 38 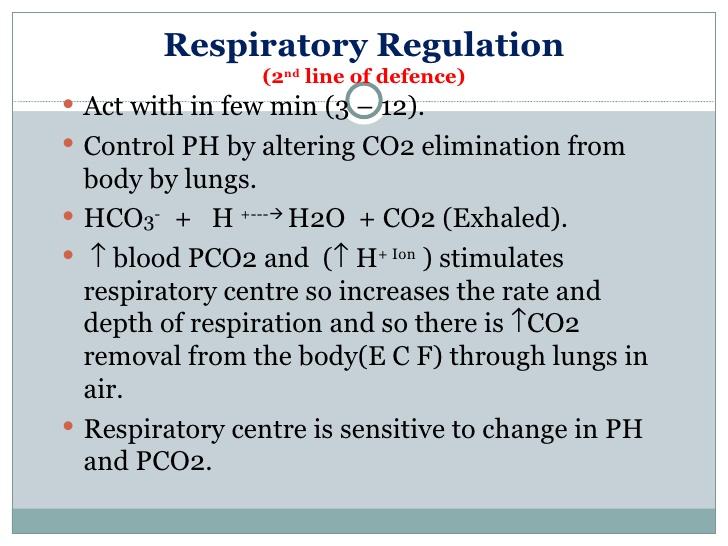 increased-breathing counteract the pH-lowering effects of exercise by removing CO 2, & pH buffer |
front 39 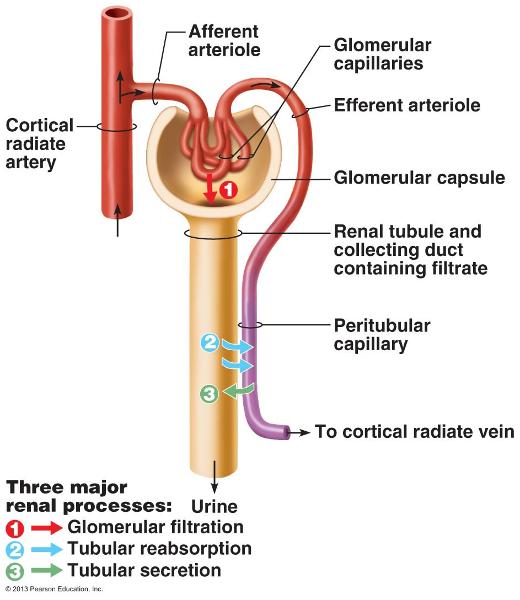 Process of urine formation and micturition | back 39 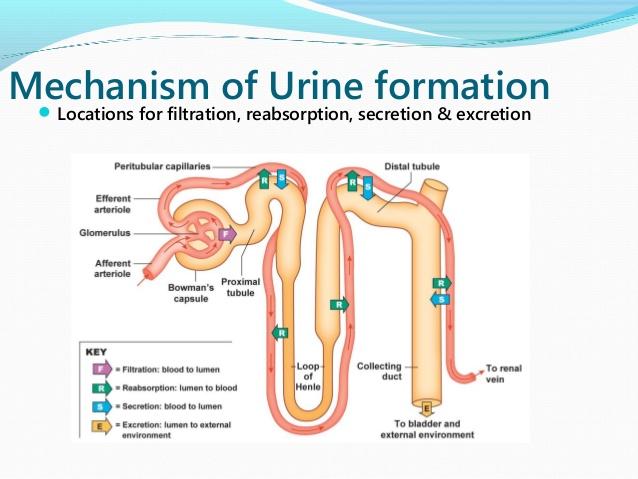
|
front 40 Flow of blood through the veins | back 40 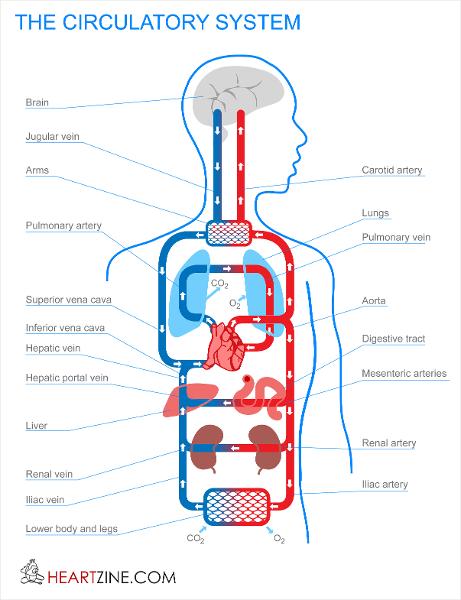 superior and inferior vena cava, -->>>right atrium-->> tricuspid valve --> right ventricle -->>pulmonic valve-->> pulmonary artery-->> lungs -->> pulmonary veins -->> left atrium -->>> mitral valve-->> left ventricle -->> aortic valve -->>> aorta-->>>> body |
front 41 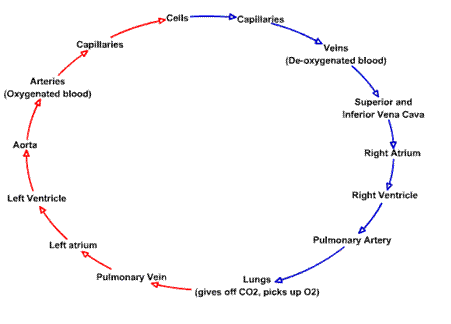 Flow of blood through the arteries | back 41 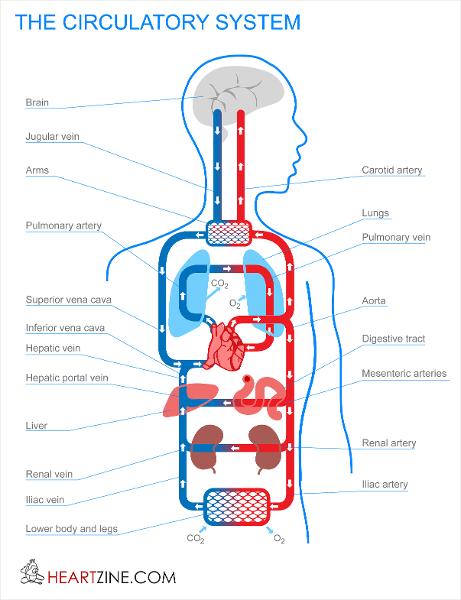 body >> vena cava >> right atrium of the heart -->> right atrium contracts -->>pumps the blood >>> tricuspid valve >>> right ventricle.>> pulmonary artery >>> lungs -->> tiny blood vessels called capillaries ( absorb carbon dioxide from the blood and replace it with oxygen) >>> pulmonary vein >>> left atrium>> mitral valve >>>> the left ventricle -->> left side of the heart >>>>> left ventricle >>>>> aortic arch -->> body -->> carotid artery and into the brain -->> auxiliary arteries -->> arms through the aorta -->> torso and legs -->> Blood >> arteries >> capillaries >>>> veins -->> >>>>> heart. |
front 42 Define Primary oocyte (egg), secondary oocyte | back 42 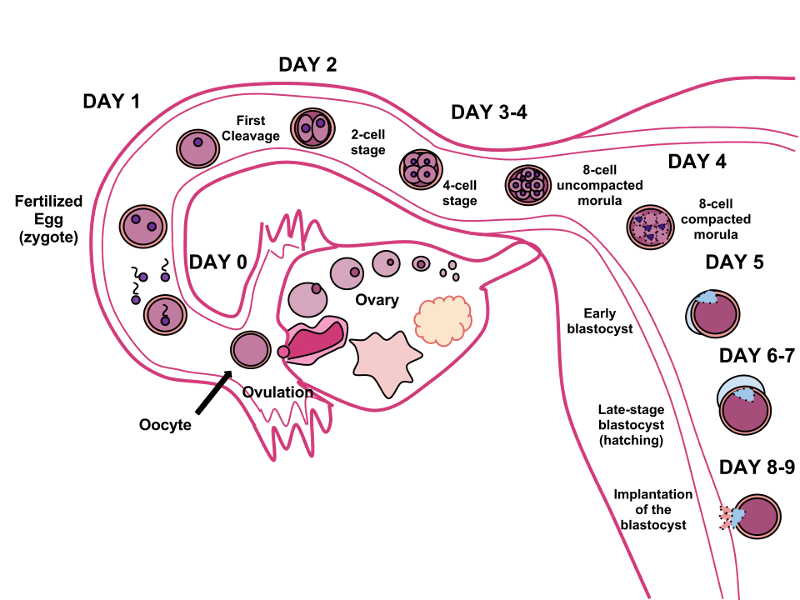 oocyte is produced in the ovary during female gametogenesis and the first meiotic division is completed. The second meiotic division usually stops short of completion unless fertilization occurs( secondary) |
front 43 Why can “tighty-whiteys” cause infertility? | back 43 temperature of the testes is at issue : HEAT |
front 44 Effects of estrogen and progesterone on the menstrual cycle. | back 44 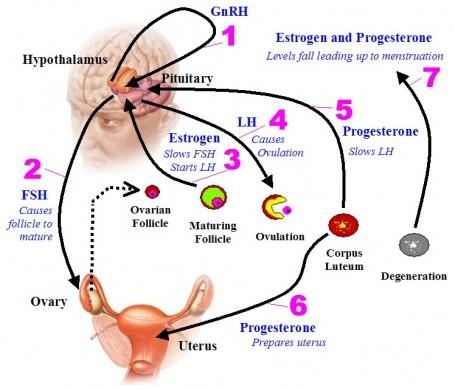 ESTROGEN creates proliferative
endometrium PROGESTERONE maintains secretory
endometrium |
front 45 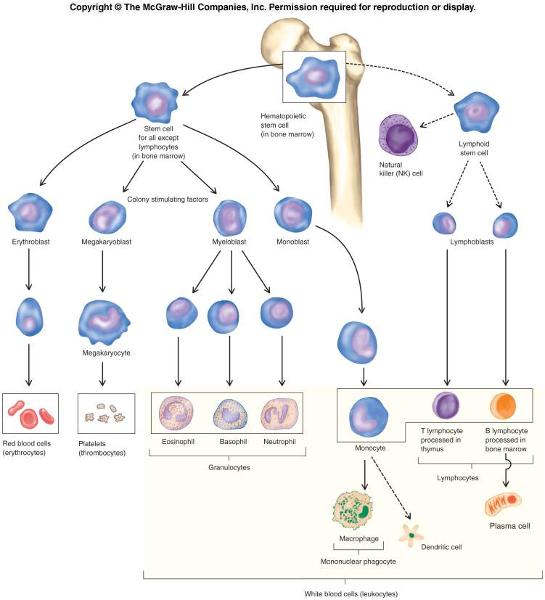 Function of T cells and B cells | back 45  T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (antibodies). function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specific “non-self” antigens, during a process known as antigen presentation. |
front 46 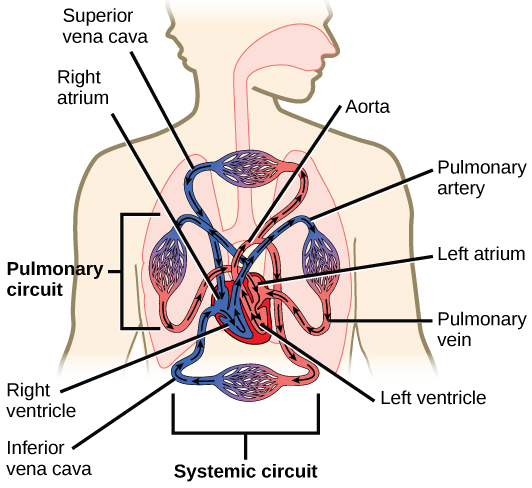 Flow of blood through the heart and all heart parts | back 46 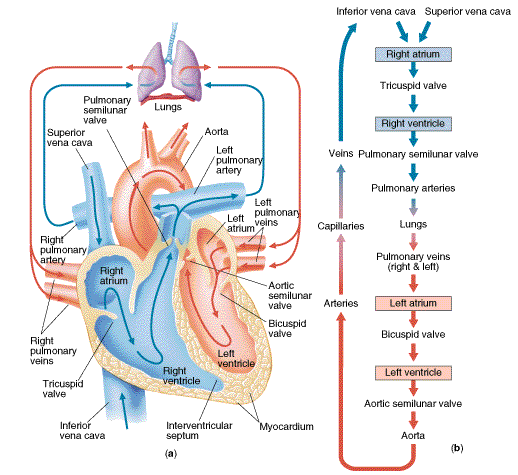 1. superior/inferior vena cava 2. right atrium 3. tricuspid valve 4. right ventricle 5. pulmonary valve 6. pulmonary artery 7. lungs 8. pulmonary veins 9. left atrium 10. mitral valve 11. left ventricle 12. aortic valve 13. aorta 14. body |
front 47 What do the ductus deferens and the esophagus have in common? | back 47 peristalsis |
front 48 Where is the egg fertilized? | back 48 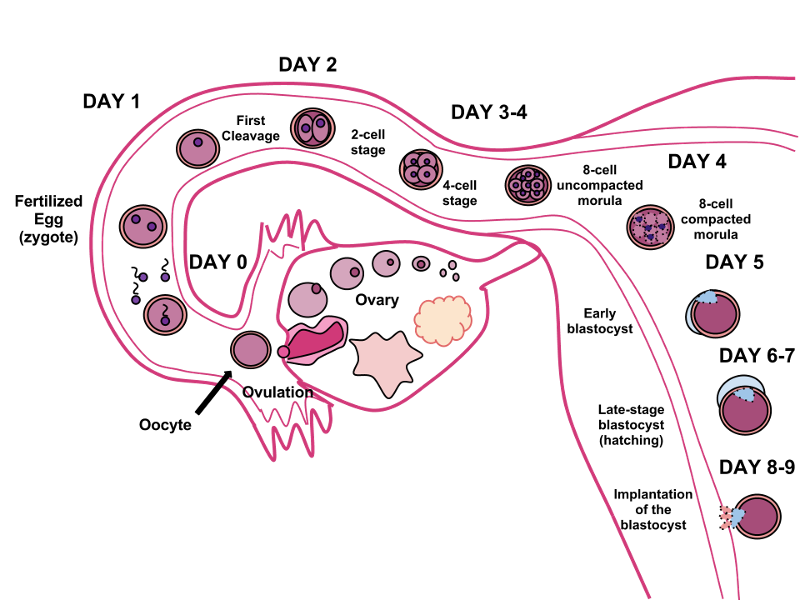 FALLOPIAN TUBES |
front 49  What hormones are in “the pill” and why? | back 49 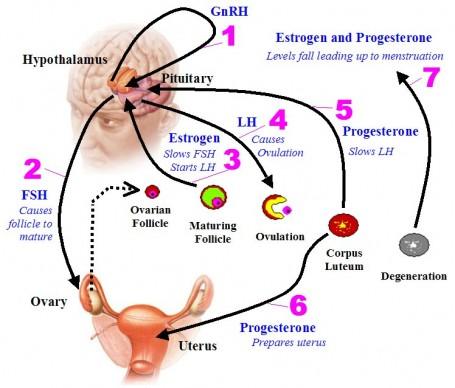 estrogen and progestin |
front 50 Functions of the liver | back 50 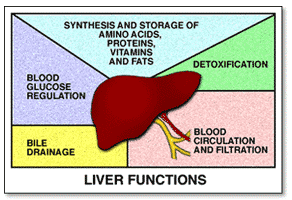
Bile production and excretion |
front 51  Identify all organs of the digestive system | back 51 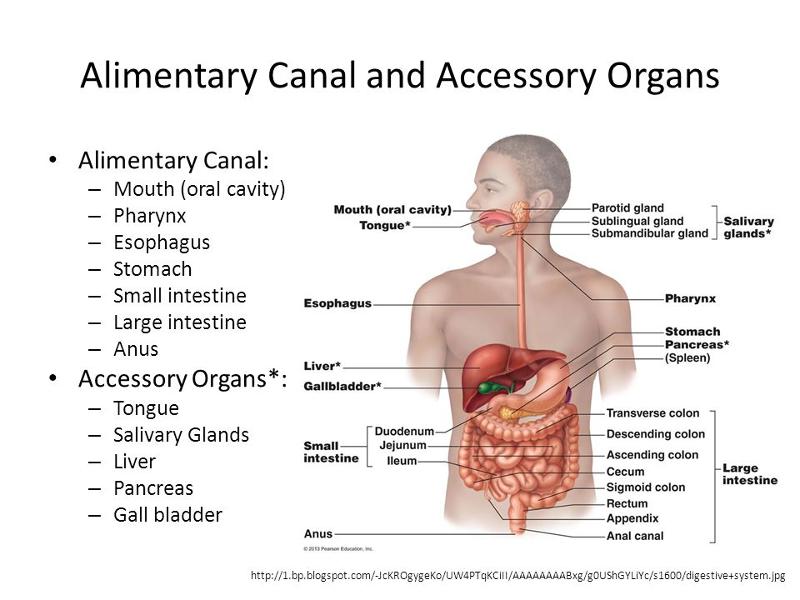 teeth, tongue, pharynx, stomach, gallbladder, liver, small intestine, colon, and pancreas. |
front 52 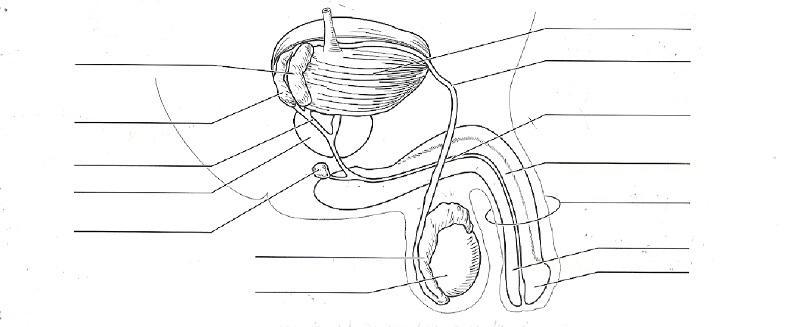 Identify all organs of the reproductive system | back 52 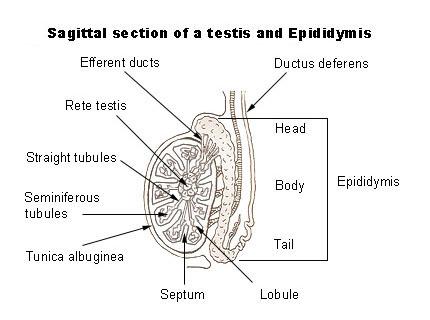
Female: ovaries, uterus, and vagina.
|
front 53 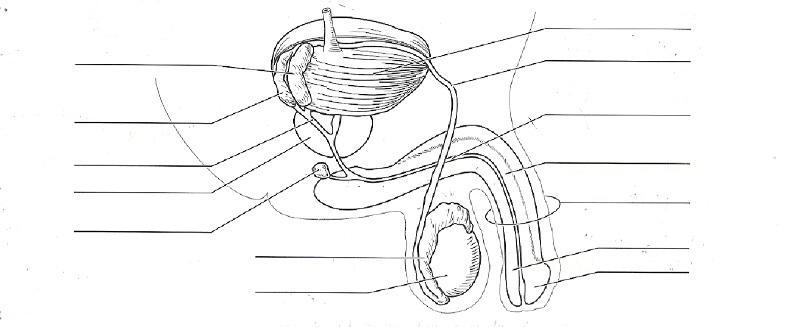 Identify all organs of the reproductive system MALE | back 53 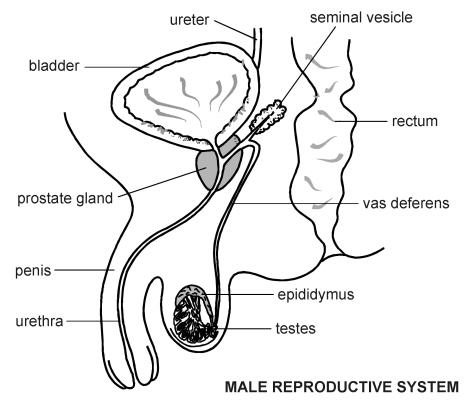
The male internal accessory organs
include: |
front 54 Identify all organs of the reproductive system FEMALE | back 54 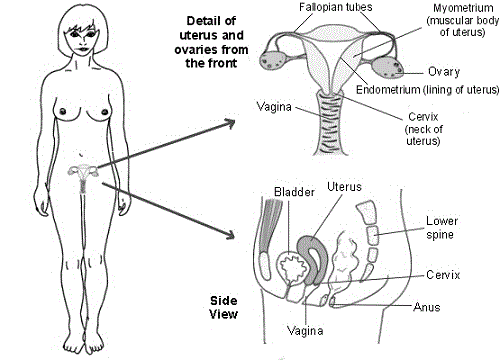
|
front 55 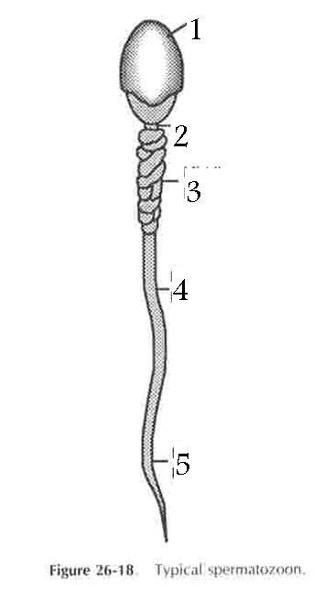 Structure of sperm | back 55 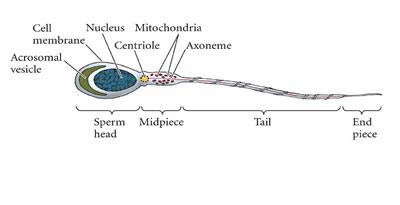 Sperm have three parts: a head chromatin; a midpiece filled with mitochondria to provide energy; and a flageullum or tail to move the sperm |
front 56
Summarize the correct sequence from the formation of a drop of
urine to the elimination from the body(Essay) | back 56 Blood leaves the heart via the aorta and enters the renal artery where it flows into the interlobar arteries. From there it branches off to the arcuate artery, blood flows to the cortical radiate arteries then into the afferent arteriole. From the afferent arteriole, it goes into the glomerulus for filtering. all waste goes to the proximal convoluted tubule, while blood that will stay in the body goes to the efferent arteriole. More blood filtering takes place in the peritubular capillaries. Blood that will stay in the body exits through the cortical radiate veins, then goes into the arcuate vein, then into the interlobar vein, then the renal vein, then back to the heart via the inferior vena cava. At the same time this is happening, the waste that was sent to the proximal convoluted tubule travels down the descending loop of henle, then up the ascending loop of henle to the distal convoluted tubule where it is dumped into the collecting duct. From the collecting duct >>>, it goes into the ureters>>>>, travels to the bladder>>>>>, and then leaves the body via the urethra. |
front 57 The dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system. Which of the following is true about the role they play? | back 57 They regulate the temperature of the testes. |
front 58 The ability of sperm cells to move along the ductus deferens is due to ________. | back 58 peristaltic contractions |
front 59 female sex hormones | back 59 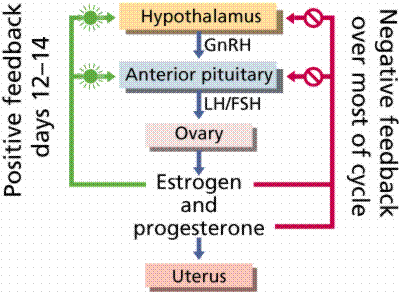 Hypothalamus →GnRH→Pituitary →FSH →Follicle →Estrogens |
front 60 The ability of a male to ejaculate is due to the action of ________. | back 60 the bulbospongiosus muscles |
front 61 Which of the gland are responsible for 60% of the synthesis of semen? | back 61 the seminal vesicles |
front 62 Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? | back 62 GnRH |
front 63 Uterine wall - has three layers | back 63
|
front 64 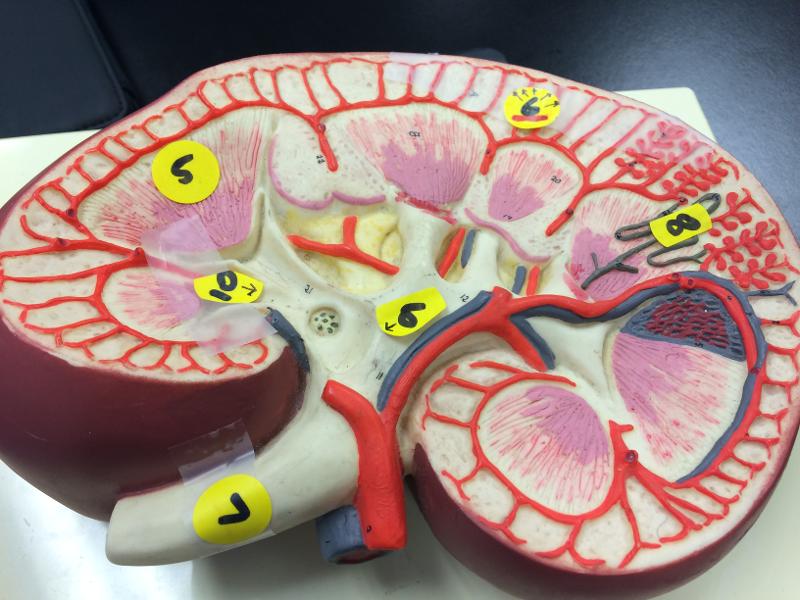 KIDNEY | back 64 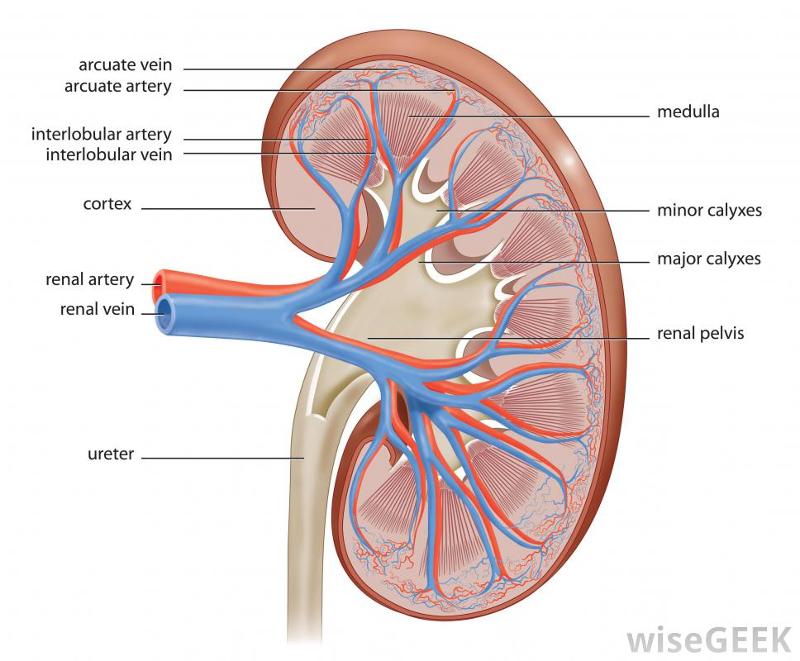 renal pyramid renal corpuscle RENAL ARTERY ureter nephron major calyx minor calyx SEGMENTAL ARTERY INTERLOBAR ARTERY CORNICAL RADIATE ARQUATE |
front 65 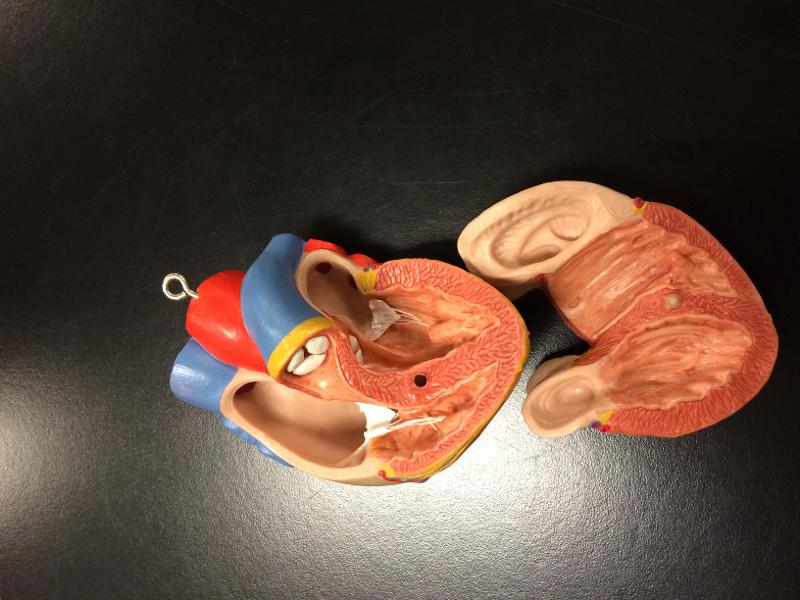 POSTERIOR (BACK SIDE) | back 65 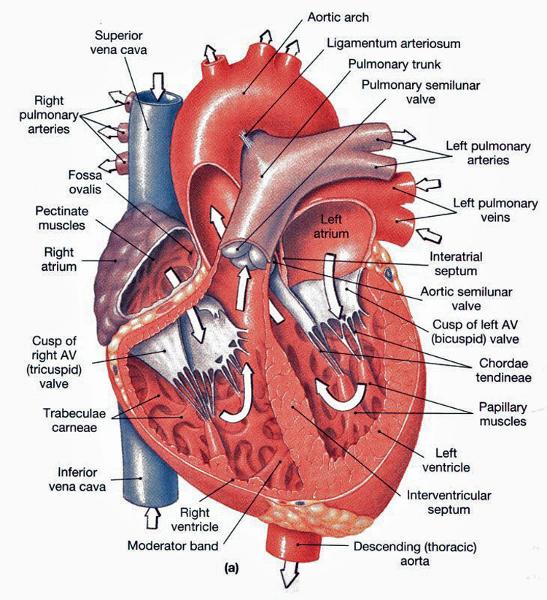 CORONARY SINUS- BIG FAT BACK GREAT CARDIAC VEIN INFERIOR VENA CAVA L/R ORICAL |
front 66 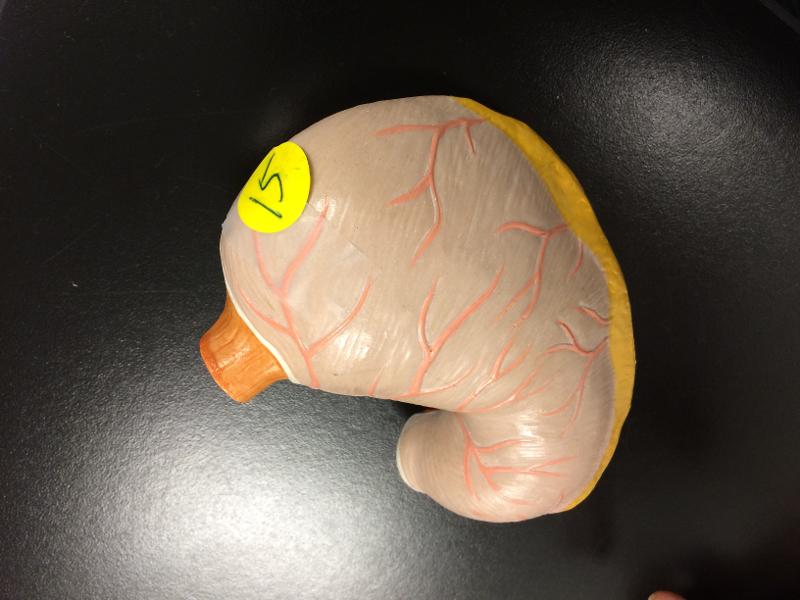 Stomach | back 66 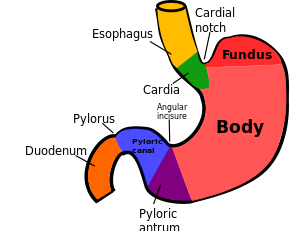 Top is fundus layers of gastrointestinal tract, the stomach walls consist of an outer mucosa, and inner submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa. CARDIAC PYLORIC REGION- PYLORIC CANAL DUODEUOM |
front 67 EPIPIMATES | back 67
Tightly coiled tubes |
front 68 Development of male reproductive structures depends on which of the following events? | back 68 secretion of male hormones prenatally and lasting into the first few months after birth |
front 69 The primary function of the uterus is to ________. | back 69 receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized ovum |
front 70 Why is the blood-testis barrier important? | back 70 cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system |
front 71 The structures that receive the ovulated oocyte, providing a site for fertilization, are called the ________. | back 71 fallopian tubes |
front 72 If gametes were diploid like somatic cells, how many chromosomes would the zygote contain? | back 72 twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur |
front 73 Human egg and sperm are similar in that ________. | back 73 they have the same number of chromosomes |
front 74 The constancy of the chromosome number from one cell generation to the next is maintained through ________. | back 74 meiosis |
front 75 Spermiogenesis involves the ________. | back 75 formation of a functional sperm by the stripping away of superfluous cytoplasm |
front 76 Which is not a part of the proliferative phase of the female menstrual cycle? | back 76 corpus luteum |
front 77 What is the difference between metabolic alkalosis vs. acidosis? | back 77 Metabolic alkalosis develops when your body loses too much acid or gains too much base. This can be attributed to:
Metabolic acidosis starts in the kidneys instead of the lungs. It occurs when they can’t eliminate enough acid or when they get rid of too much base. There are three major forms of metabolic acidosis:
|
front 78  | back 78  taenia coli Any of the three bands in which the longitudinal muscular fibers of the large intestine sigmoid epiploic appendices / omental appendices are small pouches of the peritoneum filled with fat and situated along the colon, but are absent in the rectum. |
front 79 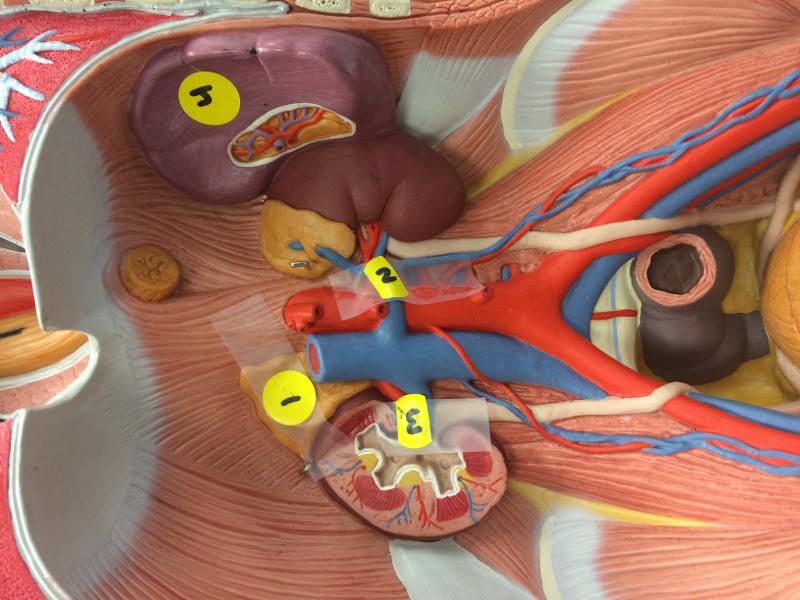 | back 79 TRACHEA - L /R BRONCHI AORTA INFERIOR VENA CAVA THYROID ESOPHAGAS SPLEEN COMMON ILIAC- DIVISION |
front 80 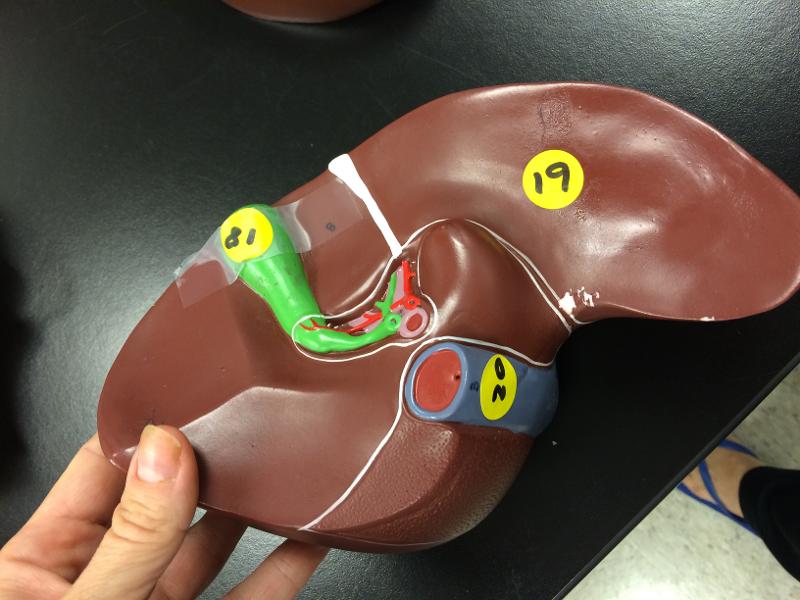 labels on liver | back 80 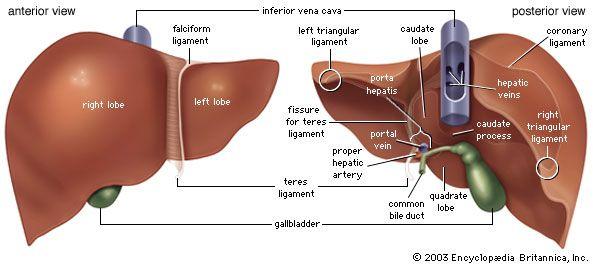 gallbladder right lobe inferior vena cava hepatic portal |
front 81 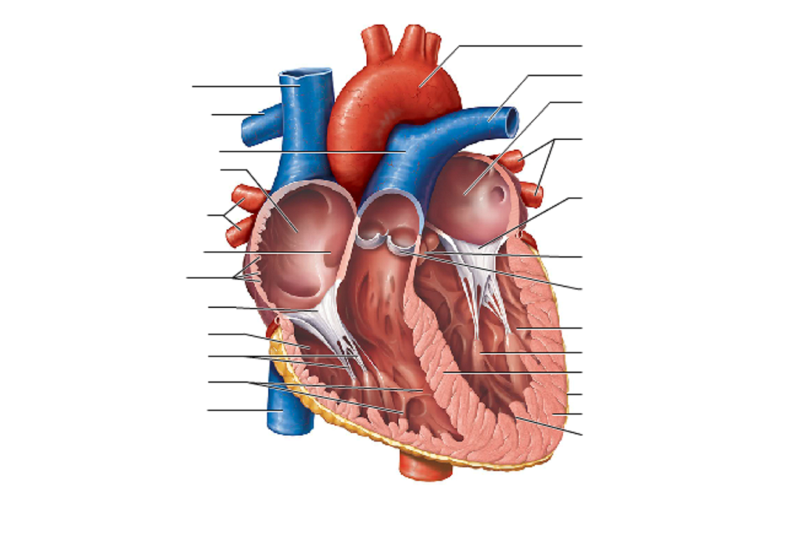 FRONTAL HEART | back 81 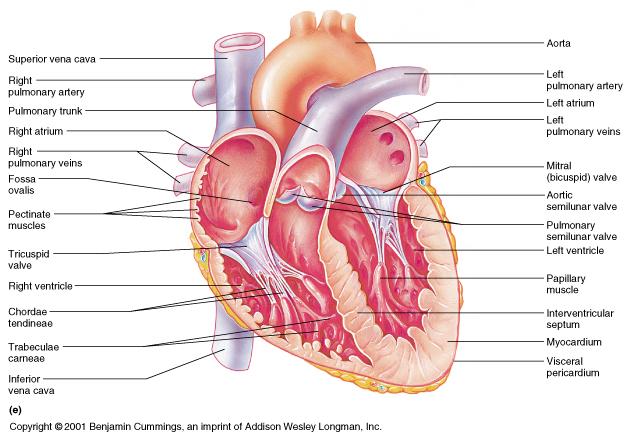 Endocardium - heart valves Myocardium - Conduction system
Pericardial cavity - Pericardial sinus |
front 82 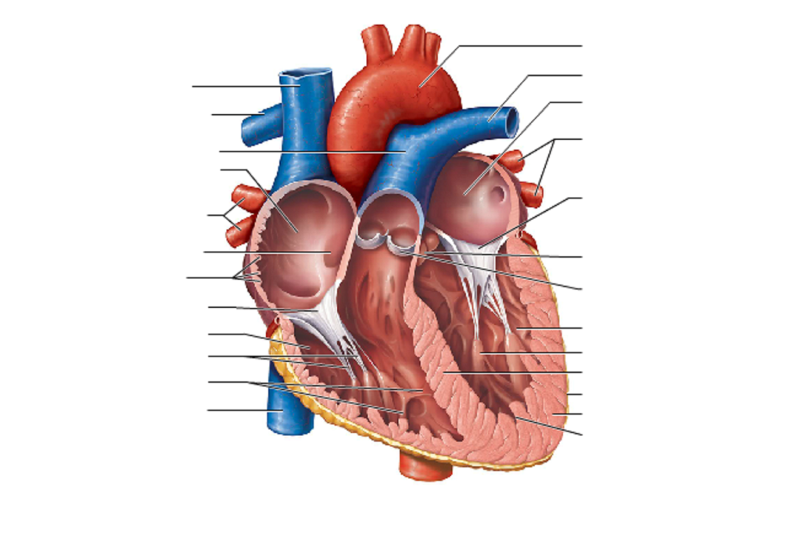 FRONTAL VIEW OF HEART | back 82 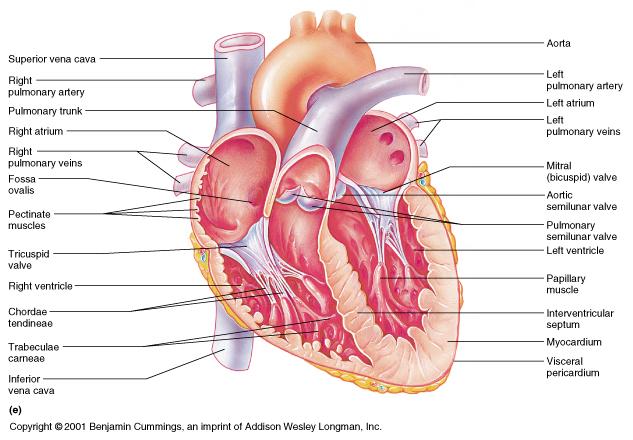
Vena Cava
Semilunar Valve
Left Atrium
Left
Ventricle
Pulmonary Artery
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Vein
Right Atrium
Aorta/ AORTIC ARCH
chordae tendineae : heart strings, are cord-like tendons that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve PAPIL |
front 83 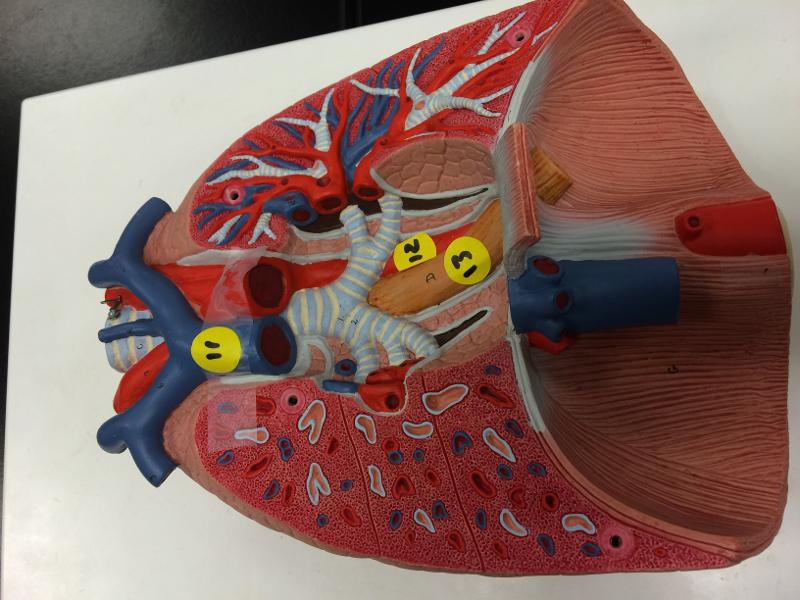 respiratory | back 83 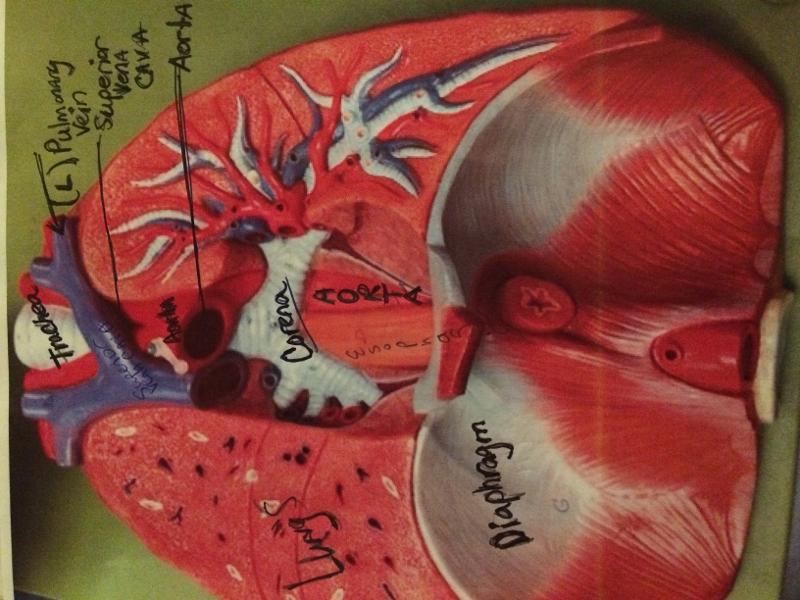 ESOPHAGAS L/R BRONCHI TRACHEA PULMONARY TRUNK AORTIC ARCH INFERIOR VENA CAVA AORTA DIAPHRAGM |
front 84 
lower digestive/ small ; large intestine( front only ) | back 84 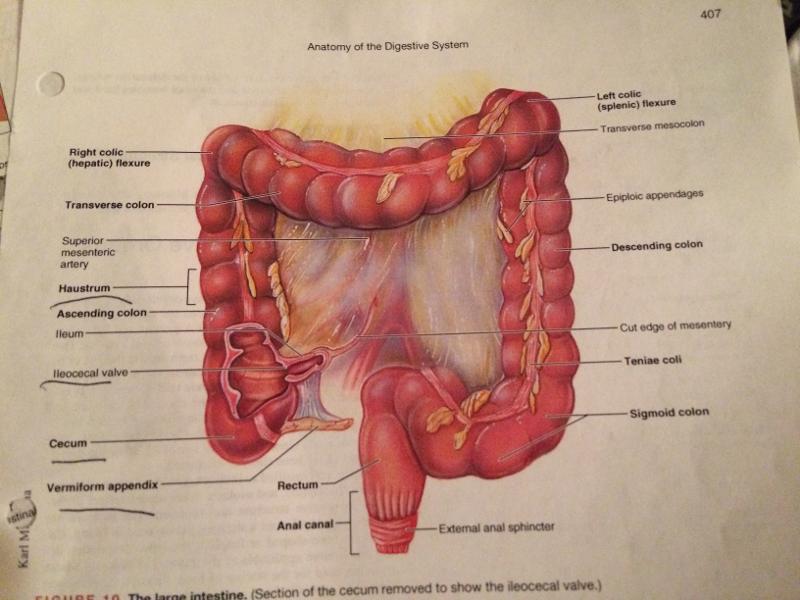
|
front 85 Ovarian hormones and cycle (essay) | back 85 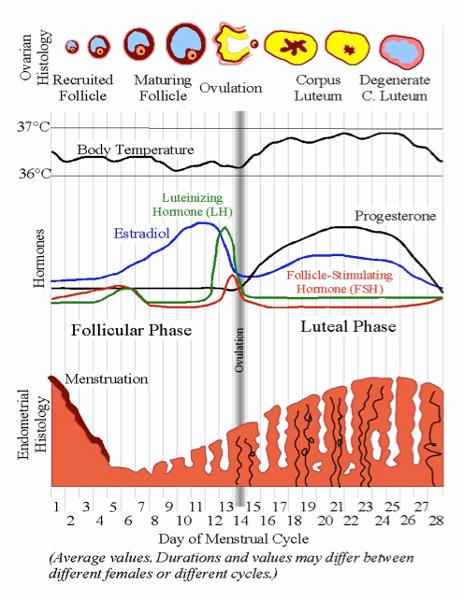 follice develops day 14 - ovulation (estrogen peaks) day 12-14 estrogen drops - more frisky (surge) day 20-21 progesterone goes up - mucus thickens - peaks estrogen peaks again pms estrogen and progesterone drop : repeat 28 days |
front 86 FINAL product of oogenesis is called ______. (HINT: this is the ovulated secondary oocyte) | back 86 ovum |
front 87 What is one of the hormones responsible for maintenance of corpus luteum after ferilization? | back 87 human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) |
front 88 Cortex of an ovary contains (4 things) | back 88
primordial follicles |
front 89 ovaries are supported by ______ | back 89
1. Mesovarium (attaches to ovary to POSTERIOR surface of
broad ligaments) |
front 90 During the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle ________. | back 90 progesterone levels are at their highest |
front 91 3 Major fx of ovary? | back 91
(1) synthesis & secretion of sex
hormones |
front 92 This membrane will eventually surround the oocyte | back 92 Zona pellucida |
front 93 FINAL product of oogenesis is called ______. (HINT: this is the ovulated secondary oocyte) | back 93 ovum |
front 94 United Secondary oocytes after the completion of meiosis II is called ____. | back 94 zygote |
front 95 Select the correct statement about the uterine cycle.
A) The menstrual phase of the cycle is from day 1 to day 8.
| back 95 If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is maintained by a hormone secreted by the developing embryo. |
front 96 Which of the choices below is not a part of the brain-testicular axis? | back 96 thalamus |
front 97 Which of the following statements is true concerning the mammary glands of both males and females? A) Both sexes are equally prone to
breast cancer. | back 97 The mammary glands are modified sweat glands that are actually part of the integumentary system. |
front 98 The basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that ________. A) during
spermatogenesis two more polar bodies are produced | back 98 in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell |
front 99 Occasionally three polar bodies are found clinging to the mature ovum. One came from an unequal division of the ovum, but from where did the other two arise? | back 99 The first polar body has also divided to produce two polar bodies. |
front 100 Why doesn’t semen enter the urinary bladder during ejaculation? | back 100 The smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes. |
front 101 Spermatogenesis ________. | back 101 involves a kind of cell division limited to the gametes |
front 102 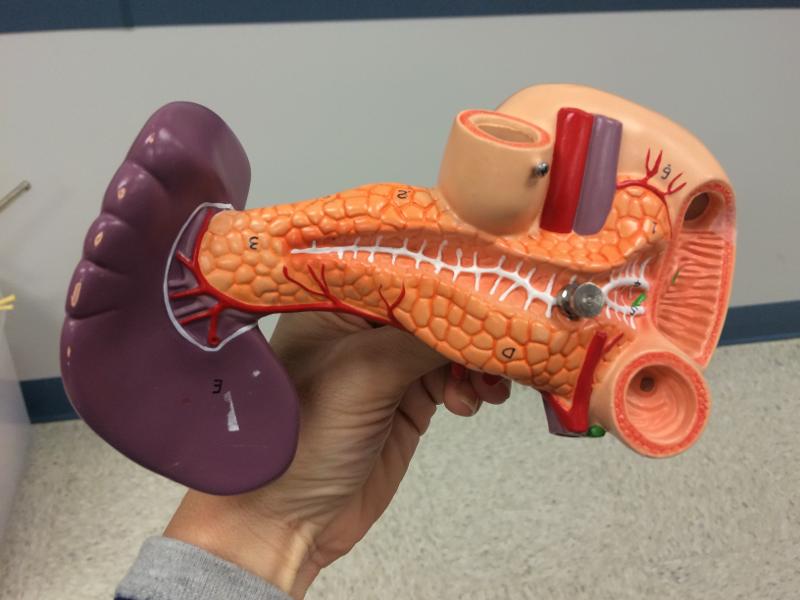 Combo pancreas / spleen | back 102 spleen - hepatic portal pancreas leading to small intestine @ dueodium |
front 103 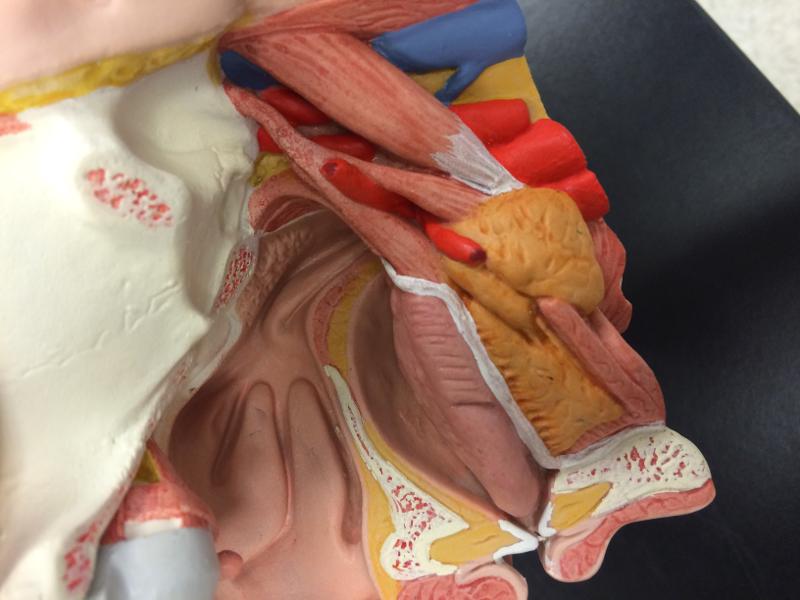 mouth / upper head glands | back 103 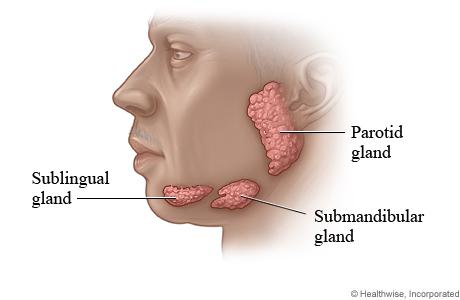 sublingual submandibular parotoid |
front 104 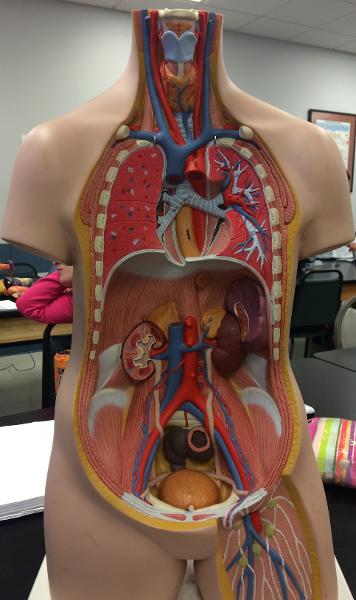 ANTERIOR CAVITY | back 104 BLADDER CURVED SIGMIOD COMMON ILIAC ARTERY INFERIOR VENA CAVA AORTA ADRENAL GLANDS KIDNEY SPLEEN DIAPHRAGM ESOPHAGUS THYROID |
front 105 Gland at neck | back 105 Thyroid |
front 106 ARTERYS SUPERIOR LIMB | back 106 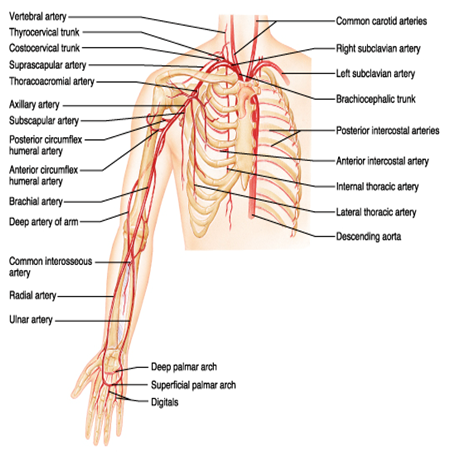 SUPERIOR LIMB- ARM COMMON CAROTID-> SUBCLAVICAN-> AXILLARY->BRACHIAL-> DEEP ARTERY OF ARM-> RADIAL/ULNAR-> DEEP PALMAR-> SUPERFICIAL PALMAR->DIGITALS |
front 107 VEINS SUPERIOR LIMB | back 107 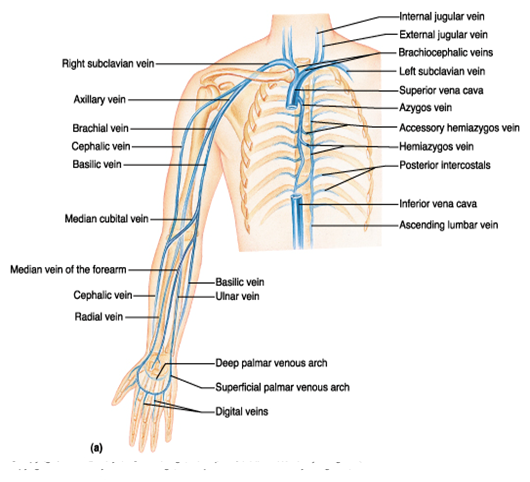
1. Palmar digital vein
17. Pulmonary veins |
front 108 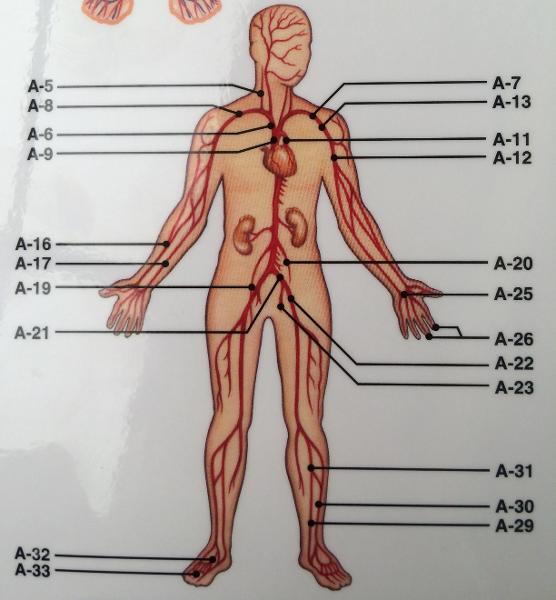 HEAD/NECK ARTERY | back 108 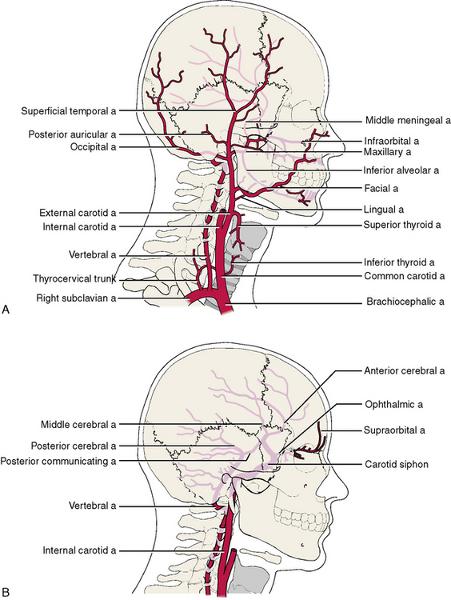 |
front 109 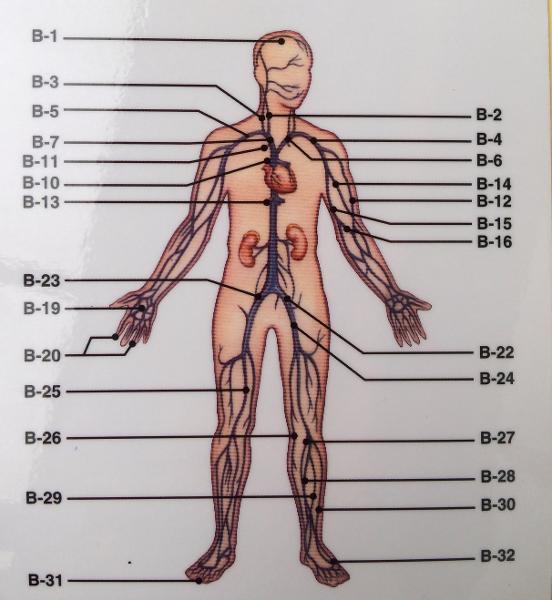 HEAD/NECK VEIN | back 109 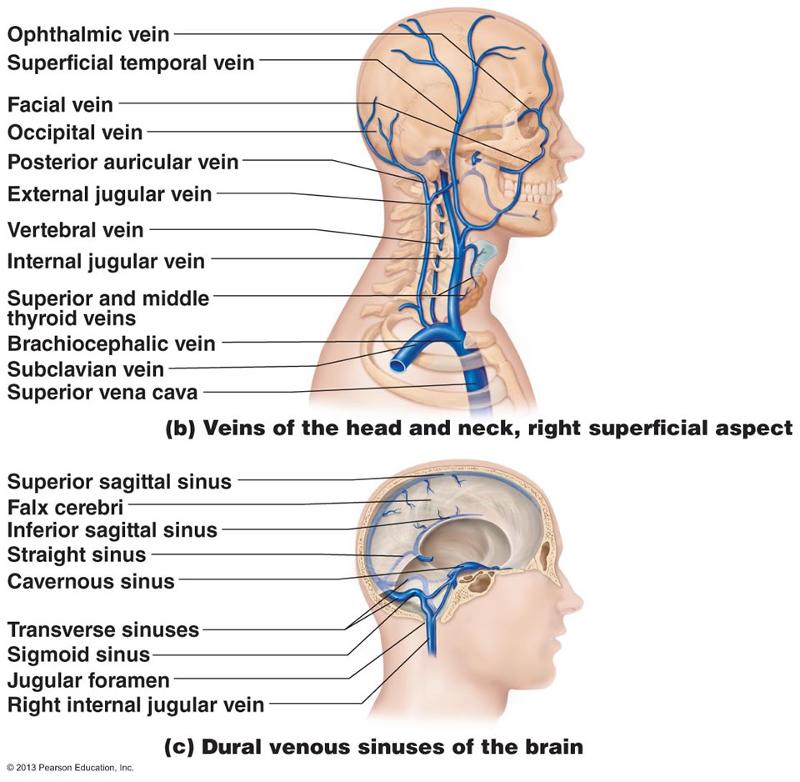 |
front 110 HEPATIC PORTAL VEIN | back 110 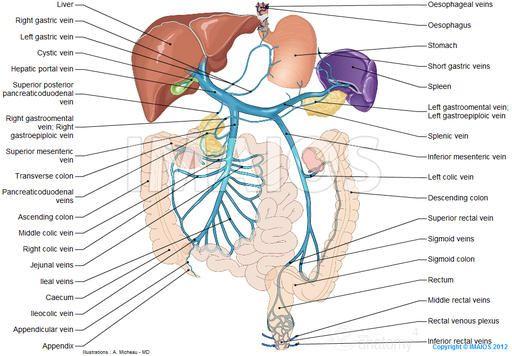 CELIAC TRUNK->LEFT GASTRIC-> COMMON HEPATIC->SPLEENIC R.GASTRIC->L. GASTROEPIPLOIC-> R. GASTROEPIPLOIC->GASTRODUODENAL |
front 111 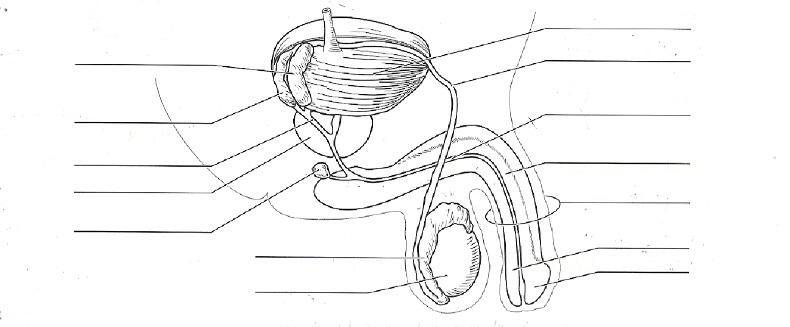 POSTERIOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE | back 111 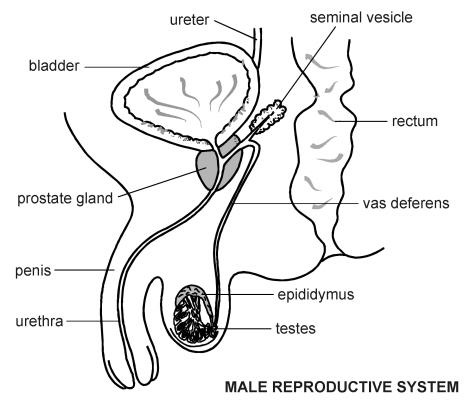 |
front 112 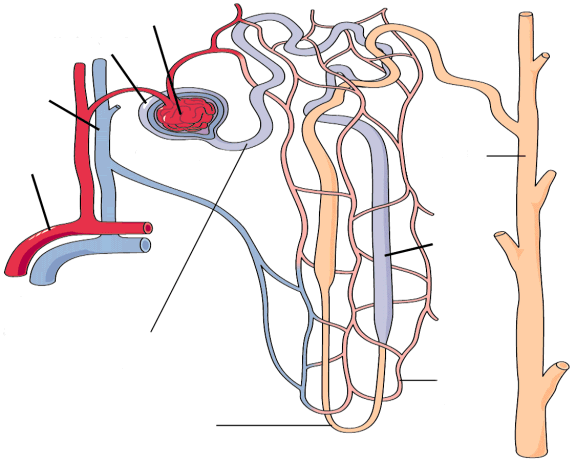 NEPHRON | back 112 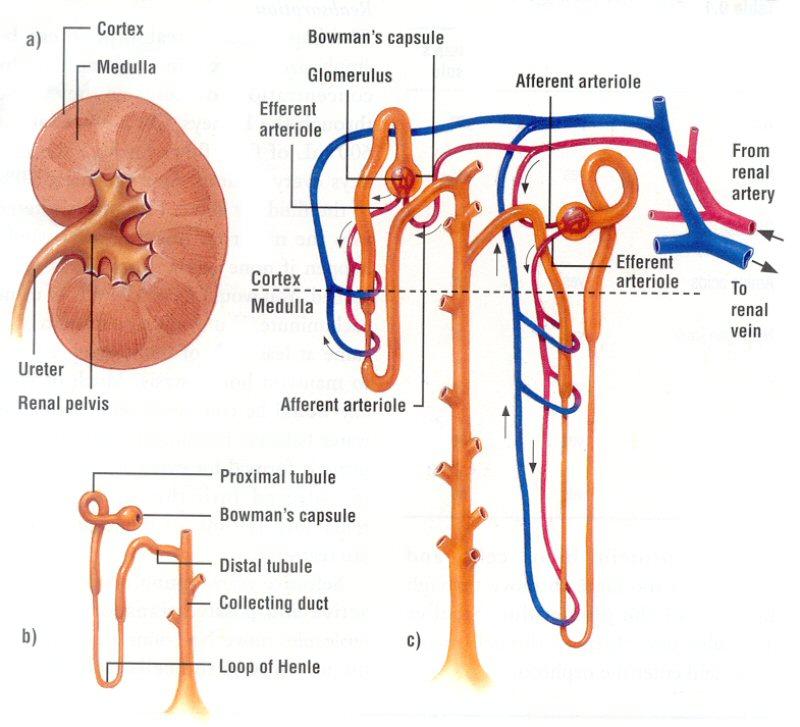 |
front 113  SAGITAL CUT TESTES | back 113 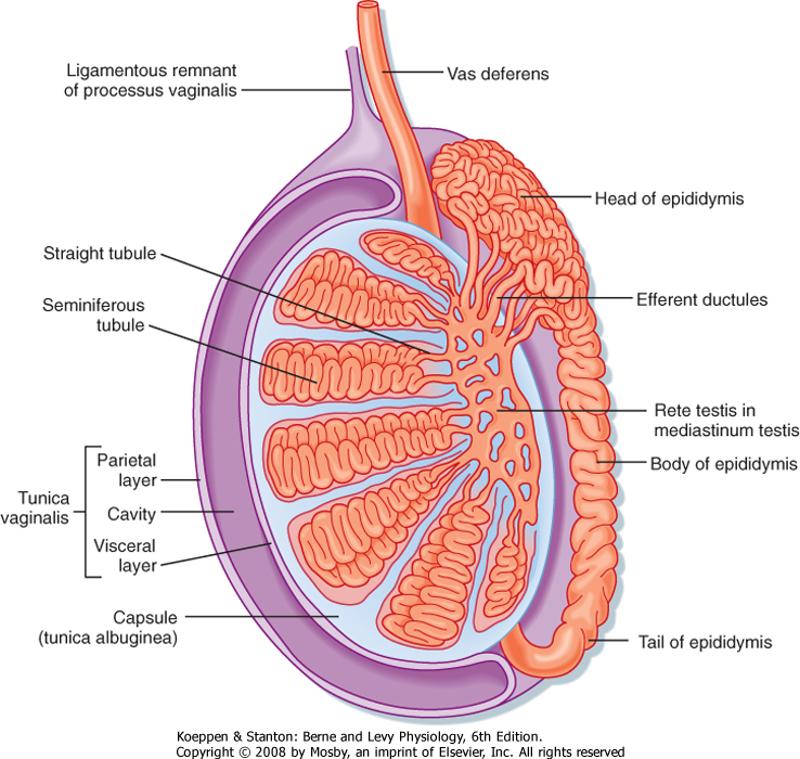 principal androgen produced by the testes is testosterone. Production of testosterone by the testes is stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH), produced by anterior pituitary secretion of LH is stimulated by (GnRH), released from the hypothalamus, inhibited by testosterone, inhibits the secretion of GnRH. These hormones constitute the (hypothalamic-pituitary-testes axis). |
front 114  PHARYNX | back 114 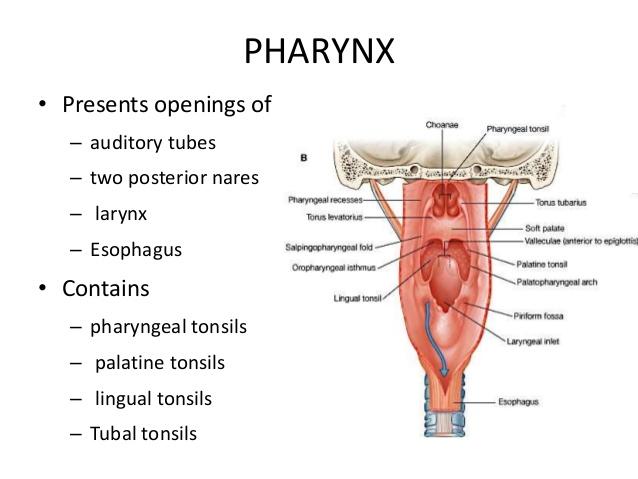 |
front 115 INFERIOR LIMB VEIN | back 115 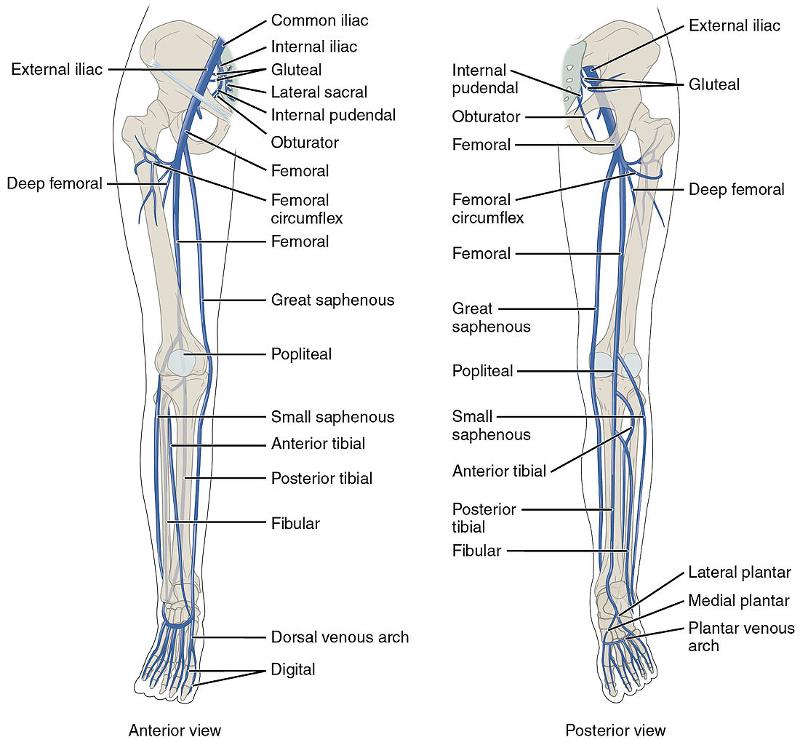 External iliac internal iliac femoral great saphenous small saphenous popliteal perioneal (Fibula) Anterior tibial posterior tibial |
front 116 WHAT IS THE MAIN BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE LOWER EXTREMITIES ?(ARTERY) | back 116 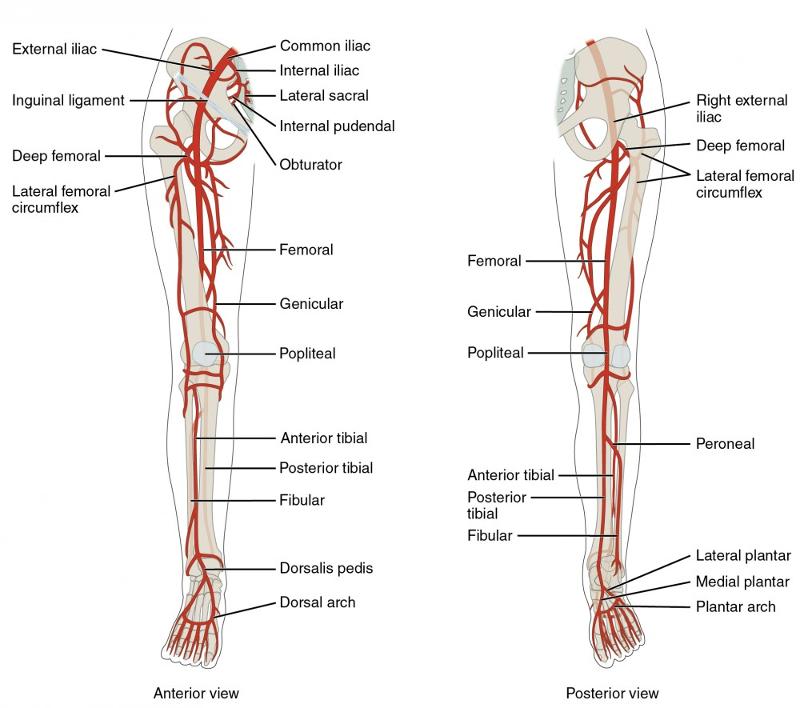 COMMON ILIAC -> FEMORAL-> DEEP ARTERY OF THE THIGH->POPLITIAL LOWER LEG->ANTERIOR TIBILIAR / POSTERIAL TIBULAR/ FIBULAR ->ARCULATE (DORSAL ASPECT OF FOOT ) _. PANTAR ARTERY->DIGITAL ARTERY |
front 117 ELECTROLYTES | back 117 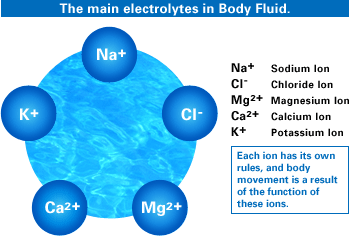 NA+ CI- MG2+ CA2+ K+ |
front 118 CAUSES UTERINE CONTRACTIONS | back 118 prostaglandins- HELP SPERM MOVE |
front 119 FUNCTIONS OF THE GALLBALDDER | back 119 BILE STORAGE |
front 120 HYPERVENTILATION | back 120 CO2 DOWN PH UP- TOO LITTLE / DECREASE IN CO2 - RISE IN PH |
front 121 WHAT DOES ADH DO TO THE COLLECTING TUBULE AND DISTAL ? | back 121 RE-ABSORPTION OF H2O: WHY ? DEHYDRATED AND NEED MORE RE-ABSORPTION OF FLUIDS DIABETES INSIPIDUS |
front 122 WHAT IS MOST IMPORTANT GAS FOR PH IN BLOOD ? | back 122 CO2 |
front 123 WHERE DOES GLUCOSE GET REABSORBED? | back 123 KIDNEY- PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE - 70 % RE-ABSORPTION |
front 124 what are the functions of the juxtaglomerular apparatus ? | back 124 FILTRATION RATE, BLOOD PRESSURE AND PH |
front 125 DIABETES MILITIS: PRODUCING KEYTONE BODIES , WHAT CONDITION DOES IT LEAD TO? | back 125 METABOLIC ACIDOSIS |
front 126 PROLONGED VOMITING OR TAKING TOO MANY ANTACIDS : WHAT DOES IT CAUSE ? | back 126 METABOLIC ALKALOSIS |
front 127 OBSTRUCTION OR BLOCKING OF THE AIRWAY CAUSES? | back 127 RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS |
front 128 IF BLOOD PRESSURE SUDDENLY DROPS, WHAT HAPPENS TO FILTRATION? | back 128 DECREASES |
front 129 FORCE THAT IS RESPONSIBLE FOR NORMAL RESPIRATION IN THE LUNGS? | back 129 EXPAND THE LUNGS : NATURAL ELASTIC RECOIL INCREASE PRESSURE / LOWER VOLUME = CO2 OUT |
front 130 IF YOU HAVE ALOT OF CARBS IN YOUR MEAL? ENZYME NEEDED | back 130 AMYLASE |
front 131 WHAT DOES CHYME DO? | back 131 MAKE BICARBONATE FROM PANCREAS BE RELEASED FOR SMALL INTESTINE |
front 132 WHAT SEX HORMONE IN MALES PRODUCES SPERM ? | back 132 FSH- FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE |
front 133 SHORTER URETHRA IN A FEMALE COMPARED TO A MALE LEADS TO MORE SUSCEPTIBILITY TO? | back 133 UTI |
front 134 WHAT IS THE MITRATION (URINATION) REFLEX CENTER CONTROLLED BY ? | back 134 SACRAL SEGMENTS OF THE SPINAL CORD |
front 135 PROTEIN AND FAT IN THE SMALL INTESTINE LEADS TO THE SECRETION OF WHAT HORMONE? | back 135 CCK |
front 136 WHICH HORMONE STIMULATES THE PANCREATIC JUICE TO RELEASE BICARBONATE TO MAKE CHYME LESS ACIDIC? | back 136 SECRETIN |
front 137 FACE AND SCALP IS DRAINED BY THE EXTERIOR JUGULAR THE DRAINS INTO WHAT VEIN ? | back 137 SUBCLAVIAN |
front 138 SUBCLAVIAN AND INTERNAL JUGULAR MERGE TO FORM? | back 138 BRACIOCEPHALLIC |
front 139 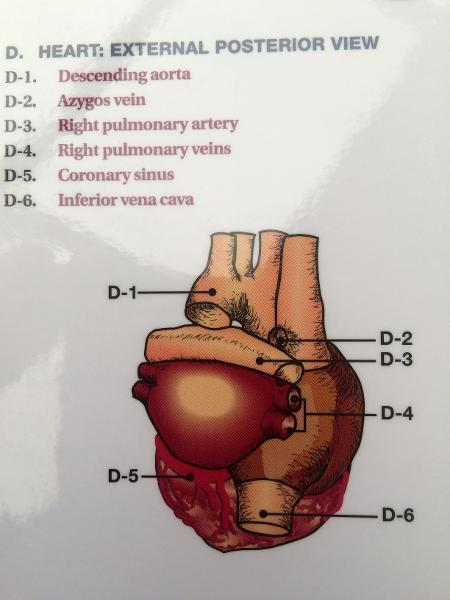 COMMON ILIAC MERGES TO FORM THE? ( 95 NORTH) | back 139 SUPERIOR VENA CAVA |
front 140 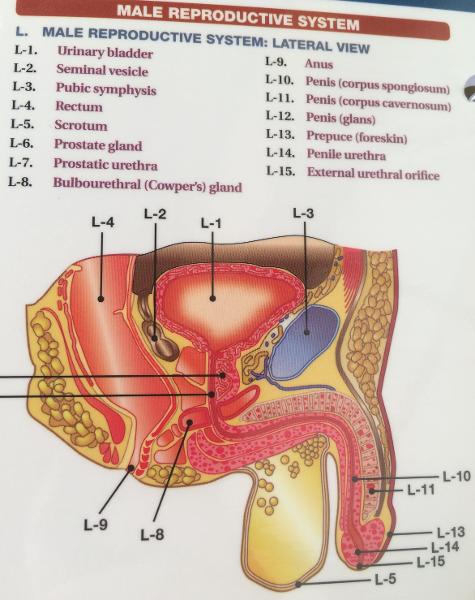 WHEN WE REMOVE THE PREPUSE( FORESKIN)? | back 140
circumcise |
front 141 UNDECENDED TESTES CAUSE INFERTILITY WHY? | back 141 heat of body will destroy it |
front 142 MECHANISM EQUAL IN/ EQUAL OUT TO HEART ? | back 142 FRANK - STERLING |
front 143 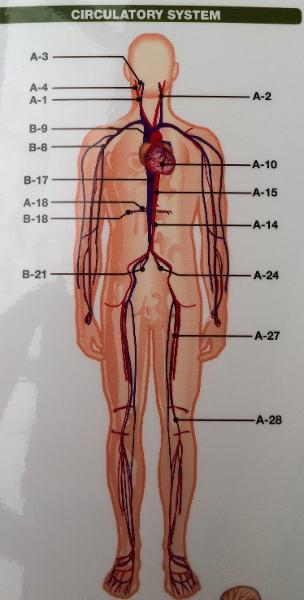 WHAT PROVIDES BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE LOWER EXTREMITIES ? | back 143 COMMON ILIAC |
front 144 WHICH PROVIDE BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE THIGH? | back 144 FEMORAL |
front 145 WHAT PROVIDES BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE KNEE? | back 145 POPLITEAL |
front 146 WHICH PROVIDES BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE LOWER LEG? ( MORE THAN ONE)? | back 146 ANTERIOR TIBULAR/ POSTERIOR TIBULAR, FIBULAR |
front 147 WHAT SUPPLY'S BLOOD TO THE FOOT ? | back 147 DORSALAS PEDIS |
front 148 B CELLS DO WHAT | back 148 DIFFERENTIATES INTO PLASMA CELLS / CREATES ANTIBODIES |
front 149 WHAT IS THE "SHRINKAGE"? REGULATES THE TESTES | back 149 dartos and cremaster muscle male shrinkage |
front 150 ABILITY OF MALE TO EJACULATE IS DUE TO WHAT MUSCLES ? | back 150  SYMPATHETIC - CORPUS SPONGIOSUM |
front 151 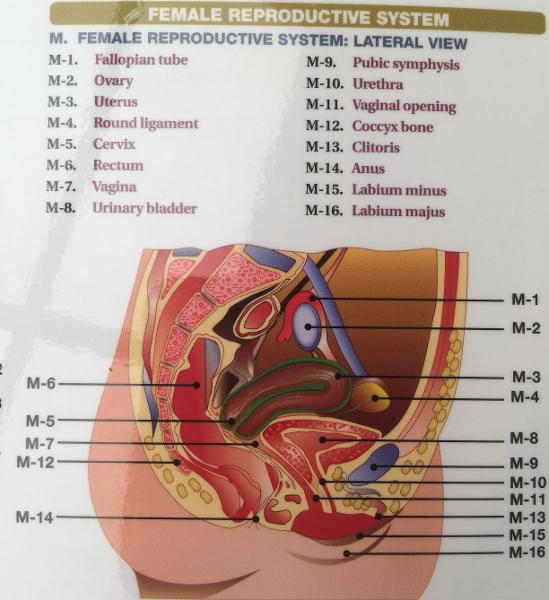 SITE OF FERTILIZATION IN A FEMALE? IMPLANTATION OCCURS? | back 151 FALLOPIAN TUBES UTERUS |
front 152 MENSTRUATION ONLY WHEN BLOOD LEVELS OCCURS WHEN TWO HORMONES ARE DIMINISHED ? | back 152 ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE |
front 153 WHAT CAUSES OVULATION ? | back 153 FIRST ESTROGEN SURGE DAY 12-14 |
front 154 WHICH IS THE HORMONE THAT PROMOTES THE UTERUS AND PREPS IT FOR PREGNANCY? PROMOTES THE UTERINE WALL | back 154 PROGESTERONE |
front 155 2 POINT ESSAY - MUST KNOW | back 155 MENSTRAL : ESTROGEN ( UP ) DAY 12-14 >>> LH/ FSH ( UP) SURGE- EGG COMES OUT >> LH/ FSH / ESTROGEN (DOWN) PROGESTRONE (UP) PEAKS AT DAY 21 >>> 2ND SURGE DAY 22-25 ESTROGEN (UP) >>> ESTROGEN (DOWN) PROGESTRON (DOWN) >>>> PMS UNTIL MENOPAUSE Blood >>> heart via >>>> aorta >>> renal artery >>> interlobar arteries >>> arcuate artery >>>> pyramids >>> arcuate artery >>> cortical radiate arteries >>>> afferent arteriole >>> ADH- DCT DISTAL CONVELATED TUBE>>> proximal convoluted tubule >>> efferent arteriole >>> peritubular capillaries >>> Blood >>> in the body exits >>>cortical radiate veins >>>> arcuate vein>>> interlobar vein >>> renal vein >> heart >>> inferior vena cava >>> waste >> proximal convoluted tubule >>> descending loop of henle >>> ascending loop of henle >>> distal convoluted tubule >>> collecting duct>>>>ureters >>> bladder >>>> leaves the body via the urethra. |
front 156 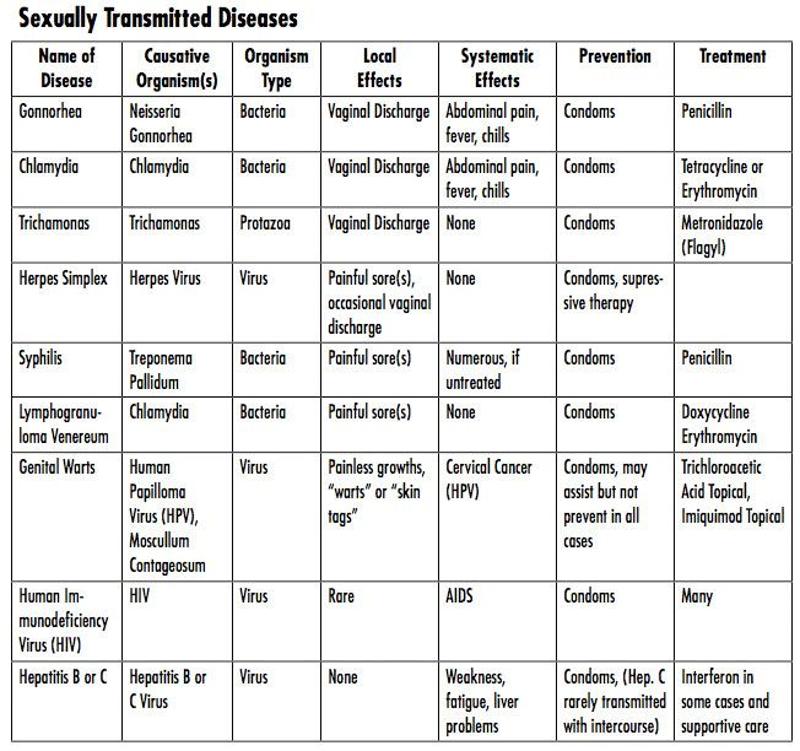 | back 156  |
front 157 urogenital infection caused by the bacterium chlamydia trachomatis | back 157 chlamydia |
front 158 STI that initially causes inflamation | back 158 gonorrhea |
front 159 STI caused by a bacterium called treponema pallidum | back 159 syphilis |
front 160 a vaginal infection caused by bacterial microorganisms | back 160 vaginitis |
front 161 form of vaginitis caused by the one-celled protozoan trichomonas vaginalis | back 161 Trichomoniasis |
front 162
How did it get so late so soon? Its night before its
afternoon. December is here before its June. My goodness how the
time has flewn. How did it get so late so soon? | back 162
The more that you read, the more things you will know. The
more that you learn, the more places you'll go.
|
front 163 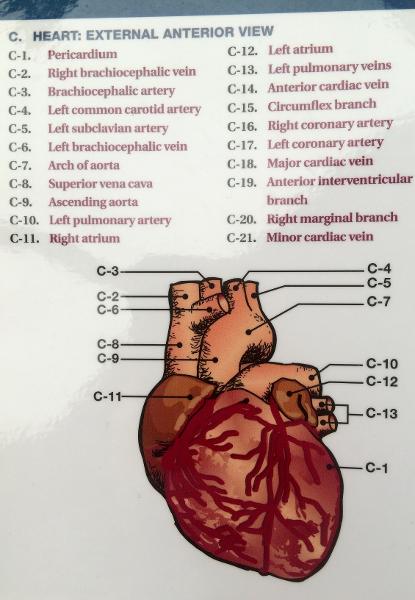 ABNORMALLY FAST HEART BEAT= 100+ BEATS ABNORMALLY LOW HEART BEAT = 60 - BEATS INADEQUATE BLOOD CIRCULATION | back 163 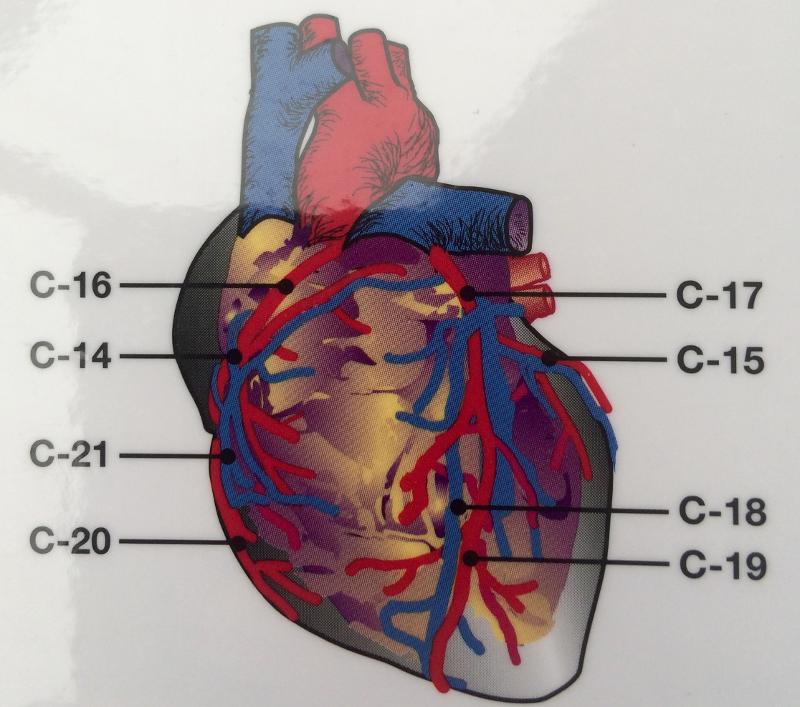 tachycardia bradycardia |
front 164 The right and left internal jugular veins and the right and left subclavian merge to form the | back 164 Brachiocephalic veins |
front 165 Which of the following arteries provide blood to the lower extremities? | back 165 Common iliac arteries |
front 166 A) Common hepatic artery | back 166
Supplies the duodenum and stomach |
front 167 Veins that drain the lateral surface of the upper arm are the: | back 167 Cephalic veins |
front 168 Which vessel drains the scalp? | back 168 External jugular vein |
front 169 Which tunic of an artery is most responsible for maintaining blood pressure and continuous blood circulation? | back 169 tunica media |
front 170 Which of the following is not a branch of the aorta? | back 170 right cartoid artery |
front 171 Which of the following supplies blood to parts of the intestinal tract? | back 171 superior mesenteric artery |
front 172 Which of the following are involved directly in pulmonary circulation? | back 172 right ventricle, pulmonary artery, and left atrium |
front 173 The mechanism that ensures the volume of blood discharged from the heart is equal to the volume entering its chambers is ______ law of the heart. | back 173 Frank-Starling's |
front 174 antenna- anterior communicating /posterior communicating /anterior cerebral eyes- internal carotid arms- posterior cerebral artery body-basilar artery leg- vertebral artery | back 174 circle of willis (brain) |
front 175 WHAT HELPS RETURN THE BLOOD TO THE HEART ? | back 175 CONTRACTION OF SKELETAL MUSCLES AND THE DIAPHRAGM GASTRAPHOLIAS : EXERCISE: SQUEEZES THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA |
front 176 WHAT IS THE MAIN BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE BRAIN ? | back 176 INTERNAL CARTOID AND VERTERBRAL |
front 177 Arch of aorta Abdominal aorta Coronary artery Subclavian A/V Axillary A/V Brachial A/V Radial A/V Ulnar A/V Vertebral artery Hepatic A/V Renal A/V Lumbar A/V | back 177 To upper body To abdominal cavity; legs Supplies oxygenated blood to the heart muscle To / From shoulder To / From underarm area To/From upper arm To/From lateral lower arm used to take pulse @ wrist To/From medial lower arm (serving brain) To brain (posterior) To/From liver To/From kidneys To/From posterior abdominal wall |
front 178 Femoral A/V Anterior/Posterior Tibial A/V Dorsalis pedis A/V Plantar A/V Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Internal jugular V External jugular V Cephalic V Median cubital V Great Saphenous V External Iliac A/V | back 178 To/From upper leg- the external iliac artery entering the thigh To/From lower leg To/From top of foot To/From bottom of foot From upper body From lower body from brain from superficial tissues of the head and neck from superficial lateral arm from superficial middle of arm (usually take blood from this vein) from superficial medial leg (longest vein) To/From superficial leg |
front 179 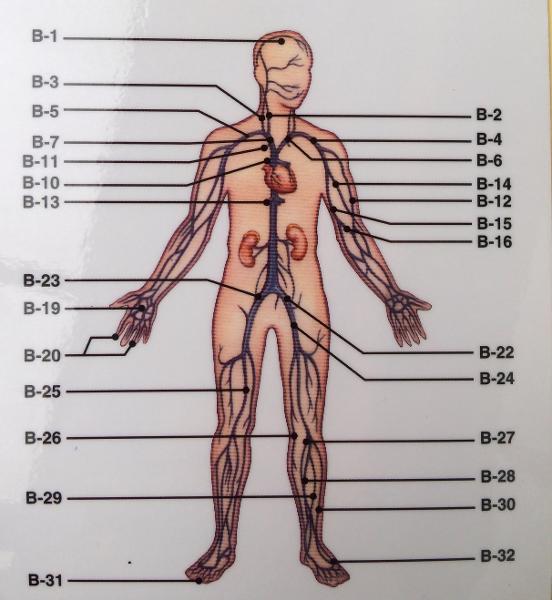 List all of the veins and their tributaries of the trunk (abdomen, thorax and neck region) | back 179 
|
front 180 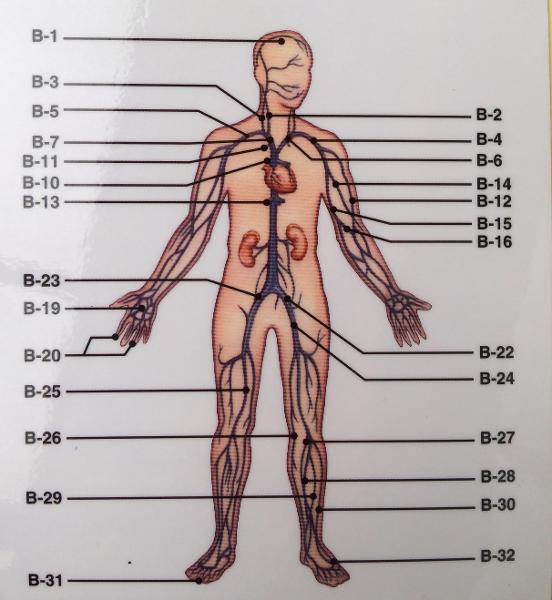 Major arteries and veins of torso | back 180  Descending aorta: descending thoracic aorta and descending abdominal aorta Renal arteries Inferior vena cava Renal veins |