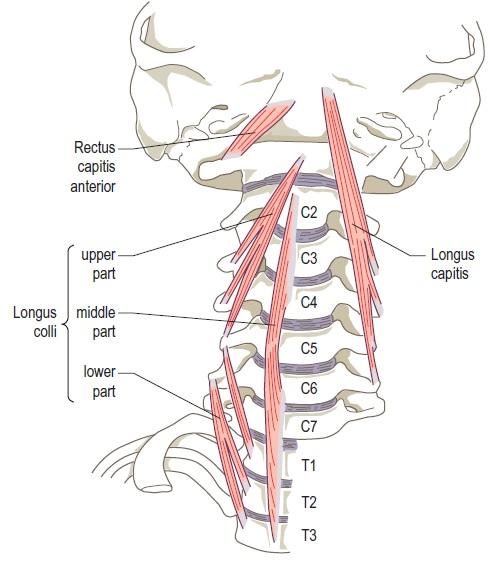
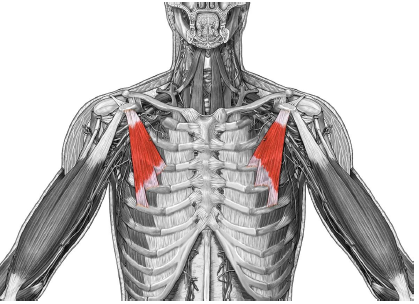
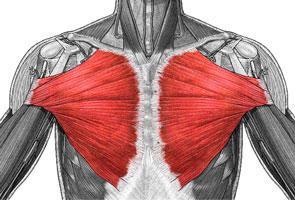
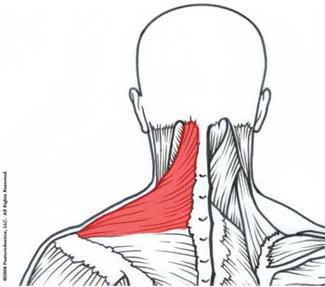
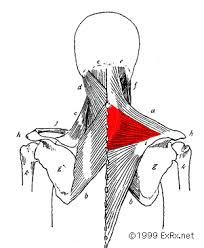
| back 1 - Concentrically accelerates cervical flexion
- flex
the head and neck, rotate the head ipsilaterally
|
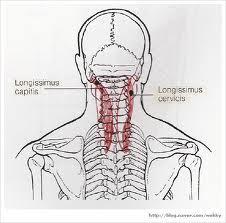
| back 2 - Concentrically accelerates cervical flexion, lateral flexion
and ipsilateral rotation
- It is commonly injured in rear end
whiplash injuries, usually resulting from a car crash. This muscle
is in front of the spine and is thought by some scientists that it
may cause some whiplash patients to have an unnatural lack of
curvature in the patients' neck.
|
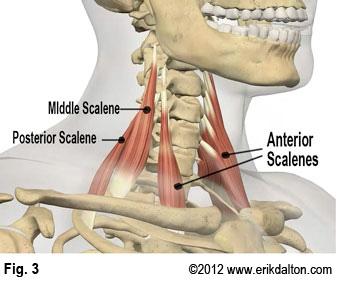
| back 3 - Concentrically accelerates cervical flexion, rotiation, and
lateral flexion
- assists rib elevation during
inhalation
|
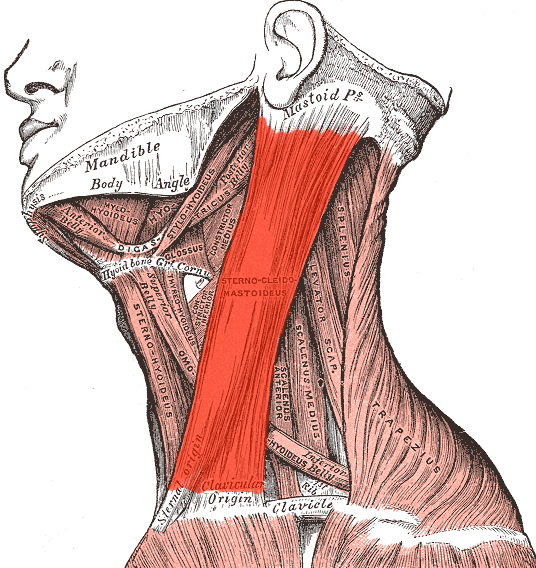
| back 4 - Concentrically accelerates cervical flexion, rotation and
lateral flexion
- When both sides of the muscle act together,
it flexes the neck and extends the head. When one side acts
alone, it causes the head to rotate to the opposite side and
flexes laterally to the same side (ipsilaterally). It also acts
as an accessory muscle of respiration, along with the scalene
muscles of the neck.
|
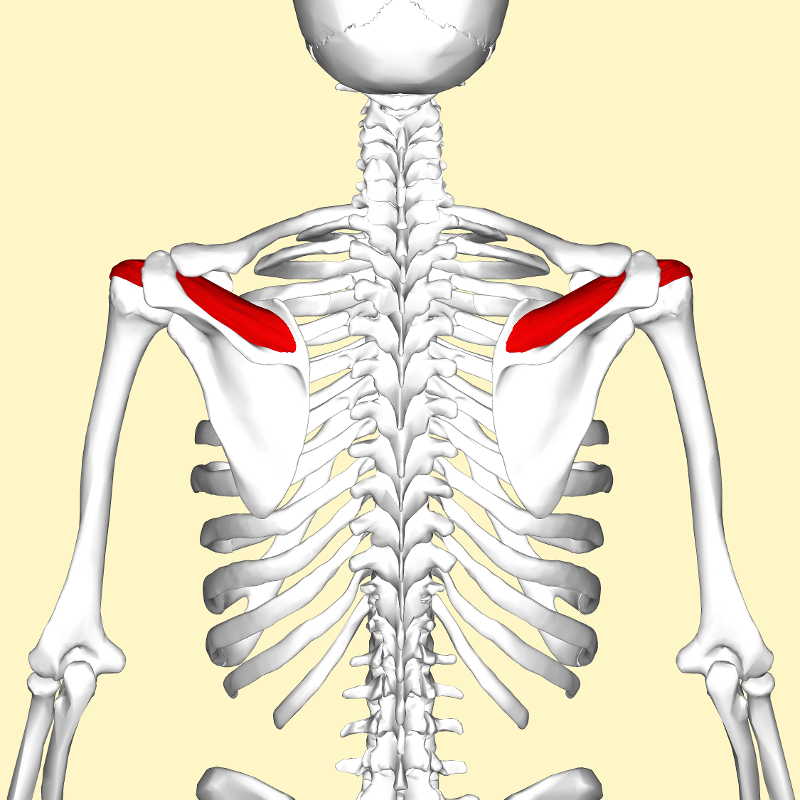
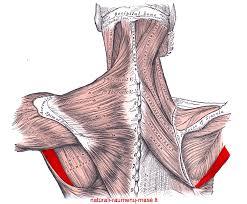
| back 5 - Concentrically accelerates cervical extension, lateral and
ipsilateral rotation when the scapulaer is anchored
- Assists
in elevation and downward rotation of the scapulae
- As
the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the
scapula
|
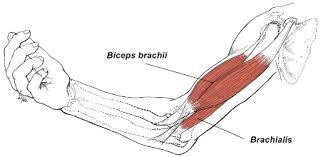
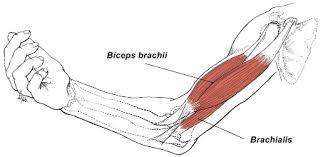
| back 6 - Concentrically accelerates elbow flexion
- is a
synergist that assists the biceps brachii in flexing at the
elbow
|
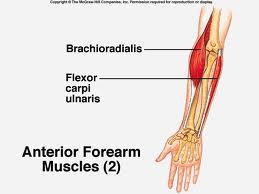
| back 7 - Concentraically accelerates elbow flexion
-
synergist that assists the biceps brachii in flexing at
the elbow
- Other name: Forearm
(Upper-outer)
|
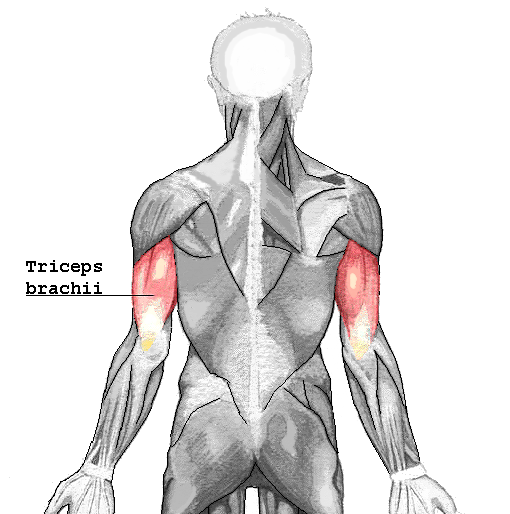
| back 8 - Concentrically accelerates elbow extension and shoulder
extension
- It is the muscle principally responsible
for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the
arm).
|
| back 9 - Concentrically accelerates elbow flexion, supination of the
radioulnar joint, and shoulder flexion
- its main
function is where it flexes the forearm at the elbow and
supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when
opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps unscrews the
cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out
(flexion).[1
|
| back 10 - Rotator Cuff
- Concentrically accelerates abduction of
the arm
|
| back 11 - Rotator Cuff
- Concentrically accelerates shoulder internal
rotation
- rotates the head of the humerus medially
(internal rotation); when the arm is raised, it draws the
humerus forward and downward. It is a powerful defense to the
front of the shoulder-joint, preventing displacement of the
head of the humerus.
|
| back 12 - Rotator Cuff
- Concentrically accelerates shoulder external rotation
- As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the
main function is to externally rotate the humerus and
stabilize the shoulder joint.
|
| back 13 - Rotator Cuff
- Concentrically accelerates shoulder
external rotation
- help hold the humeral head in the
glenoid cavity of the scapula
|
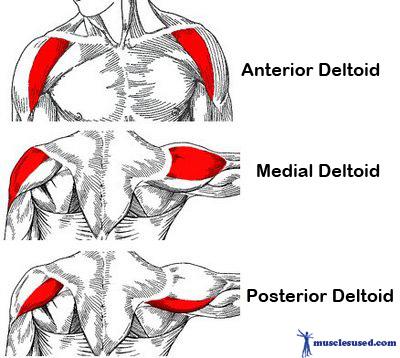
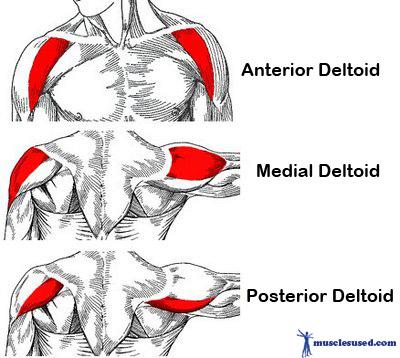
| back 14 - Concentrically accelerates shoulder internal rotation,
adduction and extension
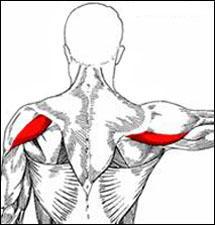
|
| back 15 - Concentrically accelerates shoulder extension and external
rotation.
- one of 3 deltoid
-
shoulder (rear)
|
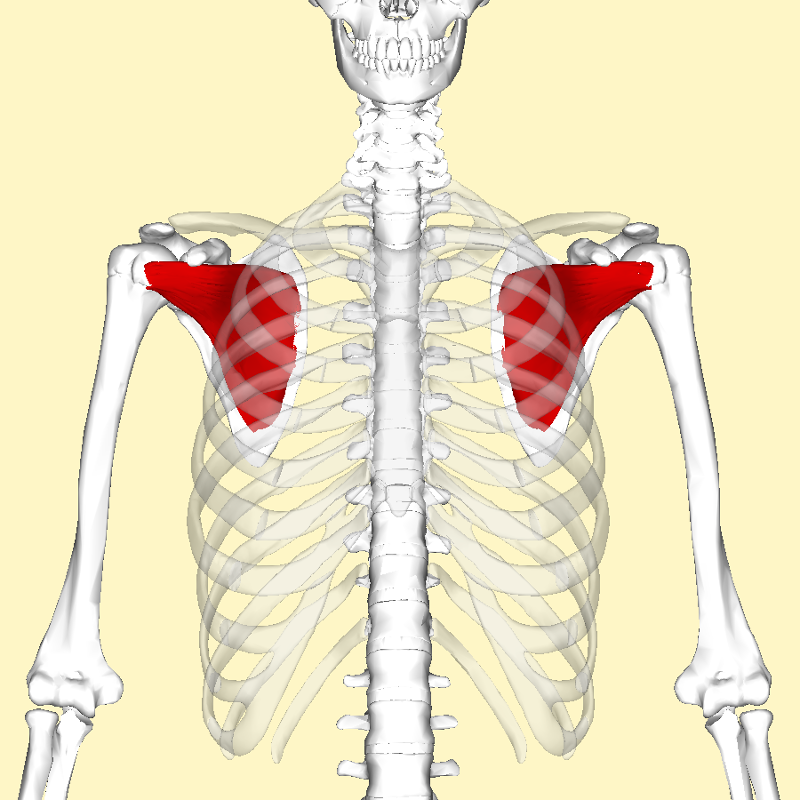
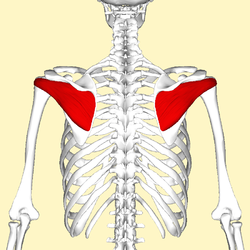
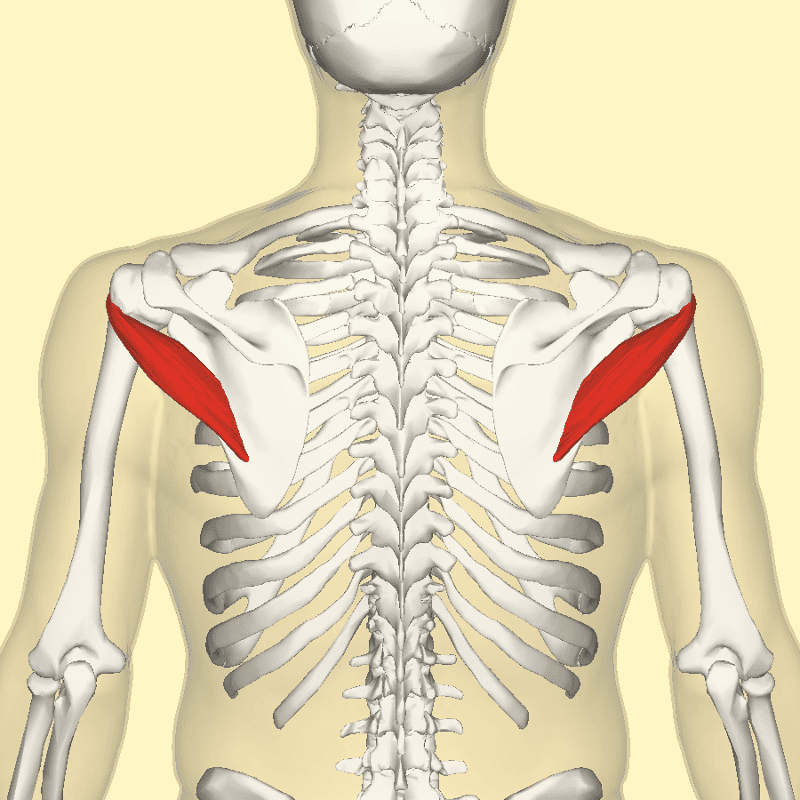
| back 16 - Concentrically accelerates shoulder abduction
- In
addition to being fuctional, this muscle helps create a
defined look to your shoulder when developed
|
| back 17 - Concentrically accelerates shoulder flexion and internal
rotation
|
| back 18 - Concentrically protacts the scapula
- Draws
scapula forward and and downward
|
| back 19 - Concentrically acceleratees shoulder flexion, horizontal
adduction and internal rotation
- predominantly used to
control the movement of the arm
- also play
a part in deep inhalation, pulling the ribcage to create room
for the lungs to expand
|
| back 20 - Concentrically accelerates cervical extension, lateral flexion,
and rotation
- Concentrically accelerates scapular elevation
(traekker skulderblade up)
|
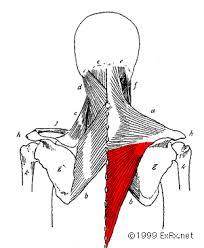
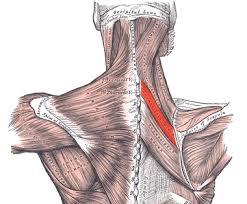
| back 21 - Cencentrically accelerates scapular retraction (traekker
skulderblade mod midten)
|
| back 22 - Concentrically accelerates scapular depression (traekker
skulderblade nedaf)
|
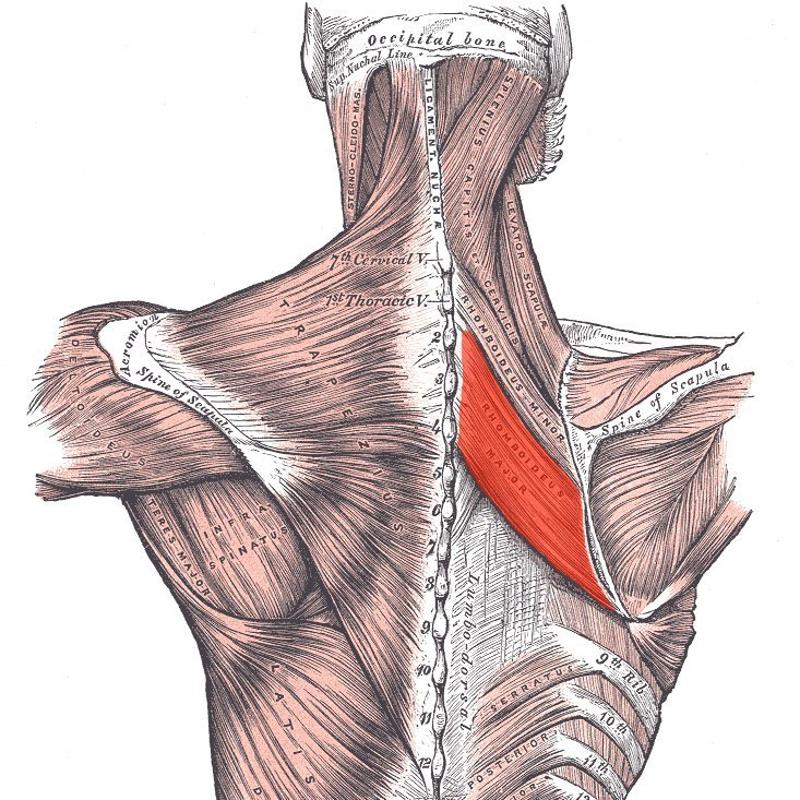
| back 23 - Concentrically produces scapular retraction and downward
rotation (smaller)
|
| back 24 - Concentrically produces scapular retraction and downward
rotation (bigger) (traekker skulder blade sammen)
|
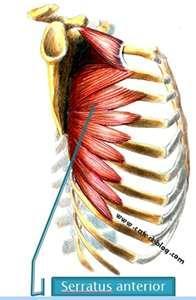
front 25 Serratus Anterior (wings) | back 25 - Concentrically accelerates scapular protraction
(Abduction)
- abduct scapula and upwardly rotates it while
abducting the arm
- Stabilize scapular by holding it to chest
wall
|
| back 26 - Concentrically accelerates shoulder extension, adduction, and
internal rotation
- Adducts the arm (at the
shoulder)
- Medially rotates the arm (at the
shoulder)
- Extends the arm (at the
shoulder)
|
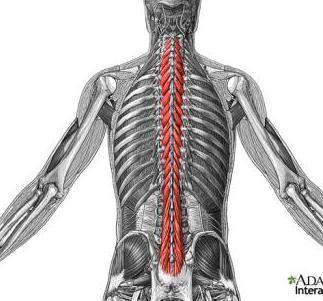
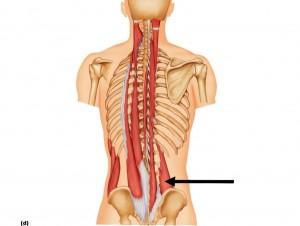
| back 27 - Concentrically accelerates spinal extension and contralateral
rotation
- Extension of vertebral column (bukke
fremover)
- Lateral flexion of vertebral colum (side
boejning)
- Contralateral (opposite side) rotation
|
| back 28 - Extension of vertebral column
- Lateral flexion of
vertebral column
"bukke fremover og boeje til siden" |
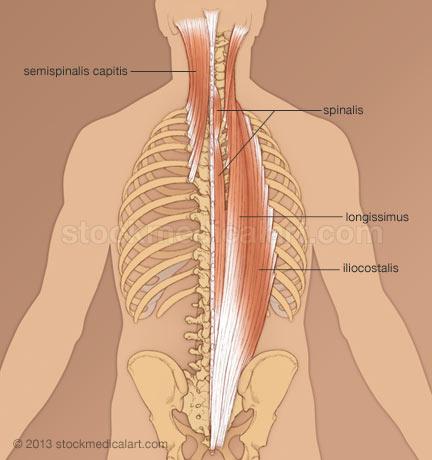
front 29 Superficial Erector Spinae:
- Iliocostalis
- Longissimus
- Spinalis
| back 29 - Concentrically accelerates spinal extension, rotation adn
lateral flexion
- 3 muscles, grouped in one...
|
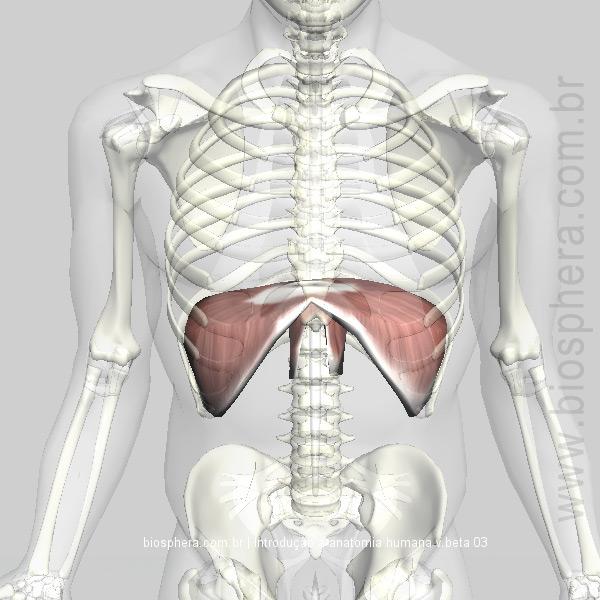
| back 30 - Concentrically pulls the central tendon inferiorly, increasing
the volume in the thoracic cavity (Vejrtraekning)
|
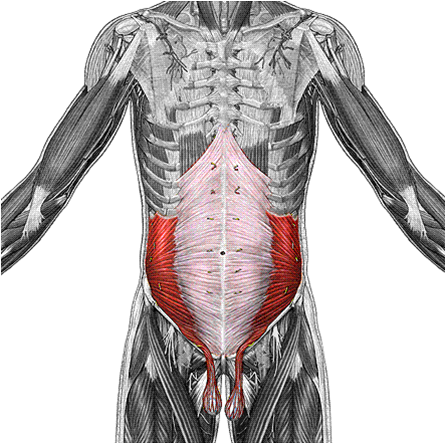
| back 31 - Increases intra-abdominal pressure
- Supports the
abdominal visecera
|
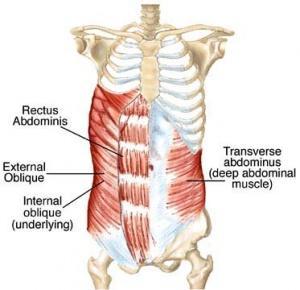
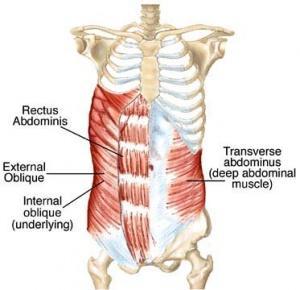
| back 32 Concentrically accelerates spinal flexion, lateral flexion, and
ipsilateral rotation |
| back 33 - Concentrically accelerates spinal flexion, laeral flexion, and
contralateral rotation
|
| back 34 - Concentrically acceleartes spinal flezion, lateral flexion, and
rotation
- Flexes vertebral column (torso)
- Compresses abdomen
|
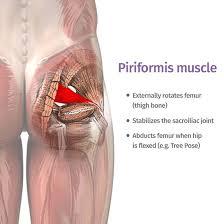
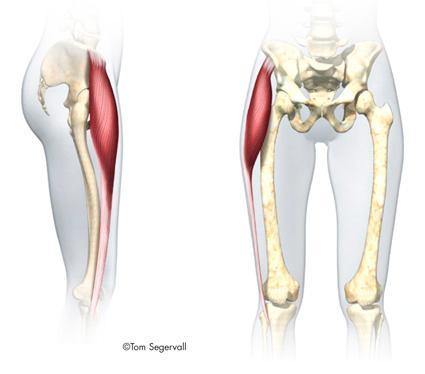
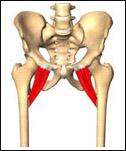
| back 35 - Concentrically accelerates hip external rotation, abduction and
extension
- muscle runs behind the hip joint and aids in
external hip rotation, or turning your leg outward. The catch here
is that the muscle crosses over the sciatic nerve.
- muscle
can become tight from, for example, too much sitting.. and then
compress and irritate the sciatic nerve.
|
| back 36 - Concentrically accelerates hip flexion, external rotation, and
abduction
- Concentrically accelerates knee flextion and
interal rotation
- muscle assists in flexing, weak abduction
and lateral rotation of hip, and flexion of knee.
Looking at the bottom of one's foot, as if checking to see if
one had stepped in gum, demonstrates all four actions of this
muscle.
|
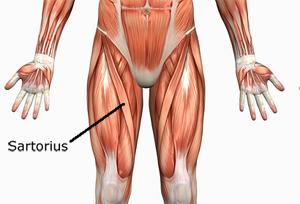
| back 37 - Concentrically accelerates hip flexion and external
rotation
- Flexes and laterally rotates thigh at hip
- Flexes trunk and hip on thigh
|
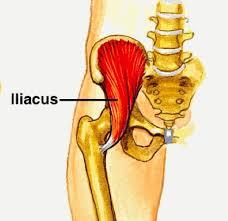
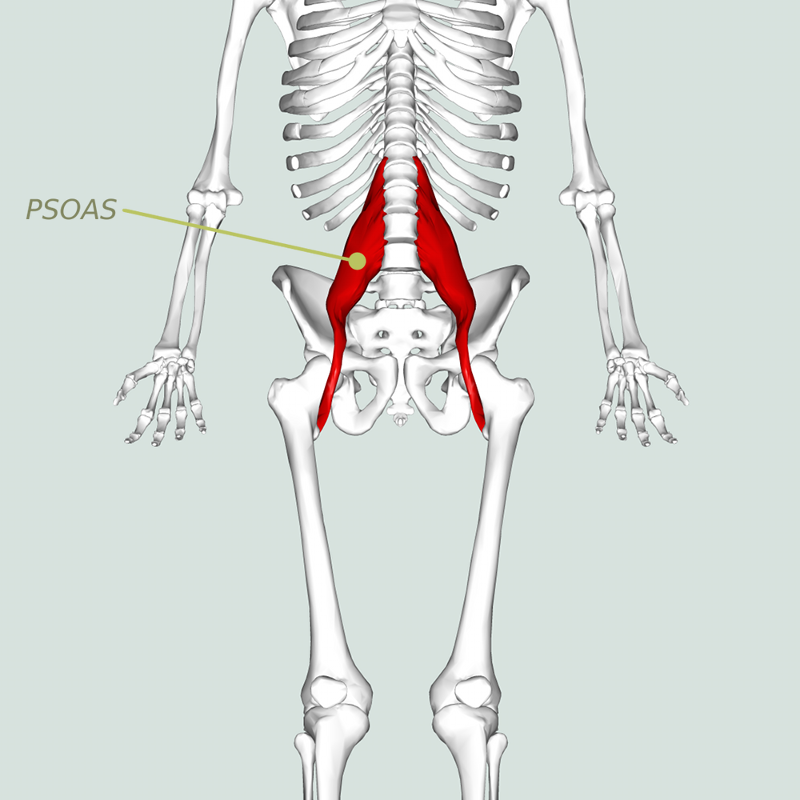
| back 38 - Concentrically accelerates hip flexion and esternal
rotation
- Concentrically extends and rotates lumbar spine
- only major muscle that connects the lower body to the torso
- When it's tight, you can lose range of motion in the lower back,
shoulders, and hips.
|
front 39 Tensor Fascia Latae
(Including the Iliotibial Band *IT-band*) | back 39 - Concentrically accelerates hip flexion, abduction, and internal
rotation
- muscle, located on the side of your pelvis, helps to
stabilize your hip through its connection into a strip of tough
connective tissue on your outer thigh called the iliotibial band.
Stretching a chronically contracted tensor fasciae latae can help
improve the range of motion of your hips
|
| back 40 - Concentrically accelerates hip extension and external
rotation
- Extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip
- Upper fibers help abduct the thigh (the inferior fibers also
help stabilize the extended knee by tightening illiotibial
tract)
|
| back 41 - Concentrically accelerates hip abduction and internal
rotation
- Abducts thigh at hip
- Anterior fibers
medially rotate thigh
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fGK-bGR_7qw
|
| back 42 - Concentrically accelerates hipabduction and internal rotation
(anterior fibers) (Abducts thigh at hip and medially rotates
thigh)
- Concentrically accelerates hip abduction and
external rotation (Posterior fibers) (Abducts thigh at hip and
laterally rotates thigh at hip)
|
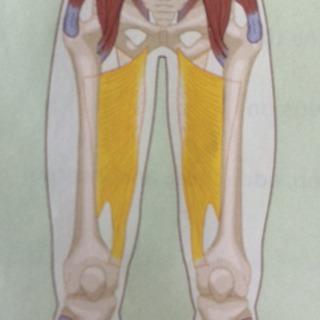
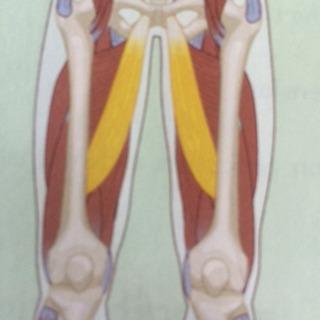
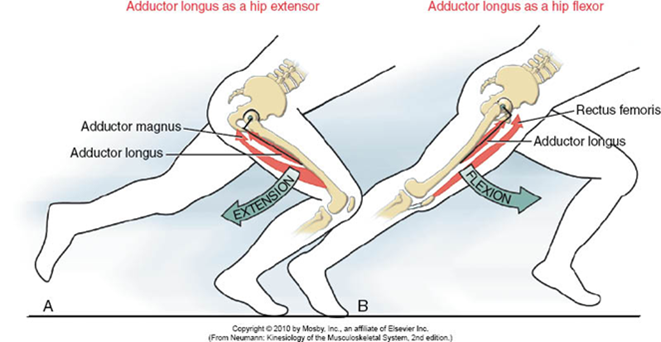
| back 43 - Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, flexion, and internal
rotation
-
Adducts and flexes thigh
|
| back 44 - a slender superficial muscle of the inner thigh
- Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, flexion, and internal
rotation
- Assists in tibial internal rotation
- Adducts
thigh at hip (also flexes the leg at the knee and medially rotates
leg when knee is flexed)
|
| back 45 - Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, flexion and internal
rotation
- Adducts and flexes thigh at hip (may also laterally
or medially rotate the thigh
|
front 46 Adductor Magnus - Posterior Fibers | back 46 - Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, extension, and external rotation
|
front 47 Adductor Magnus - Anterior Fibers | back 47 - Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, flexion and internal rotation
|
| back 48 - Concentrically accelerates hip adduction, flexion, and internal
rotation
|
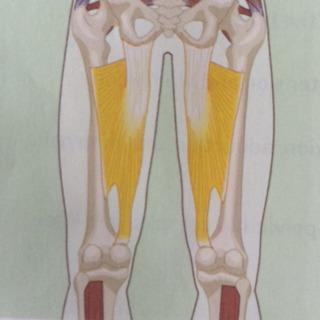
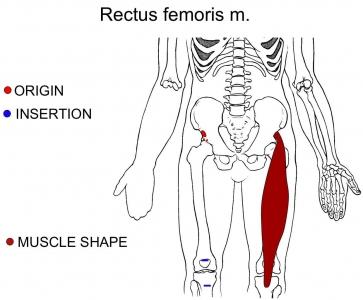
| back 49 - Concentrically accelerates knee extension and hip flexion
- Ecerxise:
- Longes, Squat, leg press, leg extension
|
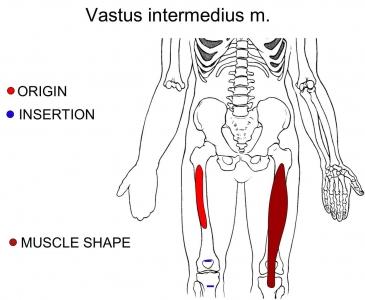
| back 50 - Concentrically accelerates knee extension
- Exercise:
- Squat, knee extension w/band
|
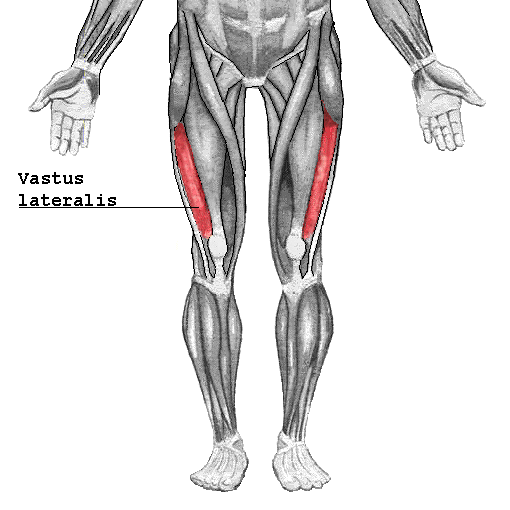
| back 51 - Concentrically accelerates knee extension
- Exercise:
- Squat, lunges, leg extension, leg press
- Exercise benefit
- knee stability, prevention of
patellofemoral joint pain, develop the outer portion of your
thighs and stop your knees from turning inward while
squatting
|
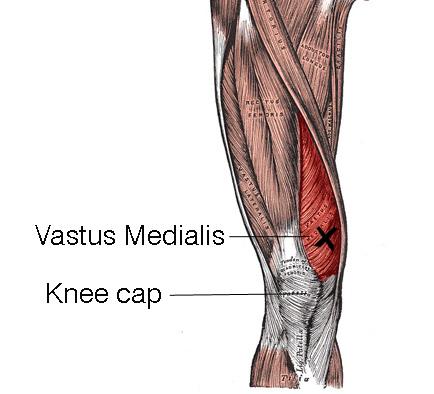
| back 52 - Concentrically accelerates knee extension
- Exercise:
- Squat - Consciously keeping your knees apart requires the
lateralis to activate and strengthen
- Exercise benefit:
- develop the outer portion of your
thighs and stop your knees from turning inward while
squatting
|
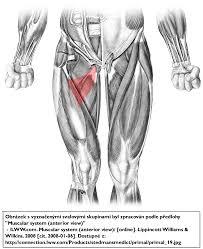
| back 53 - Concentrically accelerates knee flexion, hip extension, and
tibial internal rotation
- Exercise:
- leg curling
variations, such as the standing and seated leg curl. The
hamstrings can be effectively targeted via hip extension with
stiff leg deadlifts, traditional deadlifts and good
mornings.
- Exercise benefit:
- Strong
hamstrings are important for a healthy and injury resistant knee
joint.
|
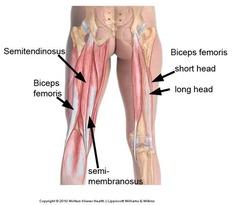
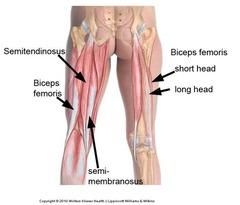
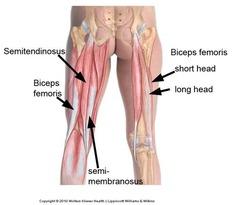
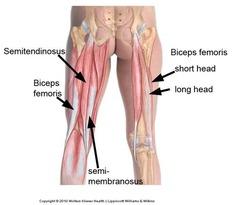
front 54 Biceps Femoris - Short Head
| back 54 - Concentrically accelerates kneww flexion and tibial external
rotation
- Exercise:
- Squat, hamstring curl,leg
lift
|
| back 55 - Concentrically accelerates knee flexion, hip extension, and
tibial internal rotation
- Execise:
- Stiff leg
deadlift, clean deadlift, traditional deadlift, hamstring
curls.
- Exercise Benefits
- The
development of the hamstrings (coupled with strengthening of the
knee extenders) is particularly important for a stable knee
joint. Strong hamstrings can reduce the stress and injury risk
to ligaments during dynamic sporting activities.
|
front 56 Biceps Femoris - Long Head
| back 56 - Concentrically acelerates knee flexion and hip extension
- Tibial external rotation
- Exercise:
- Squat,
hamstring curl,leg lift
|
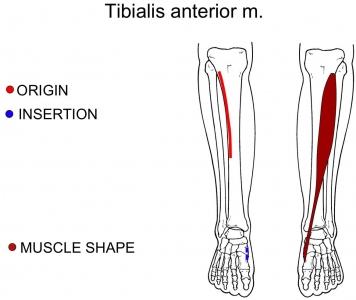
| back 57 - Concentrically accelerates dorsiflexion and inversion
- Exercise
- Standing reverse calf raise and the seated
reverse calf raise
|
| back 58 - Concentrically accelerats plantarflexion and inversion of the
foot
- Exercise:
|
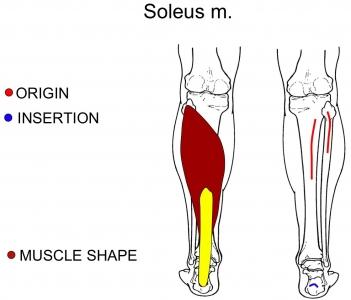
| back 59 - Concentrically accelerates plantarflexion
- Exercise:
|
| back 60 - Concentrically accelerates plantarflexion
- Exercise:
|
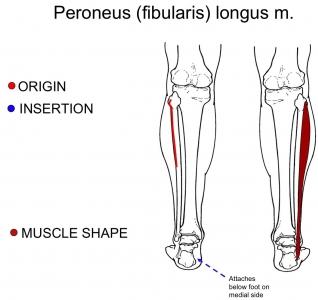
| back 61 - Concentrically plantarflexes and everts the foot
- Exercise:
- Calf raises, elevated calf raises
|