Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
bio 102 ch 5
front 1 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (A) The number of alpha glucose 1-4 linkages in cellulose (B) The number of alpha glucose 1-4 linkages in starch (A) Item (A) is greater than item (B). (B) Item (A) is less than item (B). C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (B). D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B). | back 1 Answer: B |
front 2 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (A) The probability of finding chitin in fungal cell walls (B) The probability of finding chitin in arthropod exoskeletons A) Item (A) is greater than item (B). B) Item (A) is less than item (B). C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (B). D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B). | back 2 Answer: C |
front 3 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (A) The number of cis double bonds in saturated fatty acids (B) The number of cis double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids A) Item (A) is greater than item (B). B) Item (A) is less than item (B). C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (B). D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B). | back 3 Answer: B |
front 4 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (A) The probability that amino acids with nonpolar side chains are hydrophobic. (B) The probability that amino acids with side chains containing a carboxyl group are hydrophobic. A) Item (A) is greater than item (B). B) Item (A) is less than item (B). C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (B). D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B). | back 4 Answer: A |
front 5 5) For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (A) The number of purines in the DNA strand 5ʹ-AAGAGGAGAAA-3ʹ (B) The number of pyrimidines in the DNA strand 5ʹ-AAGAGGAGAAA-3ʹ A) Item (A) is greater than item (B). B) Item (A) is less than item (B). C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (B). D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B). | back 5 Answer: A |
front 6 Which of the following is not a polymer? A) glucose B) starch C) cellulose D) chitin E) DNA | back 6 Answer: A |
front 7 What is the chemical mechanism by which cells make polymers from monomers? A) phosphodiester linkages B) hydrolysis C) dehydration reactions D) ionic bonding of monomers E) the formation of disulfide bridges between monomers | back 7 Answer: C |
front 8 How many molecules of water are needed to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long? A) 12 B) 11 C) 10 D) 9 E) 8 | back 8 Answer: C |
front 9 Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis? A) Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers. B) Macromolecular synthesis occurs through the removal of water and digestion occurs through the addition of water. C) Dehydration reactions can occur only after hydrolysis. D) Hydrolysis creates monomers, and dehydration reactions break down polymers. E) A and B are correct. | back 9 Answer: E |
front 10 Which of the following polymers contain nitrogen? A) starch B) glycogen C) cellulose D) chitin E) amylopectin | back 10 Answer: D |
front 11 The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? A) C18H36O18 B) C18H30O15 C) C6H10O5 D) C18H10O15 E) C3H6O3 | back 11 Answer: B |
front 12 The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose monomers only if the monomers are the α form. Which of the following could amylase break down? A) glycogen B) cellulose C) chitin D) A and B only E) A, B, and C | back 12 Answer: A |
front 13 On food packages, to what does the term ʺinsoluble fiberʺ refer? A) cellulose B) polypeptides C) starch D) amylopectin E) chitin | back 13 Answer: A |
front 14 A molecule with the chemical formula C6H12O6 is probably a A) carbohydrate. B) lipid. C) monosaccharide D) A and B only. E) A, B, and C. | back 14 Answer: E |
front 15 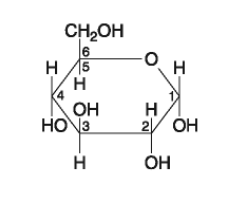 If 2 molecules of the general type shown in Figure 5.1 were linked together, carbon 1 of one molecule to carbon 4 of the other, the single molecule that would result would be A) maltose. B) fructose. C) glucose. D) galactose. E) sucrose. | back 15 Answer: A |
front 16 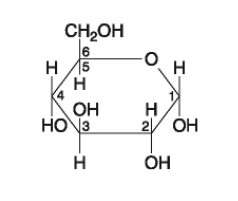 Which of the following descriptors is true of the molecule shown in Figure 5.1? A) hexose B) fructose C) glucose D) A and B only E) A and C only | back 16 Answer: E |
front 17 Lactose, a sugar in milk, is composed of one glucose molecule joined by a glycosidic linkage to one galactose molecule. How is lactose classified? A) as a pentose B) as a hexose C) as a monosaccharide D) as a disaccharide E) as a polysaccharide | back 17 Answer: D |
front 18 All of the following are polysaccharides except A) glycogen B) starch C) chitin D) cellulose E) amylopectin | back 18 Answer: A |
front 19 Which of the following is true of both starch and cellulose? A) They are both polymers of glucose. B) They are geometric isomers of each other. C) They can both be digested by humans. D) They are both used for energy storage in plants. E) They are both structural components of the plant cell wall. | back 19 Answer: A |
front 20 Which of the following is true of cellulose? A) It is a polymer composed of sucrose monomers. B) It is a storage polysaccharide for energy in plant cells. C) It is a storage polysaccharide for energy in animal cells. D) It is a major structural component of plant cell walls. E) It is a major structural component of animal cell plasma membranes. | back 20 Answer: D |
front 21 Humans can digest starch but not cellulose because A) the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is galactose. B) humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the beta (β) glycosidic linkages of starch but not the alpha (α) glycosidic linkages of cellulose. C) humans have enzymes that can hydrolyze the alpha (α) glycosidic linkages of starch but not the beta (β) glycosidic linkages of cellulose. D) humans harbor starch-digesting bacteria in the digestive tract. E) the monomer of starch is glucose, while the monomer of cellulose is maltose. | back 21 Answer: C |
front 22 All of the following statements concerning saturated fats are true except A) They are more common in animals than in plants. B) They have multiple double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. C) They generally solidify at room temperature. D) They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms. E) They are one of several factors that contribute to atherosclerosis. | back 22 Answer: B |
front 23 A molecule with the formula C18H36O2 is probably a A) carbohydrate. B) fatty acid. C) protein. D) nucleic acid. E) hydrocarbon. | back 23 Answer: B |
front 24 Which of the following statements is false for the class of biological molecules known as lipids? A) They are soluble in water. B) They are an important constituent of cell membranes. C) They contain more energy than proteins and carbohydrates. D) They are not true polymers. E) They contain waxes and steroids. | back 24 Answer: A |
front 25 What is a triacylglycerol? A) a protein with tertiary structure B) a lipid made with three fatty acids and glycerol C) a lipid that makes up much of the plasma membrane D) a molecule formed from three alcohols by dehydration reactions E) a carbohydrate with three sugars joined together by glycosidic linkages | back 25 Answer: B |
front 26 Which of the following is true regarding saturated fatty acids? A) They are the predominant fatty acid in corn oil. B) They have double bonds between carbon atoms of the fatty acids. C) They are the principal molecules in lard and butter. D) They are usually liquid at room temperature. E) They are usually produced by plants. | back 26 Answer: C |
front 27 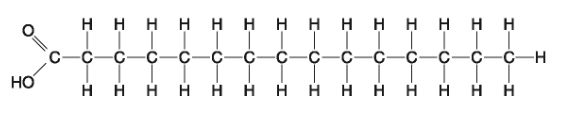 Which of the following statements is true regarding the molecule illustrated in Figure 5.2? A) It is a saturated fatty acid. B) A diet rich in this molecule may contribute to atherosclerosis. C) Molecules of this type are usually liquid at room temperature. D) A and B only E) A, B and C | back 27 Answer: D |
front 28 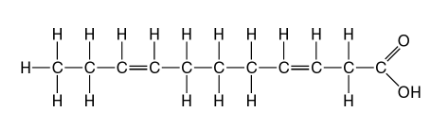 Which of the following statements is true regarding the molecule illustrated in Figure 5.3? A) It is a saturated fatty acid. B) A diet rich in this molecule may contribute to atherosclerosis. C) Molecules of this type are usually liquid at room temperature. D) A and B only E) A, B and C | back 28 Answer: C |
front 29 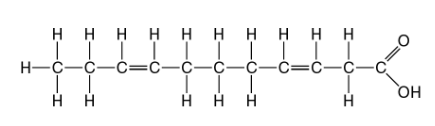 The molecule shown in Figure 5.3 is a A) polysaccharide. B) polypeptide. C) saturated fatty acid. D) triacylglycerol. E) unsaturated fatty acid. | back 29 Answer: E |
front 30 Large organic molecules are usually assembled by polymerization of a few kinds of simple subunits. Which of the following is an exception to this statement? A) a steroid B) cellulose C) DNA D) an enzyme E) a contractile protein | back 30 Answer: A |
front 31 The hydrogenation of vegetable oil results in which of the following? A) saturated fats and unsaturated fats with trans double bonds B) an increased contribution to artherosclerosis C) the oil (fat) being a solid at room temperature D) A and C only E) A, B, and C | back 31 Answer: E |
front 32 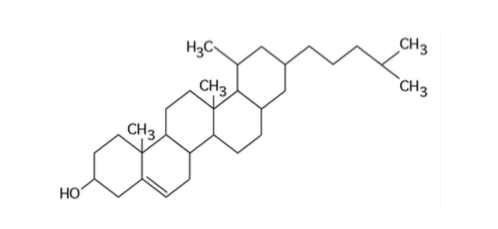 What is the structure shown in Figure 5.4? A) starch molecule B) protein molecule C) steroid molecule D) cellulose molecule E) phospholipid molecule | back 32 Answer: C |
front 33 Why are human sex hormones considered to be lipids? A) They are essential components of cell membranes. B) They are steroids, which are not soluble in water. C) They are made of fatty acids. D) They are hydrophilic compounds. E) They contribute to atherosclerosis. | back 33 Answer: B |
front 34 All of the following contain amino acids except A) hemoglobin. B) cholesterol. C) antibodies. D) enzymes. E) insulin. | back 34 Answer: B |
front 35 The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires A) the release of a water molecule. B) the release of a carbon dioxide molecule. C) the addition of a nitrogen atom. D) the addition of a water molecule. E) both B and C | back 35 Answer: A |
front 36 There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid different from another? A) different carboxyl groups attached to an alpha (α) carbon B) different amino groups attached to an alpha (α) carbon D) different alpha (α) carbons E) different asymmetric carbons | back 36 Answer: C |
front 37 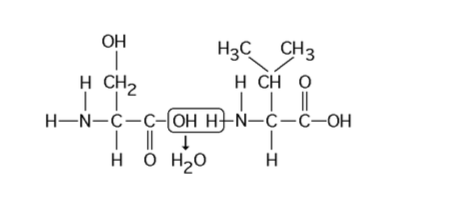 37) Which of the following statements is/are true regarding the chemical reaction illustrated in Figure 5.5? A) It is a hydrolysis reaction. B) It results in a peptide bond. C) It joins two fatty acids together. D) A and B only E) A, B, and C | back 37 Answer: B |
front 38 The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires which of the following? A) removal of a water molecule B) addition of a water molecule C) formation of an ionic bond D) formation of a hydrogen bond E) both A and C | back 38 Answer: A |
front 39 Polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are similar in that they A) are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis. B) are synthesized from monomers by dehydration reactions. C) are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers. D) are decomposed into their subunits by dehydration reactions. E) all contain nitrogen in their monomer building blocks. | back 39 Answer: B |
front 40 Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of the following compounds? A) triacylglycerides B) polysaccharides C) proteins D) A and C only E) A, B, and C | back 40 Answer: E |
front 41 Upon chemical analysis, a particular polypeptide was found to contain 100 amino acids. How many peptide bonds are present in this protein? A) 101 B) 100 C) 99 D) 98 E) 97 | back 41 Answer: C |
front 42 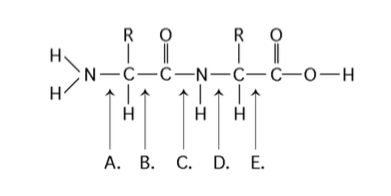 At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of the peptide, back to its component amino acid? | back 42 Answer: C |
front 43 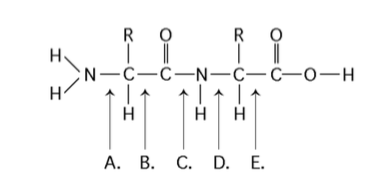 Which bond is a peptide bond? | back 43 Answer: C |
front 44 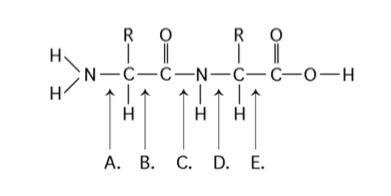 Which bond is closest to the N-terminus of the molecule? | back 44 Answer: A |
front 45 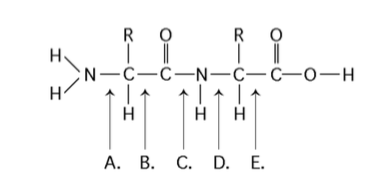 Which bond is closest to the carboxyl end of the molecule? | back 45 Answer: E |
front 46 How many different kinds of polypeptides, each composed of 12 amino acids, could be synthesized using the 20 common amino acids? A) 4^12 B) 12^20 C) 12^5 D) 20 E) 20^12 | back 46 Answer: E |
front 47 Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure of a protein? A) peptide bonds B) hydrogen bonds C) disulfide bonds D) phosphodiester bonds E) A, B, and C | back 47 Answer: A |
front 48 What maintains the secondary structure of a protein? A) peptide bonds B) hydrogen bonds C) disulfide bonds D) ionic bonds E) phosphodiester bonds | back 48 Answer: B |
front 49 Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha (α) helix and the beta (β) pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds | back 49 Answer: D |
front 50 The α helix and the β pleated sheet are both common polypeptide forms found in which level of protein structure? A) primary B) secondary C) tertiary D) quaternary E) all of the above | back 50 Answer: B |
front 51 The structure depicted in Figure 5.7 shows the A) 1-4 linkage of the α glucose monomers of starch. B) 1-4 linkage of the β glucose monomers of cellulose. C) double helical structure of a DNA molecule. D) α helix secondary structure of a polypeptide. E) β pleated sheet secondary structure of a polypeptide. | back 51 Answer: D |
front 52 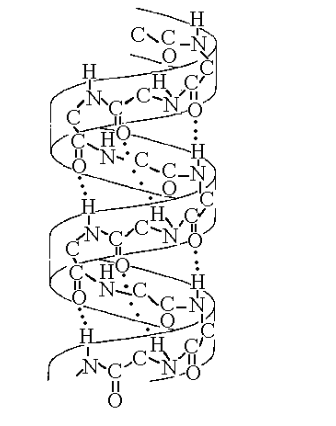 Figure 5.7 best illustrates the A) secondary structure of a polypeptide. B) tertiary structure of a polypeptide. C) quaternary structure of a protein. D) double helix structure of DNA. E) primary structure of a polysaccharide | back 52 Answer: A |
front 53 The tertiary structure of a protein is the A) bonding together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds. B) order in which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain. C) unique three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide. D) organization of a polypeptide chain into an α helix or β pleated sheet. E) overall protein structure resulting from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits | back 53 Answer: C |
front 54 A strong covalent bond between amino acids that functions in maintaining a polypeptideʹs specific three-dimensional shape is a (an) A) ionic bond. B) hydrophobic interaction. C) van der Waals interaction. D) disulfide bond. E) hydrogen bond. | back 54 Answer: D |
front 55 At which level of protein structure are interactions between the side chains (R groups) most important? A) primary B) secondary C) tertiary D) quaternary E) all of the above | back 55 Answer: C |
front 56 The R group or side chain of the amino acid serine is —CH2OH. The R group or side chain of the amino acid alanine is —CH3. Where would you expect to find these amino acids in a globular protein in aqueous solution? A) Serine would be in the interior, and alanine would be on the exterior of the globular protein. B) Alanine would be in the interior, and serine would be on the exterior of the globular protein. C) Both serine and alanine would be in the interior of the globular protein. D) Both serine and alanine would be on the exterior of the globular protein. E) Both serine and alanine would be in the interior and on the exterior of the globular protein. | back 56 Answer: B |
front 57 Misfolding of polypeptides is a serious problem in cells. Which of the following diseases are associated with an accumulation of misfolded proteins? A) Alzheimerʹs B) Parkinsonʹs C) diabetes D) A and B only E) A, B, and C | back 57 Answer: D |
front 58 What would be an unexpected consequence of changing one amino acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino acids? A) The primary structure of the protein would be changed. B) The tertiary structure of the protein might be changed. C) The biological activity or function of the protein might be altered. D) Only A and C are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. | back 58 Answer: E |
front 59 Altering which of the following levels of structural organization could change the function of a protein? A) primary B) secondary C) tertiary D) quaternary E) all of the above | back 59 Answer: E |
front 60 What method did Frederick Sanger use to elucidate the structure of insulin? A) X-ray crystallography B) bioinformatics C) analysis of amino acid sequence of small fragments D) NMR spectroscopy E) high-speed centrifugation | back 60 Answer: C |
front 61 Roger Kornberg used this method for elucidating the structure of RNA polymerase. A) X-ray crystallography B) bioinformatics C) analysis of amino acid sequence of small fragment D) NMR spectroscopy E) high-speed centrifugation | back 61 Answer: A |
front 62 Which of the following uses the amino acid sequences of polypeptides to predict a proteinʹs three -dimensional structure? A) X-ray crystallography B) bioinformatics C) analysis of amino acid sequence of small fragments D) NMR spectroscopy E) high-speed centrifugation | back 62 Answer: B |
front 63 The function of each protein is a consequence of its specific shape. What is the term used for a change in a proteinʹs three-dimensional shape or conformation due to disruption of hydrogen bonds, disulfide bridges, or ionic bonds? A) hydrolysis B) stabilization C) destabilization D) renaturation E) denaturation | back 63 Answer: E |
front 64 What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins? A) tertiary protein B) chaperonin C) enzyme protein D) renaturing protein E) denaturing protein | back 64 Answer: B |
front 65 DNAase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. What would first happen to DNA molecules treated with DNAase? A) The two strands of the double helix would separate. B) The phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribose sugars would be broken. C) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. D) The pyrimidines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. E) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. | back 65 Answer: B |
front 66 Which of the following statements about the 5ʹ end of a polynucleotide strand of DNA is correct? A) The 5ʹ end has a hydroxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. B) The 5ʹ end has a phosphate group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. C) The 5ʹ end has thymine attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. D) The 5ʹ end has a carboxyl group attached to the number 5 carbon of ribose. E) The 5ʹ end is the fifth position on one of the nitrogenous bases. | back 66 Answer: B |
front 67 Of the following functions, the major purpose of RNA is to A) transmit genetic information to offspring. B) function in the synthesis of protein. C) make a copy of itself, thus ensuring genetic continuity. D) act as a pattern or blueprint to form DNA. E) form the genes of higher organisms. | back 67 Answer: B |
front 68 Which of the following best describes the flow of information in eukaryotic cells? A) DNA → RNA → proteins B) RNA → proteins → DNA C) proteins → DNA → RNA D) RNA → DNA → proteins E) DNA → proteins → RNA | back 68 Answer: A |
front 69 Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides? A) a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group B) a nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar C) a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar D) a phosphate group and an adenine or uracil E) a pentose sugar and a purine or pyrimidine | back 69 Answer: C |
front 70 Which of the following are nitrogenous bases of the pyrimidine type? A) guanine and adenine B) cytosine and uracil C) thymine and guanine D) ribose and deoxyribose E) adenine and thymine | back 70 Answer: B |
front 71 Which of the following are nitrogenous bases of the purine type? A) cytosine and guanine B) guanine and adenine C) adenine and thymine D) thymine and uracil E) uracil and cytosine | back 71 Answer: B |
front 72 If a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine? A) 10 B) 20 C) 40 D) 80 E) impossible to tell from the information given | back 72 Answer: C |
front 73 A double-stranded DNA molecule contains a total of 120 purines and 120 pyrimidines. This DNA molecule could be composed of A) 120 adenine and 120 uracil molecules. B) 120 thymine and 120 adenine molecules. C) 120 cytosine and 120 thymine molecules. D) 240 adenine and 240 cytosine molecules. E) 240 guanine and 240 thymine molecules. | back 73 Answer: B |
front 74 The difference between the sugar in DNA and the sugar in RNA is that the sugar in DNA A) is a six-carbon sugar and the sugar in RNA is a five-carbon sugar. B) can form a double-stranded molecule. C) has a six-membered ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. D) can attach to a phosphate. E) contains one less oxygen atom. | back 74 Answer: E |
front 75 Which of the following statements best summarizes the structural differences between DNA and RNA? A) RNA is a protein, whereas DNA is a nucleic acid. B) DNA is a protein, whereas RNA is a nucleic acid. C) DNA nucleotides contain a different sugar than RNA nucleotides. D) RNA is a double helix, but DNA is single-stranded. E) A and D are correct. | back 75 Answer: C |
front 76 In the double helix structure of nucleic acids, cytosine hydrogen bonds to A) deoxyribose. B) ribose. C) adenine. D) thymine. E) guanine. | back 76 Answer: E |
front 77 If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5ʹATTGCA3ʹ, the other complementary strand would have the sequence A) 5ʹTAACGT3ʹ. B) 3ʹTAACGT5ʹ. C) 5ʹUAACGU3ʹ. D) 3ʹUAACGU5ʹ. E) 5ʹUGCAAU3ʹ. | back 77 Answer: B |
front 78 What is the structural feature that allows DNA to replicate? A) sugar-phosphate backbone B) complementary pairing of the nitrogenous bases C) disulfide bonding (bridging) of the two helixes D) twisting of the molecule to form an α helix E) three-component structure of the nucleotides | back 78 Answer: B |
front 79 A new organism is discovered in the forests of Costa Rica. Scientists there determine that the polypeptide sequence of hemoglobin from the new organism has 72 amino acid differences from humans, 65 differences from a gibbon, 49 differences from a rat, and 5 differences from a frog. These data suggest that the new organism A) is more closely related to humans than to frogs. B) is more closely related to frogs than to humans. C) may have evolved from gibbons but not rats. D) is more closely related to humans than to rats. E) may have evolved from rats but not from humans and gibbons. | back 79 Answer: B |
front 80 Which of the following is an example of hydrolysis? A) the reaction of two monosaccharides, forming a disaccharide with the release of water B) the synthesis of two amino acids, forming a peptide with the release of water C) the reaction of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the release of water D) the reaction of a fat, forming glycerol and fatty acids with the utilization of water E) the synthesis of a nucleotide from a phosphate, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base with the production of a molecule of | back 80 Answer: D |
front 81 The element nitrogen is present in all of the following except A) proteins. B) nucleic acids. C) amino acids. D) DNA. E) monosaccharides. | back 81 Answer: E |
front 82 Which of the following is a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules? A) carbohydrates B) lipids C) proteins D) nucleic acids | back 82 Answer: B |
front 83 Which of the following store and transmit hereditary information? A) carbohydrates B) lipids C) proteins D) nucleic acids | back 83 Answer: D |
front 84 Enzymes are B) lipids. | back 84 Answer: C |
front 85 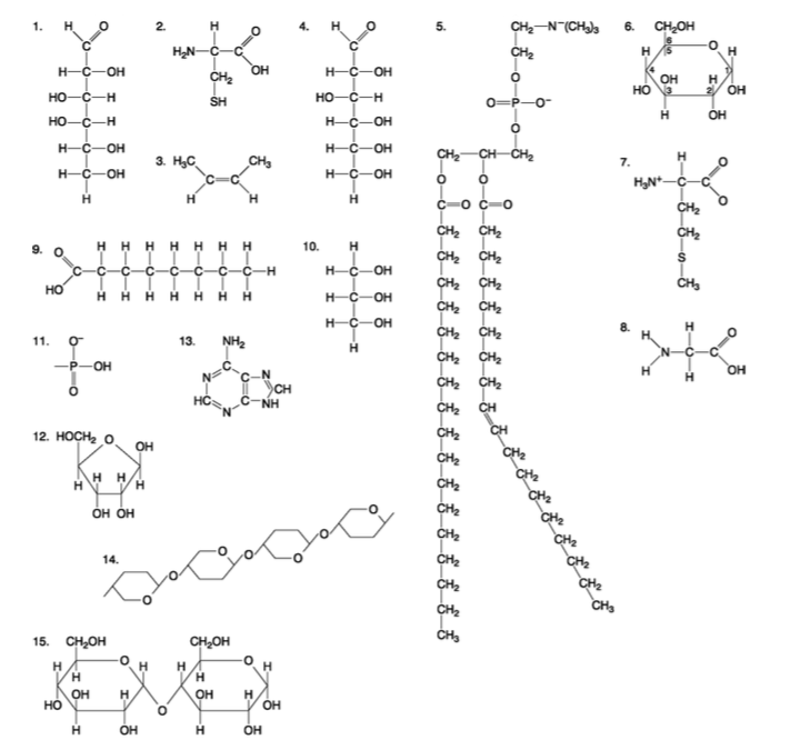 Which molecule has hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and would be found in plasma membranes? A) 1 B) 5 C) 6 D) 12 E) 14 | back 85 Answer: B |
front 86 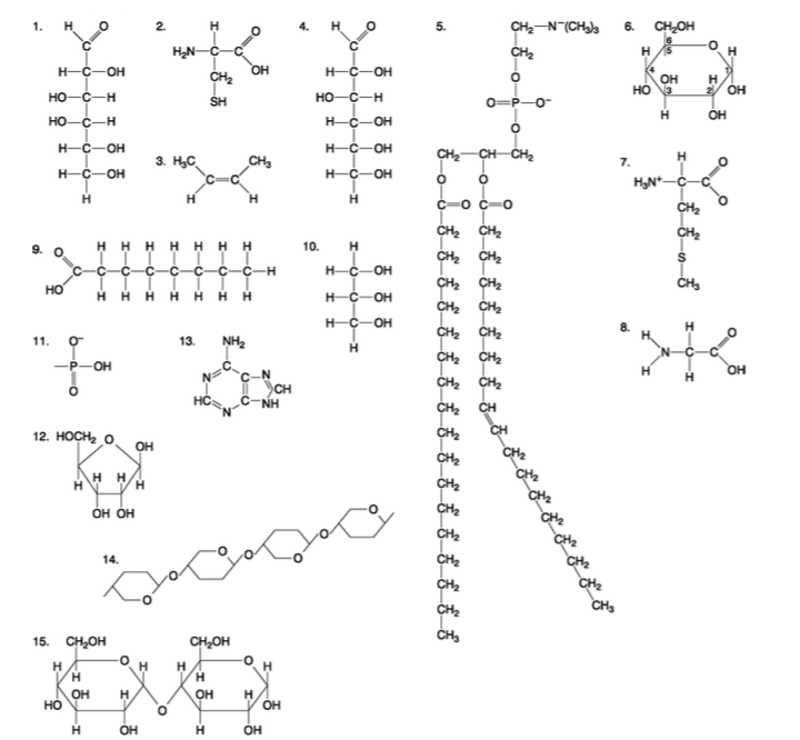 Which of the following combinations could be linked together to form a nucleotide? A) 1, 2, and 11 B) 3, 7, and 8 C) 5, 9, and 10 D) 11, 12, and 13 E) 12, 14, and 15 | back 86 Answer: D |
front 87 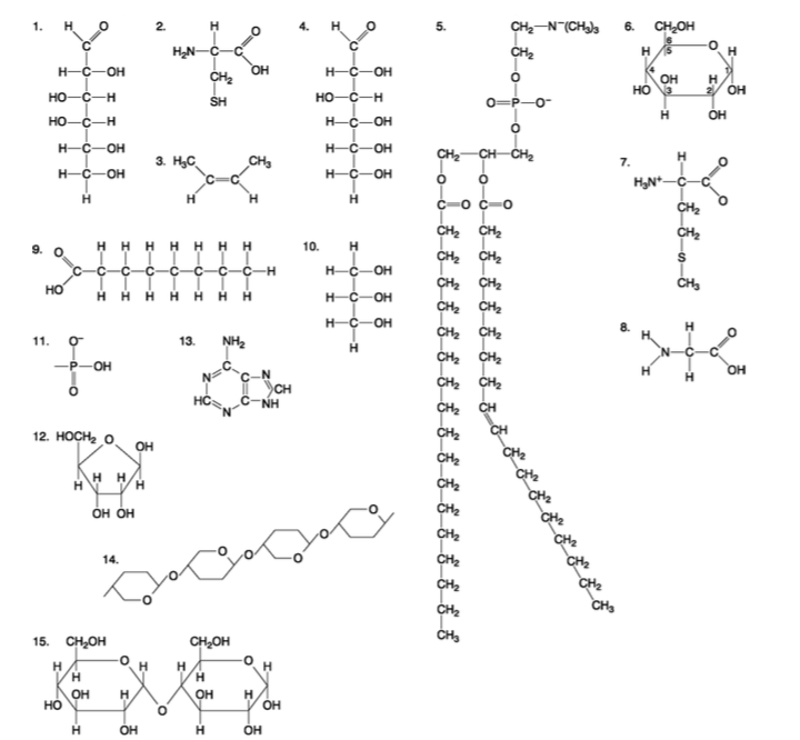 Which of the following molecules contain(s) an aldehyde type of carbonyl functional group? A) 1 B) 4 C) 8 D) 10 E) 1 and 4 | back 87 Answer: E |
front 88  Which molecule is glycerol? A) 1 B) 6 C) 10 D) 14 E) 15 | back 88 Answer: C |
front 89 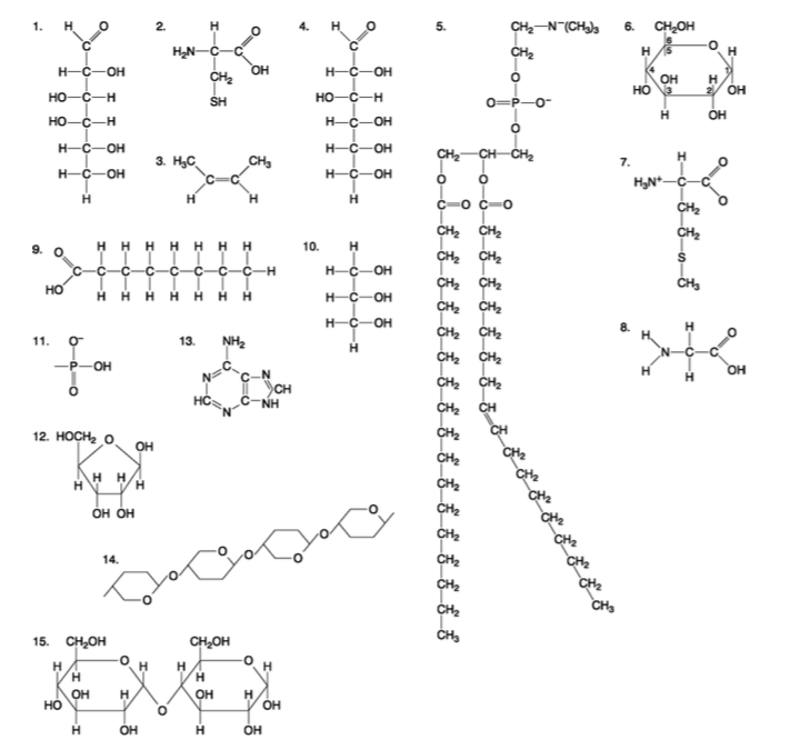 Which molecule is a saturated fatty acid? A) 1 B) 5 C) 6 D) 8 E) 9 | back 89 Answer: E |
front 90 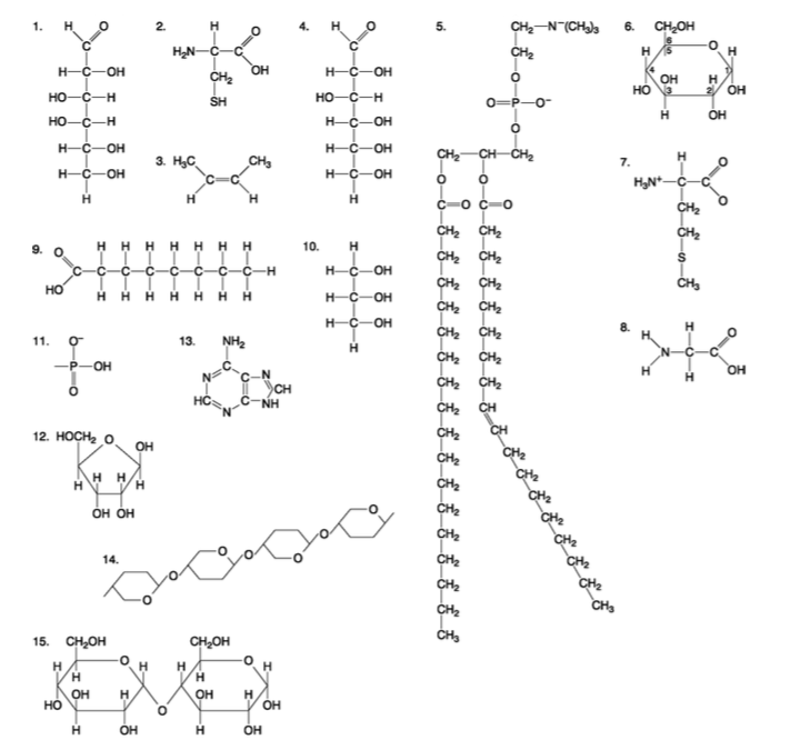 Which of the following molecules is a purine type of nitrogenous base? A) 2 B) 3 C) 5 D) 12 E) 13 | back 90 Answer: E |
front 91 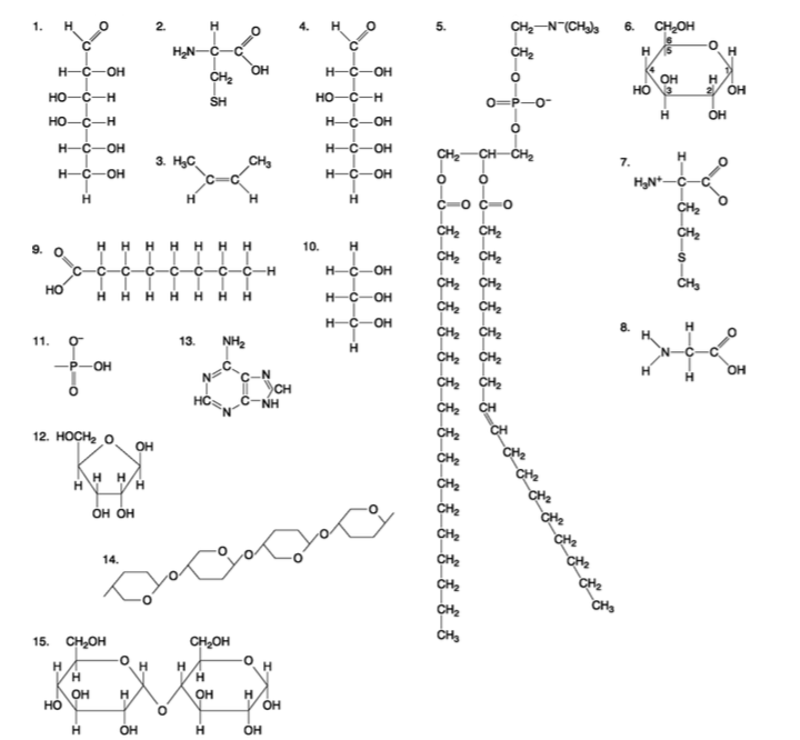 Which of the following molecules act as building blocks (monomers) of polypeptides? A) 1, 4, and 6 B) 2, 7, and 8 C) 7, 8, and 13 D) 11, 12, and 13 E) 12, 13, and 15 | back 91 Answer: B |
front 92 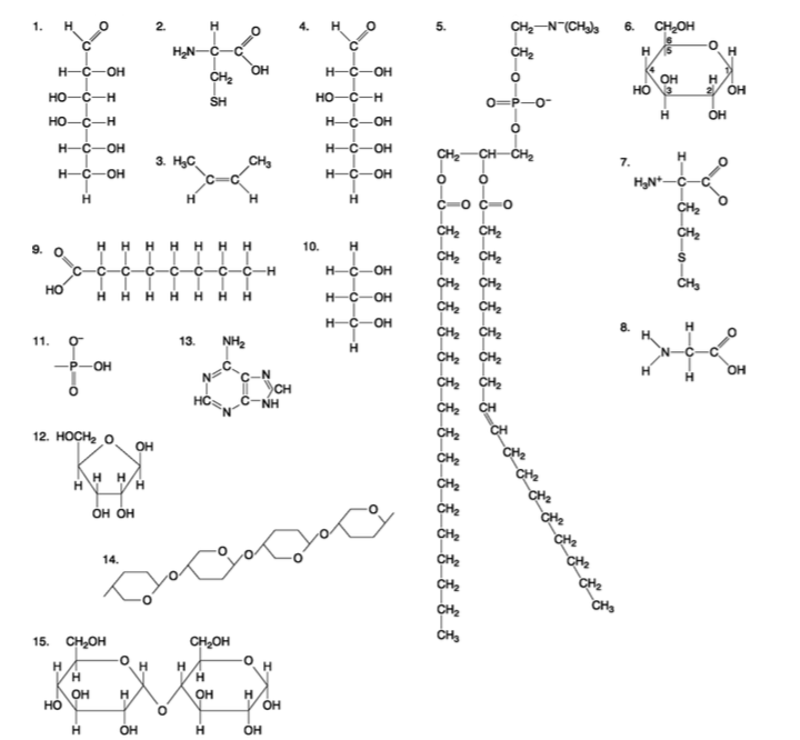 Which of the following molecules is an amino acid with a hydrophobic R group or side chain? A) 3 B) 5 C) 7 D) 8 E) 12 | back 92 Answer: C |
front 93 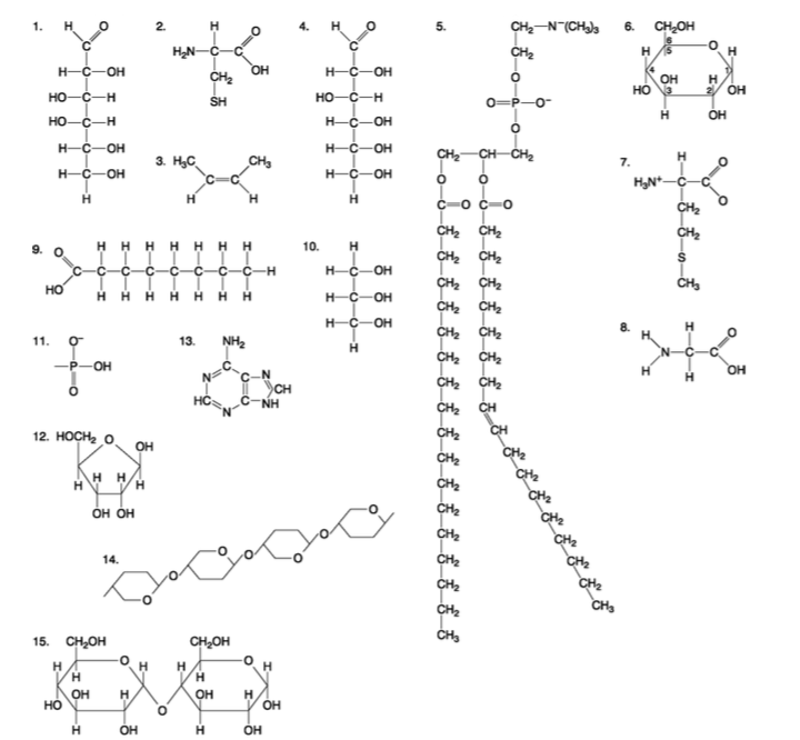 Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a peptide bond as a result of a dehydration reaction? A) 2 and 3 B) 3 and 7 C) 7and8 D) 8 and 9 E) 12 and 13 | back 93 Answer: C |
front 94 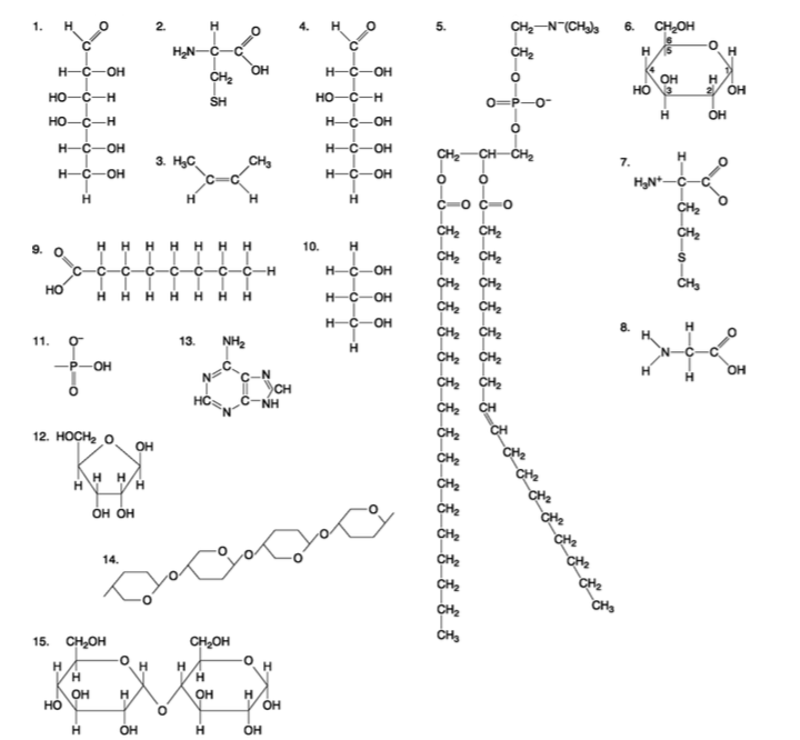 A fat (or triacylglycerol) would be formed as a result of a dehydration reaction between A) one molecule of 9 and three molecules of 10. B) three molecules of 9 and one molecule of 10. C) one molecule of 5 and three molecules of 9. D) three molecules of 5 and one molecule of 9. E) one molecule of 5 and three molecules of 10. | back 94 Answer: B |
front 95  Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a phosphodiester type of covalent bond? A) 3 and 4 B) 3 and 8 C) 6 and 15 D) 11 and 12 E) 11 and | back 95 Answer: D |
front 96 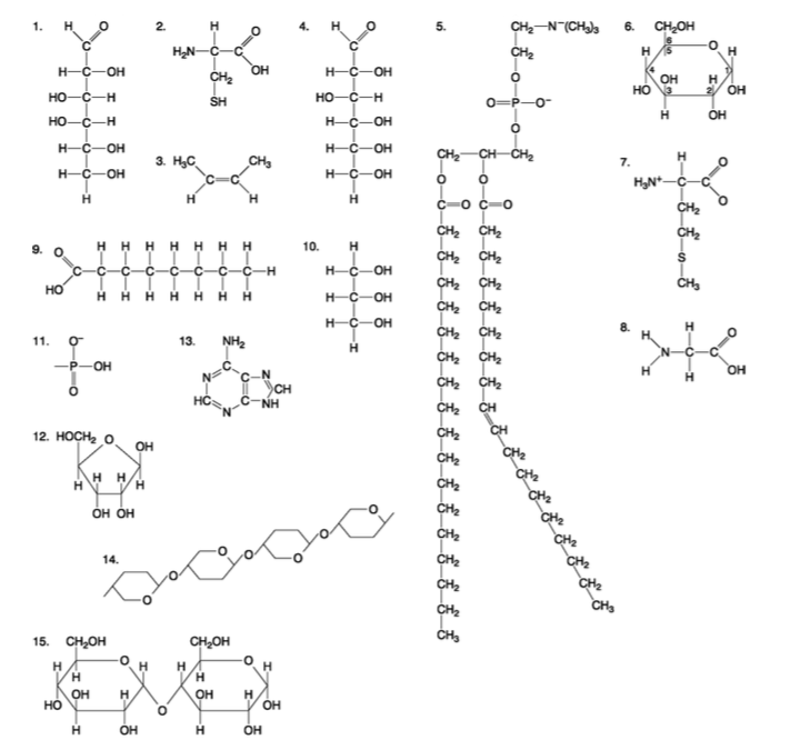 Which of the following molecules is the pentose sugar found in RNA? A) 1 B) 4 C) 6 D) 12 E) 13 | back 96 Answer: D |
front 97  Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type of covalent bond? A) 4 B) 6 C) 12 D) 13 E) 15 | back 97 Answer: E |
front 98 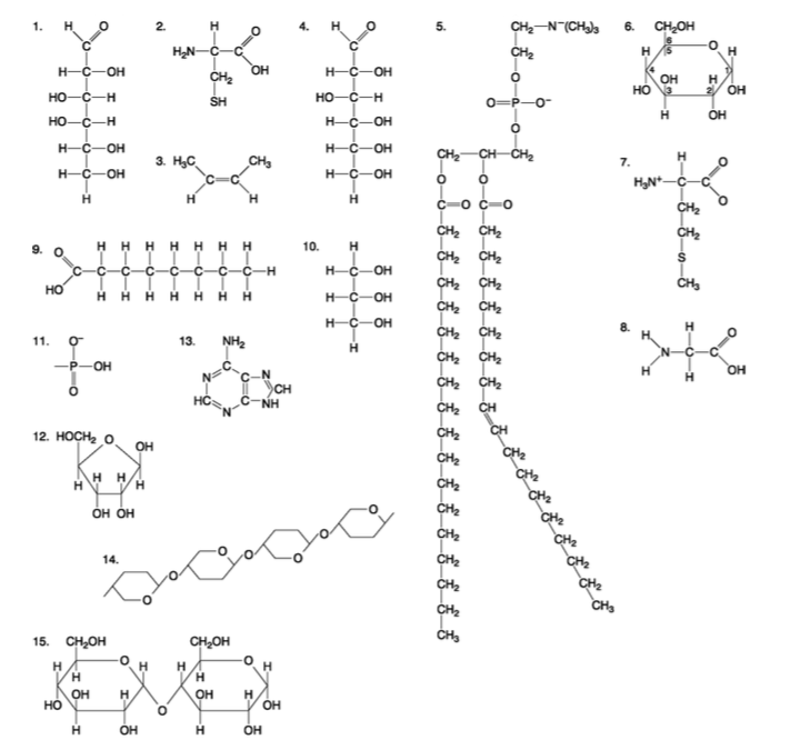 Which of the following molecules has (have) a functional group that frequently is involved in maintaining the tertiary structure of a protein? A) 2 B) 3 C) 9 D) 11 E) 9 and 11 | back 98 Answer: A |
front 99 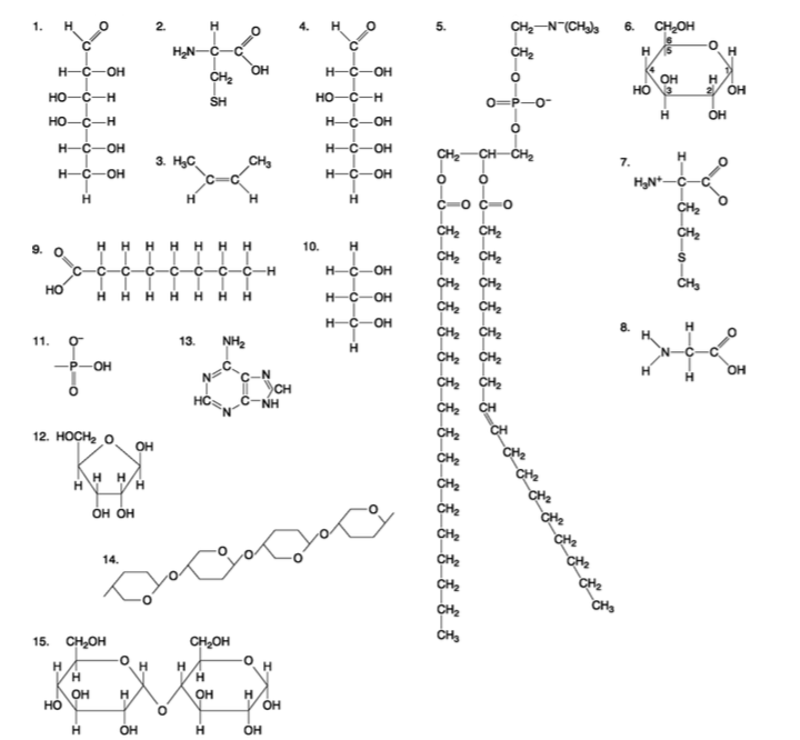 Which of the following molecules consists of a hydrophilic ʺheadʺ region and a hydrophobic ʺtailʺ region? A) 2 B) 5 C) 7 D) 9 E) 11 | back 99 Answer: B |
front 100  Which of the following statements is false? A) 1 and 4 could be joined together by a glycosidic linkage to form a disaccharide. B) 9 and 10 could be joined together by ester bonds to form a triacylglycerol. C) 2 and 7 could be joined together to form a short peptide. D) 2, 7, and 8 could be joined together to form a short peptide. E) 14 and 15 could be joined together to form a polypeptide. | back 100 Answer: E |
front 101 Which term includes all others in the list? A) monosaccharide B) disaccharide C) starch D) carbohydrate E) polysaccharide | back 101 Answer: D |
front 102 The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the molecular formula for a polymer made by linking ten glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? A) C60H120O60 B) C6H12O6 C) C60H102O51 D) C60H100O50 E) C60H111O51 | back 102 Answer: C |
front 103 The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose monomers only if the monomers are the α form. Which of the following could amylase break down? A) glycogen, starch, and amylopectin B) glycogen and cellulose C) cellulose and chitin D) starch and chitin E) starch, amylopectin, and cellulose | back 103 Answer: A |
front 104 Which of the following statements concerning unsaturated fats is true? A) They are more common in animals than in plants. B) They have double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. C) They generally solidify at room temperature. D) They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms. E) They have fewer fatty acid molecules per fat molecule. | back 104 Answer: B |
front 105 The structural level of a protein least affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding is the A) primary level. B) secondary level. C) tertiary level. D) quaternary level. E) All structural levels are equally affected. | back 105 Answer: A |
front 106 Which of the following pairs of base sequences could form a short stretch of a normal double helix of DNA? A) 5ʹ-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-3ʹ with 3ʹ-purine-pyrimidine-purine-pyrimidine-5ʹ B) 5ʹ-A-G-C-T-3ʹ with 5ʹ-T-C-G-A-3ʹ C) 5ʹ-G-C-G-C-3ʹ with 5ʹ-T-A-T-A-3ʹ D) 5ʹ-A-T-G-C-3ʹ with 5ʹ-G-C-A-T-3ʹ E) All of these pairs are correct. | back 106 Answer: D |
front 107 Enzymes that break down DNA catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. What would happen to DNA molecules treated with these enzymes? A) The two strands of the double helix would separate. B) The phosphodiester linkages between deoxyribose sugars would be broken. C) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. D) The pyrimidines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. E) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. | back 107 Answer: B |