Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 12
front 1 Where is Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulate? | back 1 lateral ventricles: line each hemisphere 3rd, 4th ventricle: in brain sterm subrachnoid space |
front 2 What cells make CSF | back 2 Neuroglia cells called ependymal cells |
front 3 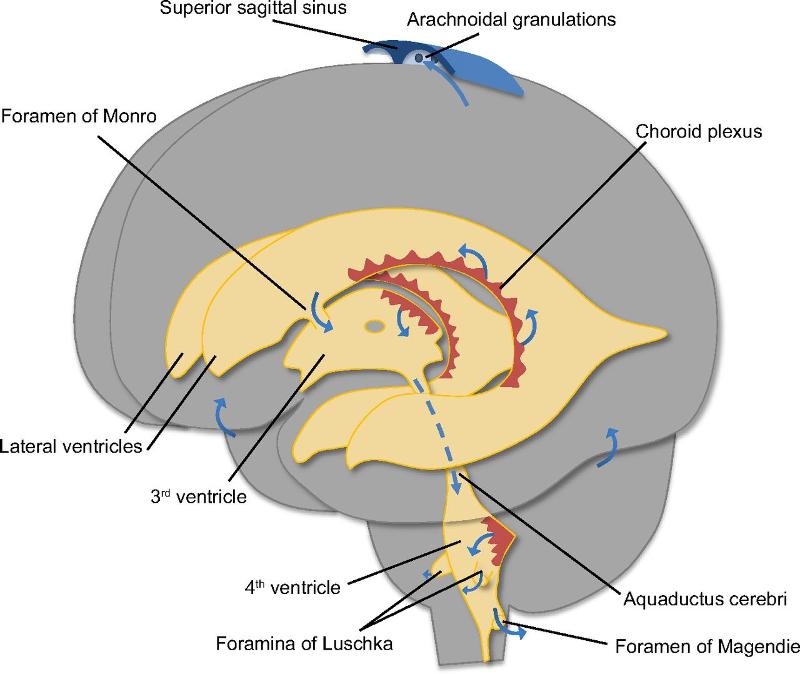 what is choroid plexus ? | back 3 Ependymal cells associated BV that produce CSF |
front 4 What is the funtion of CSF? | back 4 protects brain from movement of the skull + vertebral column -> brain floats buoyancy -> weight brain is reduced |
front 5 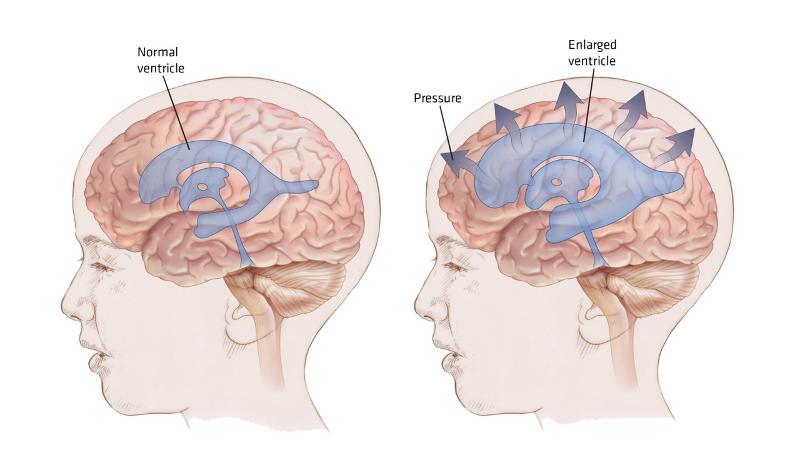 What is hydrocephalus? | back 5 Result from blockage of CSF through CNS (cerebral aqueduct) |
front 6 When hydrocephalus occur ? | back 6 Elderly people |
front 7 What are regions of the brain? | back 7
|
front 8 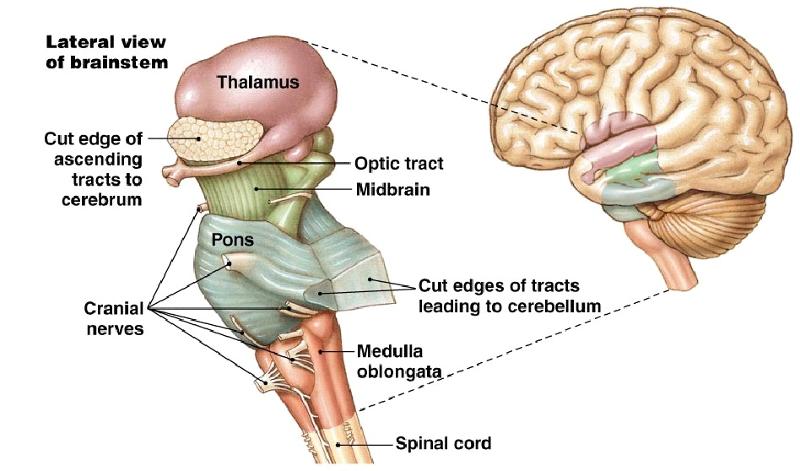 What is Brain Stem? | back 8 Connect the spinal cord and cerebellum |
front 9 What is structure of brain sterm | back 9 Anterior part: contain descending tracts involved with motor control Posterior: contain ascending tracts from the spinal cord, cerebellum and craial nerve |
front 10 what are funtions of Brain stem | back 10 Control of hear rate, blood pressure, breathing |
front 11 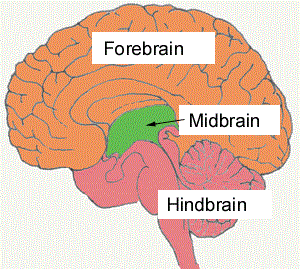 Part of the brain stem Midbrain | back 11 Smallest region of brain stem Composed of tracts of nerve fibers |
front 12 what is corpora quadrigemina | back 12 the largest midbrain nuclei |
front 13 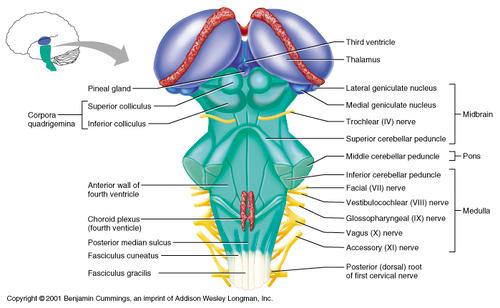 What are 2 superior colliculus? | back 13 Visual reflexes |
front 14 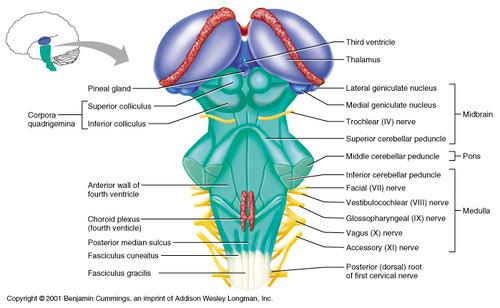 What are 2 inferior colliculus? | back 14 Auditory reflexes |
front 15 Midbrain contain pain perception | back 15 Receptors respond to opiates (thuoc phien) |
front 16 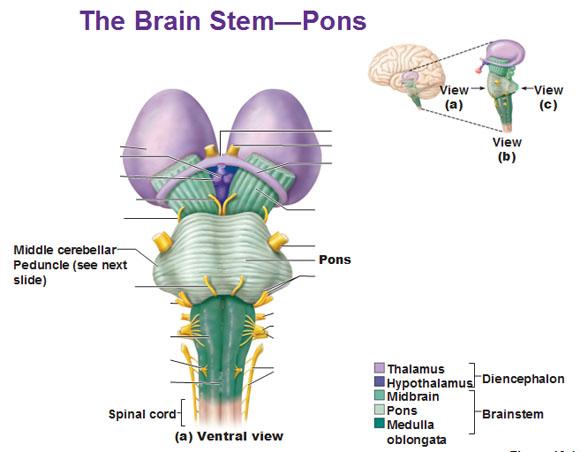 Part of the brain stem Pons(bridge) | back 16
|
front 17 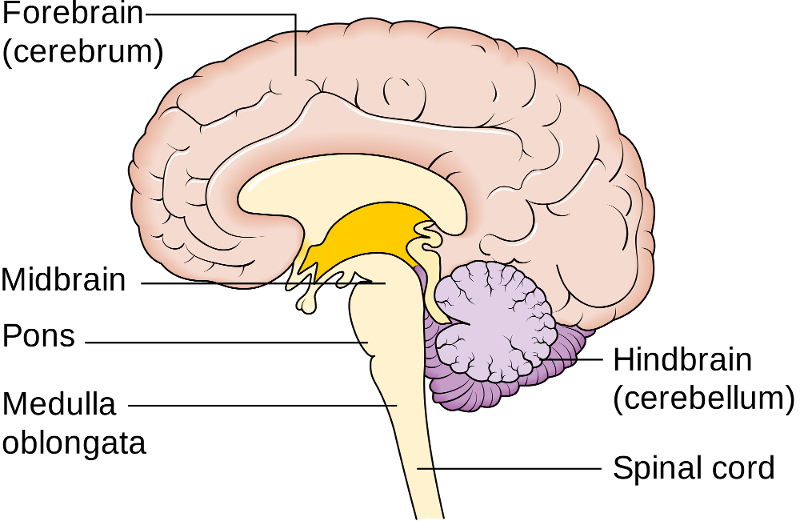 part of brain stem Medulla Oblongata | back 17
|
front 18 What are funtions of Medualla Oblongata | back 18
|
front 19 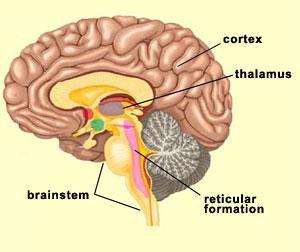 What is Reticular Formation? | back 19
|
front 20 Funtion of Reticular Formation | back 20
|
front 21 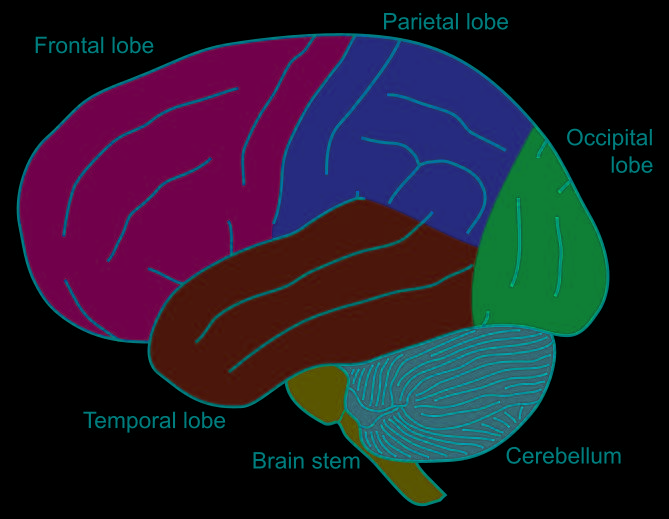 Part of the brain stem Cerebellum | back 21 (little brain) smaller version of cerebrum |
front 22 What part cerebellum attach to brain stem | back 22 Cerebellar peduncle |
front 23 What is Cerebellar peduncle | back 23
|
front 24 Gray matter of cerebellum | back 24 consists of outer cortex and nuclei deep within the cerebellum |
front 25 White matter of cerebellum | back 25 consists of tracts collectively called arbor vitae |
front 26 Parts of Cerebellum | back 26 Flocculonodular lobe, vermis, lateral he,ispheres |
front 27 Flocculonodular lobe: | back 27 • a small inferior part • Help control balance and coordination • Alcohol depresses cerebellum so, drinking driver test walking with imbalance |
front 28 Lateral hemisphere | back 28 two large hemispheres |
front 29 Funtion of lateral hemisphere | back 29 concert with the frontal lobes of |
front 30 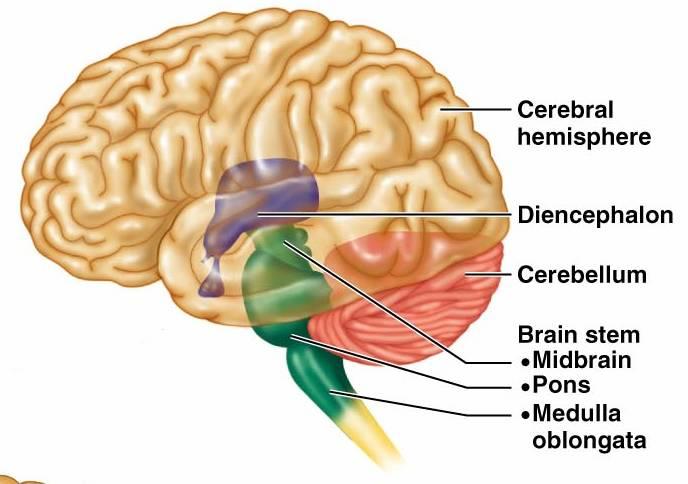 Part of brain stem Diencephalon | back 30 Location: between brain stem and cerebrum Main components: the thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus |
front 31 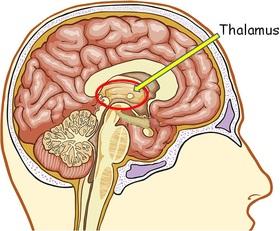 what is Thalamus | back 31
|
front 32 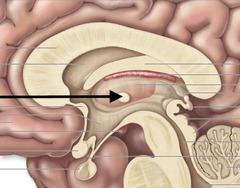 What is Interthamaic adhesion of thalamus ? | back 32 a small stalk in the center connecting two |
front 33 What does Sensory area do? | back 33 Ascending axons carrying sensory information project to the thalamus |
front 34 How does Sensory area work? | back 34 they synapse with thalamic neurons -> thalamic neurons send their axons to the cerebral cortex -> most awareness of sensory input occurs. (audiotory, visual,, pain, touch pass through thalamus) |
front 35 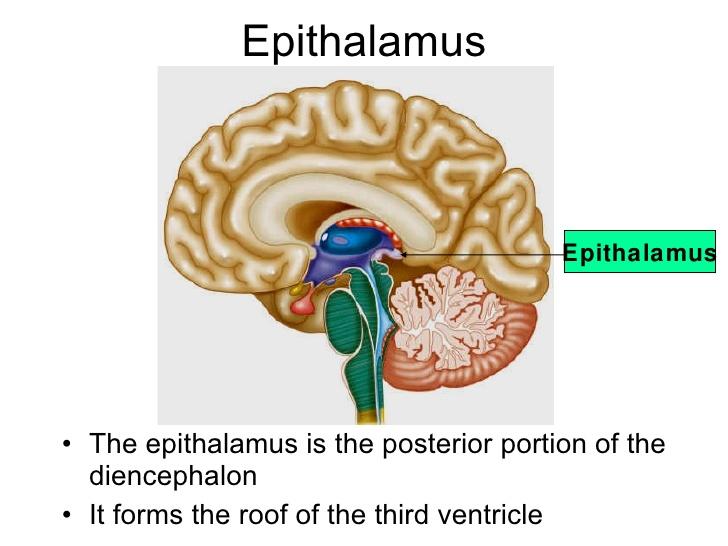 What is Epithlamus ? | back 35 Small area, superior and posterior to the thalamus |
front 36 What does Epithalamus consit ? | back 36 habenular nuclei and pineal body |
front 37 What is habenular nuclei | back 37 influenced by the sense of smell involved in emotional visceral responses to odors. (mui hoi) |
front 38 What is pineal body | back 38 Influence the sleep-wake cycle |
front 39 What is Hypothalamus | back 39 The most inferior part of the diencephalon • A collection of nuclei: connect to many other parts of the brain and spinal cord Involved with autonomic, endocrine, emotional (limbic system) |
front 40 Autonomic nervous system (ANS) | back 40 helpingcontrol heart rate, blood vessel diameter, urine release from the urinary bladder, and the movement of food through the digestive tract. |
front 41 Limbic system | back 41 HT is a part of the limbic system and affects mood, motivation, and emotions. Feeling relaxed, sexual pleasure, rage, and fear are related to HT |
front 42 What is Mammillary body? | back 42 involved in emotional response to order, olfactory |
front 43 Cerebrum | back 43 Logitudinal fissure: divide into left and right hemispheres |
front 44 Frontal lobe | back 44 voluntary motor function, motivation, aggression, the sense of smell, and mood. |
front 45 Parietal lobe | back 45 the reception and evaluation of most sensory information, such as touch, pain, temperature, balance, and taste. • The frontal and parietal lobes are |
front 46 Occipital lobe | back 46 reception and integration of visual input. |
front 47 Temporal lobe | back 47 Receive and evaluate input for smell and hearing. |
front 48 Cortex | back 48 the gray matter on the outer surface of the cerebrum |
front 49 Nuclei | back 49 clusters of gray matter deep inside the brain |
front 50 Cerebral medulla | back 50 white matter of the brain between the cortex and nuclei Consist of tracts that connect areas of the cerebral cortex to each other or to other parts of the CNS |
front 51 Parts of Cerebral medulla | back 51 Association fibers, Commissural fibers, Projection fibers |
front 52 Association fibers | back 52 connect areas of the cerebral cortex within the same hemisphere |
front 53 Commissural fibers | back 53 connect one cerebral hemisphere to the other. |
front 54 Projection fibers | back 54 between the cerebrum and other parts of the brain and spinal cord |
front 55 Sensory area of the Cerebral Cortex | back 55 Sensory pathways project to specific regions of the cerebral cortex,
called primary |
front 56 primary sensory areas. | back 56 Visual cortex: processing visual images in the occipital lobe auditory cortex: processing auditory stimuli in the temporal lobe Taste area: perceive in the parietal lobe Olfactory cortex: conscious and unconscious responses to odor on the inferior surface of the temporal lobe |
front 57 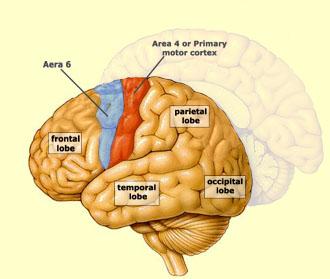 Motor area of Cerebral Cortex | back 57 primary motor cortex and premotor area |
front 58 primary motor cortex | back 58 controlling motor functions of the feet are in the most superior. controlling the face are in the inferior region |
front 59 premotor area | back 59 the staging area in which motor functions are organized before they are initiated in the motor cortex |
front 60 5) Basal Nuclei | back 60 A group of functionally related nuclei located in the inferior cerebrum, diencephalon, and midbrain Control of motor funtion |
front 61 subthalamic nucleus | back 61 is located in the diencephalon. |
front 62 substantial nigra | back 62 is located in the midbrain |
front 63 6) LImbic system | back 63 Parts of the cerebrum and diencephalon are grouped together |
front 64 Funtion of Limbic system | back 64 memory, reproduction, and nutrition |